Progress in the Construction and Commissioning of the LEAF Facility
-
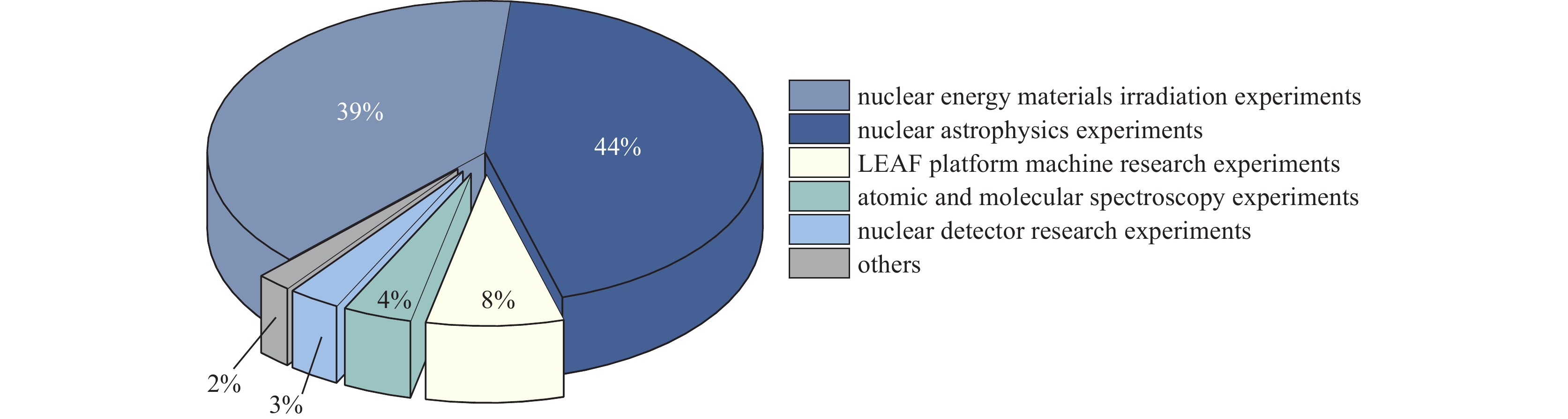
摘要: 低能量强流高电荷态重离子加速器装置(LEAF)是中国科学院近代物理研究所承担的国家重大科研仪器项目,旨在构建一台具备高电荷态、高流强、全谱系离子加速能力的低能重离子综合实验装置。系统介绍了该装置的结构、核心部件设计参数及束流调控策略,并重点报告了装置试运行期间在束流加速能力、多离子混合束制备及低能散碳离子束调控等方面取得的代表性进展。截至目前,LEAF已累计为终端实验提供超过13 000小时束流支持,覆盖质荷比A/q=2~7的多种离子种类,实现了高电荷态、高流强重离子束流的稳定加速。平台构建了适用于协同辐照研究的“鸡尾酒束”运行模式,并建立了具备高流强与低能散特性的12C2+束流系统,用于伽莫夫能区核反应的精密测量。最后,文章结合终端实验需求,提出了装置未来的发展方向,包括调能系统拓展与三离子协同供束能力增强等,以期进一步提升平台对核天体物理、核能材料等领域的支撑能力。Abstract:The Low Energy High Intensity High Charge State Heavy Ion Accelerator Facility (LEAF) is a national scientific instrument developed by the Institute of Modern Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, to provide high-current, high-charge-state, full-spectrum low-energy heavy ion beams for interdisciplinary studies.
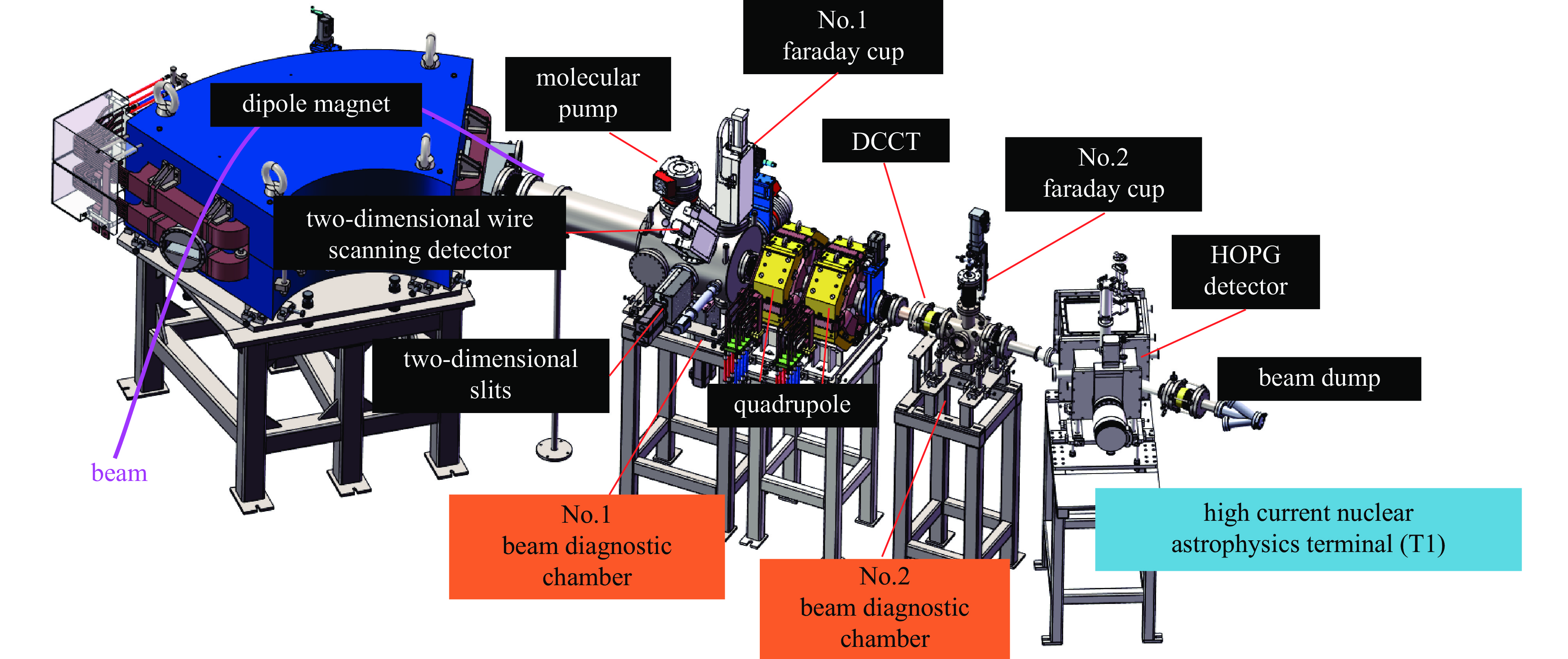
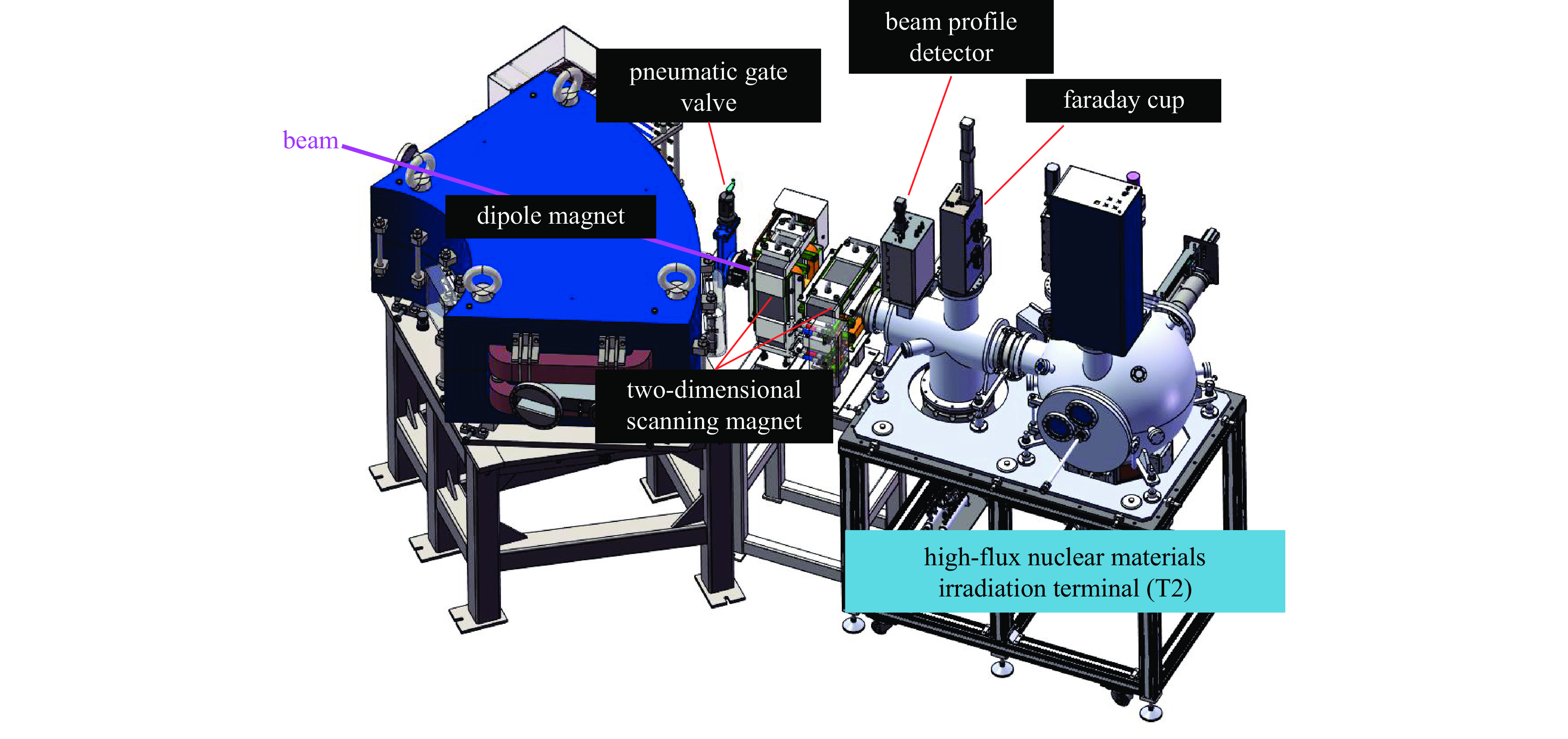
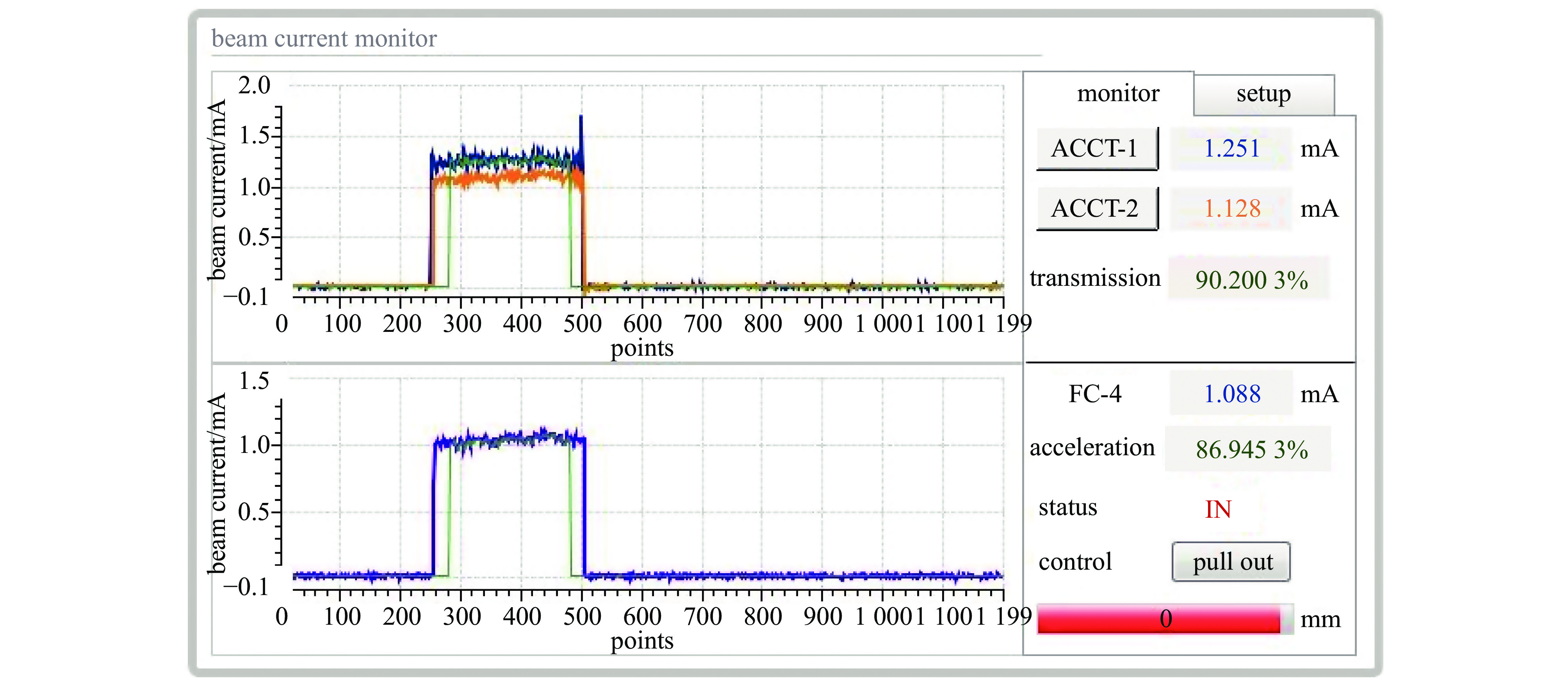
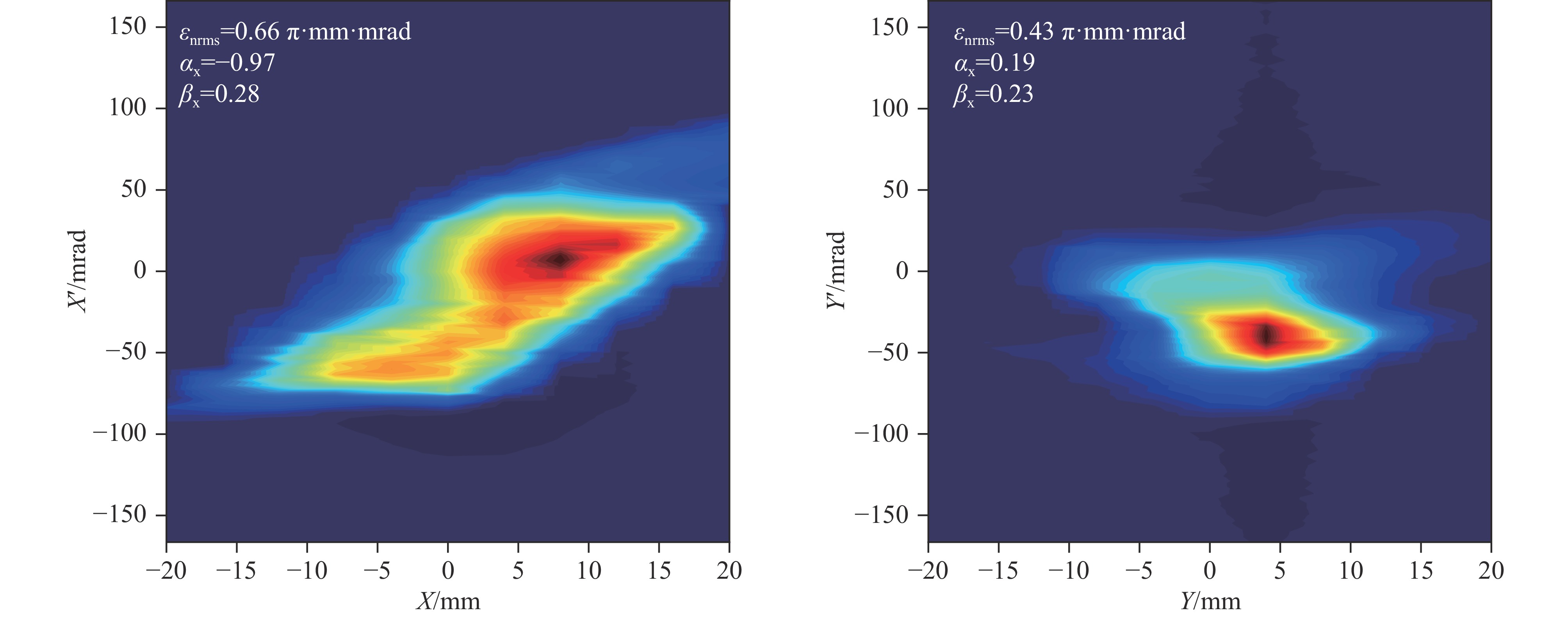
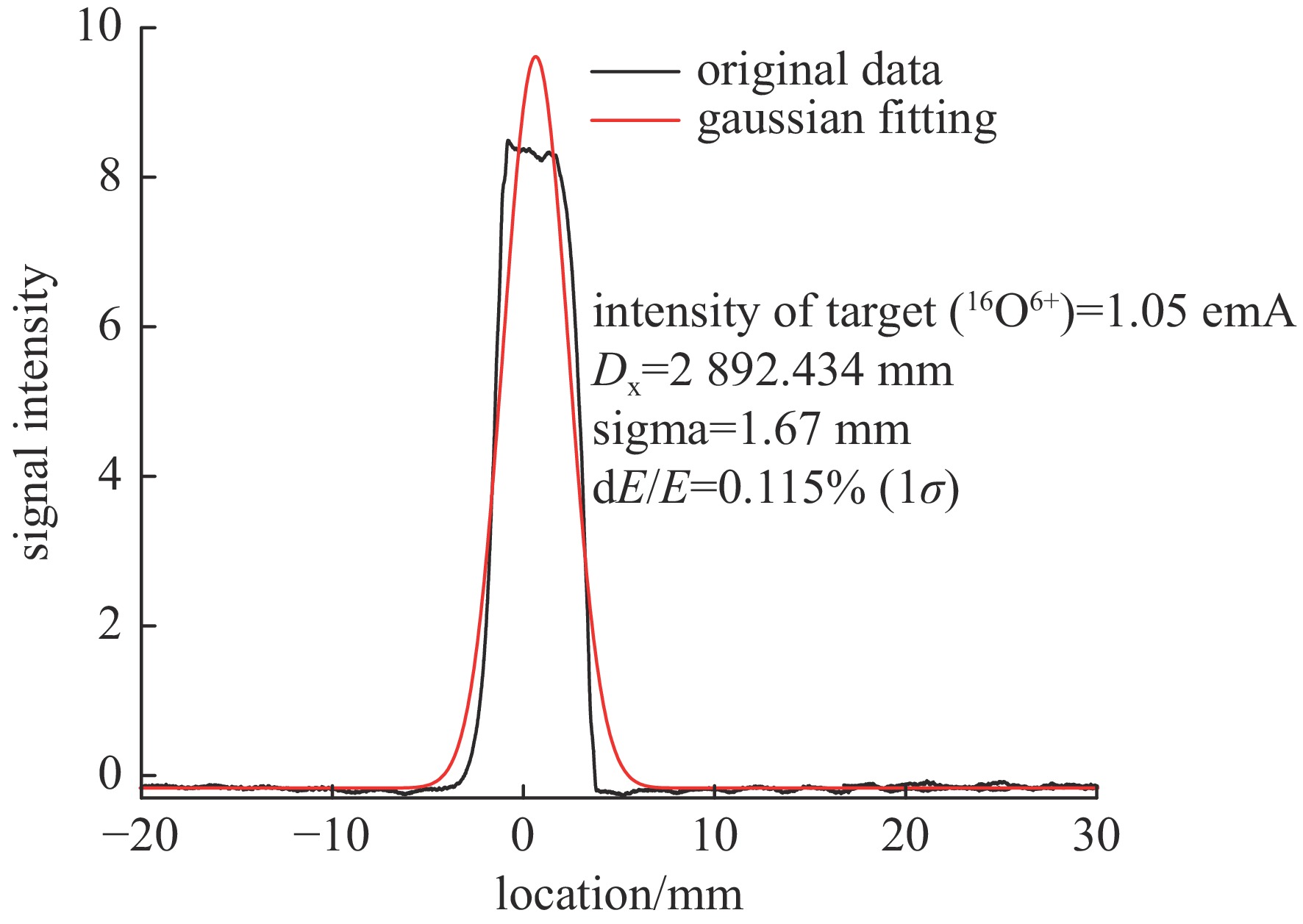
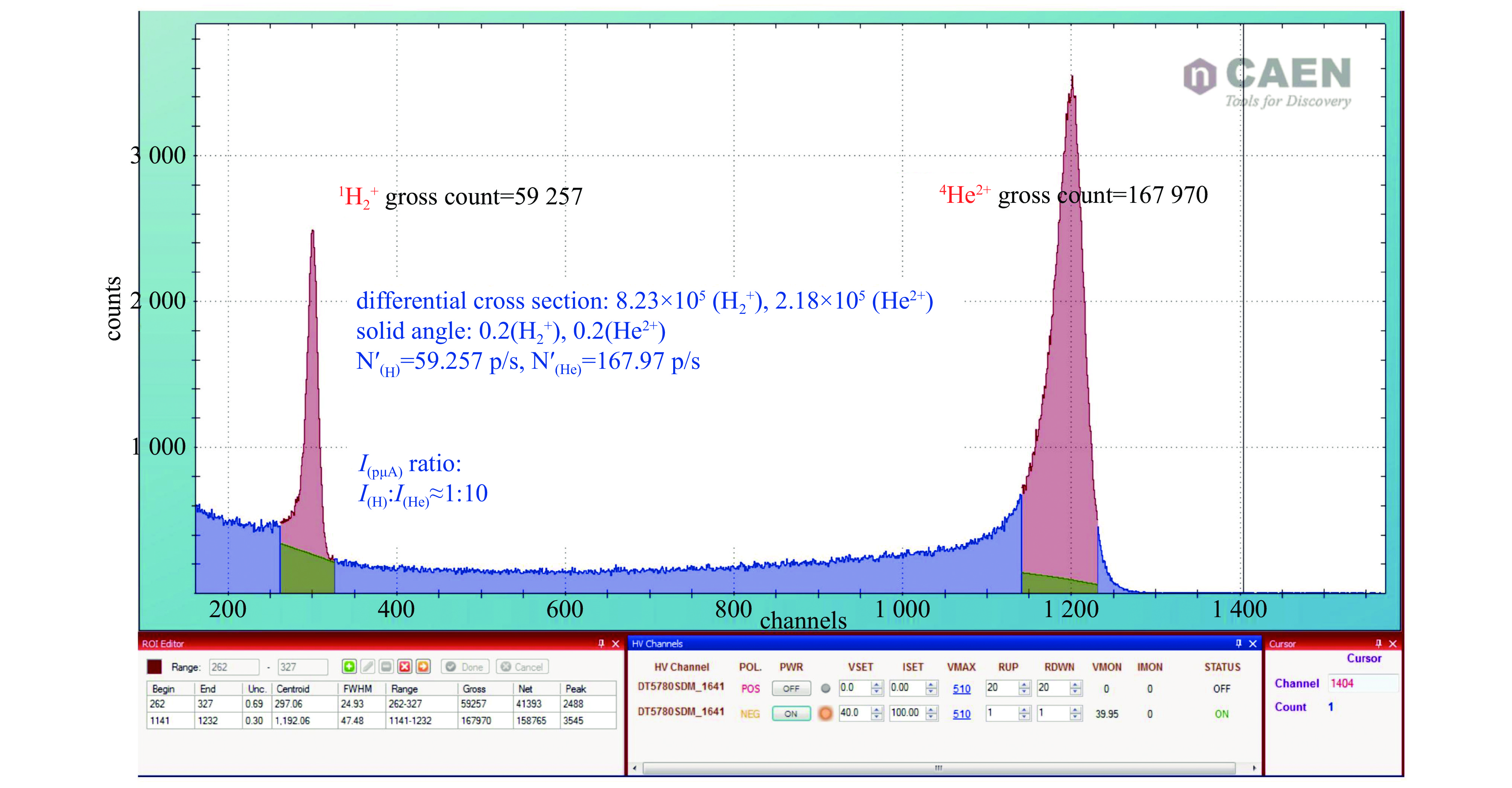
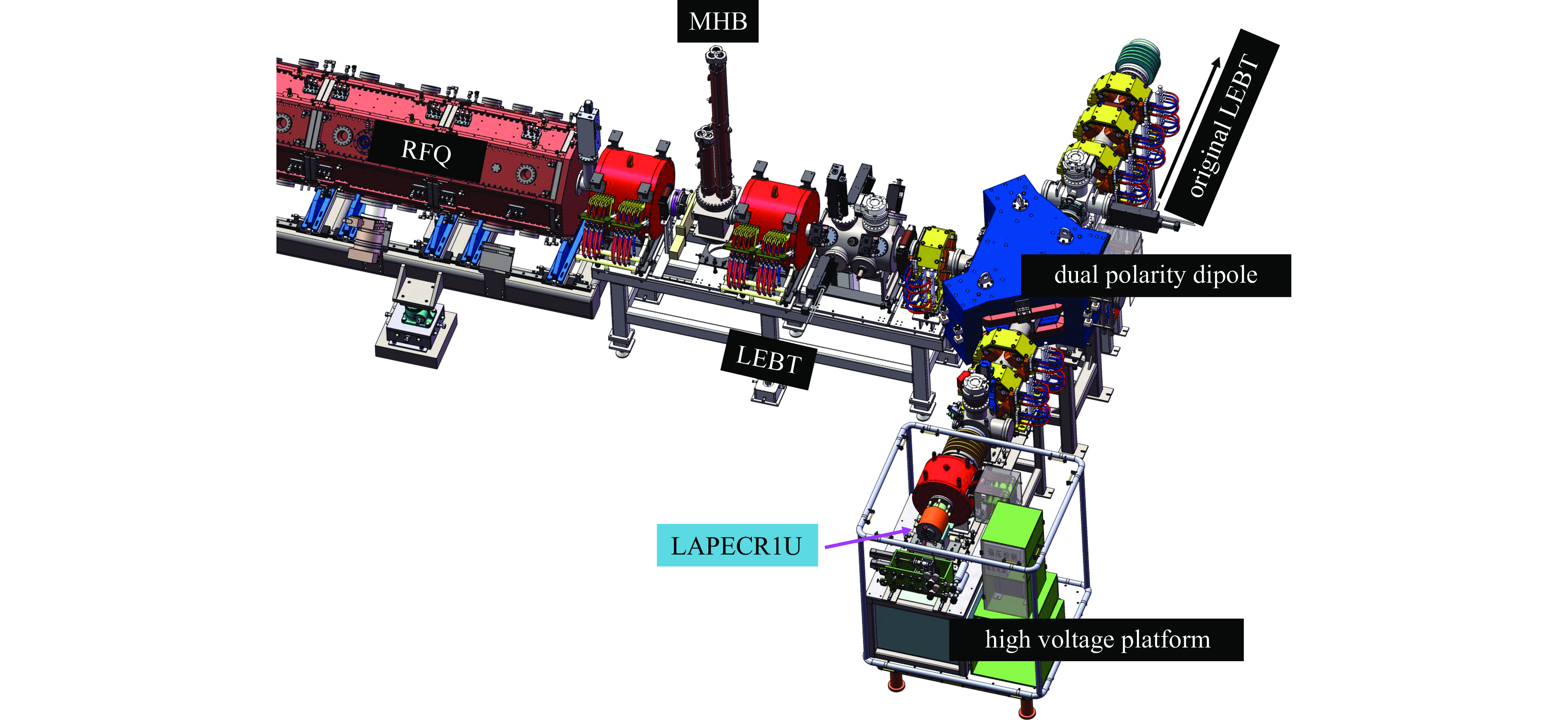
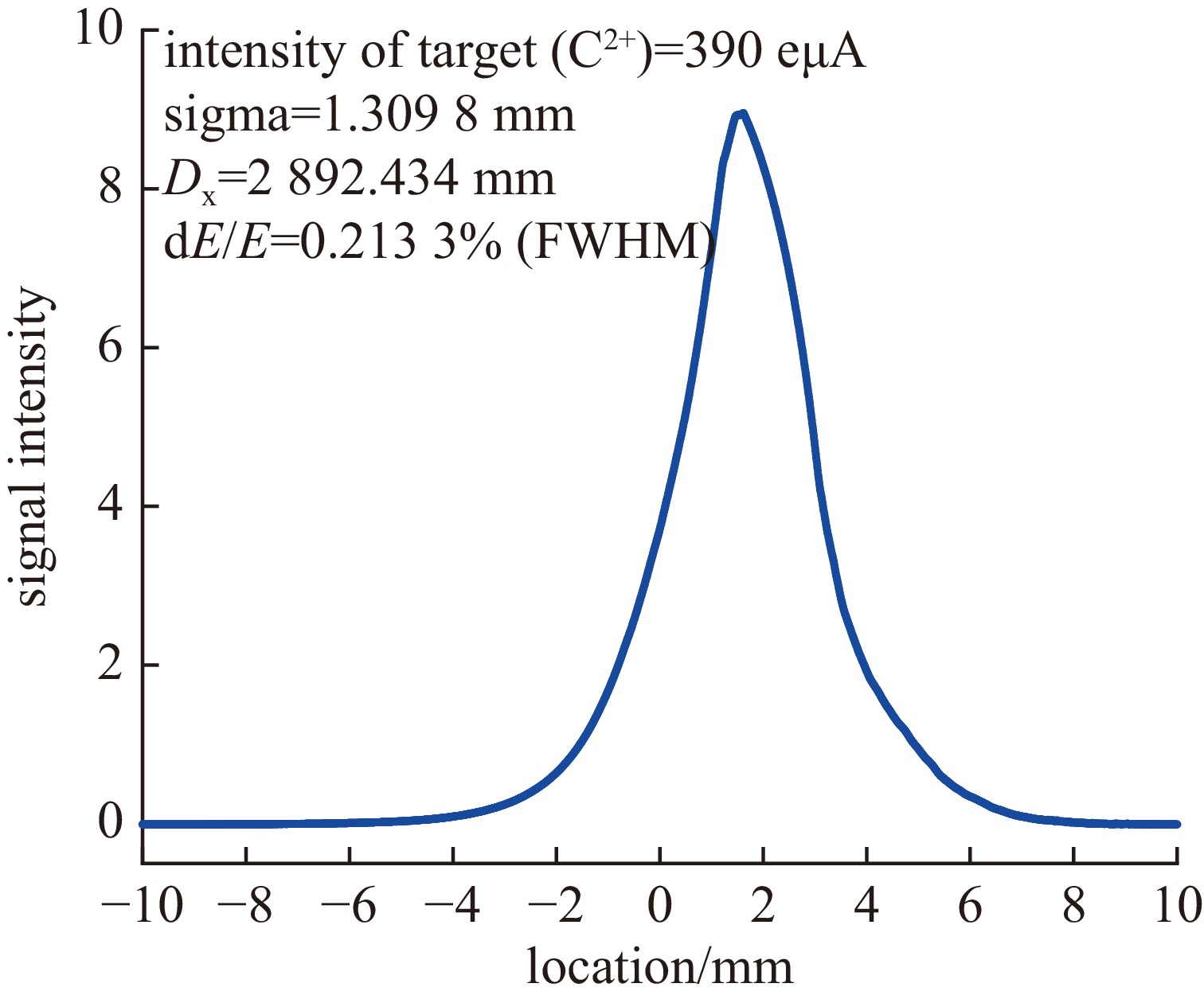
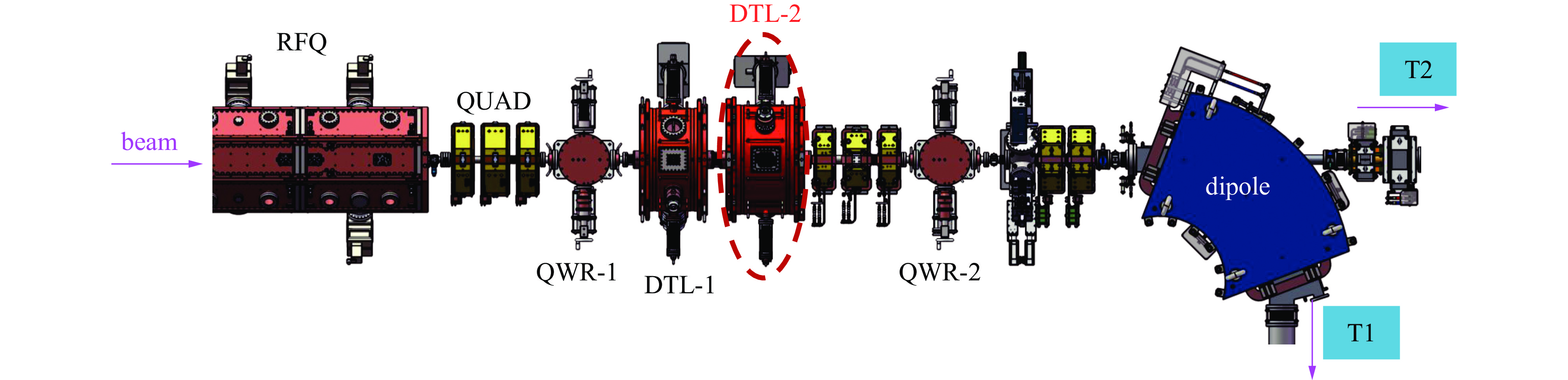
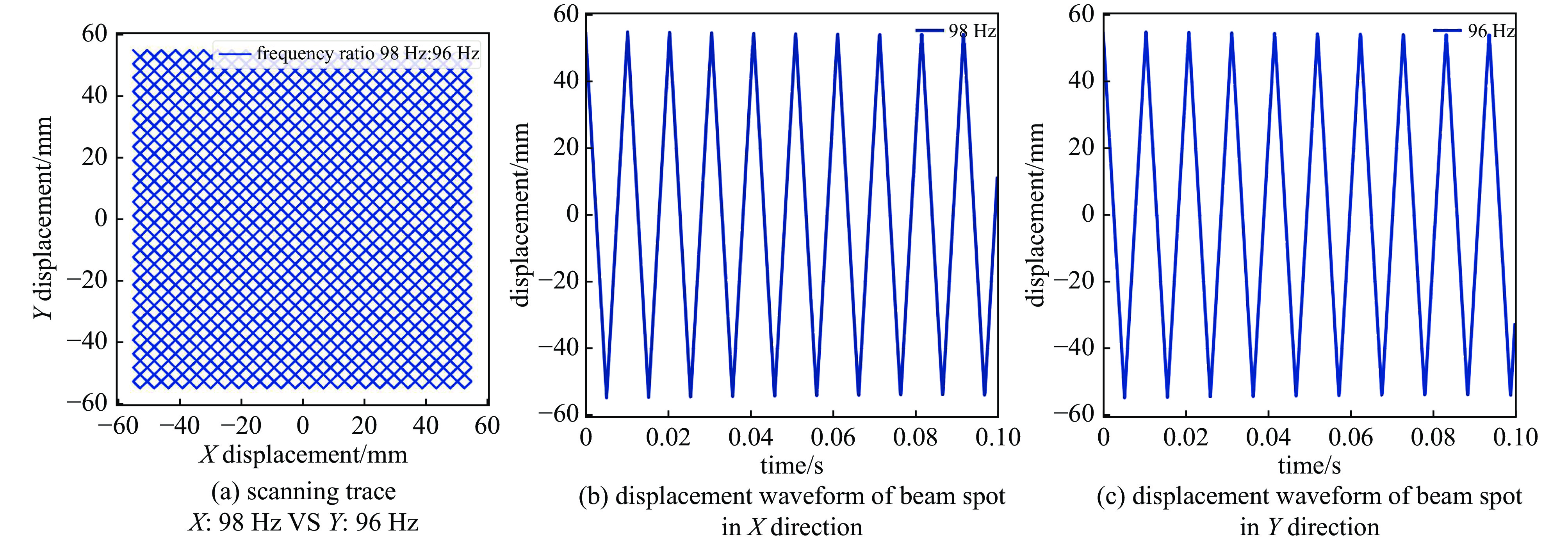
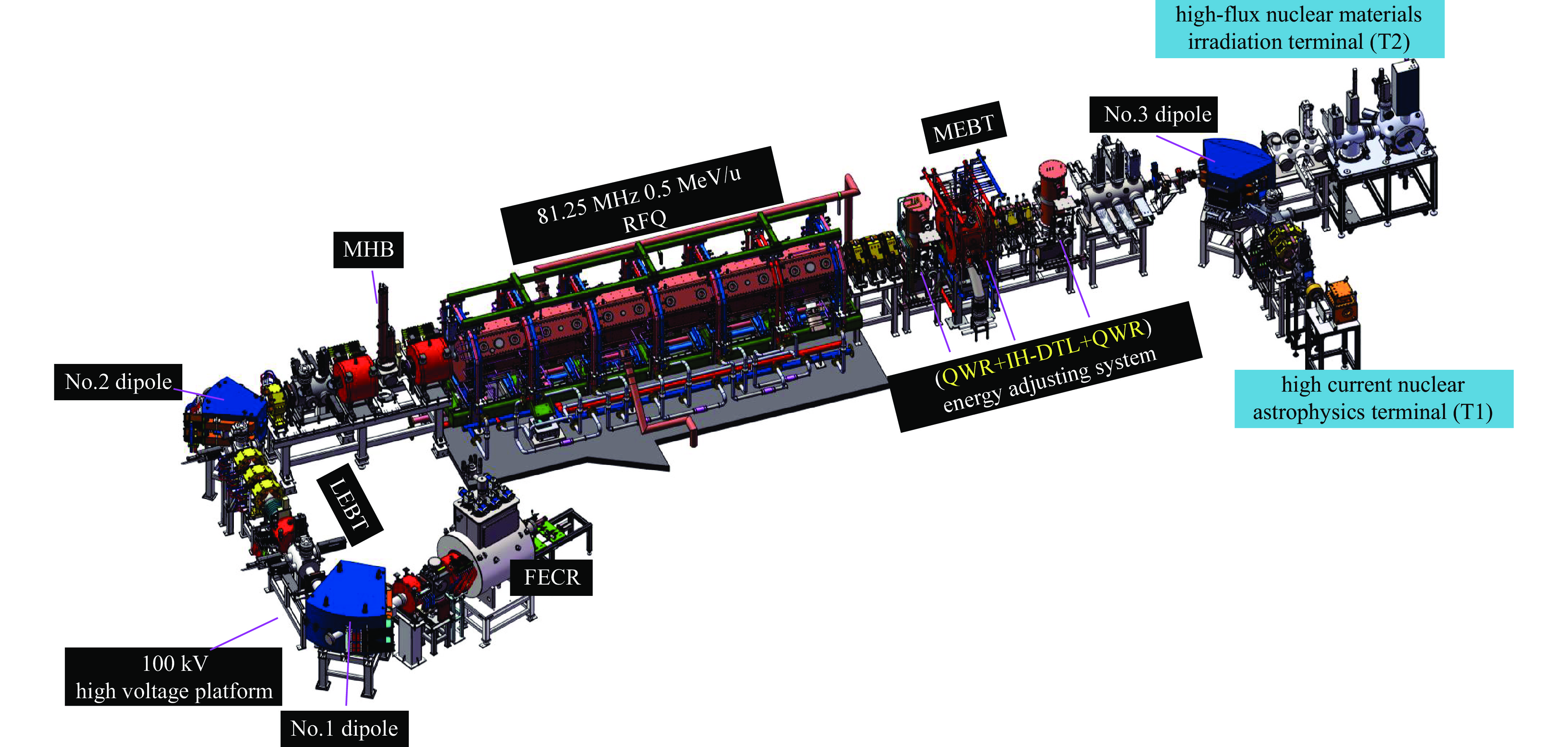
Background To meet research needs in nuclear astrophysics, atomic and molecular physics, and nuclear materials, LEAF offers tunable energies from 0.3 to 0.7 MeV/u and supports continuous-wave acceleration for ions with A/q = 2-7.Purpose This paper presents an overview of the construction progress, key design parameters, and operational performance of the facility, summarizing recent achievements and outlining future development goals.Methods The paper introduces the system architecture—comprising the 45 GHz superconducting ECR ion source FECR, RFQ, IH-DTL, and terminal beamlines—and describes beam commissioning and diagnostic approaches.Results LEAF has successfully achieved stable acceleration of multi-species, high-charge-state heavy ion beams with intensities up to 1 emA. It has delivered more than 13,000 hours of beam time, realized efficient operation of“cocktail”multi-ion beams, and established a high-current, low-energy-spread 12C2+ beamline for precise reaction measurements in the Gamow window.Conclusions These results verify LEAF’s excellent beam quality and operational reliability. Planned upgrades—including an extended energy tuning range and triple-ion beam capability—will further enhance its role as a frontier platform for experimental studies in nuclear astrophysics and radiation effects in advanced materials.-
Key words:
- heavy ion accelerator /
- beam control /
- cocktail beam /
- high current carbon ion beam /
- energy tuning
-
表 1 FECR 主要设计参数
Table 1. The main design parameters of FECR
operating frequency /GHz RF power /kW magnet coils mirror fields/T Brad chamber ID/mm mirror length/mm 28~45 > 20 Nb3Sn ~6.4 ~3.2 ~Ø140 ~500 表 2 LEAF-RFQ 主要设计参数
Table 2. The main design parameters of LEAF-RFQ
duty
cycleoperating
frequency/MHzresonant
typeinput particle
energy/(keV·u−1)output particle
energy/(keV·u−1)M/q
rangelength of the
RFQ vane/cmmaximum vane
voltage/kV100% (CW mode) 81.25 4~vane 14 500 2 (H2+)~7 (238U34+) ~596.4 70 表 3 IH-DTL主要设计参数
Table 3. The main design parameters of IH-DTL
duty
cycleoperating
frequency/MHznumber
of gapsGap/mm tube
length/mmmaximum gap
voltage/kVinput particle
energy/(keV·u−1)output particle
energy/(keV·u−1)cavity
length/mm100% (CW mode) 81.25 8 25.96 32 195 500 300~700 ~563.7 -
[1] Yang Yao, Zhai Yuhan, Jiang P Y, et al. Commissioning progress of LEAF at IMP[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2020, 1401: 012019. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1401/1/012019 [2] Yang Jiancheng, Xia Jiawen, Xiao Guoqing, et al. High intensity heavy ion accelerator facility (HIAF) in China[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2013, 317: 263-265. doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2013.08.046 [3] Zhao H W, Sun L T, Guo J W, et al. Superconducting ECR ion source: from 24-28 GHz SECRAL to 45 GHz fourth generation ECR[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2018, 89: 052301. doi: 10.1063/1.5017479 [4] Yang Yao, Tian Ruixia, Zhai Yuhan, et al. Development of a beam energy adjustment system after a Radio-Frequency-Quadrupole[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2022, 1039: 167095. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2022.167095 [5] Yang Yao, Zhai Yuhan, Tian Ruixia, et al. Longitudinal emittance measurement for an external-bunching-based heavy-ion RFQ[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2022, 1029: 166457. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2022.166457 [6] Barrón-Palos L, Aguilera E F, Aspiazu J, et al. Absolute cross sections measurement for the 12C + 12C system at astrophysically relevant energies[J]. Nuclear Physics A, 2006, 779: 318-332. doi: 10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2006.09.004 [7] Wang Shuo, Li Yunzhen, Ru Longhui, et al. 12C+12C fusion reaction at astrophysical energies using HOPG target[J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2025, 36: 143. doi: 10.1007/s41365-025-01714-3 [8] Yang Yao, Sun L T, Zhai Yuhan, et al. Heavy ion accelerator facility front end design and commissioning[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2019, 22: 110101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.22.110101 [9] Wu Zhengrong, Sun Liepeng, Qiu Feng, et al. A new multi-harmonic buncher for the LEAF project[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2023, 1047: 167856. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2022.167856 [10] Chauvin N. Space-charge effect[DB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1410.7991, 2014. [11] Zhai Yuhan, Yang Yao, Sun Liangting, et al. Production of high intensity highly charged cocktail beams at LEAF[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2022, 1027: 166157. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2021.166157 [12] Zhai Yuhan, Yang Yao, Liu Yong, et al. Variable-energy cocktail beam technology for investigating synergistic damage in nuclear materials on LEAF platform[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2024, 1069: 169987. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2024.169987 [13] Li J Q, Sun L T, Yang Yao, et al. Development of an all permanent magnet ECR ion source for low and medium charge state ions production[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2020, 1401: 012022. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1401/1/012022 [14] Baluc N. Materials for fusion power reactors[J]. Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 2006, 48(12B): B165-B177. doi: 10.1088/0741-3335/48/12B/S16 [15] Zinkle S J. Fusion materials science: overview of challenges and recent progress[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2005, 12: 058101. doi: 10.1063/1.1880013 -




 下载:
下载: