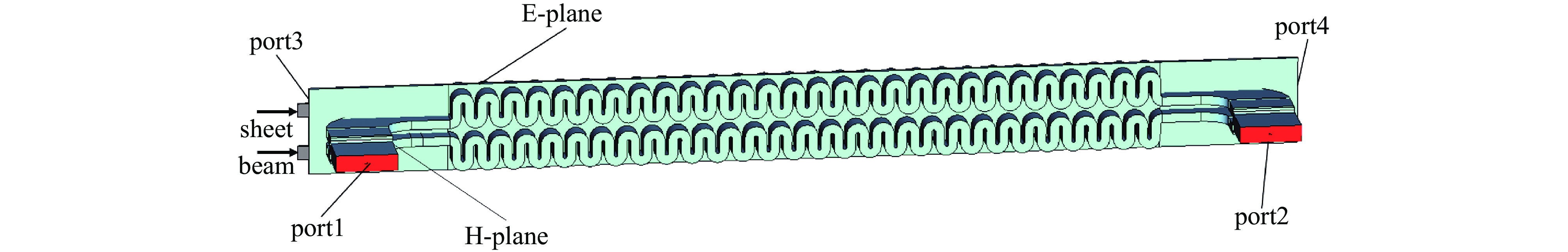
W-band folded-waveguide traveling-wave tube with dual electron beams and H-plane power combining
-
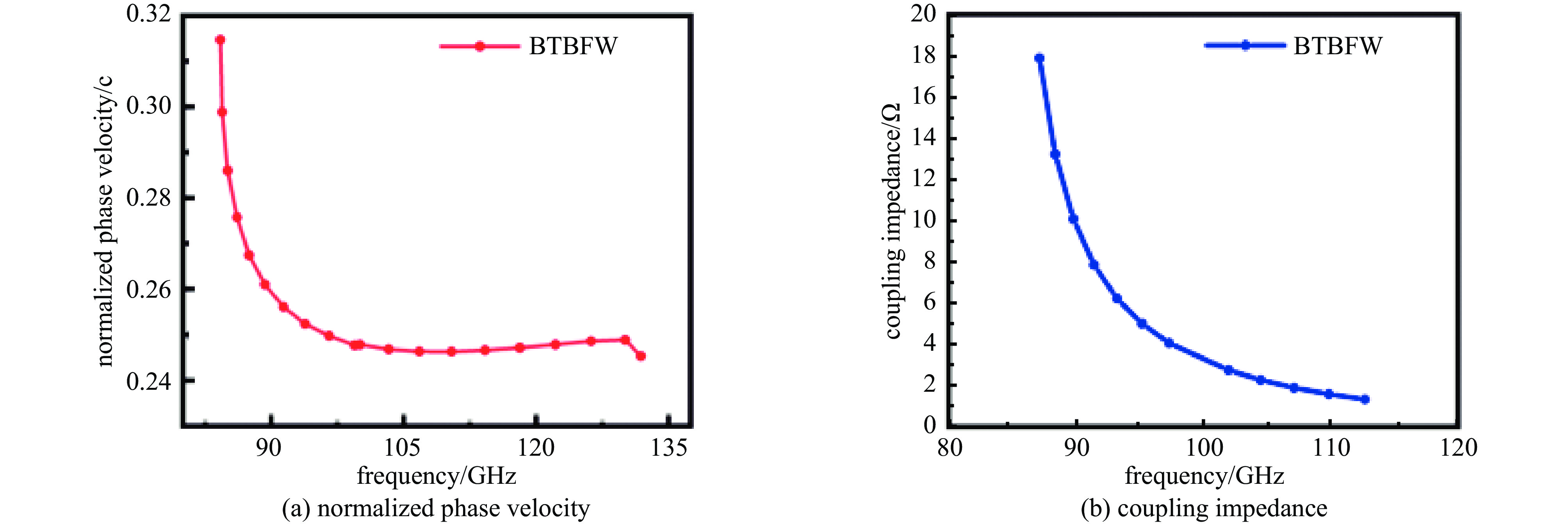
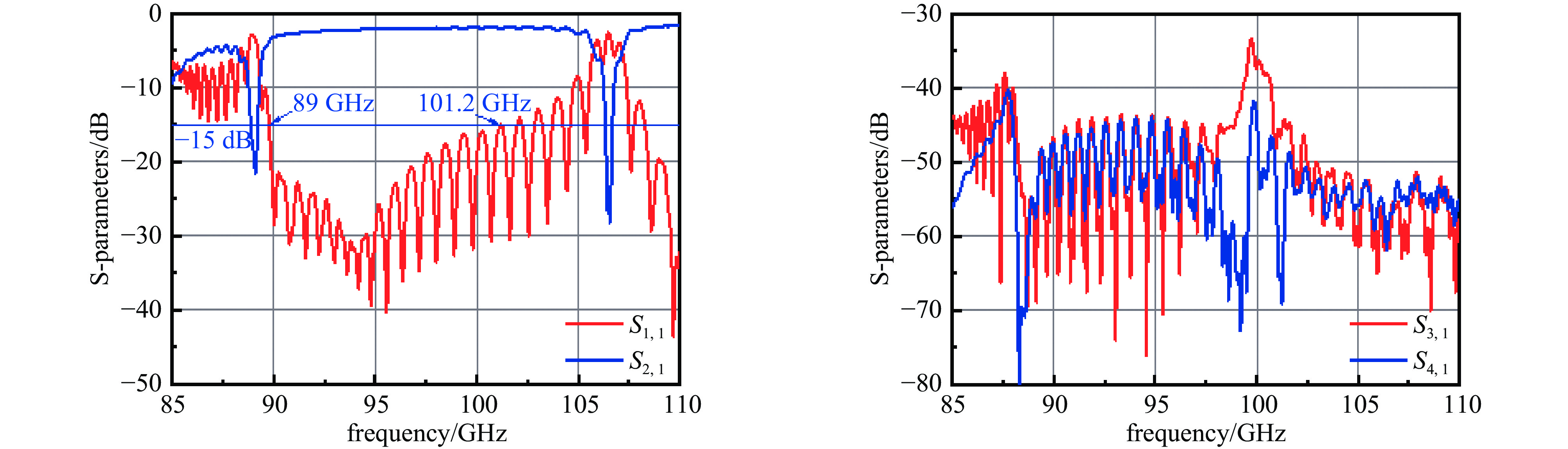
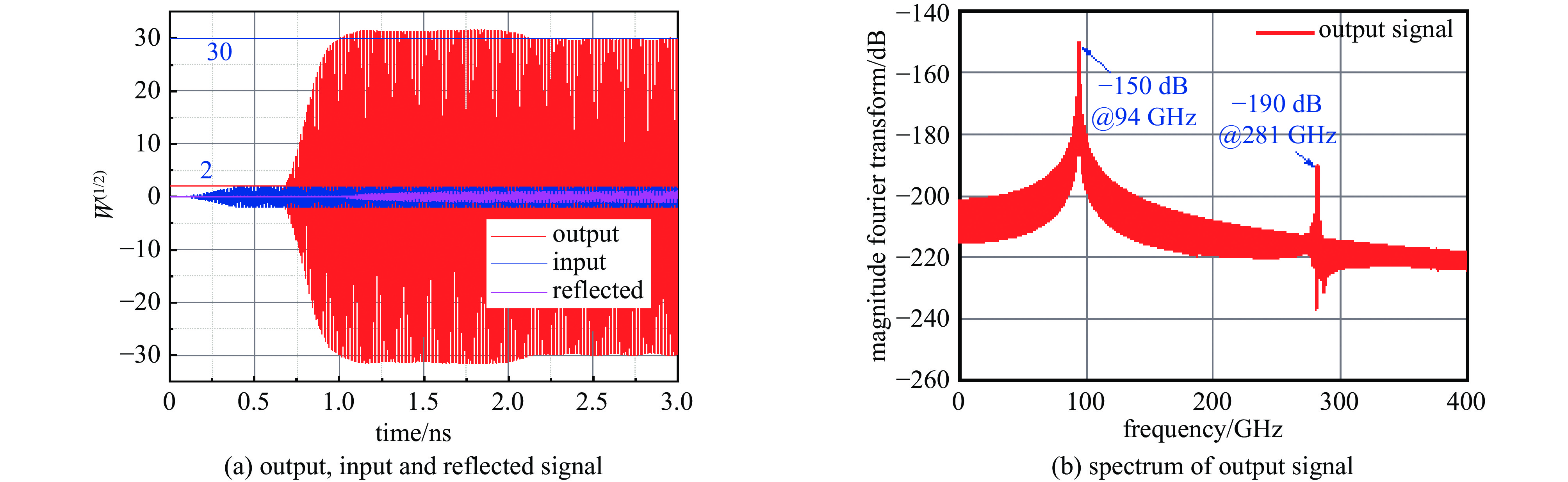
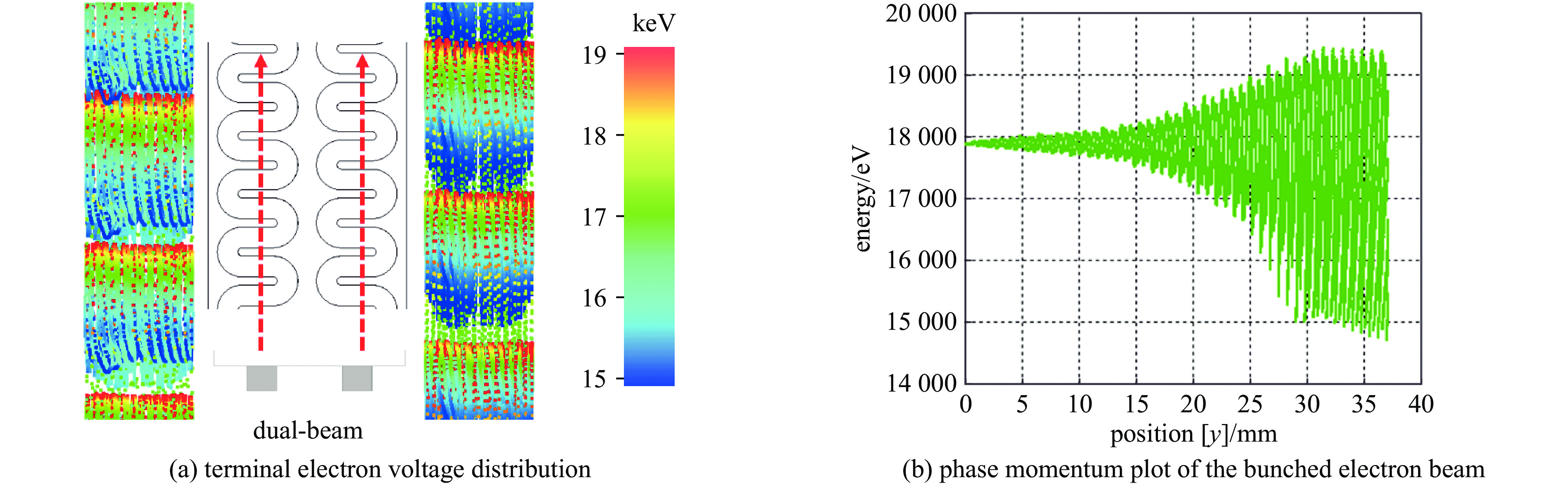
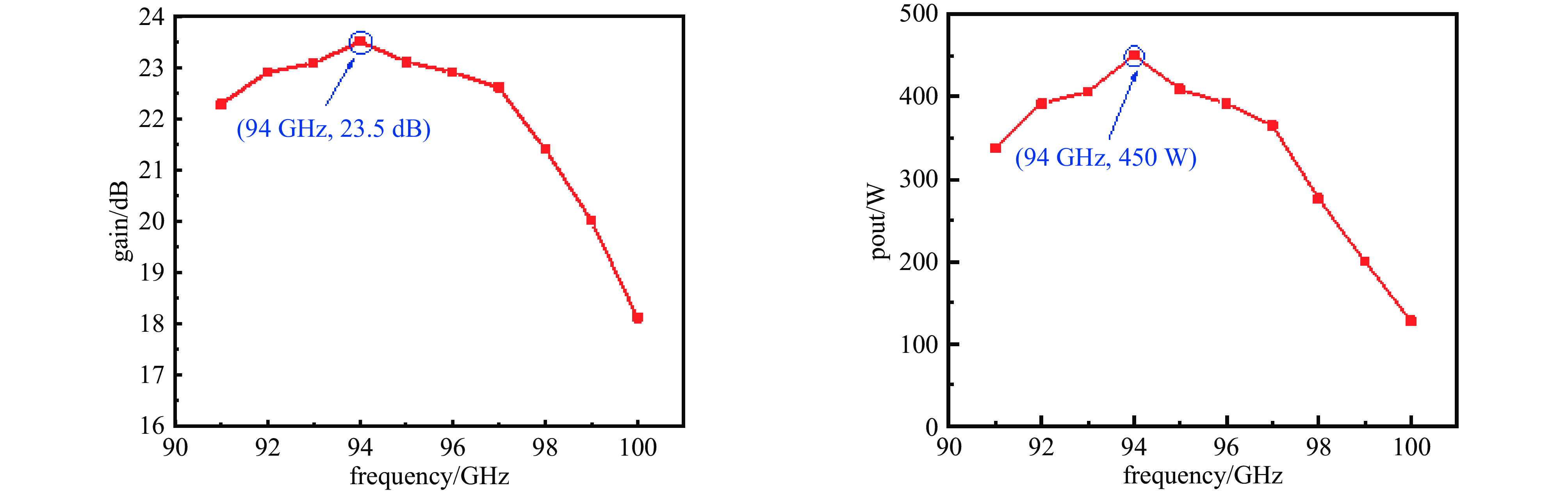
摘要: 设计了一种W波段双注多通道H面功率合成折叠波导行波管,利用三维电磁仿真软件CST对所设计的慢波结构的高频特性、电场特性、放大特性进行了仿真分析。经计算,所设计的两路折叠波导功率合成结构能够实现10 GHz的传输带宽。在电子注电压为17.9 kV,电流0.35 A的条件下,能够在94 GHz实现450 W的功率输出,效率达7.18%,对应增益23.5 dB。固定电子注的电流与电压后,所设计的行波管在91~99 GHz频段内实现了超过200 W的输出功率,其3 dB带宽为91~98.5 GHz。并且调制后的粒子电压分布图进一步验证了模式分析的准确性。Abstract:
Background Traveling-wave tubes (TWTs) are widely applied in radar, imaging, and military systems owing to their excellent amplification characteristics. Miniaturization and integration are critical to the future of TWTs, with multi-channel slow-wave structures (SWSs) forming the foundation for their realization in high-power vacuum electronic devices.Purpose To offer design insights into multi-channel TWTs and simultaneously enhance output power, a W-band folded-waveguide TWT with dual electron beams and H-plane power combining was proposed.Methods Three-dimensional electromagnetic simulations in CST were conducted to verify the high-frequency characteristics, electric field distribution, and amplification performance of the proposed SWS, thereby confirming the validity of the design.Results Results indicate that the designed TWT achieves a transmission bandwidth of 10 GHz. With an electron beam voltage of 17.9 kV and a current of 0.35 A, the output power reaches 450 W at 94 GHz, corresponding to an efficiency of 7.18% and a gain of 23.5 dB. Moreover, with fixed beam voltage and current, the TWT delivers over 200 W output power across 91–99 GHz, with a 3 dB bandwidth of 91–98.5 GHz. The particle voltage distribution after modulation further validates the mode analysis.Conclusions These results demonstrate the feasibility of compact dual-beam power-combining structures and provide useful guidance for the design of future multi-channel TWTs.-
Key words:
- double electron beam /
- folded waveguide /
- slow-wave structure /
- power combining /
- beam-wave interaction /
- w-band
-
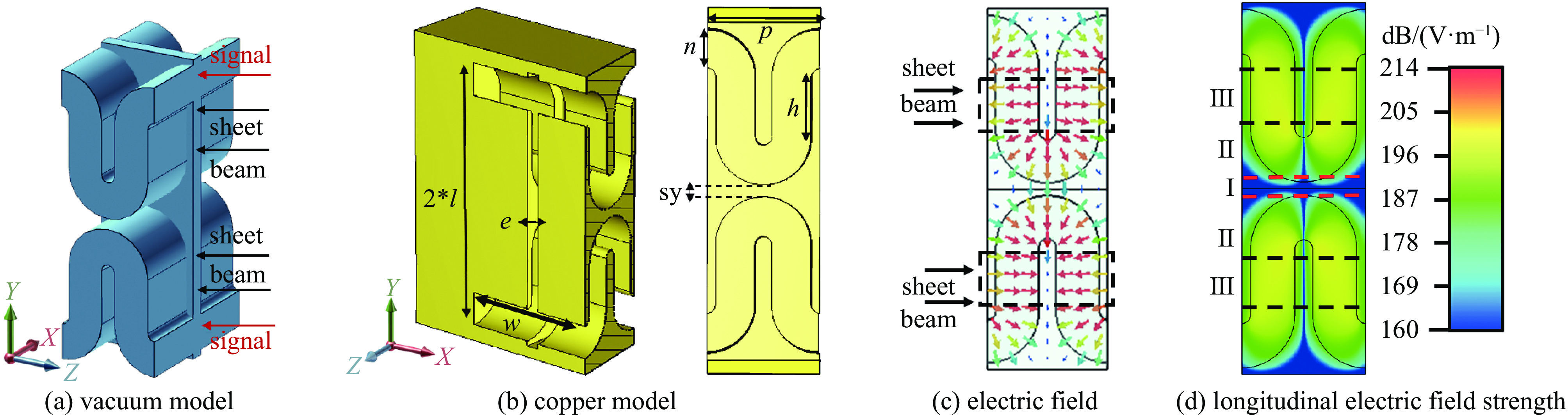
Table 1. Structure parameters of slow wave structure
(mm) w n h p e l. sy 1.8 0.40 0.60 1.12 0.16 1.68 0.36 -
[1] Booske J H, Dobbs R J, Joye C D, et al. Vacuum electronic high power terahertz sources[J]. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2011, 1(1): 54-75. doi: 10.1109/TTHZ.2011.2151610 [2] Sherwin M. Terahertz power[J]. Nature, 2002, 420(6912): 131-133. doi: 10.1038/420131a [3] Himdi M, Aouial Y, Lafond O. Integrated slotted serpentine waveguide to enhance radiation properties and efficiency[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 51093-51099. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3172952 [4] Jaque Jiménez Á, Zamora G, Bonache J. Frequency-scanning leaky-wave slot antenna array based on serpentine waveguide with open stopband suppression[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2024, 23(1): 344-348. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2023.3324063 [5] Rouhi K, Marosi R, Mealy T, et al. Parametric modeling of serpentine waveguide traveling wave tubes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2024, 52(4): 1247-1263. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2024.3379944 [6] Cook A M, Wright E L, Nguyen K T, et al. Demonstration of a W-band traveling-wave tube power amplifier with 10-GHz bandwidth[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2021, 68(5): 2492-2498. doi: 10.1109/TED.2021.3068926 [7] Cai Jun, Feng Jinjun, Hu Yinfu, et al. 10 GHz bandwidth 100 watt W-band folded waveguide pulsed TWTs[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2014, 24(9): 620-621. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2014.2328891 [8] Li Fei, Xiao Liu, Ma Tianjun, et al. W-Band 30W continuous wave wide band folded waveguide TWT[C]//2020 IEEE 21st International Conference on Vacuum Electronics (IVEC). 2020: 29-30. [9] Tian Yanyan, Wang Hexin, Shu Guoxiang, et al. Parallel arrangement folded double-ridge groove waveguide for high-power terahertz traveling-wave tube[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2021, 49(11): 3519-3523. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2021.3118371 [10] Duan Jingrui, Lu Zhigang, Gao Peng, et al. Quadruple folded groove-guide slow wave structure with power synthesis circuit for terahertz TWT[J]. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2025, 46(2): 302-305. doi: 10.1109/LED.2024.3515646 [11] Joye C D, Vlasov A N, Jaynes R, et al. Ka-band low-voltage multiple-beam mini-TWT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2023, 70(6): 2828-2833. doi: 10.1109/TED.2023.3239839 [12] Eun Choi H, Choi W, Lee J, et al. Experimental investigation of a dual-beam traveling wave tube[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2024, 71(7): 4336-4341. doi: 10.1109/TED.2024.3405398 [13] Tian Yanyan, Yue Lingna, Xu Jin, et al. A novel slow-wave structure—folded rectangular groove waveguide for millimeter-wave TWT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2012, 59(2): 510-515. doi: 10.1109/TED.2011.2175929 [14] Marosi R, Mealy T, Figotin A, et al. Three-way serpentine slow wave structures with stationary inflection point and enhanced interaction impedance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2022, 50(12): 4820-4833. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2022.3218040 [15] Zhang Keqian, Li Dejie. Electromagnetic theory for microwaves and optoelectronics[M]. 2nd ed. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2008: 228-301. [16] Pierce J R. Traveling-wave tubes[M]. New York: Van Nostrand, 1950: 123-135. [17] Duan Jingrui, Lu Zhigang, Zhu Junwan, et al. A modified fold waveguide slow wave structure for W-band dual-beam TWT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2023, 70(6): 2786-2791. doi: 10.1109/TED.2023.3239459 [18] Wang Huanyu, Wang Zhanliang, Liu Xing, et al. Simulation and experimental investigation on W-band back-to-back longitudinal serpentine groove slow wave structures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2025, 72(7): 3875-3880. doi: 10.1109/TED.2025.3572878 -




 下载:
下载: