Prototype development of ion source control and acquisition system based on wireless optical communication
-
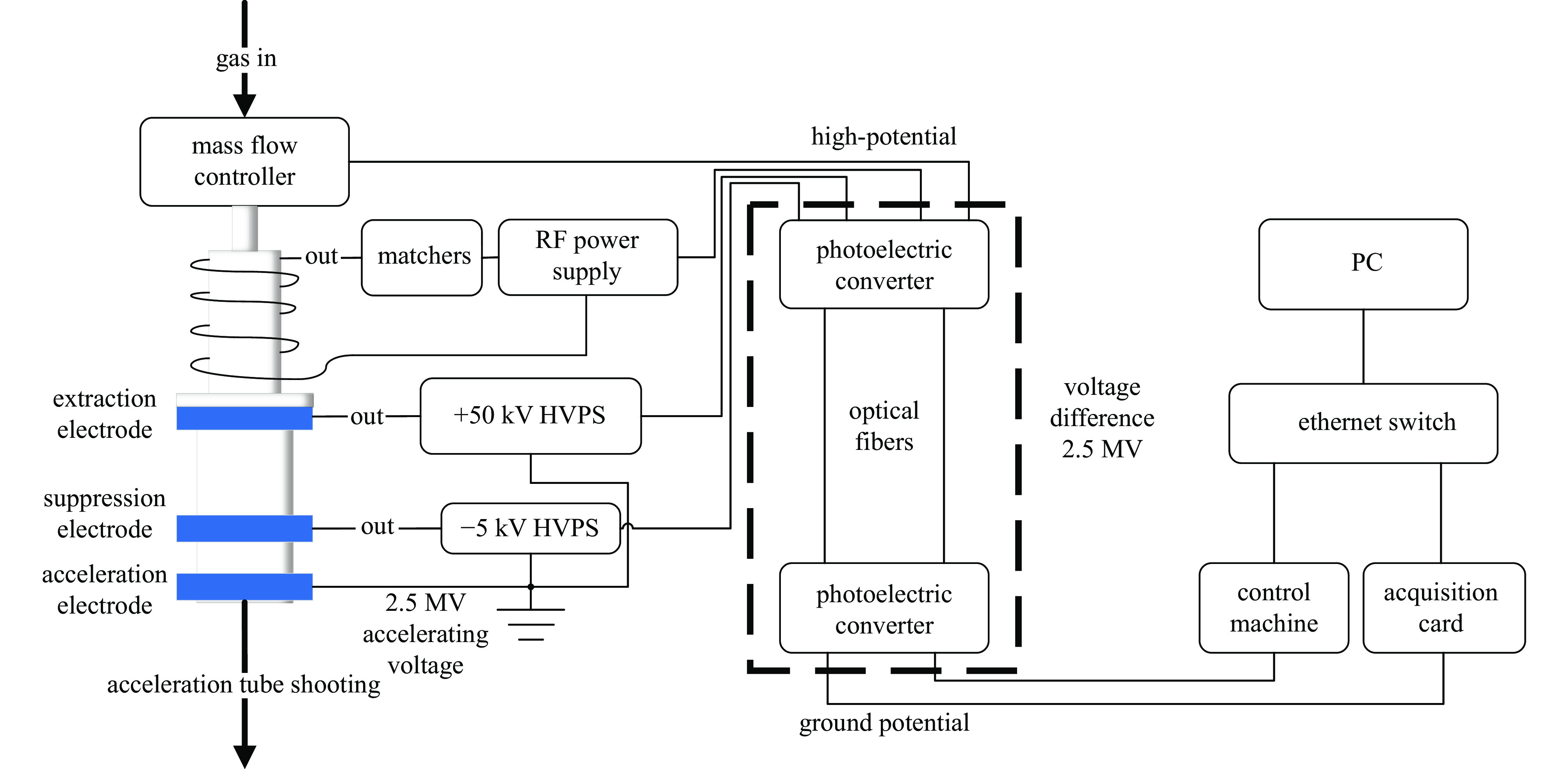
摘要: 直流高压加速器离子源系统需在兆伏级高压平台运行,有线通信介质如光纤在紧凑型使用工况下由于耐压局限性而存在击穿风险。为此,设计并研制了一种基于无线光通信(WOC)的离子源控制与采集系统样机,针对2.5 MV直流高压加速器中电感耦合等离子体(ICP)离子源系统中的高压电源、射频电源和质量流量计所需的模拟量控制与采集要求,采用差分输入模数转换(ADC)对控制与采集原始信号进行采样,经数字处理后通过无线光通信传输;无线光信号通过光电转换,再经数模转换(DAC)和放大电路重构原始信号。通过搭建离线测试平台,验证所设计的无线光系统能够稳定控制直流高压加速器离子源系统相关设备。实验测试结果表明,该无线光系统满足硼中子俘获治疗(BNCT)项目的技术要求,具备在2.5 MV直流高压加速器离子源系统中应用的可行性。Abstract:
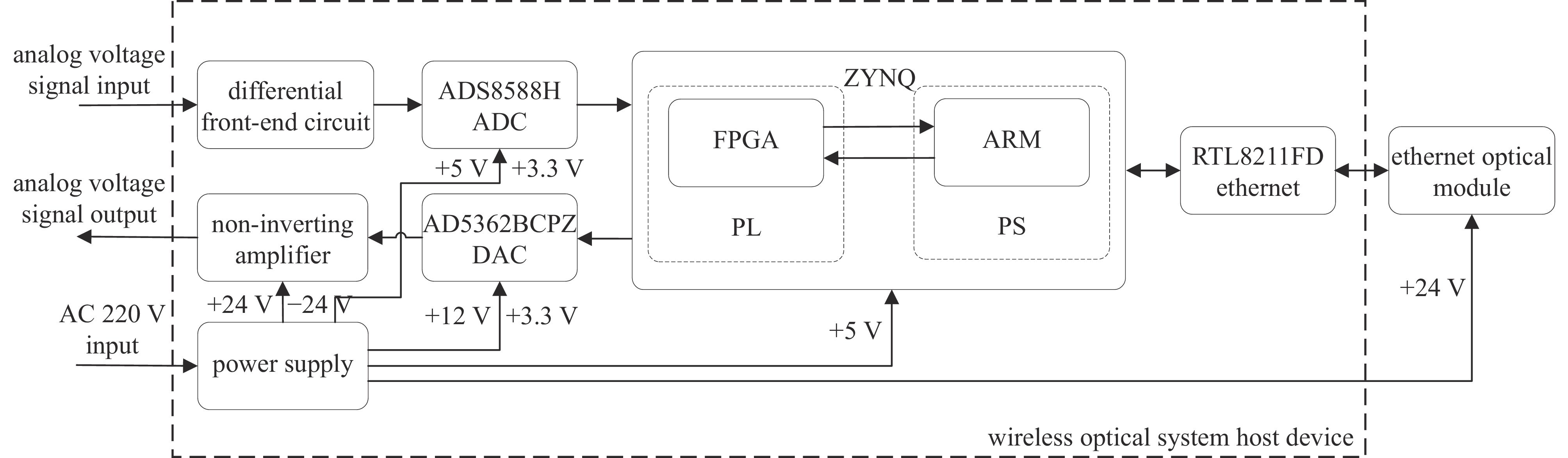
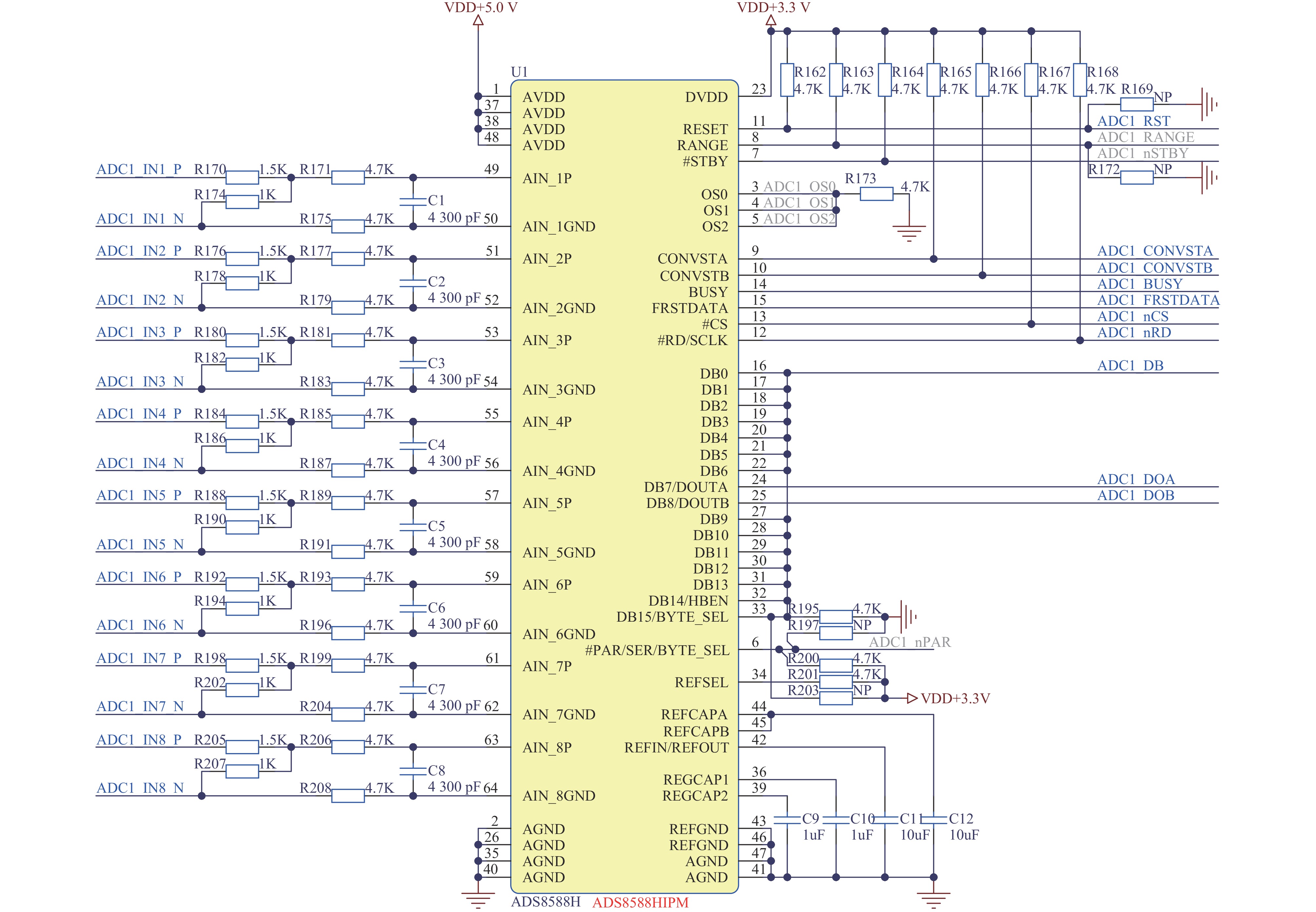
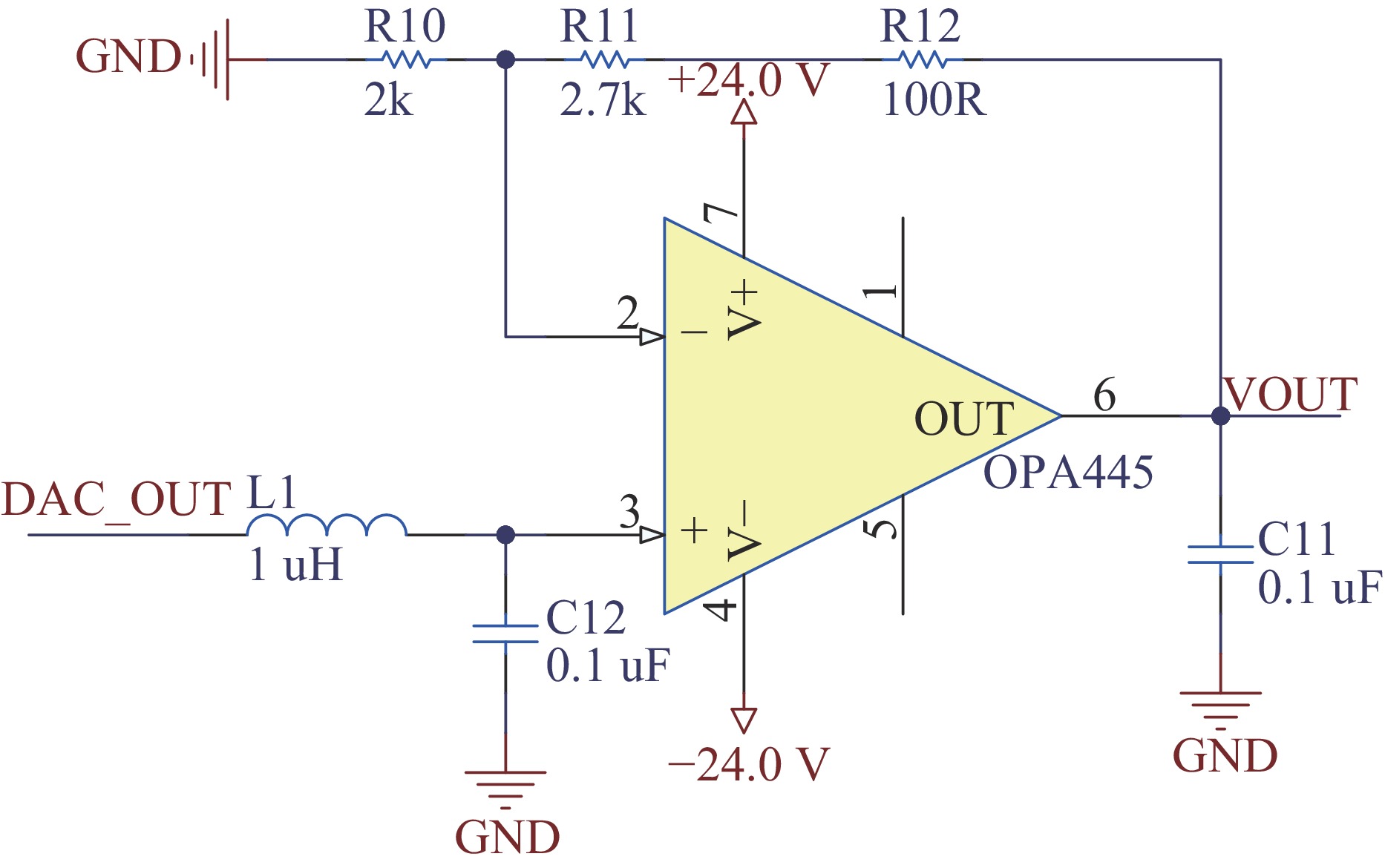
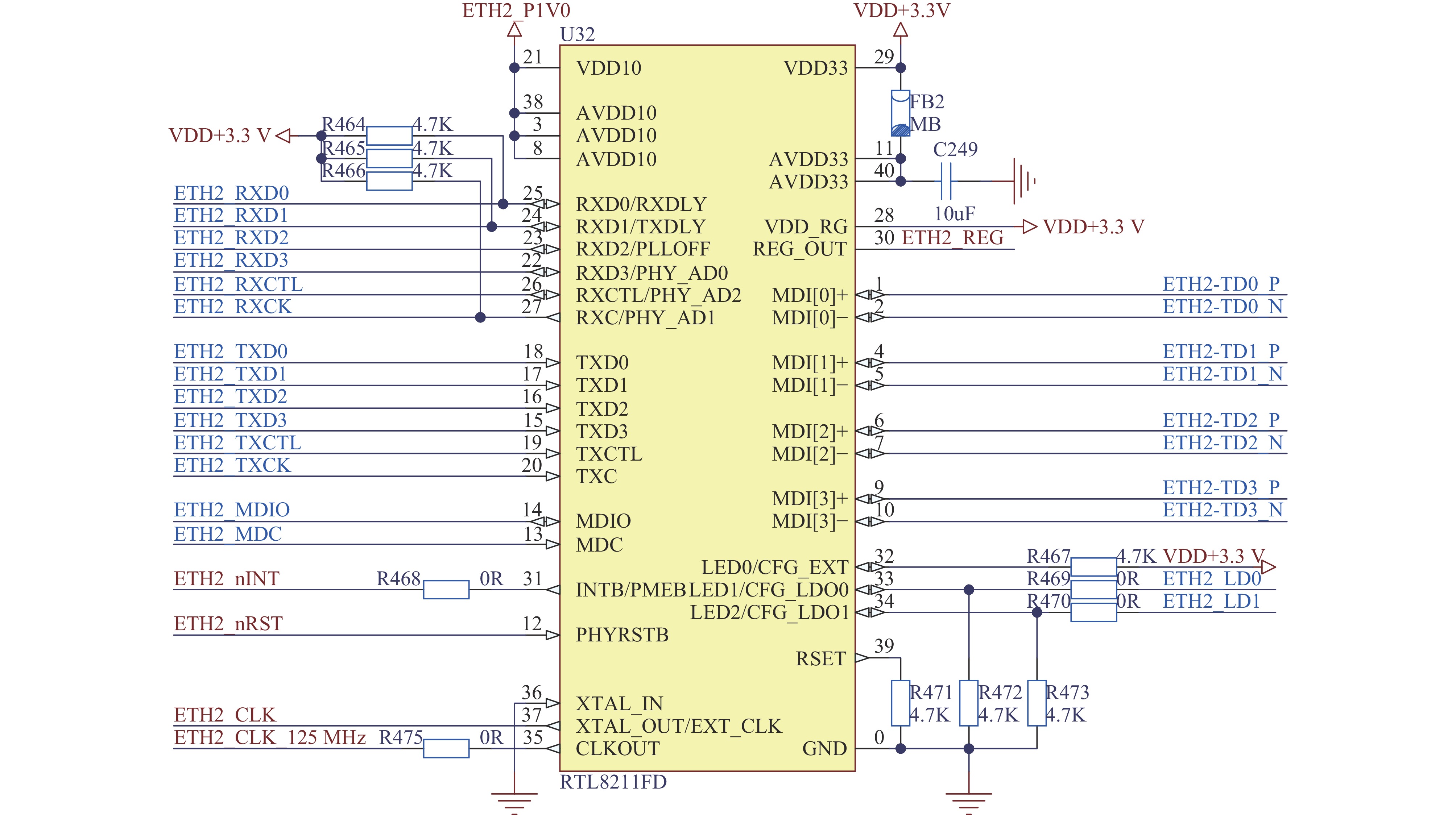
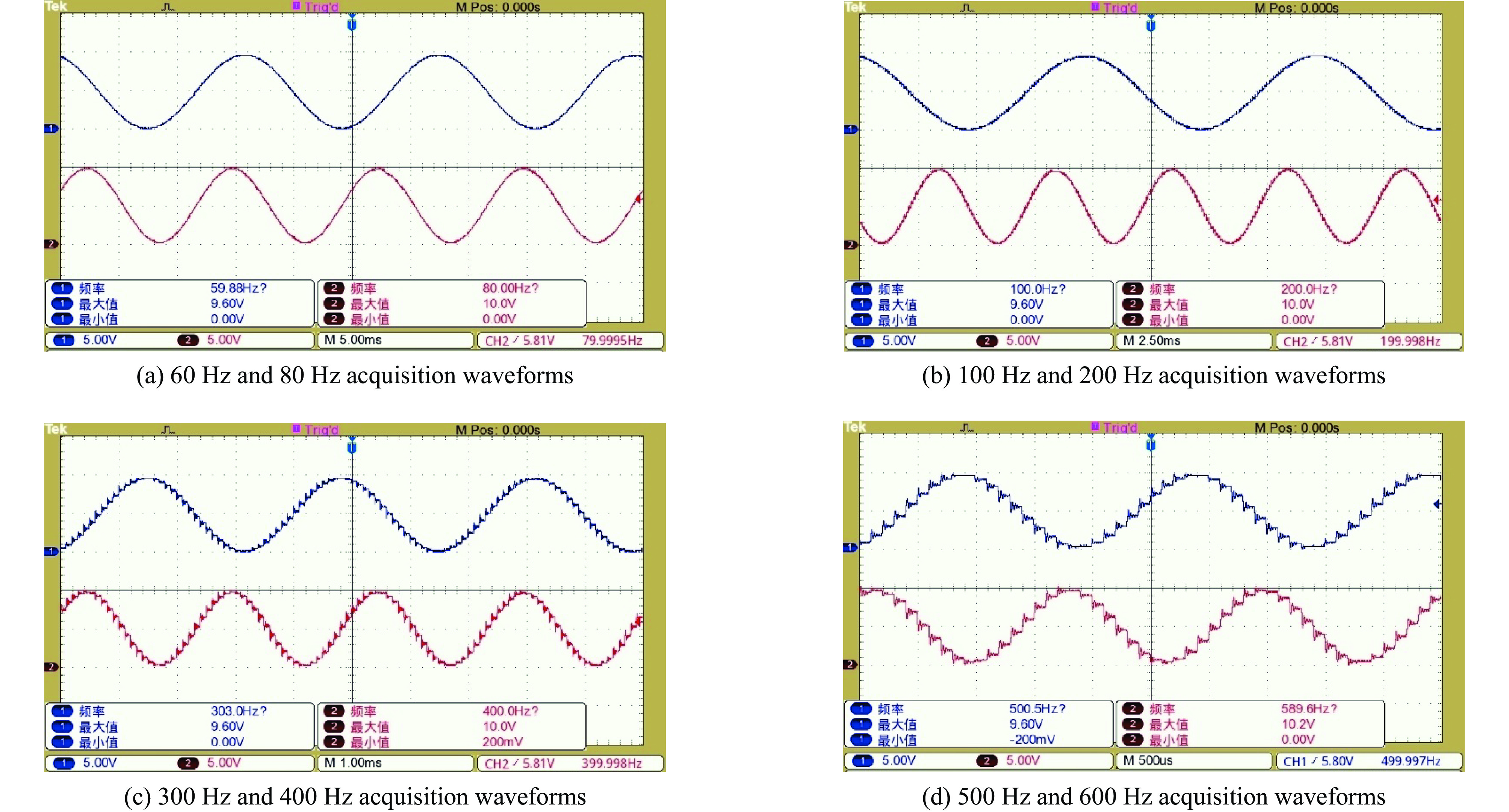
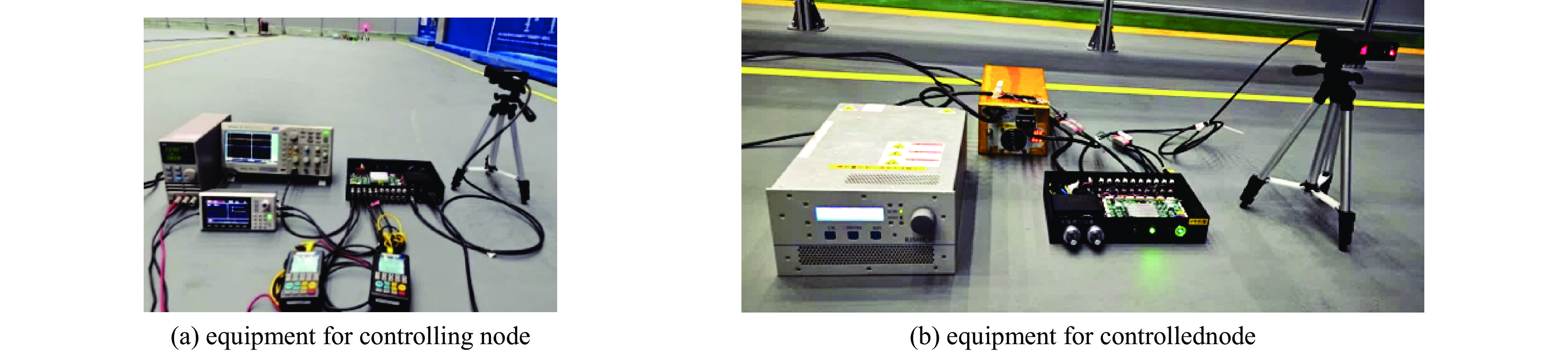
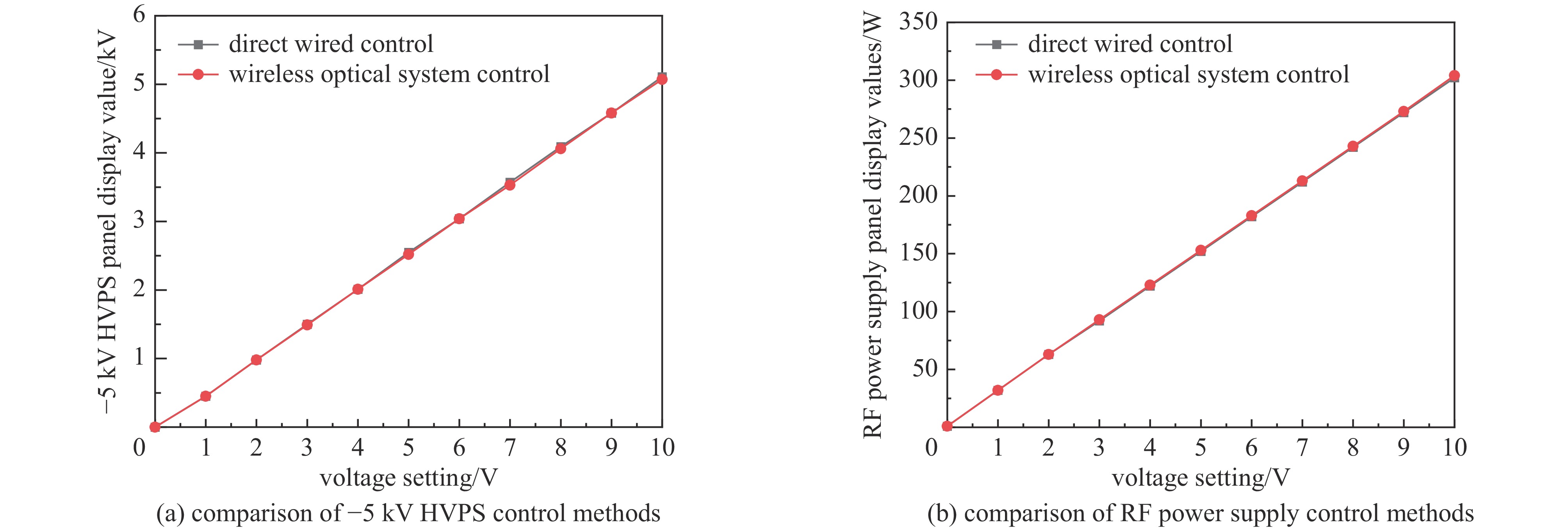
Background The ion source system for DC high-voltage accelerators operates at megavolt-level high-potential platforms, where wired communication media such as optical fibers face the risk of dielectric breakdown in compact applications due to voltage withstand constraints.Purpose To address this, a prototype of ion source control and acquisition system based on wireless optical communication (WOC) is designed.Methods For the analog control and acquisition requirements of high-voltage power supplies, RF power sources, and mass flow controllers in the 2.5 MV DC high-voltage accelerator’s inductively coupled plasma (ICP) ion source system, differential-input analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) is adopted to sample raw control and acquisition signals. After digital processing, signals are transmitted via WOC. The optical signals are converted via photoelectric conversion, then reconstructed into original analog signals through digital-to-analog conversion (DAC) and amplification circuits. In this design, a ZYNQ-based digital processing platform coordinates the acquisition, transmission, and reconstruction processes, which enables ADC/DAC data interaction and stable Ethernet optical communication, ensuring the overall integrity of the wireless optical control system.Results An offline test platform verified that the designed WOC system can stably control the relevant equipment in the DC high-voltage accelerator ion source system. The transmission accuracy remained within the 1.5% deviation requirement, and the link operated reliably over long durations.Conclusions Experimental results indicate that the WOC system meets the technical requirements of the BNCT project and is feasible for application in the 2.5 MV DC high-voltage accelerator ion source system.-
Key words:
- wireless optical communication /
- DC high-voltage accelerator /
- ion source system /
- ADC/DAC /
- ZYNQ
-
表 1 离子源设备控制和采集通道
Table 1. Ion source equipment control and acquisition channels
control signal/V acquisition signal/V mass flow controller 0-10 (setting, 1 path) unused RF power supply 0-10 (setting, 1 path) 22-24 (start, 1 path) 0-10 (2 paths) HVPS 0-10 (setting, 2 paths) 12 (start, 1 path) 0-10 (2 paths) 表 2 激光中心光斑到激光接收平面距离
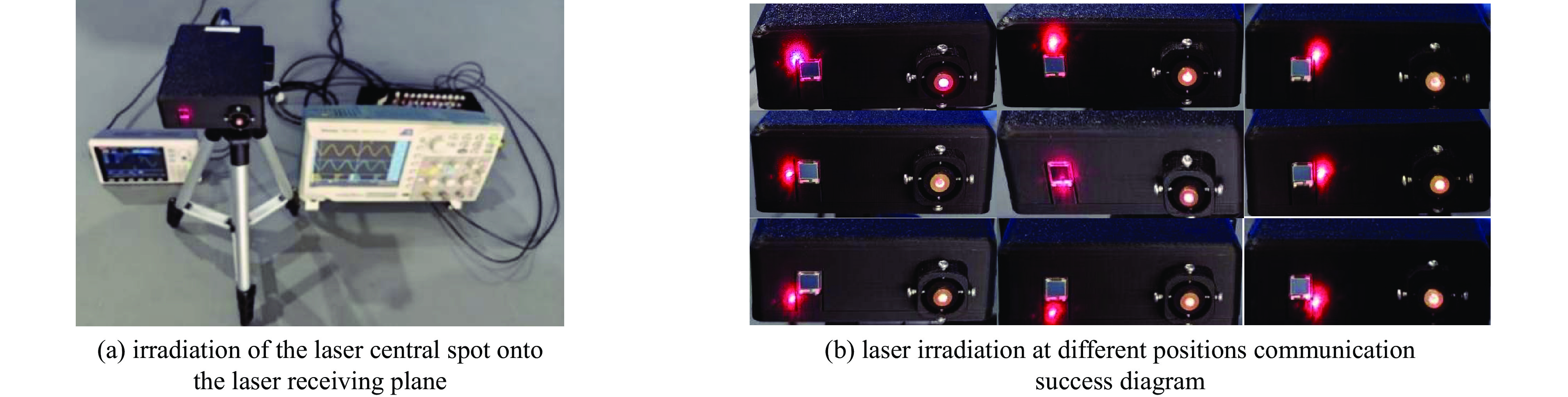
Table 2. Distance from laser central spot to laser receiving plane
horizontal distance/mm vertiacl distance/mm top left corner 1.43 1.52 top 0 4.02 top right corner 1.60 1.19 right 2.28 0 bottom right corner 1.34 2.38 bottom 0 5.17 bottom left corner 1.98 2.74 left 2.98 0 -
[1] 徐川, 付恩刚, 高原, 等. 北京大学静电加速器及其应用[J]. 科学通报, 2023, 68(9): 1096-1103 doi: 10.1360/TB-2022-1132Xu Chuan, Fu Engang, Gao Yuan, et al. Electrostatic accelerator facilities and their applications at Peking University[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2023, 68(9): 1096-1103 doi: 10.1360/TB-2022-1132 [2] 傅世年, 梁天骄, 陈和生. BNCT中子源的研发现况与展望[J]. 科学通报, 2022, 67(14): 1471-1478 doi: 10.1360/TB-2021-1254Fu Shinian, Liang Tianjiao, Chen Hesheng. Status and outlook: research and development on the neutron source for BNCT[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2022, 67(14): 1471-1478 doi: 10.1360/TB-2021-1254 [3] Wang Tianyu, Mao Jie, Zhang Boya, et al. Polymeric insulating materials characteristics for high-voltage applications[J]. Nature Reviews Electrical Engineering, 2024, 1(8): 516-528. doi: 10.1038/s44287-024-00070-5 [4] 刘顺明, 欧阳华甫, 胡志良, 等. 硼中子俘获治疗(BNCT)真空系统[J]. 真空, 2020, 57(6): 64-68Liu Shunming, Ouyang Huafu, Hu Zhiliang, et al. Vacuum system for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT)[J]. Vacuum, 2020, 57(6): 64-68 [5] 孙振武, 李玉晓, 姜胜南, 等. 4 MV静电加速器调试中出现的问题及解决方案[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2005, 17(7): 1117-1120Sun Zhenwu, Li Yuxiao, Jiang Shengnan, et al. Debugging of 4 MV electrostatic accelerator[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2005, 17(7): 1117-1120 [6] 王鹏鹏, 张玮, 武启, 等. 锦屏深地强流离子源控制系统的研制[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2023, 35: 104001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.220356Wang Pengpeng, Zhang Wei, Wu Qi, et al. Development of control system for JUNA ion source[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2023, 35: 104001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.220356 [7] Ding Jupeng, Liu Wenwen, I C L, et al. Advanced progress of optical wireless technologies for power industry: an overview[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10: 6463. doi: 10.3390/app10186463 [8] 李日正, 倪国华, 孙红梅, 等. 感应耦合等离子体离子源放电特性仿真研究[J]. 真空科学与技术学报, 2024, 44(9): 819-824Li Rizheng, Ni Guohua, Sun Hongmei, et al. Simulation of discharge characteristics of inductively coupled plasma ion source[J]. Chinese Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 2024, 44(9): 819-824 [9] 李帅, 孟献才, 钱玉忠. 紧凑型电感耦合加速器中子源控制系统设计[J]. 工业控制计算机, 2025, 38(4): 4-5,8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-182X.2025.04.002Li Shuai, Meng Xiancai, Qian Yuzhong. Design of compact inductively coupled accelerator neutron source control system[J]. Industrial Control Computer, 2025, 38(4): 4-5,8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-182X.2025.04.002 [10] Zhang Jiawen, Lin Zhenhui, Hu Jie, et al. Design of readout and characterization system for multi-pixel superconducting terahertz MKIDs[J]. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2025, 25: 045002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4527/adbd9e [11] 熊绪文, 孟献才, 洪兵, 等. 基于ZYNQ的γ能谱采集系统研制[J]. 核电子学与探测技术, 2024, 44(6): 1069-1077 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2024.06.014Xiong Xuwen, Meng Xiancai, Hong Bing, et al. Development of a gamma spectrum acquisition system based on ZYNQ[J]. Nuclear Electronics & Detection Technology, 2024, 44(6): 1069-1077 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2024.06.014 [12] Zayed A, Trabes E, Tarrillo J, et al. Efficient embedded system for drowsiness detection based on EEG signals: features extraction and hardware acceleration[J]. Electronics, 2025, 14: 404. doi: 10.3390/electronics14030404 [13] Oleszek M, Rymarczyk T, Adamkiewicz P. Next generation of hybrid tomograph for acquisition of measurement data[C]//Proceedings of 2019 Applications of Electromagnetics in Modern Engineering and Medicine (PTZE). 2019: 125-129. [14] Mauch S, Reger J, Reinlein C, et al. FPGA-accelerated adaptive optics wavefront control[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 8978, MEMS Adaptive Optics VIII. 2014: 897802. [15] 李涛. 面向超快激光的高精度温控驱动系统及其应用[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2024: 42-45Li Tao. High-precision temperature control drive system for ultrafast lasers and its applications[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, 2024: 42-45 [16] 关鑫. 固体火箭发动机尾焰红外亮度光纤测试系统研制[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2024: 33-58Guan Xin. Development of optical fiber testing system for solid rocket motor tail flame infrared brightness[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2024: 33-58 [17] Xiao Yang, Ai Jiakang, Chen Xiangyang, et al. 30 Gbps visible light communication in rainy environments based on laser diodes[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2025, 23: 060604. doi: 10.3788/COL202523.060604 [18] 姚琰昕. 基于LED阵列光源的QAM-OFDM水下无线光通信系统研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2022: 30-55Yao Yanxin. Research on QAM-OFDM underwater wireless optical communication system based on LED array light source[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2022: 30-55 [19] 李璞. 面向深海应用的水下无线光通信调制技术研究[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2021: 41-55Li Pu. Research on the modulation technology of underwater wireless optical communication for deep sea applications[D]. Xi'an: Xidian University, 2021: 41-55 [20] 王楚鸣, 洪涛, 钟志伟, 等. 基于Chirp波形的物联信号在低轨卫星信道上的适应性分析[J]. 无线电通信技术, 2024, 50(4): 739-749 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2024.04.016Wang Chuming, Hong Tao, Zhong Zhiwei, et al. Adaptive analysis of IoT signals based on Chirp modulation in low earth orbit satellite channels[J]. Radio Communications Technology, 2024, 50(4): 739-749 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2024.04.016 -




 下载:
下载: