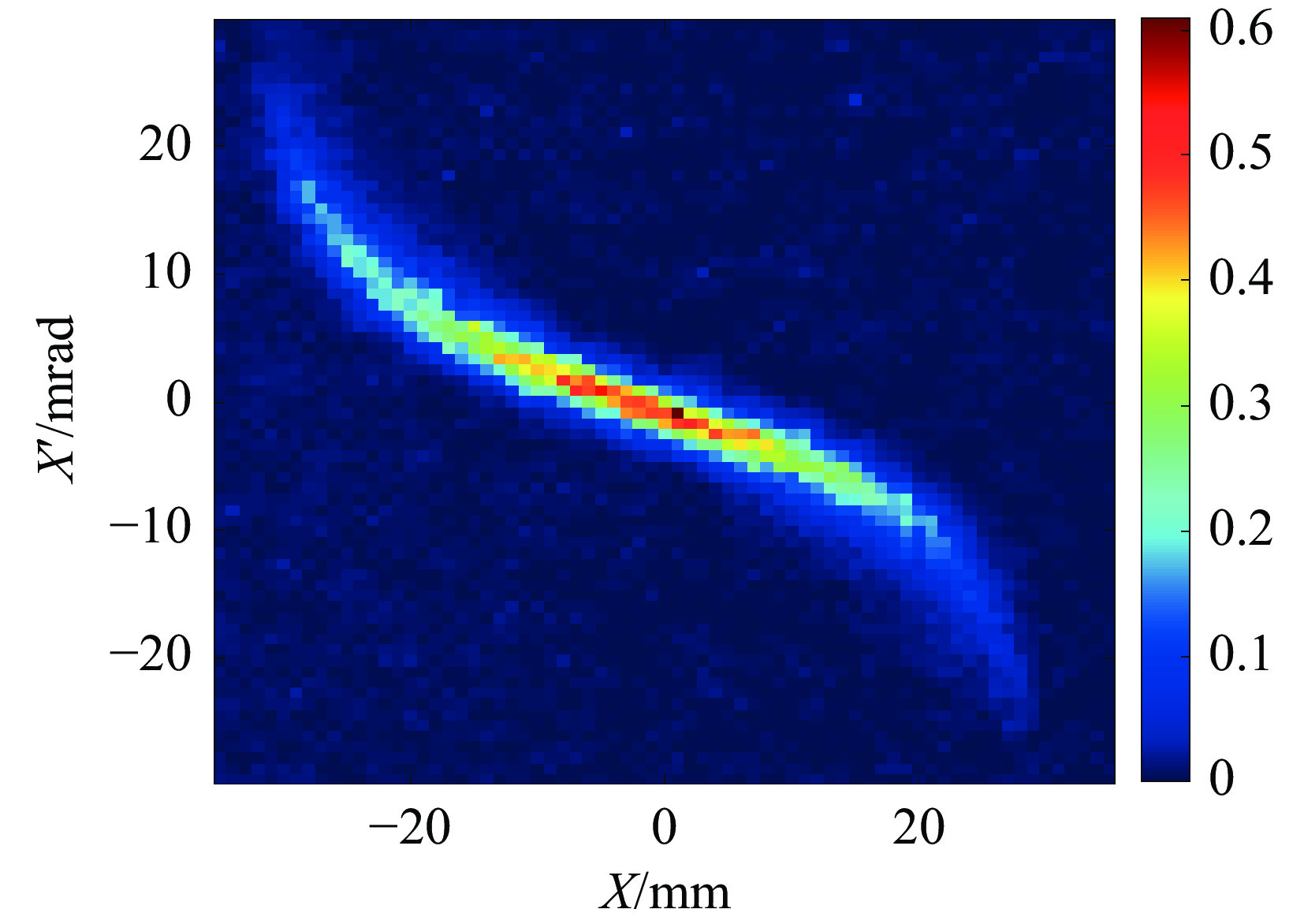
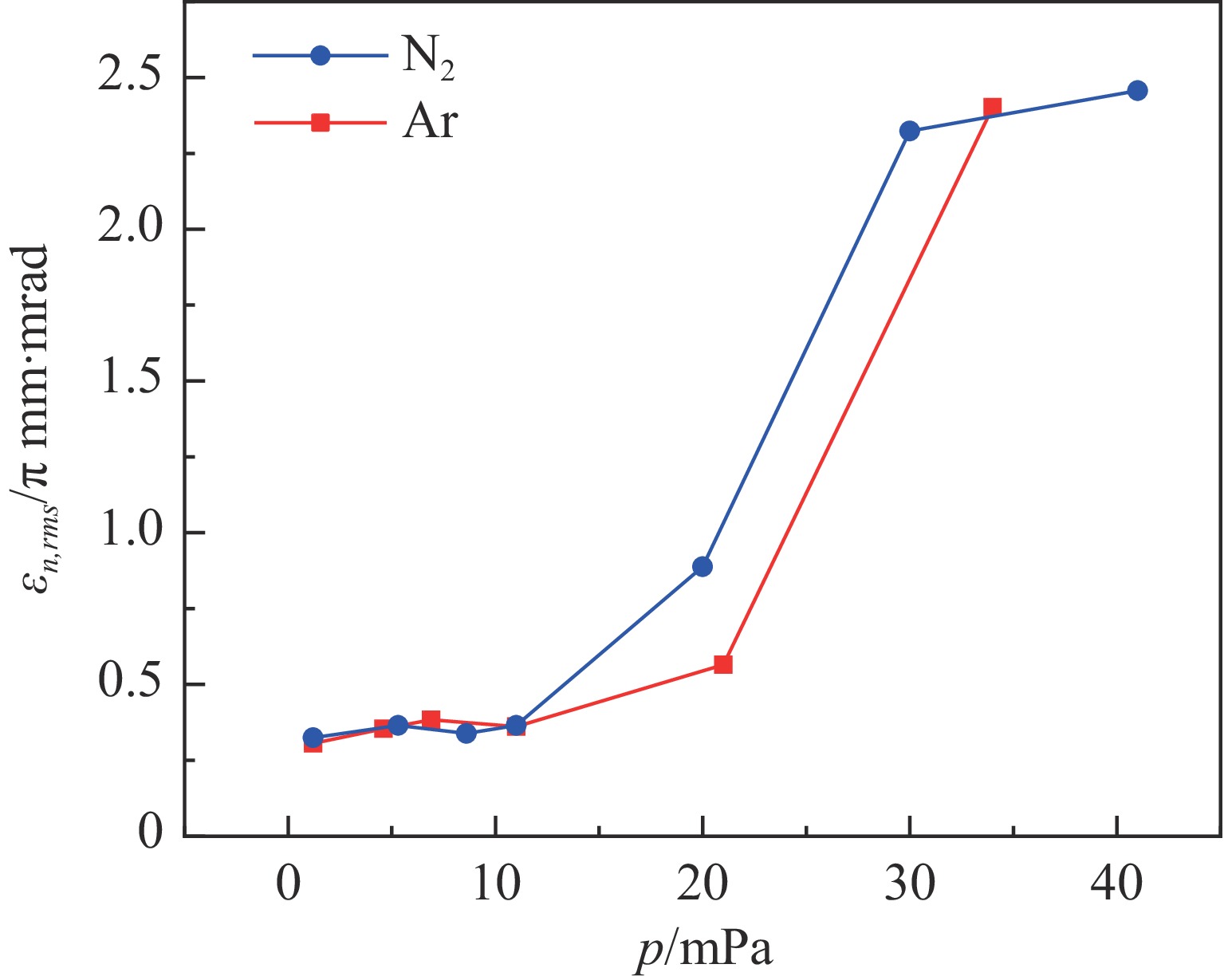
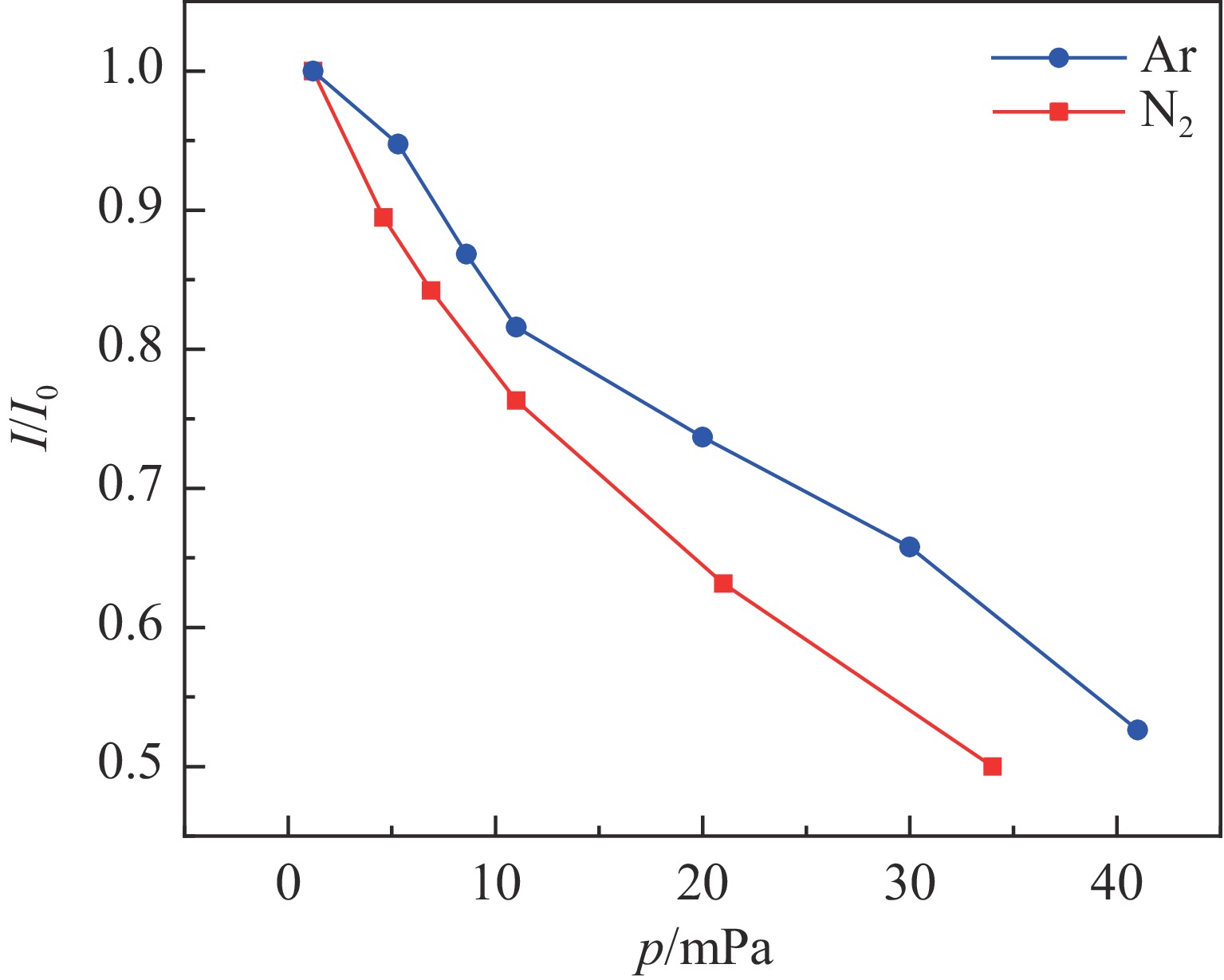
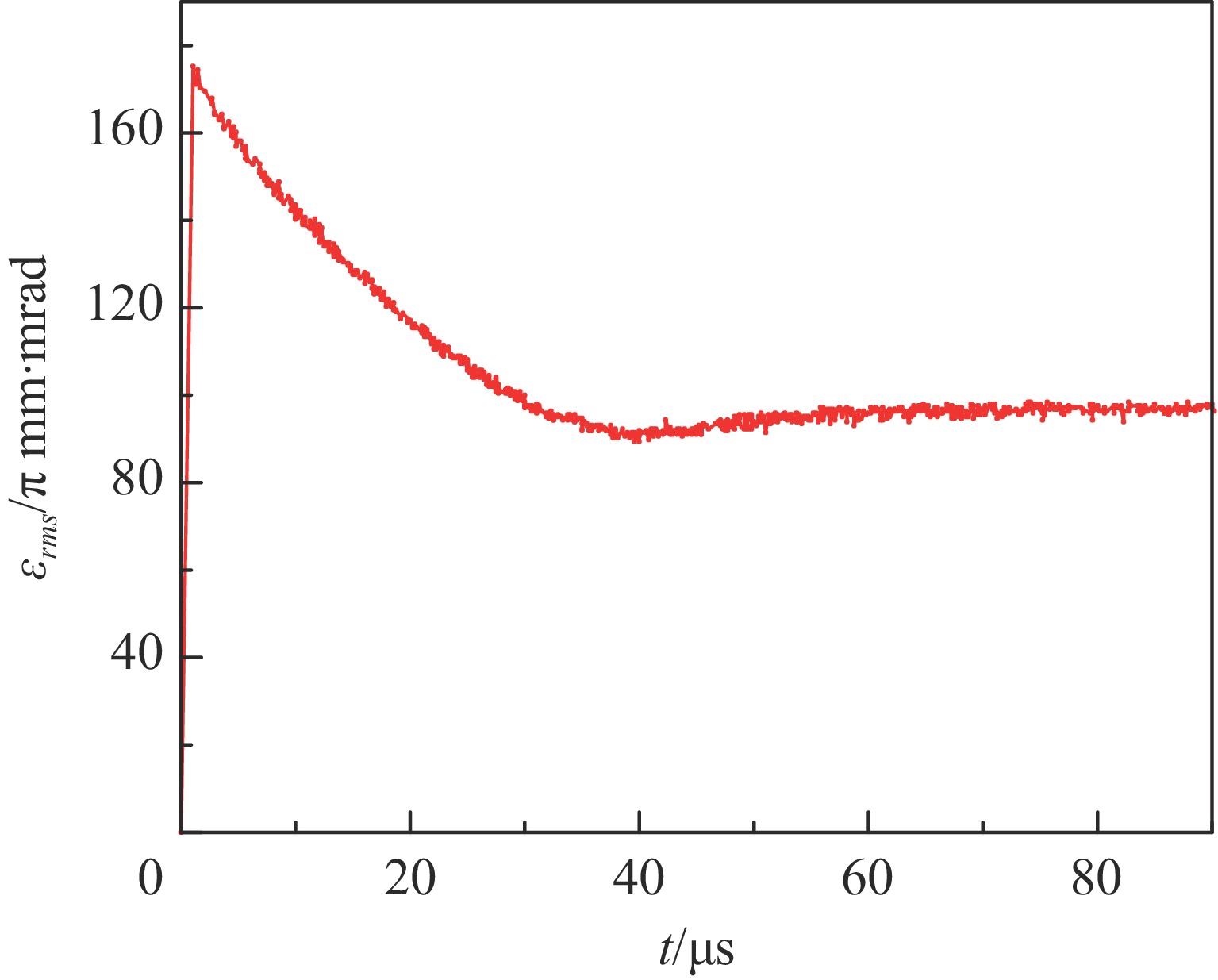
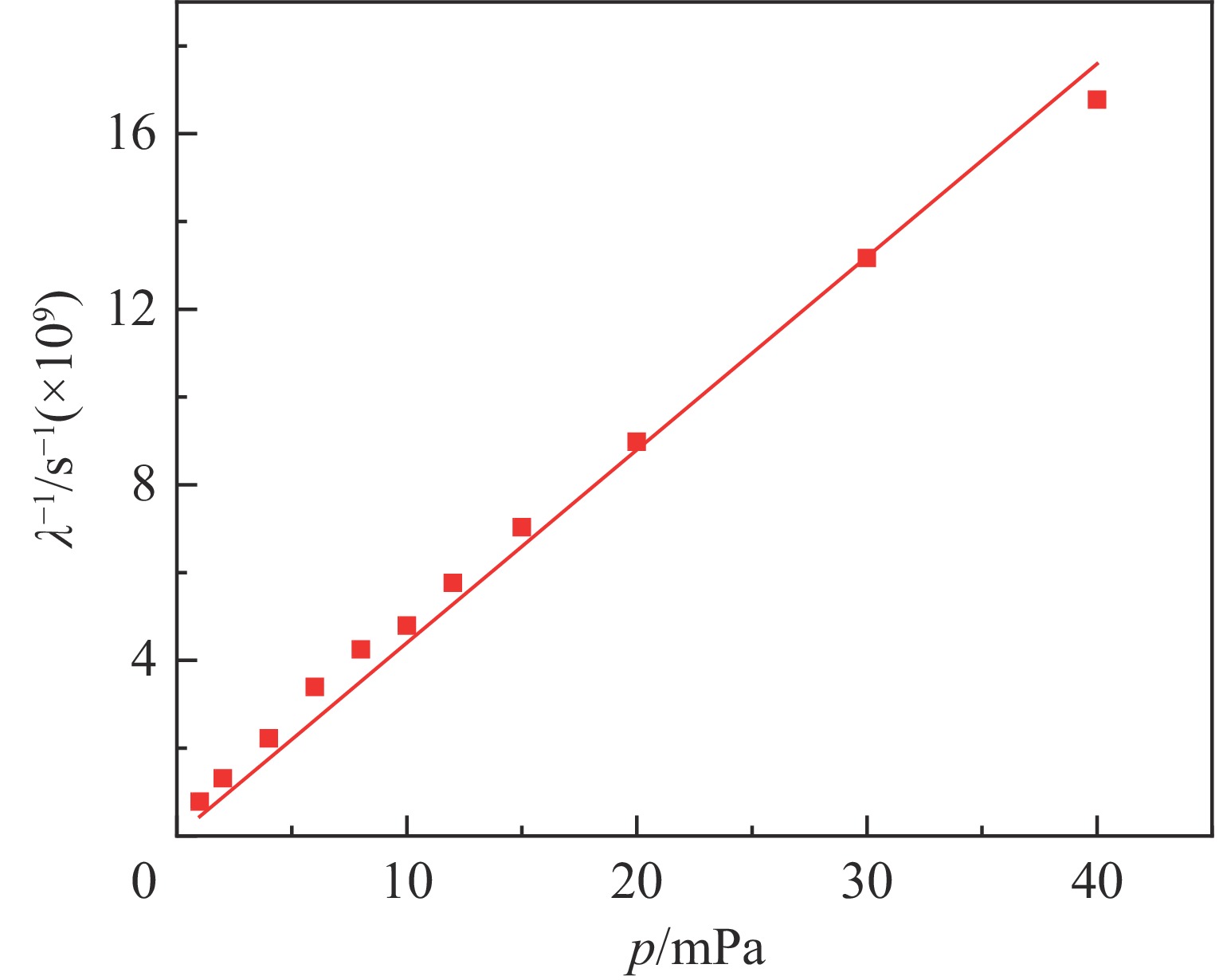
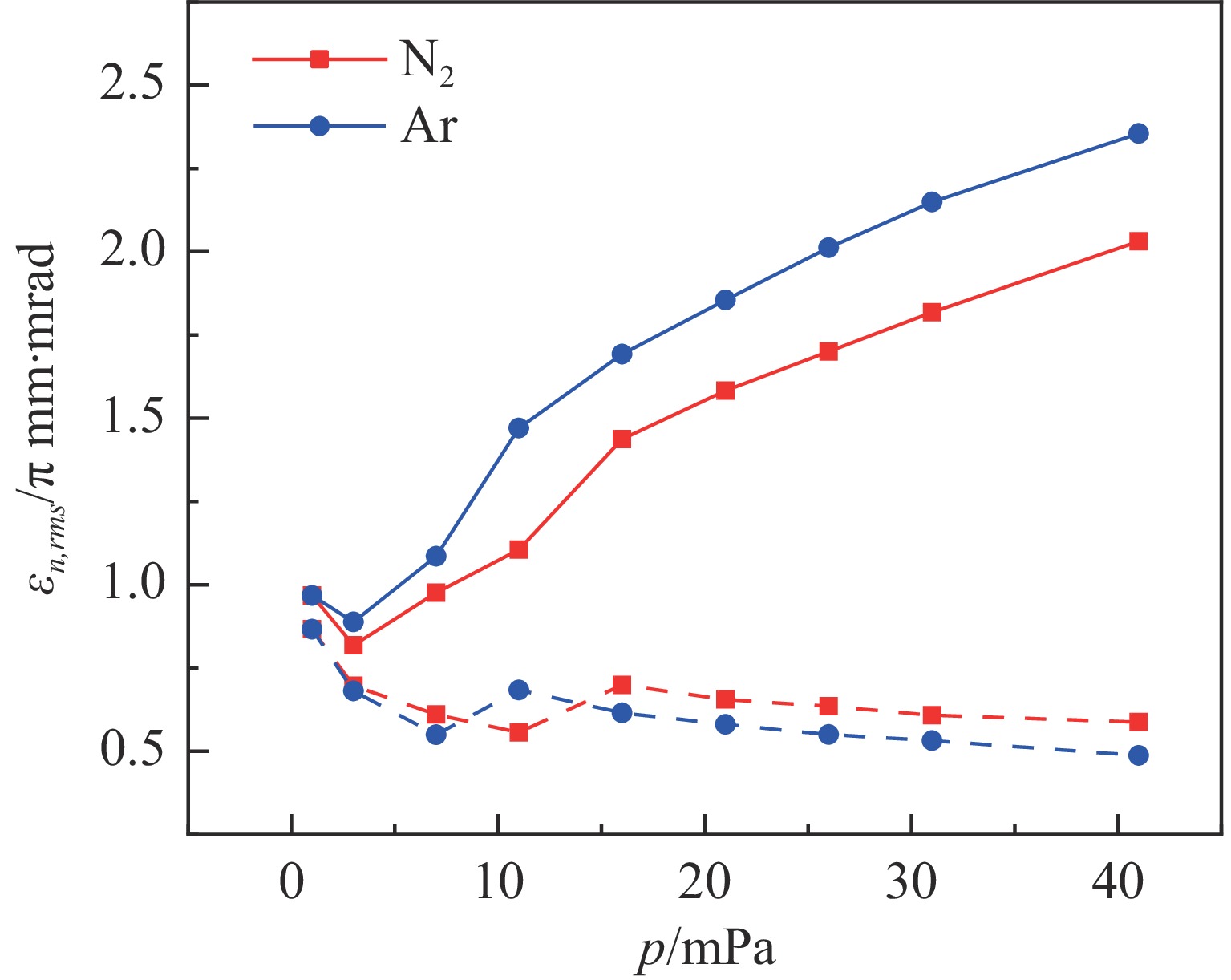
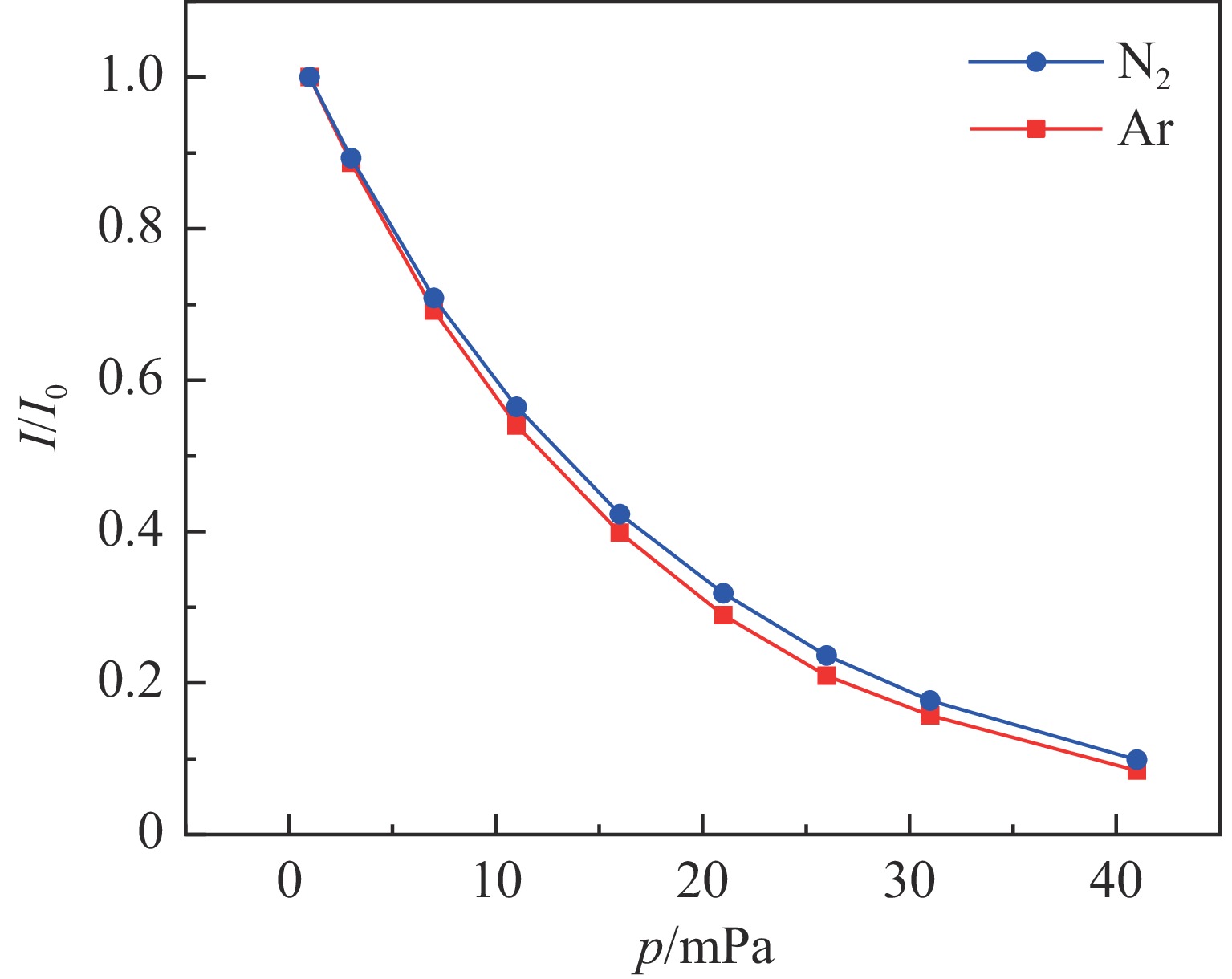
Investigation of impact mechanisms in low-energy high- current H− beam interactions with compensation gases
-
摘要: 空间电荷效应是制约强流离子束稳定传输的主要因素,主动馈入补偿气体被认为是一种能够抑制空间电荷效应的有效手段。但在强流负氢离子加速器中,负氢离子与补偿气体的作用机制十分复杂,存在多种互相竞争的物理过程。本研究通过数值模拟与实验测量,探究了负氢粒子与补偿气体在低能束流传输线中的相互作用机制。通过基于PIC方法的仿真程序,构建了包含电离反应、电子剥离反应和弹性碰撞散射等物理过程的三维仿真模型,研究了补偿气体为氮气和氩气时空间电荷补偿效应随气压、气体种类的变化对束流参数的影响规律。研究结果表明, 对负氢束流进行空间电荷补偿研究时,补偿气体对束流的散射与剥离效应不可忽略。Abstract:
Background Space charge effects pose a significant challenge in high current ion beam transport, particularly in low energy beam transport (LEBT) systems where beam intensity is high and energy is relatively low. Active injection of gas has been proposed as an effective method to mitigate these effects. However, for negative hydrogen ion beams, the physical mechanisms involved are highly complex due to competing processes such as ionization, electron stripping, etc.Purpose This study aims to investigate the interaction mechanisms between negative hydrogen ion beams and gas within an LEBT system, and to evaluate the influence of gas species and pressure on beam parameters including emittance and beam current.Methods Numerical simulations based on the Particle-In-Cell (PIC) method were conducted using the Warp code, incorporating physical processes including ionization, electron stripping, and elastic scattering. A three-dimensional simulation model was established to analyze space charge compensation effects under nitrogen and argon gas environments. Experimental measurements of beam current and emittance were simultaneously carried out on the XiPAF accelerator facility to validate simulation results.Results Both simulations and experiments revealed that the effects of gas scattering and electron stripping cannot be neglected in space charge compensation of negative hydrogen ion beams.Conclusions This research highlights the complexity of space charge compensation in negative hydrogen ion beams and emphasizes the need to consider multiple physical interactions in the design and operation of high-current LEBT systems. The findings provide practical insights for optimizing gas compensation parameters in similar accelerator facilities.-
Key words:
- low energy beam transport line /
- XiPAF /
- space charge compensation /
- elastic scattering
-
表 1 模拟中采用的LEBT入口束流参数
Table 1. Beam parameters at LEBT entrance used in simulation
voltage/kV peak beam current/mA normalized RMS emittance/(mm∙mrad) α β/(mm∙mrad−1) 50 5 0.2π 2.895 1 0.043 8 -
[1] 夏慧琴, 刘纯亮. 束流传输原理[M]. 西安: 西安交通大学出版社, 1991Xia Huiqin, Liu Chunliang. Beam transmission theory[M]. Xi'an: Xi'an Jiaotong University Press, 1991 [2] Valerio-Lizarraga C A. Emittance growth due to space charge compensation and beam intensity instabilities in negative ion beams[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2018, 21: 030101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.21.030101 [3] Gabovich M D, Katsubo L P, Soloshenko I A. Self-decompensation of a stable quasi-neutral ion beam by coulomb collisions[J]. Fizika Plazmy, 1975, 1(2): 304-308. [4] Gabovich M D. Ion-beam plasma and the propagation of intense compensated ion beams[J]. Soviet Physics Uspekhi, 1977, 20(2): 134-148. doi: 10.1070/PU1977v020n02ABEH005331 [5] Soloshenko I A. Problems of intense negative ion beam transport (invited)[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2004, 75(5): 1694-1698. doi: 10.1063/1.1695608 [6] 彭士香, 吕鹏南, 任海涛, 等. 低能强流离子束空间电荷补偿的研究[C]//2010全国荷电粒子源、粒子束学术会议论文集. 2010: 58-63Peng Shixiang, Lyu Pengnan, Ren Haitao, et al. Research of space charge compensation in low energy high intensity ion beam[C]//Proceedings of 2010 National Conference on Charged Particle Sources and Beams. 2010: 58-63 [7] 肖仁珍. 相对论返波管研究进展[J]. 现代应用物理, 2022, 13: 020101 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2022.020101Xiao Renzhen. Research progress of relativistic backward wave oscillator[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2022, 13: 020101 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2022.020101 [8] 陈再高, 史雪婷, 王建国, 等. 基于多层次深度神经网络的相对论返波管优化技术[J]. 现代应用物理, 2025, 16: 011315 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.202412010Chen Zaigao, Shi Xueting, Wang Jianguo, et al. Optimization method of relativistic backward wave oscillator based on multi-level deep neural network[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2025, 16: 011315 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.202412010 [9] 李小泽, 王建国, 童长江, 等. 充填不同气体相对论返波管特性的PIC-MCC模拟[J]. 物理学报, 2008, 57(7): 4613-4622 doi: 10.7498/aps.57.4613Li Xiaoze, Wang Jianguo, Tong Changjiang, et al. PIC-MCC simulations on characteristics of RBWO filled with different gases[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2008, 57(7): 4613-4622 doi: 10.7498/aps.57.4613 [10] Tan Biao, Wu Qi, Yang Yao, et al. Preliminary measurement of space charge neutralization level for proton beam[J]. Nuclear Physics Review, 2016, 33(1): 36-40. [11] Valerio-Lizarraga C A, Leon-Monzon I, Scrivens R. Negative ion beam space charge compensation by residual gas[J]. Physical Review Special Topics-Accelerators and Beams, 2015, 18: 080101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.18.080101 [12] 王忠明, 王敏文, 闫逸花, 等. 西安200 MeV质子应用装置开放运行情况及下一步升级改造计划[J]. 现代应用物理, 2024, 15: 040402 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2024.040402Wang Zhongming, Wang Minwen, Yan Yihua, et al. Current status and upgrade plan of Xi'an 200 MeV proton application facility[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2024, 15: 040402 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2024.040402 [13] Chung M, Shiltsev V, Prost L. Space-charge compensation for high-intensity linear and circular accelerators at Fermilab[R]. Batavia: Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, 2013. [14] Sherman J, Pitcher E, Stevens R, et al. H− beam neutralization measurements in a solenoidal beam transport system[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 1992, 287(1): 686-694. [15] Reiser M. Theory and design of charged particle beams[M]. 2nd ed. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, 2008. [16] Friedman A, Grote D P, Haber I. Three-dimensional particle simulation of heavy-ion fusion beams[J]. Physics of Fluids B: Plasma Physics, 1992, 4(7): 2203-2210. doi: 10.1063/1.860024 [17] 王百川, 王忠明, 刘卧龙, 等. 西安200 MeV质子应用装置负氢离子源及低能束流传输线实验研究[J]. 现代应用物理, 2021, 12: 030401 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2021.030402Wang Baichuan, Wang Zhongming, Liu Wolong, et al. Experimental study on H− ion source and low energy beam transport line of Xi'an 200 MeV proton application facility[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2021, 12: 030401 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2021.030402 [18] Chauvin N, Delferrière O, Duperrier R, et al. Transport of intense ion beams and space charge compensation issues in low energy beam lines (invited)[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2012, 83: 02B320. doi: 10.1063/1.3678658 [19] Easton M J, Li Haipeng, Wang Zhi, et al. Simulations of particle interactions in a high-current RFQ[J]. Journal of Instrumentation, 2019, 14: T02003. doi: 10.1088/1748-0221/14/02/T02003 [20] Benisma A, Duperrier R, Uriot D, et al. A space charge compensation study of low energy hydrogen ion beams[C]//Proceedings of the 2005 Particle Accelerator Conference. 2005: 2947-2949. [21] Benismail A, Duperrier R, Uriot D, et al. Space charge compensation studies of hydrogen ion beams in a drift section[J]. Physical Review Special Topics-Accelerators and Beams, 2007, 10: 070101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.10.070101 [22] Zhang A L, Peng S X, Ren H T, et al. Study on space charge compensation in negative hydrogen ion beam[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2016, 87: 02B915. doi: 10.1063/1.4932557 [23] Noll D, Droba M, Meusel O, et al. The particle-in-cell code bender and its application to non-relativistic beam transport[C]//Proceedings of HB2014. 2014: 304-308. [24] Chancé A, Chauvin N. Simulation of the extraction and transport of a beam from the SILHI source with the warp code[C]//Proceedings of the 5th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2014: 385-387. [25] Grote D P, Friedman A, Haber I, et al. New developments in WARP: progress toward end-to-end simulation[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 1998, 415(1/2): 428-432. [26] Barnett C F, Ray J A, Ricci E, et al. Atomic data for controlled fusion research[R]. Oak Ridge: Oak Ridge National Laboratory, 1977. [27] Winklehner D, Leitner D. A space charge compensation model for positive DC ion beams[J]. Journal of Instrumentation, 2015, 10: T10006. doi: 10.1088/1748-0221/10/10/T10006 [28] Lund S M, Kikuchi T, Davidson R C. Generation of initial kinetic distributions for simulation of long-pulse charged particle beams with high space-charge intensity[J]. Physical Review Special Topics-Accelerators and Beams, 2009, 12: 114801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.12.114801 [29] Ji Qing, Grote D, Staples J, et al. Beam dynamics studies of H− beam chopping in a LEBT for Project X[C]//Proceedings of HB2012. 2012: 546-549. [30] Rudd M E. Energy and angular distributions of secondary electrons from 5-100-keV-proton collisions with hydrogen and nitrogen molecules[J]. Physical Review A, 1979, 20(3): 787-796. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.20.787 [31] Jackson J D. Classical electrodynamics[M]. 3rd ed. New York: Wiley, 1999: 5. -




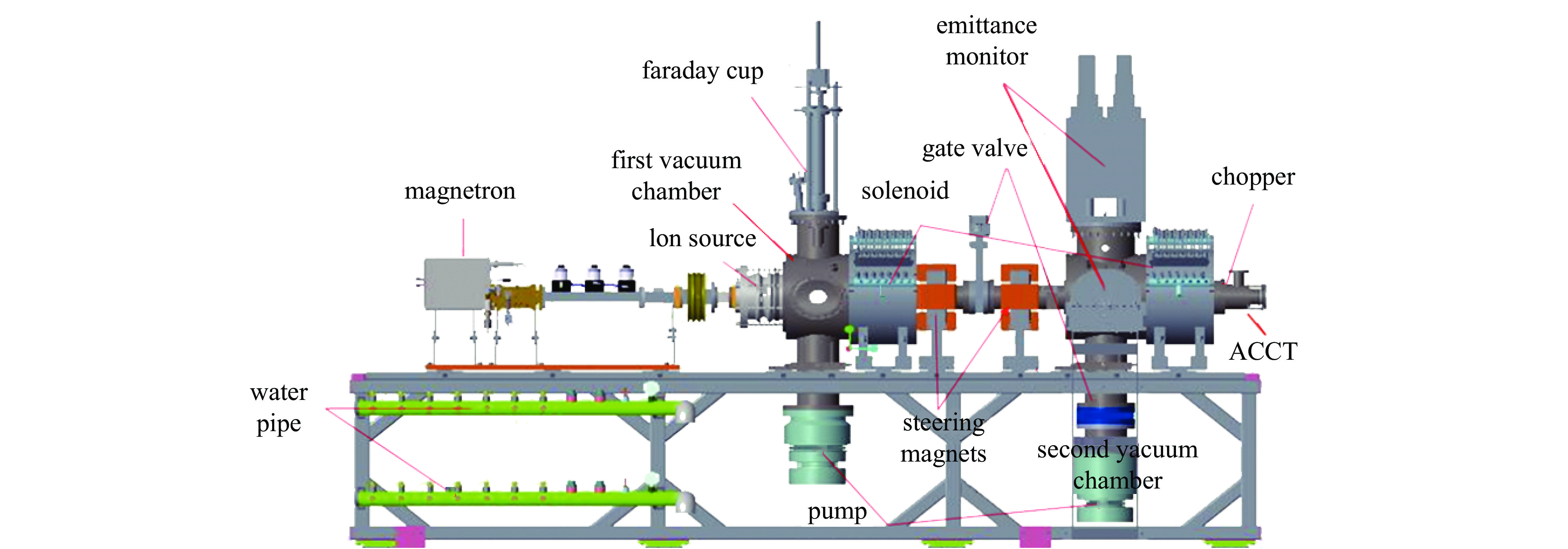
 下载:
下载: