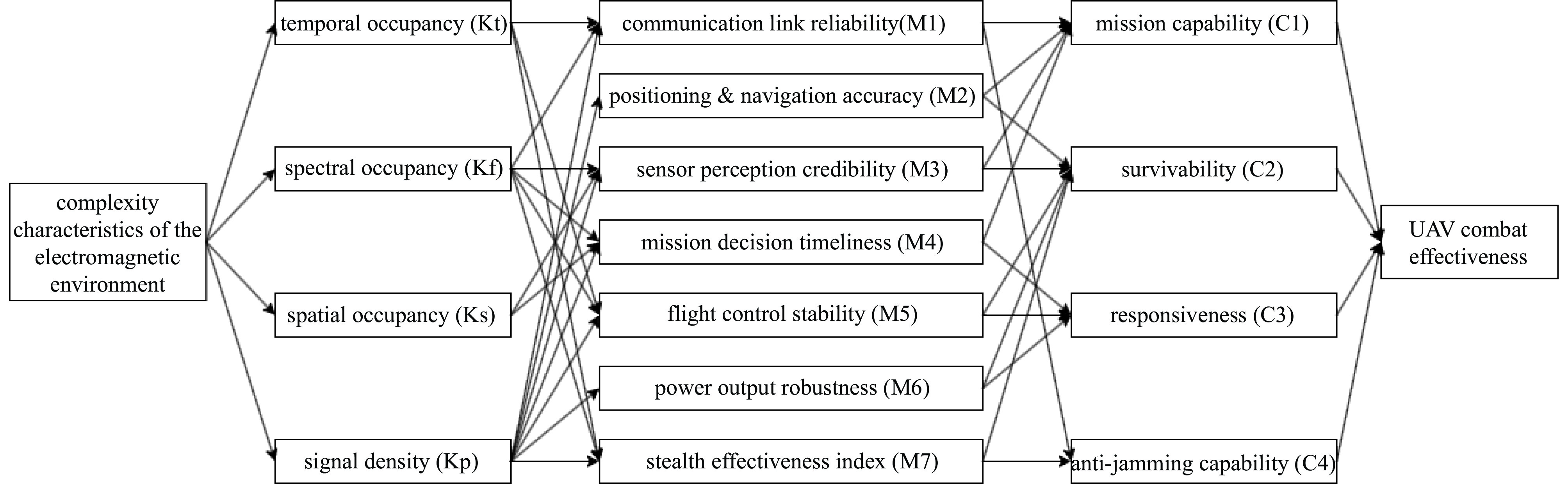
Modeling the impact of complex electromagnetic environments on UAV combat effectiveness
-
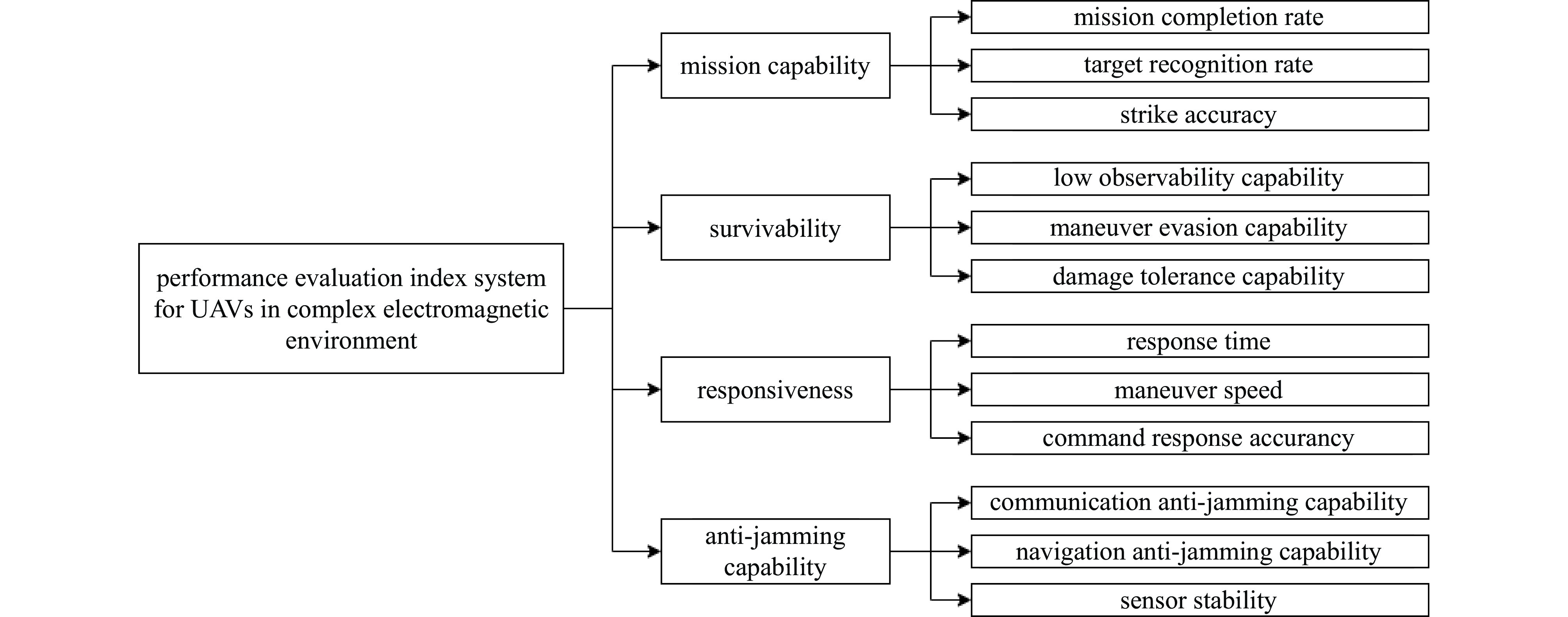
摘要: 为分析复杂电磁环境对无人机作战效能的影响,建立“复杂度特征-子系统性能-作战能力”三层评估体系。首先区分电磁环境的复杂度特征为时间占用度、频谱占用度、空间占用度及信号密度,并采用层次分析法确定特征权重,其次分解出通信可靠性、导航精度等7项无人机子系统性能指标与任务能力、生存能力、响应能力及抗干扰能力4项作战能力,并建立三者的耦合关系模型,然后通过归一化处理与敏感系数聚合推导出作战效能量化公式,表明电磁复杂度与无人机作战效能呈显著负相关,最后基于MATLAB软件构建复杂电磁战场环境,对不同电磁环境下无人机的作战效能进行仿真,进一步论证结果,并证明相同电磁环境下抗干扰能力强的无人机作战效能更优秀。Abstract:
Background Modern battlefields are increasingly characterized by complex electromagnetic environments (EME), posing significant challenges to unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) operational effectiveness.Purpose To address this issue, this study aims to quantitatively evaluate how complex EME affects UAV operational effectiveness using a multi-level framework, incorporating defined key metrics including anti-jamming capability verification.Methods A three-tier evaluation model was developed, incorporating EME complexity, subsystem performance, and operational capabilities. EME complexity was characterized by four metrics weighted via AHP. Critical subsystem indicators—such as communication reliability and navigation accuracy—and operational capabilities like mission execution and anti-jamming performance were causally mapped within an environment-effectiveness mapping. This mapping enabled the model to be normalized and integrated using sensitivity coefficients, and stochastic jamming scenarios were simulated in MATLAB to validate the approach.Results The results demonstrated a distinct negative exponential relationship between EME complexity and operational effectiveness. Performance declined progressively with intensified EME, but notably, UAVs equipped with advanced anti-jamming systems maintained higher effectiveness under identical conditions.Conclusions This study confirms the critical importance of anti-jamming technologies in preserving UAV combat capability in complex EME, the evaluation framework offers practical insights for developing robust UAV systems suited to contested electromagnetic spectra. -
表 1 复杂电磁环境内辐射源的初始参数
Table 1. The initial parameters of the radiation sources in CEME
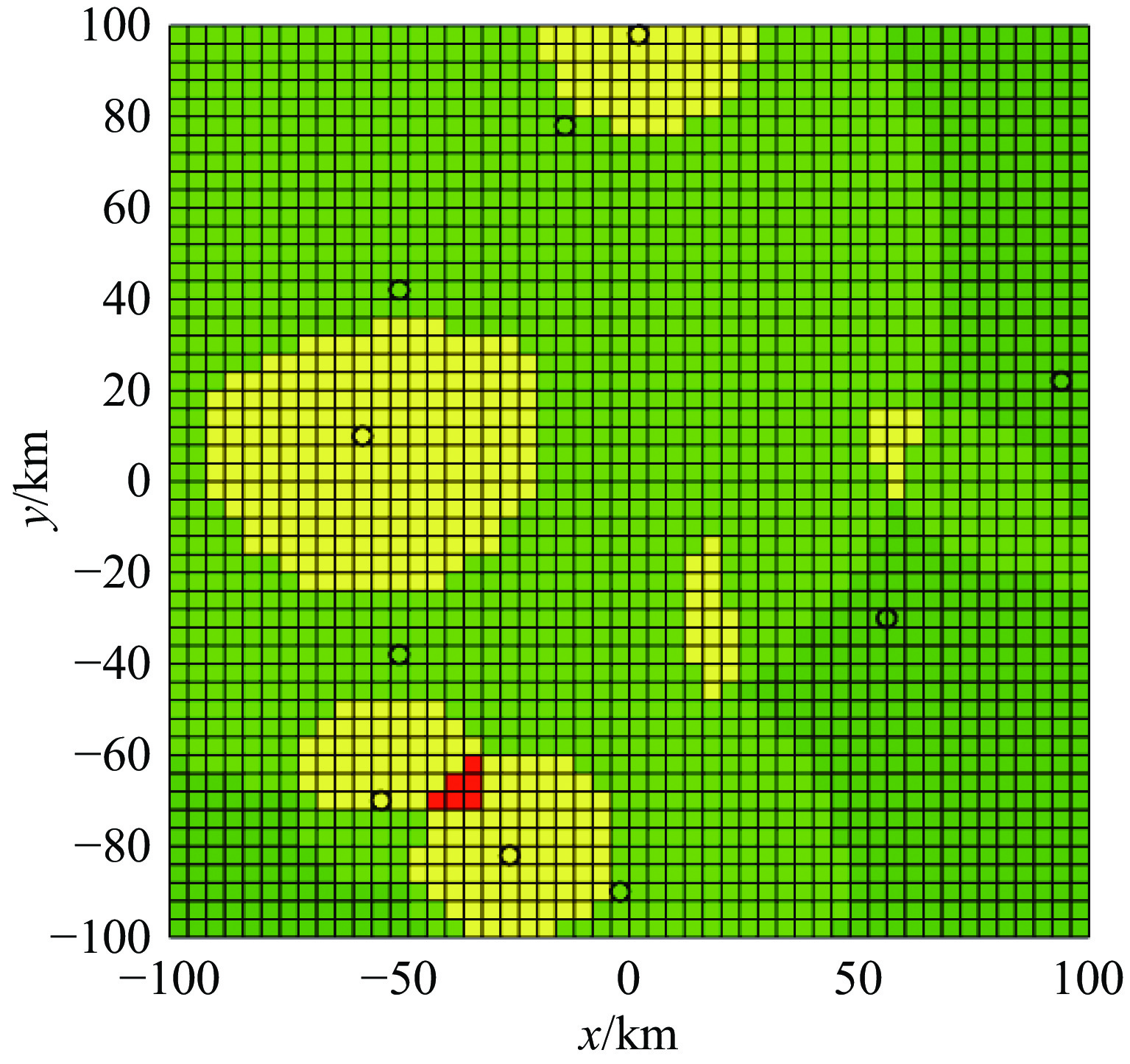
No. working duration/h frequency/MHz power/dBW location/km bandwidth/MHz 1 [20,22] 187 11 (56,−30) 20 2 [5,17] 76 7 (−50,−38) 20 3 [5,18] 195 5 (−26,−82) 30 4 [6,22] 72 3 (−2,−90) 30 5 [6,21] 73 11 (−50,42) 20 6 [14,21] 178 5 (2,98) 20 7 [13,22] 116 7 (94,22) 30 8 [4,22] 181 9 (−58,10) 20 9 [19,23] 200 5 (−54,−70) 30 10 [16,19] 167 10 (−14,78) 30 表 2 无人机在复杂电磁环境下的作战能力分级标准
Table 2. Classification criteria for UAV combat capability in CEME
classification of UAV operational zones combat capability value of UAVs color advantageous zone $ {{\mathrm{C}}\geqslant0.75 \text{β}} $ dark green controllable zone 0$ {.65\text{β} \leqslant {\mathrm{C}} < 0.75\text{β}} $ light green risky zone 0$ {.55\text{β} \leqslant {\mathrm{C}} < 0.65\text{β}} $ yellow dangerous zone $ {{\mathrm{C}} < 0.55\text{β}} $ red 表 3 复杂电磁环境内辐射源变化参数
Table 3. Variable parameters of the radiation sources in CEME
No. working
duration/hfrequency/
MHzpower/
dBWlocation/
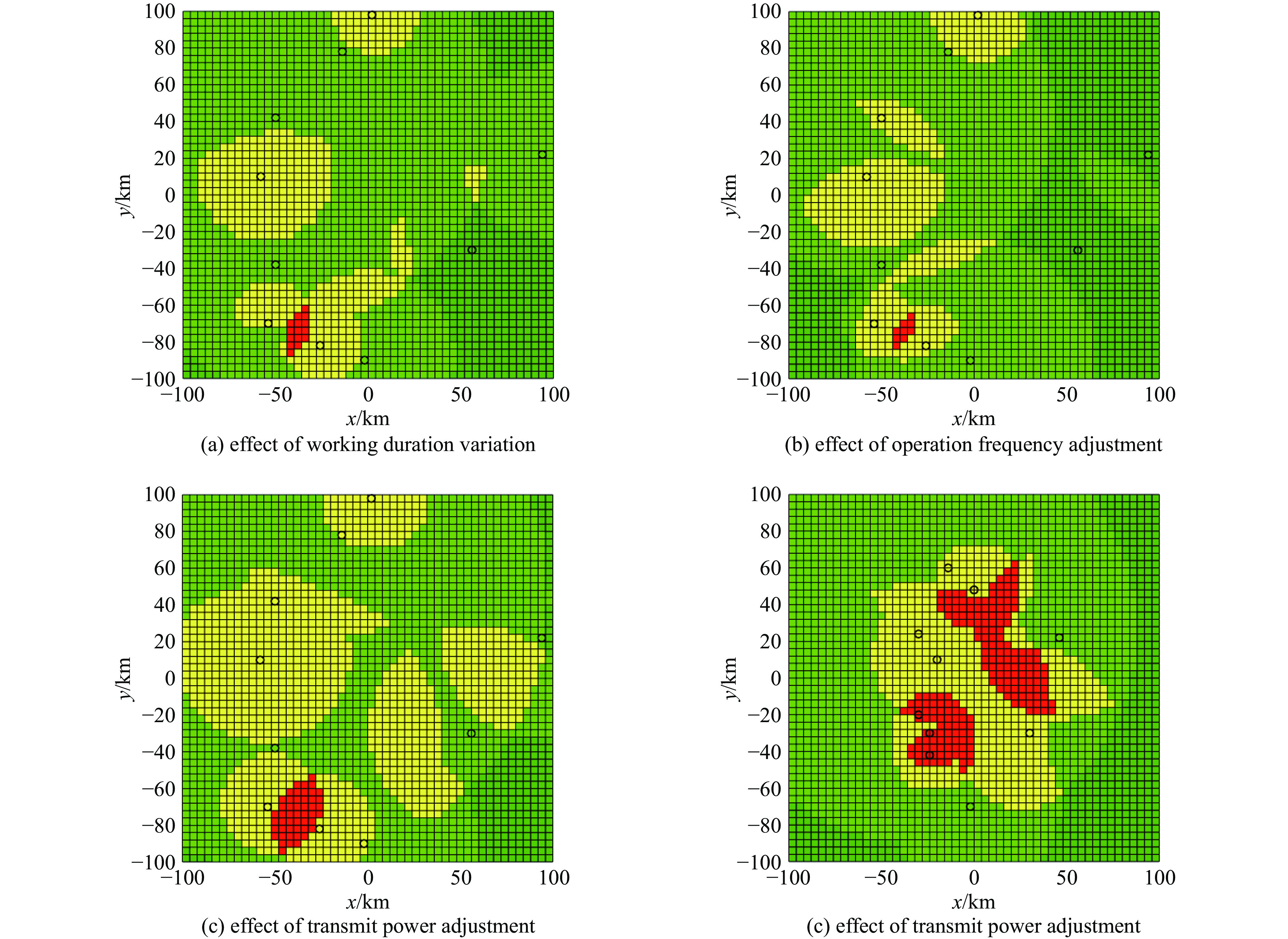
km1 [18,24] 167 13 (30,−30) 2 [3,19] 96 9 (−30,−20) 3 [3,20] 215 7 (−24,−42) 4 [4,24] 52 5 (−2,−70) 5 [4,23] 93 13 (−30,24) 6 [12,23] 158 7 (0,48) 7 [11,24] 136 9 (46,22) 8 [2,24] 161 11 (−20,10) 9 [15,23] 220 7 (−24,−30) 10 [14,21] 127 12 (−14,60) 表 4 改变电磁环境复杂度后无人机作战效能区域占比
Table 4. Proportions distribution of UAV operational zones under varied electromagnetic complexity
parameters of the
radiation sourcesclassification of UAV operational zones/% advantageous zone controllable zone risky zone dangerous zone time 17.03 63.67 18.72 0.58 frequency 32.53 50.40 16.72 0.35 power 9.19 48.44 40.48 1.88 location 18.99 52.90 20.11 8.00 表 5 改变最大可承受信号数量后无人机作战效能区域占比
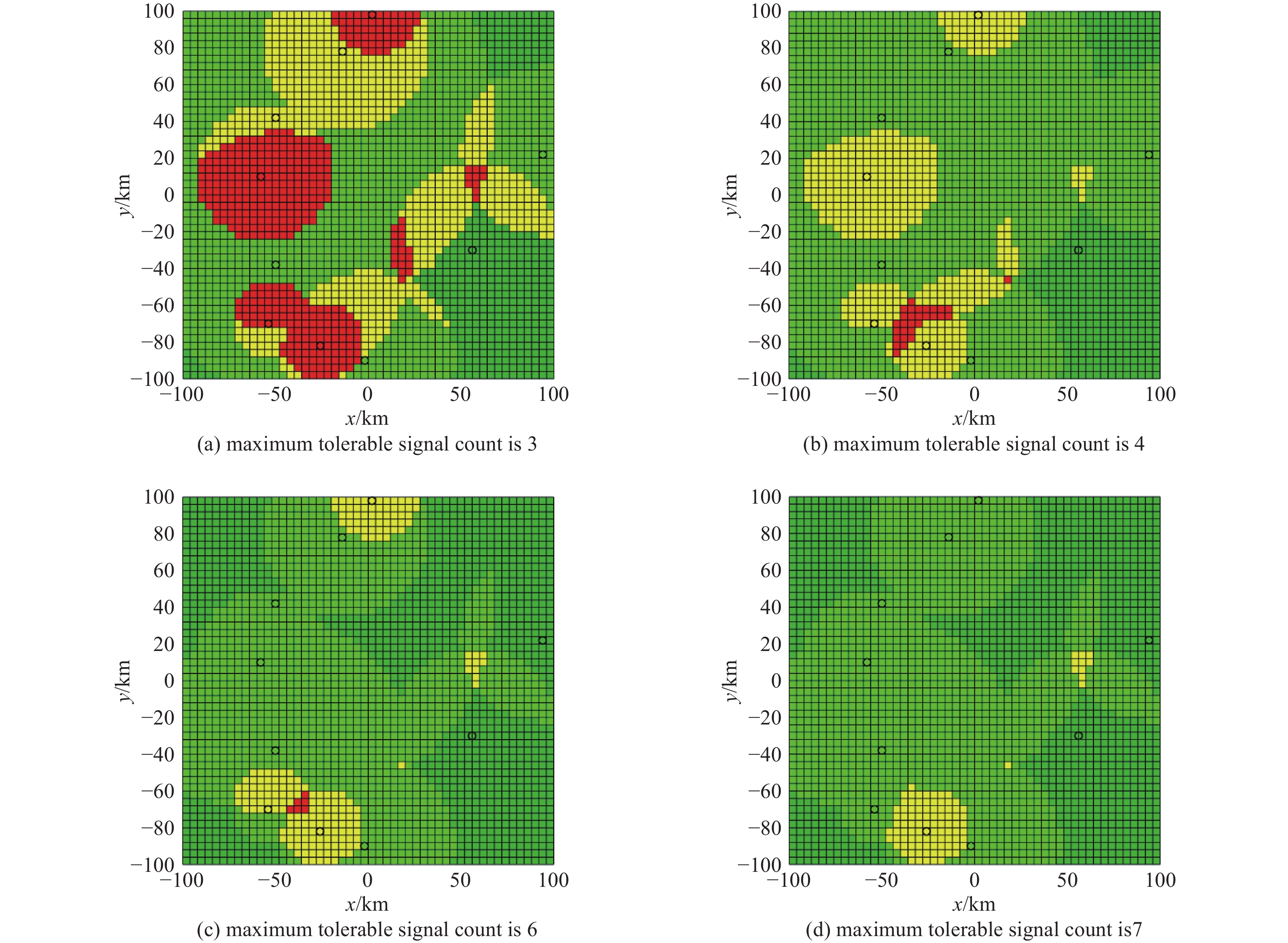
Table 5. Proportion distribution of UAV operational zones after adjusting maximum tolerable signal count
maximum tolerable signal
count for UAVsclassification of UAV operational zones/% advantageous zone advantageous zone advantageous zone advantageous zone 3个 17.03 41.68 23.95 17.34 4个 17.03 63.67 18.19 1.11 6个 42.48 49.25 8.04 0.23 7个 42.48 53.59 3.92 0 -
[1] 王汝群. 战场电磁环境[M]. 北京: 解放军出版社, 2006Wang Ruqun. Battle field electromagnetic environment[M]. Beijing: PLA Press, 2006 [2] 宣源, 田晓凌, 程德胜, 等. 战场电磁环境对无人机系统的干扰分析[J]. 装备环境工程, 2008, 5(1): 99-102 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9242.2008.01.025Xuan Yuan, Tian Xiaoling, Cheng Desheng, et al. Analysis of the battle field electromagnetic interference on unmanned aerial vehicle system[J]. Equipment Environmental Engineering, 2008, 5(1): 99-102 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9242.2008.01.025 [3] 钟科. 复杂电磁场对机载设备的干扰研究[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2012Zhong Ke. The research on complex electromagnetic field interfereing the airborne equipment[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2012 [4] Zhang S, Li. Bit error rate degradation of UAV data links under pulsed electromagnetic interference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic. Compatibility, 2022, 64(5): 1423-1431. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2022.3179676 [5] Johnson A B, Smith R L, et al. GPS spoofing impact on UAV navigation in contested environments[J]. The Journal of Navigation, 2021, 75(3): 567-580. [6] Wang L, Zhou Q, et al. Electromagnetic pulse effects on infrared sensors for military UAVs[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2023, 344: 113701. [7] Johnson A B, Williams C D, Brown K L. Deep reinforcement learning for anti-jamming UAV communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(2): 1021-1035. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3117073 [8] Wang Jianjun, Liu Bin, et al. Spectrum conflict prediction model for UAV swarms in complex electromagnetic environments[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2023, 44: 226541. [9] Garcia M P, et al. Limitations of isolated subsystem analysis for UAV EM vulnerability assessment[J]. IEEE Aerosp. Electron Syst Mag, 2022, 37(4): 30-45. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2021.3052307 [10] Chen Xiaolong, Zhang Hua, Li Wei. Qualitative vs quantitative approaches in UAV combat effectiveness evaluation[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 33(5): 1129-1141. [11] 柯宏发, 张军奇, 祝冀鲁, 等. 电子装备作战试验电磁环境的逼真性评估[J]. 兵工学报, 2016, 37(4): 756-762 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2016.04.026Ke Hongfa, Zhang Junqi, Zhu Jilu, et al. Fidelity evaluation of electromagnetic environment in operational tests of electronic equipment[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2016, 37(4): 756-762 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2016.04.026 [12] 胡媛媛, 武云鹏, 丁玲, 等. 地面无人装备环境感知能力评价方法研究[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2022, 47(2): 88-92 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2022.02.015Hu Yuanyuan, Wu Yunpeng, Ding Ling, et al. Assessment method of environmental perception ability in unmanned-ground equipment[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2022, 47(2): 88-92 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2022.02.015 [13] 段继琨, 韩鹏. 基于相似理论的复杂电磁环境逼真度评估研究[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2020, 40(5): 184-188 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2020.05.043Duan Jikun, Han Peng. Research on the evaluation of complex electromagnetic environment fidelity based on similitude theory[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2020, 40(5): 184-188 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2020.05.043 [14] 王睿, 姜宁, 陈奇. 基于训练效果评估需求的战场电磁环境复杂度研究[J]. 舰船电子对抗, 2015, 38(4): 89-92Wang Rui, Jiang Ning, Chen Qi. Research into battlefield electromagnetic environment complexity based on evaluation requirement of training effect[J]. Shipboard Electronic Countermeasure, 2015, 38(4): 89-92 [15] 金朝, 丁竑, 徐忠富, 等. 基于物元模型-AHP的战场电磁环境复杂度评估[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2010, 30(12): 165-169 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1627-9730.2010.12.048Jin Zhao, Ding Hong, Xu Zhongfu, et al. Complexity evaluation method of battlefield electromagnetic environment based on matter-element model and AHP[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2010, 30(12): 165-169 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1627-9730.2010.12.048 [16] 王东. 复杂电磁环境数字仿真系统研究[J]. 装备环境工程, 2018, 15(1): 100-104Wang Dong. Digital simulation system of complex electromagnetic environment[J]. Equipment Environmental Engineering, 2018, 15(1): 100-104 [17] 马艳艳, 林强, 李旭辉. 基于层次分析法的电磁环境复杂度计算与评估[J]. 现代防御技术, 2024, 52(6): 17-23 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2024.06.003Ma Yanyan, Lin Qiang, Li Xuhui. Calculation and evaluation method of complex electromagnetic environment based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. Modern Defense Technology, 2024, 52(6): 17-23 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2024.06.003 [18] 焦彦维, 侯德亭, 周东方, 等. 无人机在复杂电磁环境下的效能评估[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2014, 26: 073201 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201426.073201Jiao Yanwei, Hou Deting, Zhou Dongfang, et al. Efficiency evaluation of unmanned aerial vehicle in complex electromagnetic environment[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2014, 26: 073201 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201426.073201 [19] 陈强, 魏光辉, 陈亚洲, 等. 3维电介质击穿模型在雷电防护系统评估试验中的应用[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2011, 23(3): 721-726 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20112303.0721Chen Qiang, Wei Guanghui, Chen Yazhou, et al. Application of three-dimensional dielectric breakdown model to lightning protection system evaluation[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2011, 23(3): 721-726 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20112303.0721 [20] 郭宝录, 李朝荣, 乐洪宇. 国外无人机技术的发展动向与分析[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2005, 28(9): 46-49,112Guo Baolu, Li Chaorong, Le Hongyu. Development trend and analysis of the technology of the abroad UAV[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2005, 28(9): 46-49,112 [21] 马艳艳, 金宏斌, 李浩, 等. 改进粒子群算法在雷达组网优化布站中的应用[J]. 现代防御技术, 2020, 48(3): 104-112 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2020.03.017Ma Yanyan, Jin Hongbin, Li Hao, et al. Application of improved PSO algorithm in radar-net deployment[J]. Modern Defense Technology, 2020, 48(3): 104-112 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2020.03.017 [22] Rappaport T S. Wireless communications: principles and practice[M]. Prentice Hall PTR, 1996. -




 下载:
下载: