A light and small C-band metamaterial relativistic magnetron
-
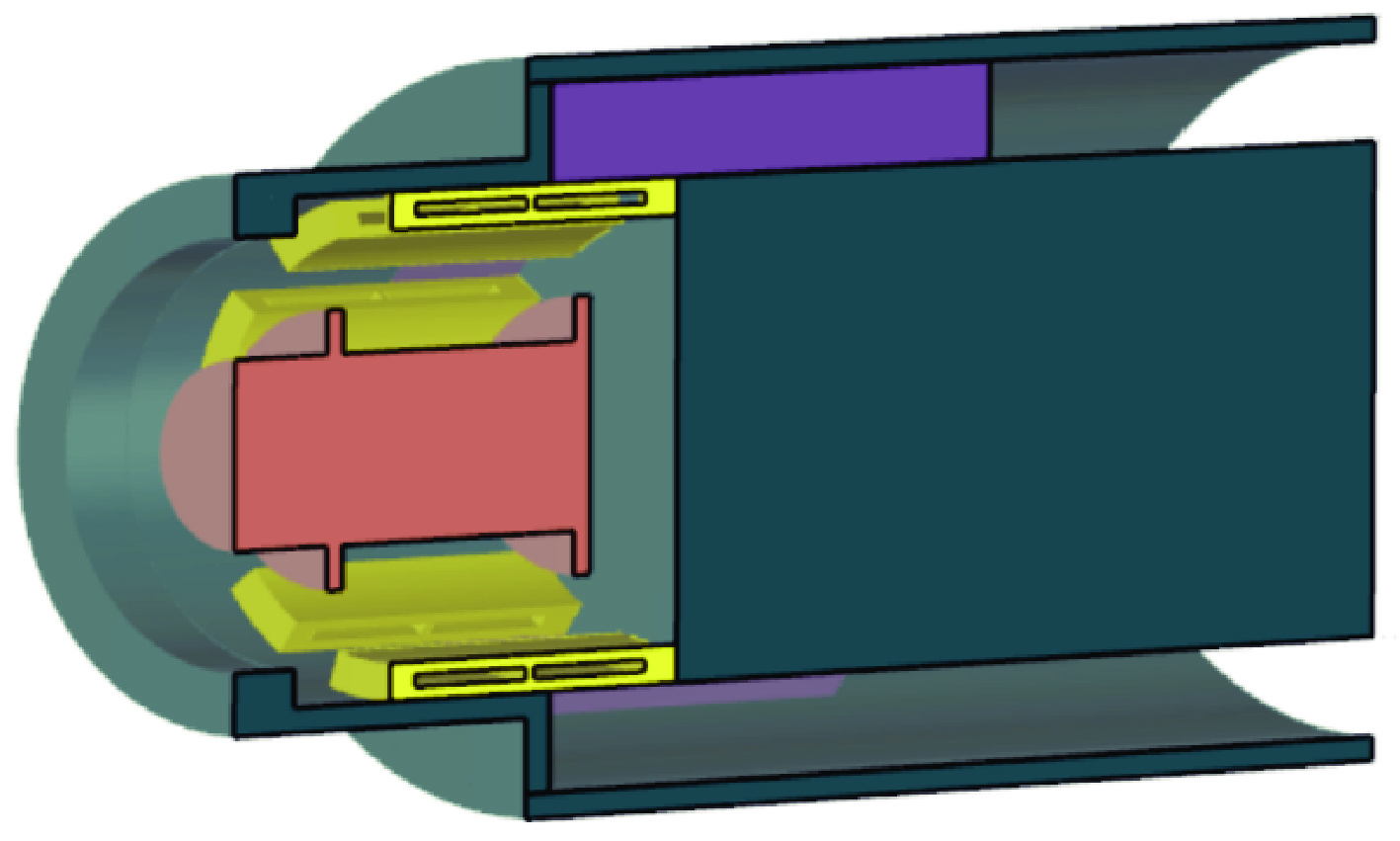
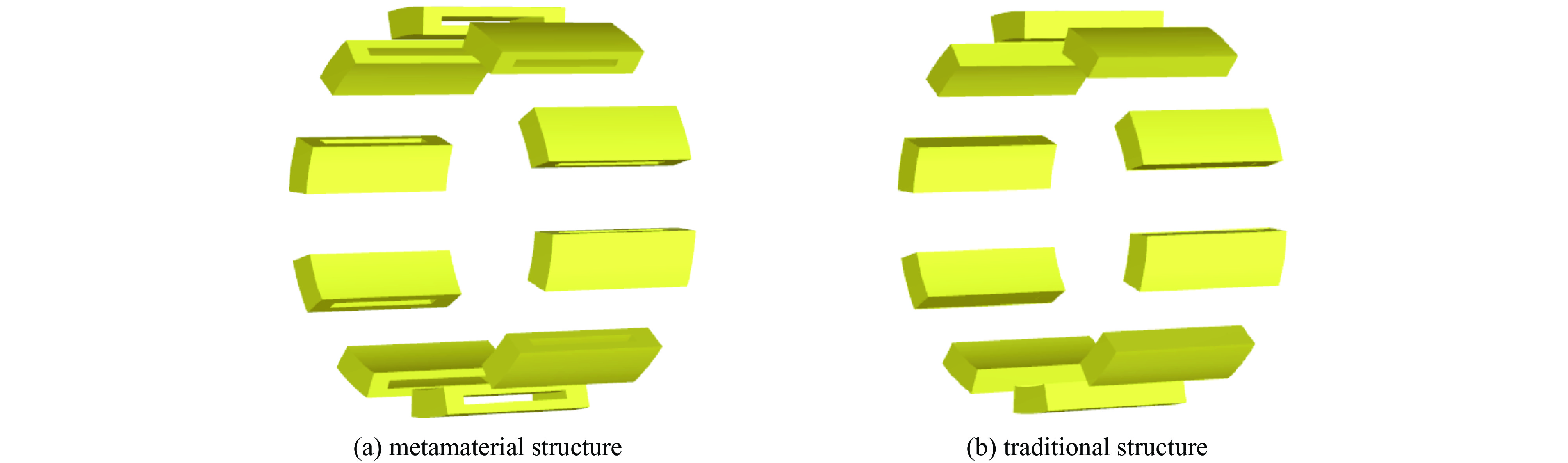
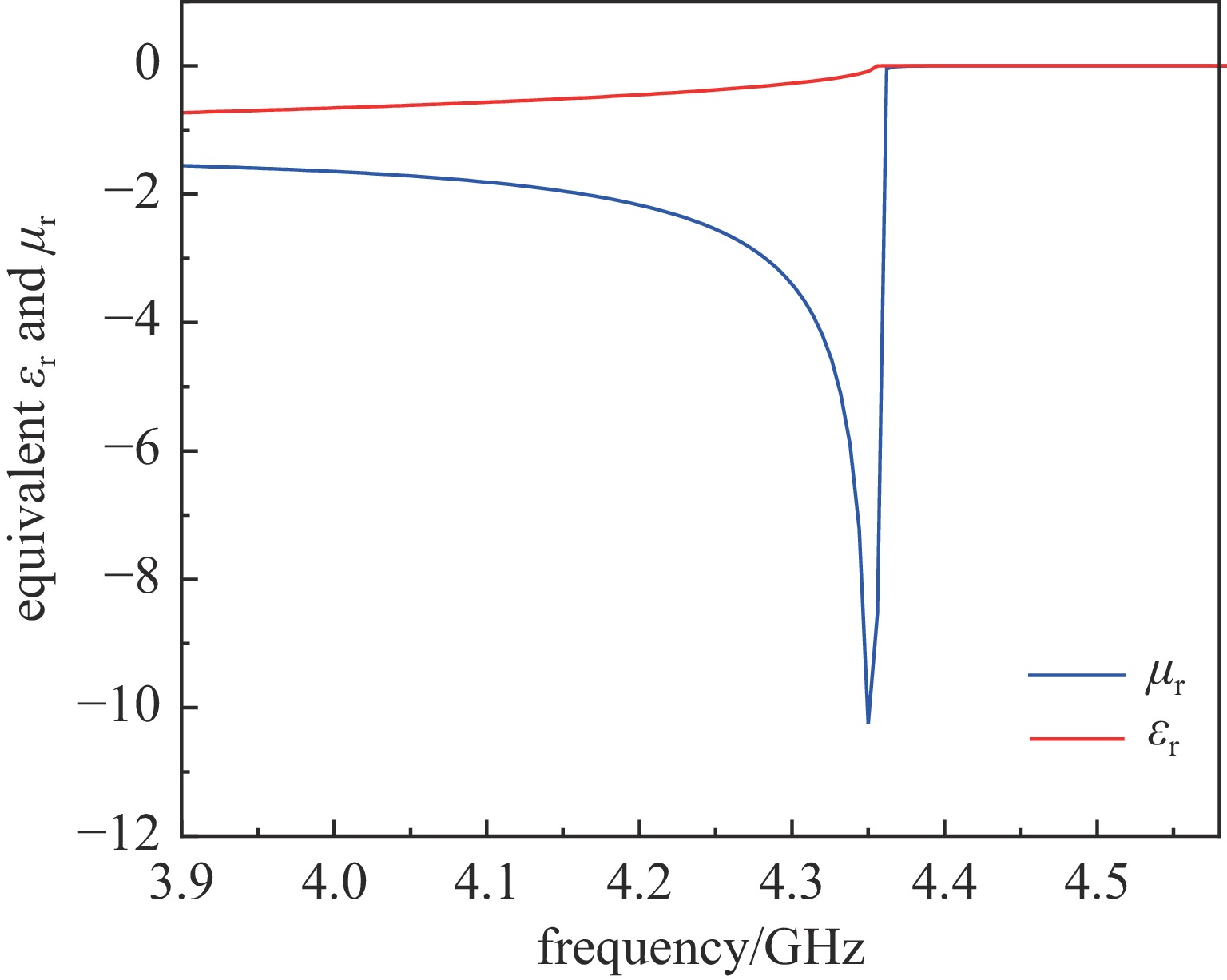
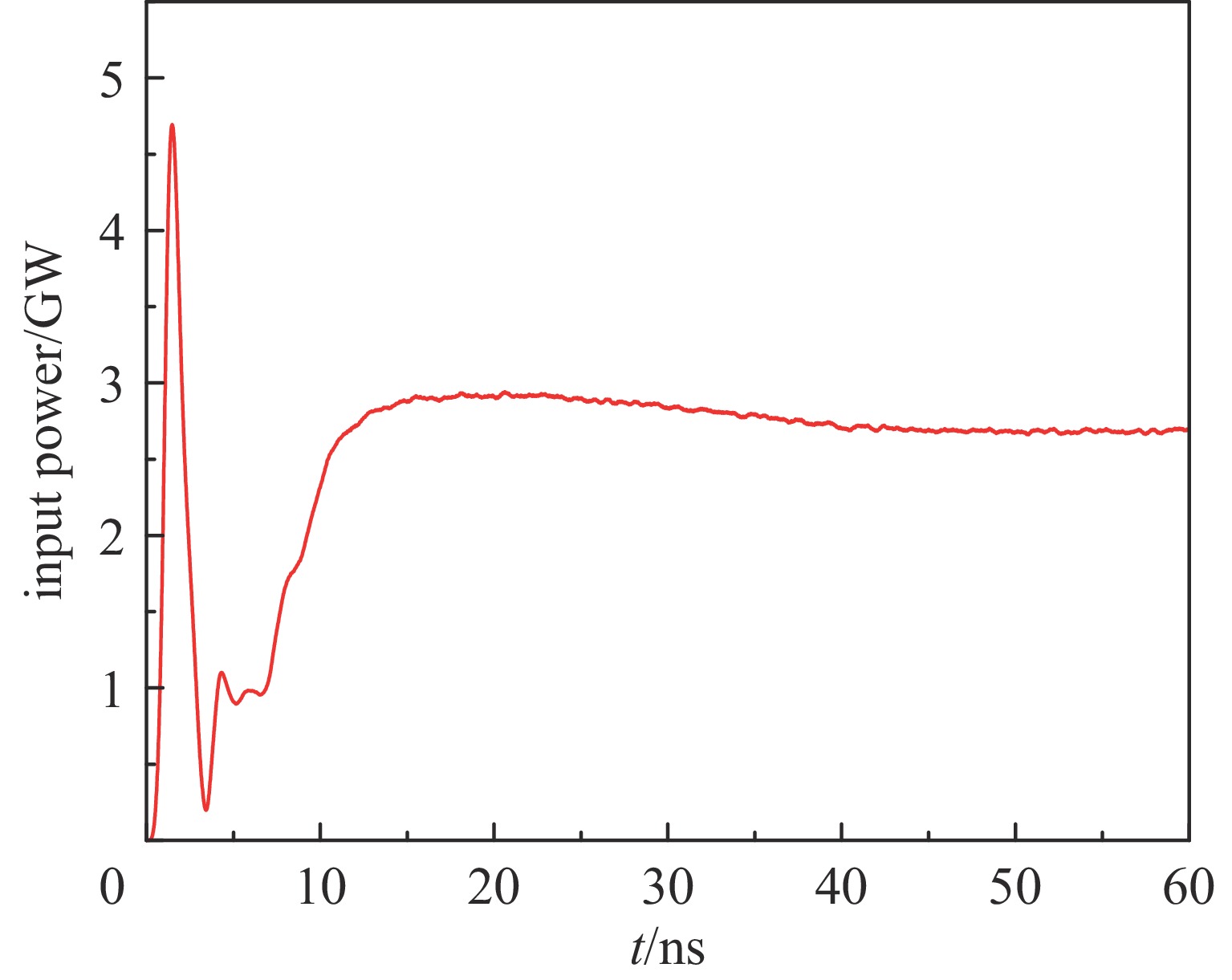
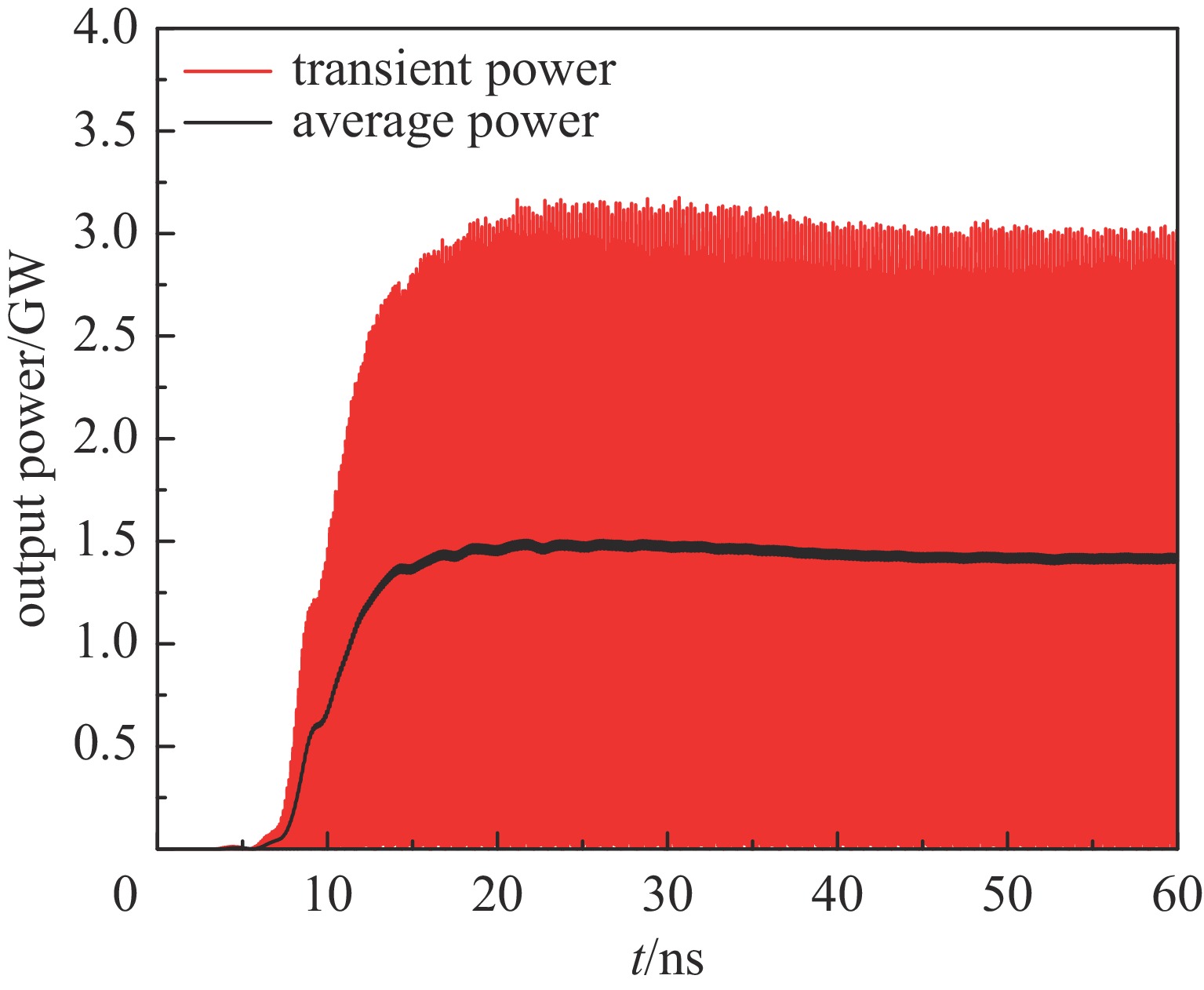
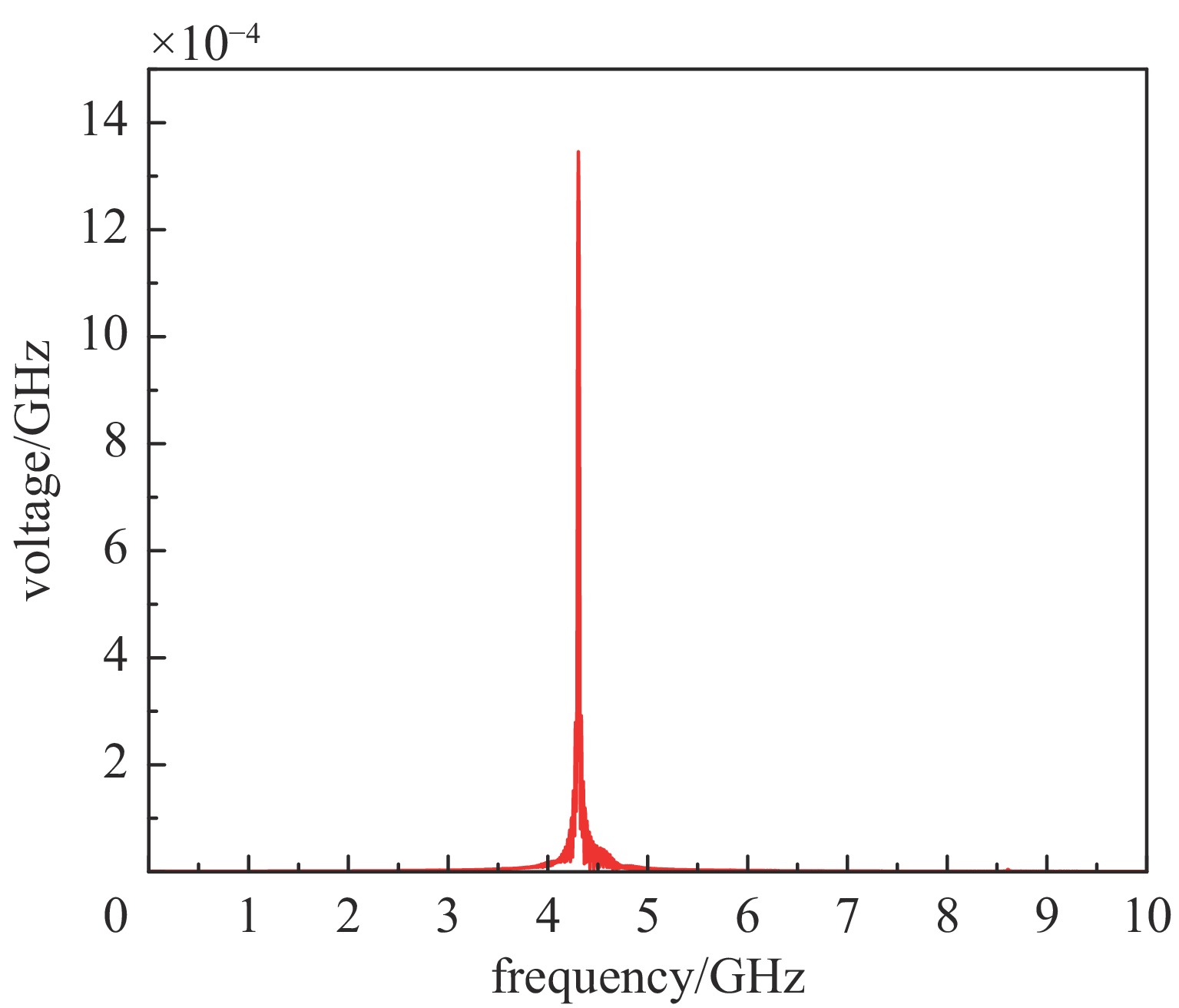
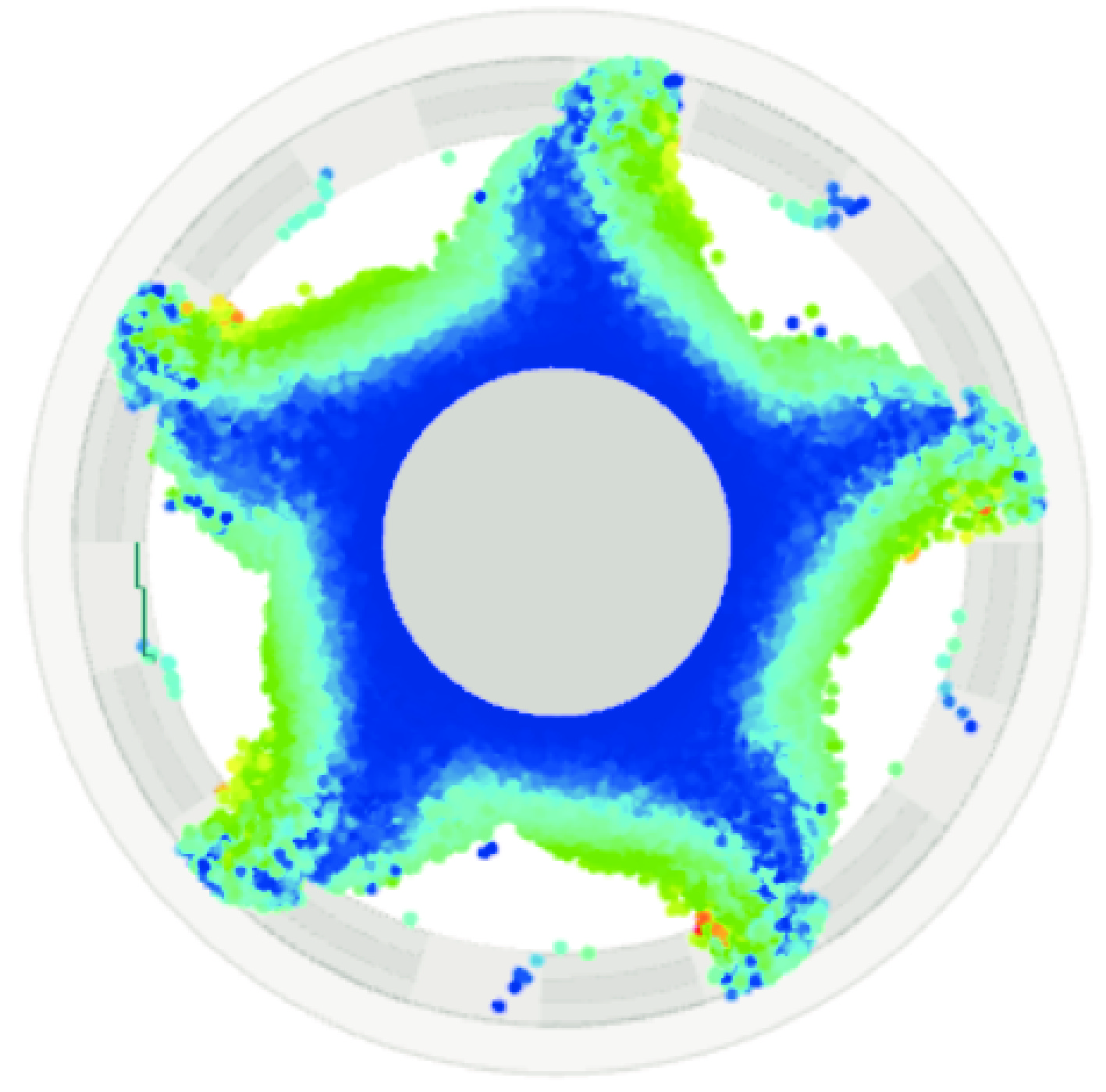
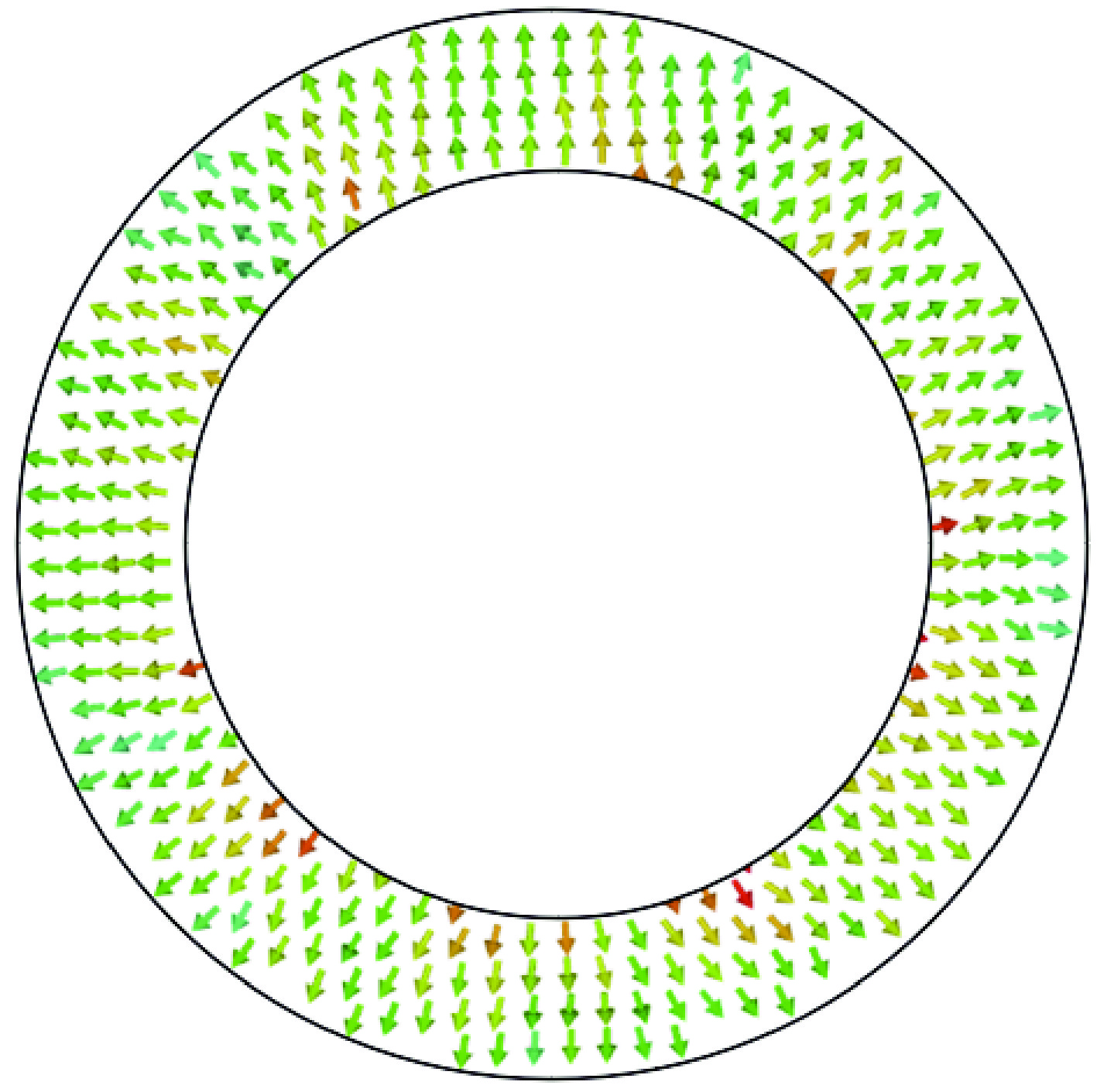
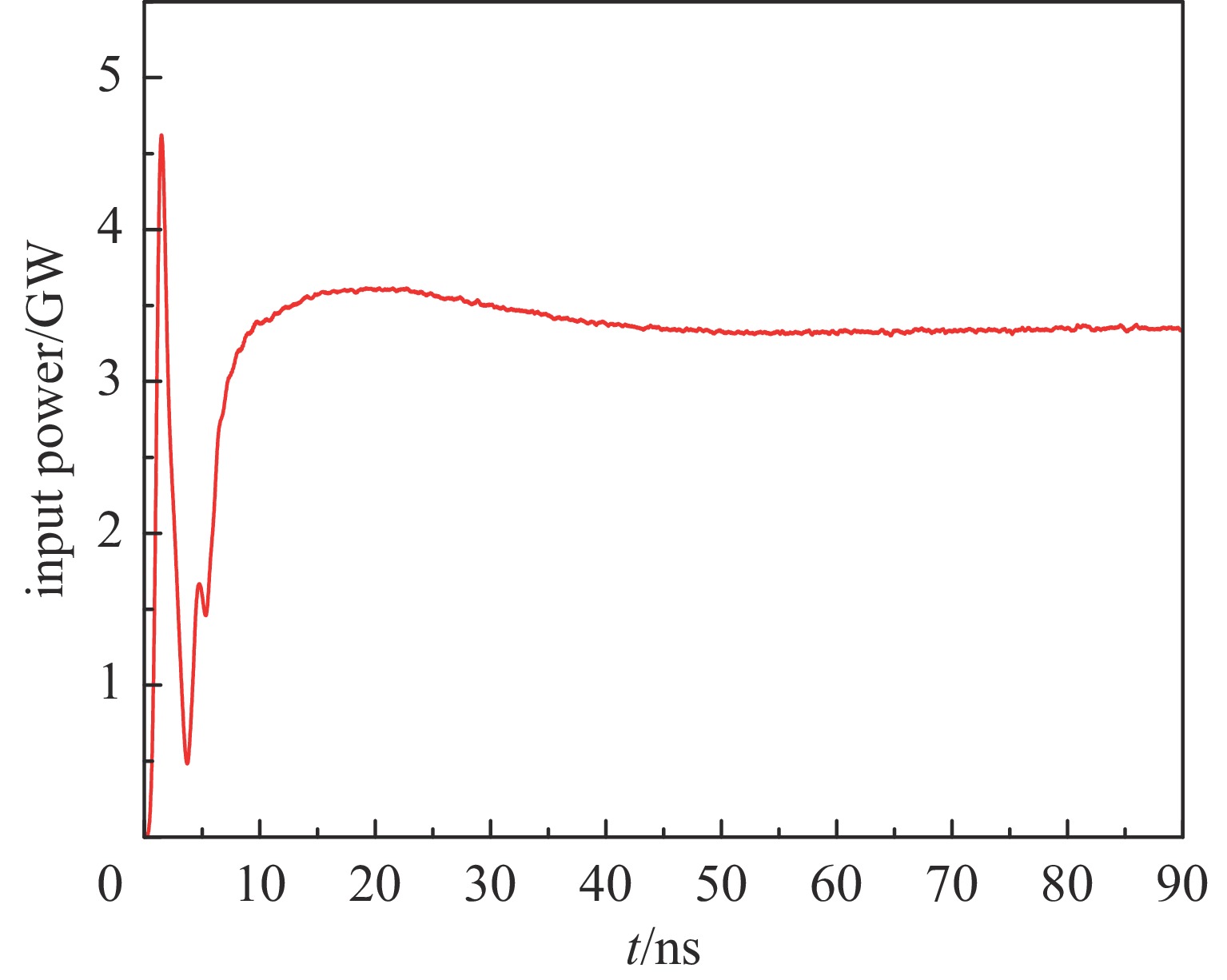
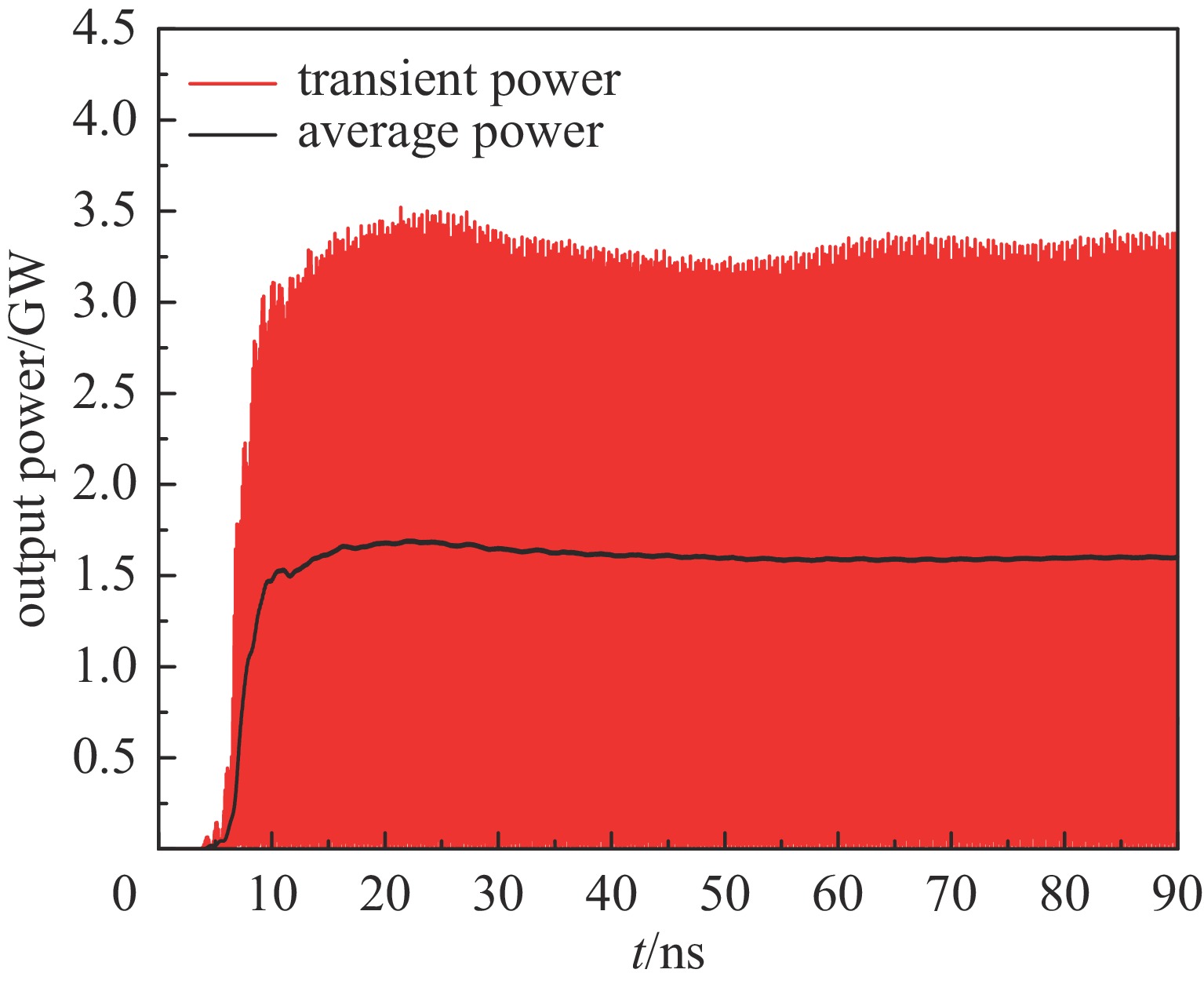
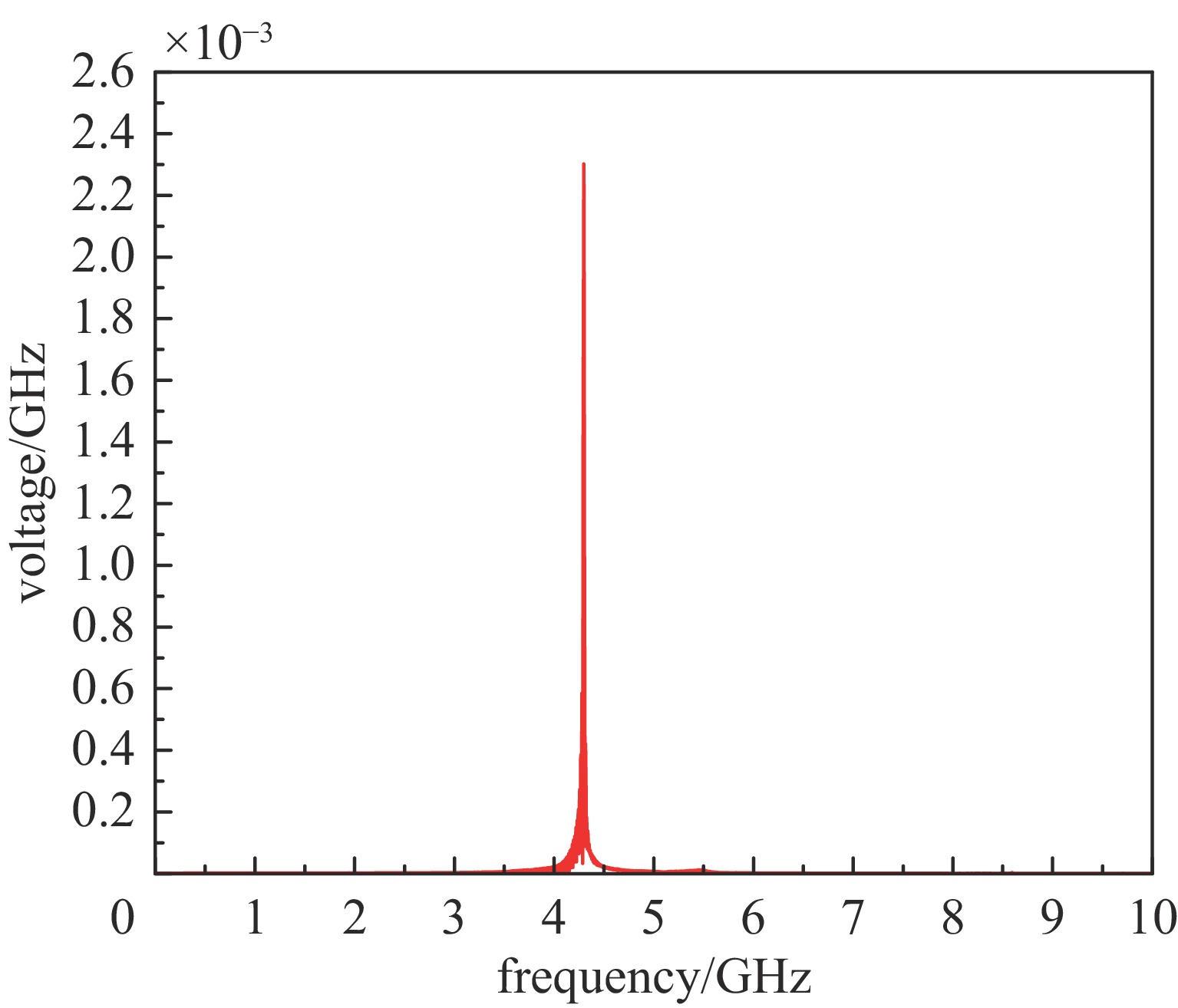
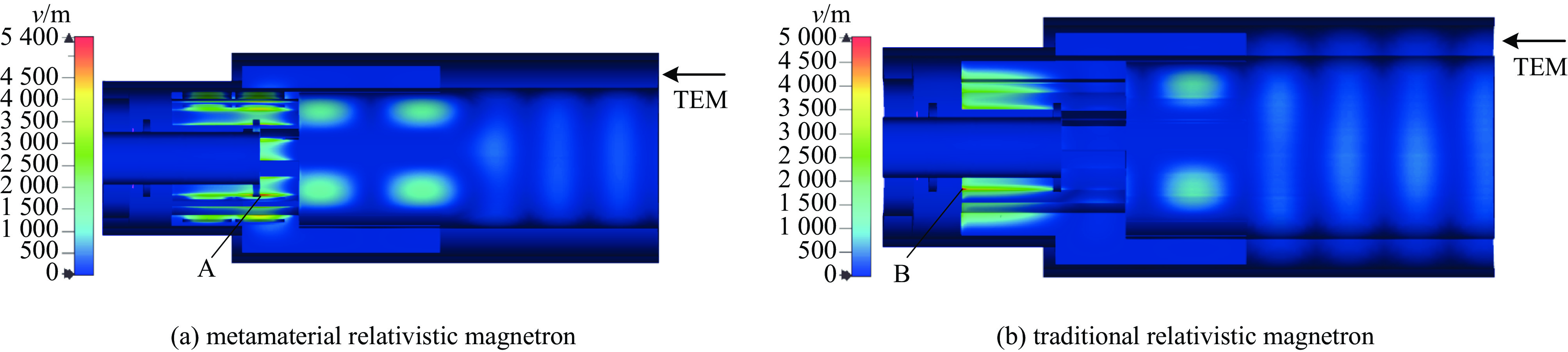
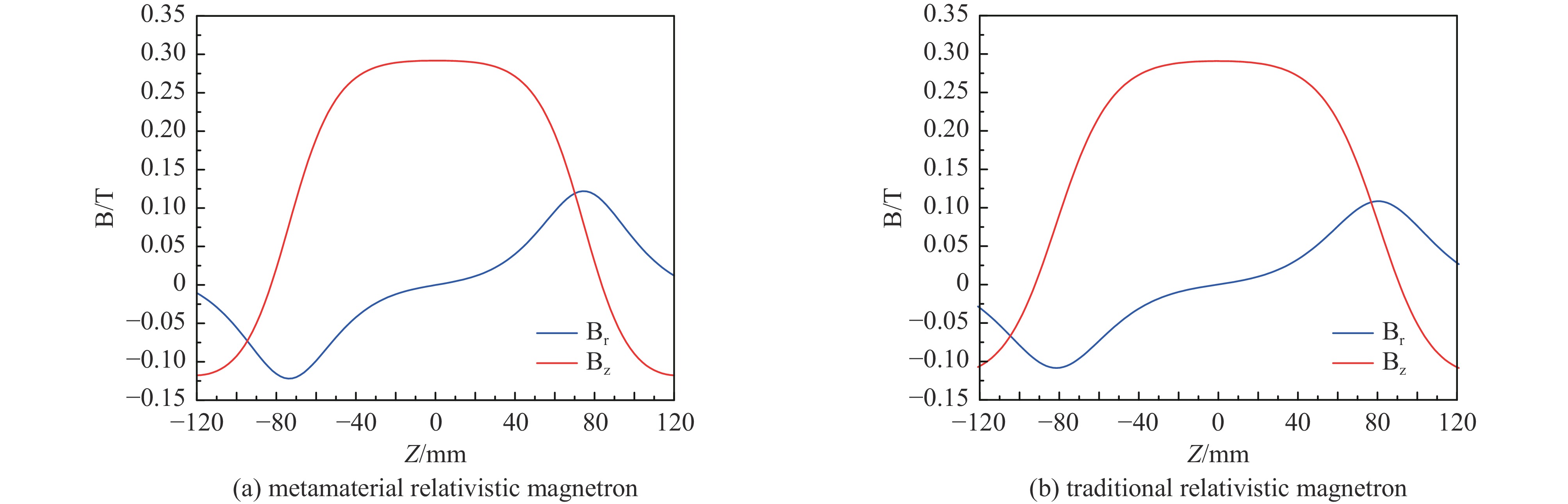
摘要: 相对论磁控管因其高功率转换效率、低工作磁场、结构简单紧凑等特性,已成为高功率微波源领域的研究热点。为了拓宽其应用场景,系统小型化与轻量化已成为相对论磁控管的重点技术攻关方向。传统微波源尤其是低频段微波源,受波长与径向尺寸的共度性约束,其慢波结构的径向尺寸往往需与工作波长同量级,这严重限制了其小型化和紧凑化设计。提出一种基于超材料的C波段全腔提取相对论磁控管,通过引入具有双负特性的超材料,突破传统共度性关系的限制,实现器件径向尺寸和重量的减小。仿真结果显示:在输入电压675 kV、磁场0.29 T条件下,器件输出功率为1.42 GW,功率转换效率为52.6%,频率为4.3 GHz。与传统相对论磁控管结构对比,当以上工作性能基本相同时,超材料的引入使阳极外半径缩减5.5 mm,尺寸减小幅度达12%,相应的永磁体重量可减轻22.8%。Abstract: Relativistic magnetrons (RMs) are promising high-power microwave (HPM) sources due to their high efficiency, low operating magnetic field, and compact configuration. Miniaturization and lightweight design are critical for expanding their application scope. However, the structural dimensions of traditional microwave sources, particularly those operating in low-frequency bands, are constrained by the correlation between wavelength and radial size. As a result, the radial size of their slow-wave structures often needs to be of the same magnitude as the working wavelength, which seriously limits their miniaturization and compact design. To address this issue, a C-band RM with all-cavity extraction based on metamaterials (MTMs) is proposed in this paper. This design aims to overcome the traditional design limitations, enabling effective reduction in device radial size and weight. Particle-in-cell (PIC) simulations are conducted using CST Studio Suite to verify the performance of the MTM-based RM. For comparison, a traditional RM with identical key operating parameters such as voltage, magnetic field, internal anode radius, and frequency is simulated to validate the impact of MTMs on reducing the anode outer radius. In addition, preliminary designs of the permanent magnets for both structures are carried out using the magnetic field simulation software. Simulation results show that under an input voltage of 675 kV and a magnetic field of 0.29 T, the designed MTM-based RM generates a TEM-mode output with a power of 1.42 GW at a frequency of 4.3 GHz, corresponding to an efficiency of 52.6%. Compared with the traditional RM, when the operating performance metrics are nearly the same, the external anode radius is reduced by 5.5 mm, representing a 12% reduction in size, and the weight of the permanent magnet is reduced by 22.8%. These results demonstrate that the integration of MTMs effectively reduces the radial size of the C-band RM and the weight of the corresponding permanent magnet, which highlights the significant potential of MTMs in miniaturizing low-frequency HPM sources and provides a viable pathway for the development of lightweight, compact, and practical HPM systems.
-
Key words:
- high-power microwave /
- relativistic magnetron /
- metamaterials /
- miniaturization /
- all-cavity extraction
-
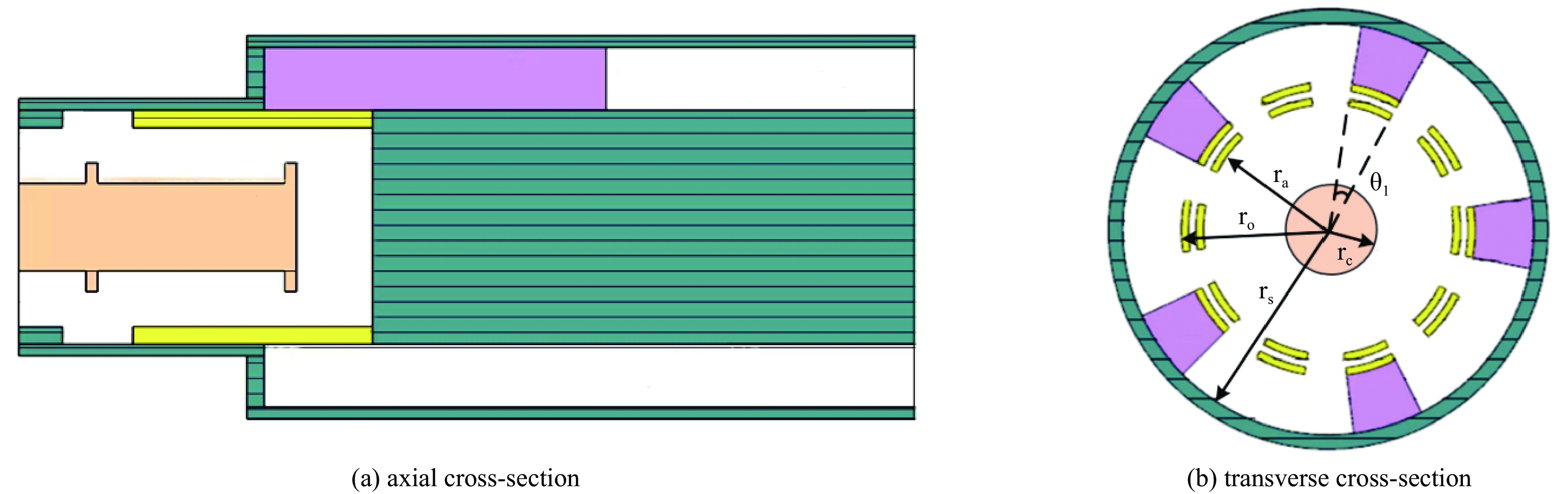
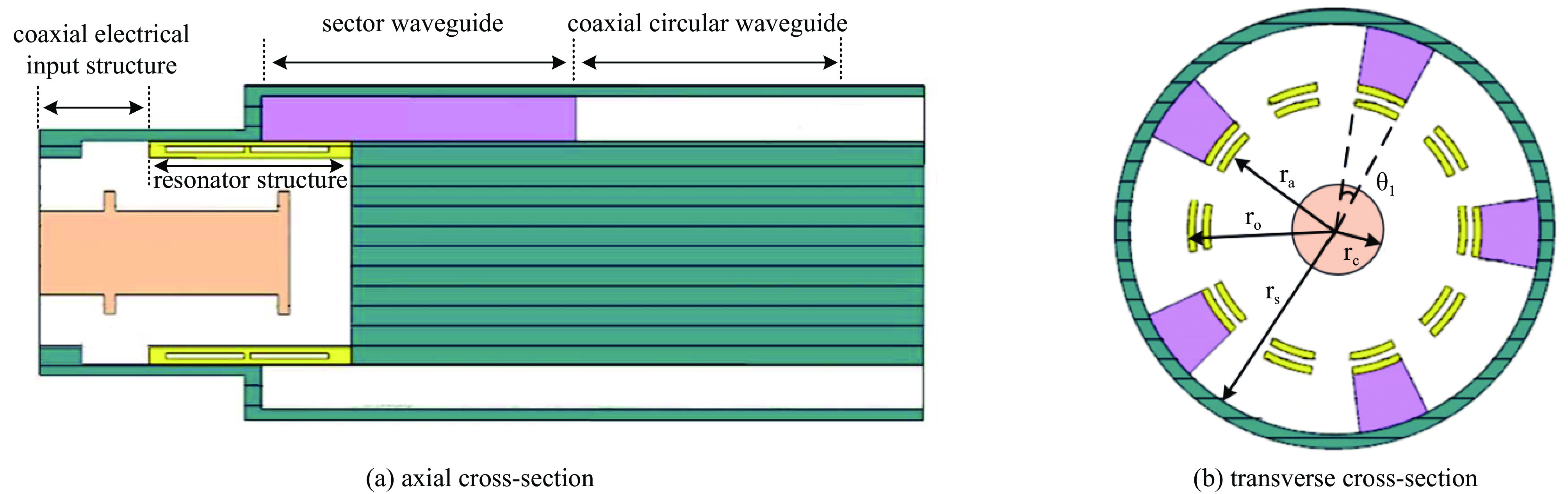
表 1 相关主要参数
Table 1. Relevant main parameters
rc/mm ra/mm ro/mm rs/mm θ1/(°) 15 34 40 56 20 表 2 相关主要参数
Table 2. Relevant main parameters
rc/mm ra/mm ro/mm rs/mm θ1/(°) 15 34 45.5 60.5 20 -
[1] Andreev D, Kuskov A, Schamiloglu E. Review of the relativistic magnetron[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2019, 4: 067201. doi: 10.1063/1.5100028 [2] Benford J, Swegle J A, Schamiloglu E. High power microwaves[M]. 2nd ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2007. [3] 何朝雄, 李天明, 胡标. 相对论磁控管技术及其应用[J]. 真空电子技术, 2016(6):1-6He Chaoxiong, Li Tianming, Hu Biao. Technology and applications of relativistic magnetrons[J]. Vacuum Electronics, 2016(6): 1-6 [4] 王冬, 秦奋, 杨郁林, 等. L波段全腔提取轴向输出相对论磁控管设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2016, 28:033013 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201628.033013Wang Dong, Qin Fen, Yang Yulin, et al. Design of L band all cavity axial extraction relativistic magnetron[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2016, 28: 033013 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201628.033013 [5] Fuks M I, Schamiloglu E. 70% efficient relativistic magnetron with axial extraction of radiation through a horn antenna[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2010, 38(6): 1302-1312. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2010.2042823 [6] Leach C, Prasad S, Fuks M I, et al. Experimental demonstration of a high-efficiency relativistic magnetron with diffraction output with spherical cathode endcap[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2017, 45(2): 282-288. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2016.2644625 [7] He Chaoxiong, Wang Keqiang, Li Tianming, et al. A compact relativistic magnetron with diffraction output of TE11 mode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2024, 52(2): 285-290. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2024.3369932 [8] Li Wei, Liu Yonggui, Zhang Jun, et al. Experimental investigations on the relations between configurations and radiation patterns of a relativistic magnetron with diffraction output[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 113: 023304. doi: 10.1063/1.4774245 [9] Xu Sha, Lei Lurong, Qin Fen, et al. Compact, high power and high efficiency relativistic magnetron with L-band all cavity axial extraction[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2018, 25: 083301. doi: 10.1063/1.5041860 [10] Liu Zeyang, Fan Yuwei, Wang Xiaoyu, et al. A high-efficiency relativistic magnetron with a novel all-cavity extraction structure[J]. AIP Advances, 2020, 10: 035104. doi: 10.1063/1.5102151 [11] Liu Zeyang, Fan Yuwei, Wang Xiaoyu, et al. An improved high-efficiency relativistic magnetron with a novel cathode endcap[J]. AIP Advances, 2021, 11: 025239. doi: 10.1063/5.0028617 [12] Xu Haodong, Wang Xiaoyu, Liu Zeyang, et al. A C-band relativistic magnetron with a novel extraction structure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2023, 70(3): 1270-1274. doi: 10.1109/TED.2023.3234017 [13] 秦奋, 徐莎, 张勇, 等. Ku波段全腔提取相对论磁控管仿真设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2024, 36:103007 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.240165Qin Fen, Xu Sha, Zhang Yong, et al. Simulation investigation of Ku-band relativistic magnetron with all-cavity-axial-extraction[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2024, 36: 103007 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.240165 [14] Shi Difu, Qian Baoliang, Wang Honggang, et al. A modified relativistic magnetron with TEM output mode[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2017, 24: 013118. doi: 10.1063/1.4975006 [15] Shi Difu, Qian Baoliang, Wang Honggang, et al. A novel relativistic magnetron with circularly polarized TE11 coaxial waveguide mode[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2016, 49: 465104. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/49/46/465104 [16] Smith D R, Padilla W J, Vier D C, et al. Composite medium with simultaneously negative permeability and permittivity[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2000, 84(18): 4184-4187. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.84.4184 [17] Marqués R, Martel J, Mesa F, et al. Left-handed-media simulation and transmission of EM waves in subwavelength split-ring-resonator-loaded metallic waveguides[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2002, 89: 183901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.89.183901 [18] Esteban J, Camacho-Penalosa C, Page J E, et al. Simulation of negative permittivity and negative permeability by means of evanescent waveguide modes-theory and experiment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2005, 53(4): 1506-1514. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2005.845194 [19] Dai Ouzhixiong, He Juntao, Ling Junpu, et al. A novel L-band metamaterial relativistic cherenkov oscillator with high conversion efficiency[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2019, 26: 023104. doi: 10.1063/1.5082754 [20] 周传明, 刘国治, 刘永贵, 等. 高功率微波源[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 2007Zhou Chuanming, Liu Guozhi, Liu Yonggui, et al. High-power microwave sources[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 2007 [21] Smith D R, Vier D C, Koschny T, et al. Electromagnetic parameter retrieval from inhomogeneous metamaterials[J]. Physical Review E, 2005, 71: 036617. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.71.036617 -




 下载:
下载: