Experimental study on long-range blur of radiation imaging system by ring-aperture method
-
摘要: 辐射成像技术作为一种重要的诊断手段,被广泛应用于惯性约束聚变、闪光照相等各类科学装置上。实践中发现,成像系统点扩散函数通常存在预期之外的低频成分,导致图像出现低频模糊退化、图像灰度分布与射线注量分布之间呈现复杂的非线性关系,进而干扰源区强度分布或客体密度分布等关键物理量的诊断分析。由于点扩散函数低频成分强度极低,实验测量难度较大,其具体来源及份额目前尚未明确。针对这一难题,提出了基于环孔法的点扩散函数低频成分测量方法,首次获得了辐射成像系统点扩散函数低频成分的直接测量结果,将测量下限扩展至点扩散函数峰下10−6量级。同时,发现了闪烁屏表面状态对低频成分存在显著影响;将闪烁屏的非成像面涂覆黑色吸光材料后,可大幅降低闪烁屏导致的低频模糊。Abstract:
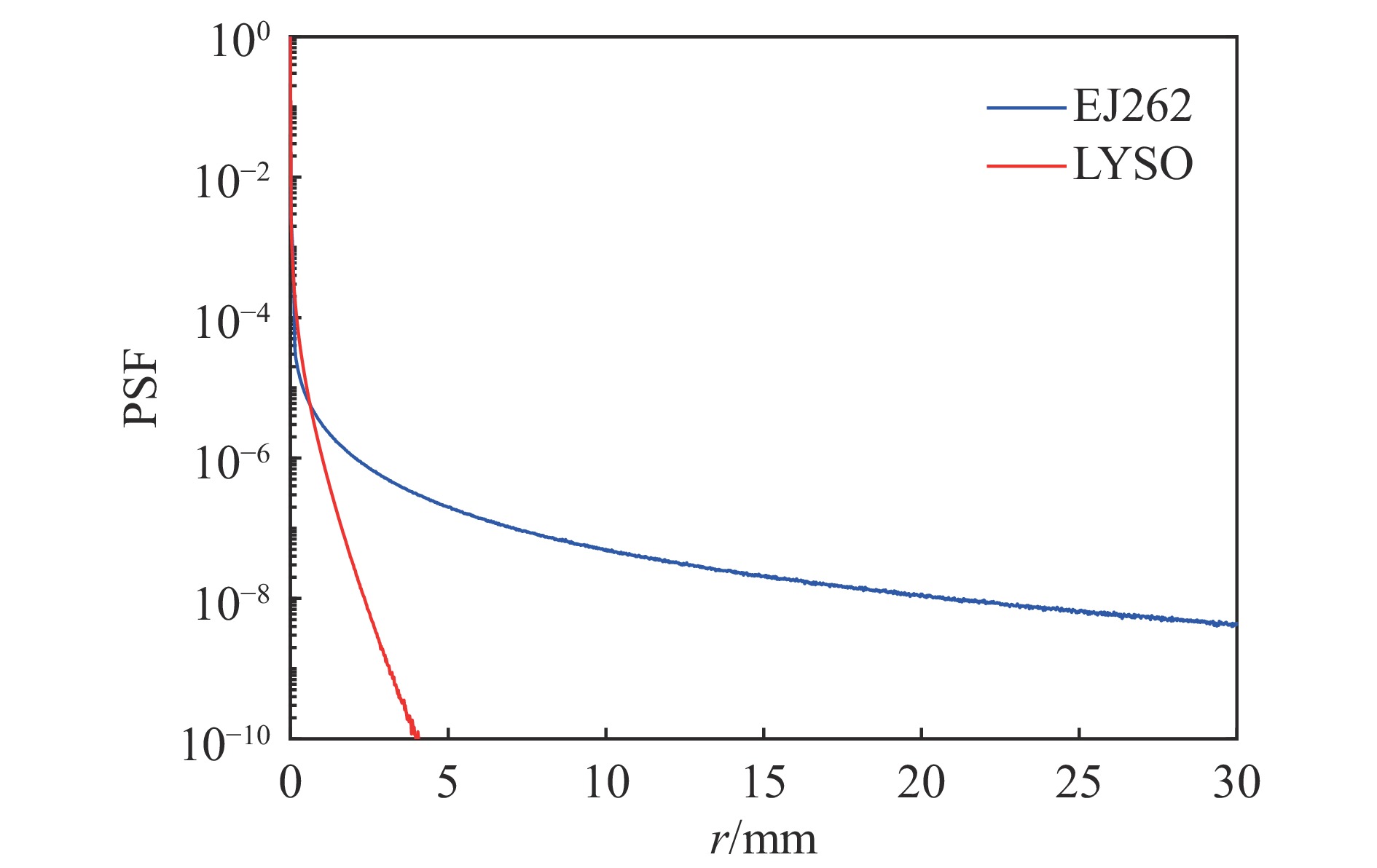
Background The radiation imaging technology, as an important diagnostic, has been widely used in scientific devices such as inertial confinement fusion and flash photography. It has been found that unexpected low-frequency components usually exit in the point spread function (PSF) of radiation imaging system, leading to the so-called low-frequency blur or long-range blur. Because of long-range blur, the image grayscale varies nonlinearly with the ray flux, which in turn interferes with the analysis of the object density or the source intensity. An experimental measurement of the low-frequency components is challenging because of the extremely low intensity. The specific sources of low-frequency components are not very clear currently.Purpose This study aims to address these challenges by proposing a new experimental method for the low-frequency components. The goal is to ensure the reliability of the measurement data on low-frequency components and to identify the main sources of low-frequency components.Methods A series of experiments were conducted on different components of the imaging system. A collimator called ring-aperture is used to modulate the x-ray or optical photons into a circular pattern, which led to a significant increase in the signal strength from low-frequency components by orders of magnitude.Results A direct measurement result of the low-frequency components was obtained for the first time, and the measurement lower limit was extended to 10−6 orders below the peak of PSF. Experiments shown that the surface state of scintillators can have a significant impact on low-frequency components. By blackening the non-light-emitting surface, the low-frequency components caused by scintillator can be reduced by 22%~62%.Conclusions The ring- aperture method provides a reliable experimental approach for measuring low-frequency components of PSF. The research results indicate that optical photon transport is an important factor leading to long-range blur. By surface treatment of scintillators, such as blackening and polishing, long-range blur can be effectively suppressed.-
Key words:
- radiation imaging /
- image degradation /
- long-range blur /
- PSF /
- scintillator
-
表 1 不同PSF测量方法的定性比较
Table 1. Comparison of different PSF measurement methods
method formula prior information data processing methods applications experimental conditions knife-edge method $ \displaystyle\int_{ - \infty }^{ + \infty } {{H_{PSF}}(x,y)} dy = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}{H_{ESF}}(x) $ PSF should be circularly and symmetrically distributed solving ill posed inverse problems and is sensitive to measurement errors usually used for high-frequency component measurement low source strength requirements, good radiation shielding, high dynamic range recording unit point source method $ {H_{PSF}}(x,y) $ —— no need to solve ill posed problems usually used for high-frequency component measurement high source strength, good radiation shielding, high dynamic range recording unit ring-aperture method $ {H_{PSF}}(R) = \dfrac{1}{{2\pi }}\displaystyle\int_0^{2\pi } {{H_{PSF}}(R,\theta )} d\theta $ PSF should be circularly and symmetrically distributed no need to solve ill posed problems suitable for low-frequency component measurement, but not for high-frequency component measurement the requirements for source strength, radiation shielding, and dynamic range of recording units are relatively low 表 2 主要部组件
Table 2. Main components
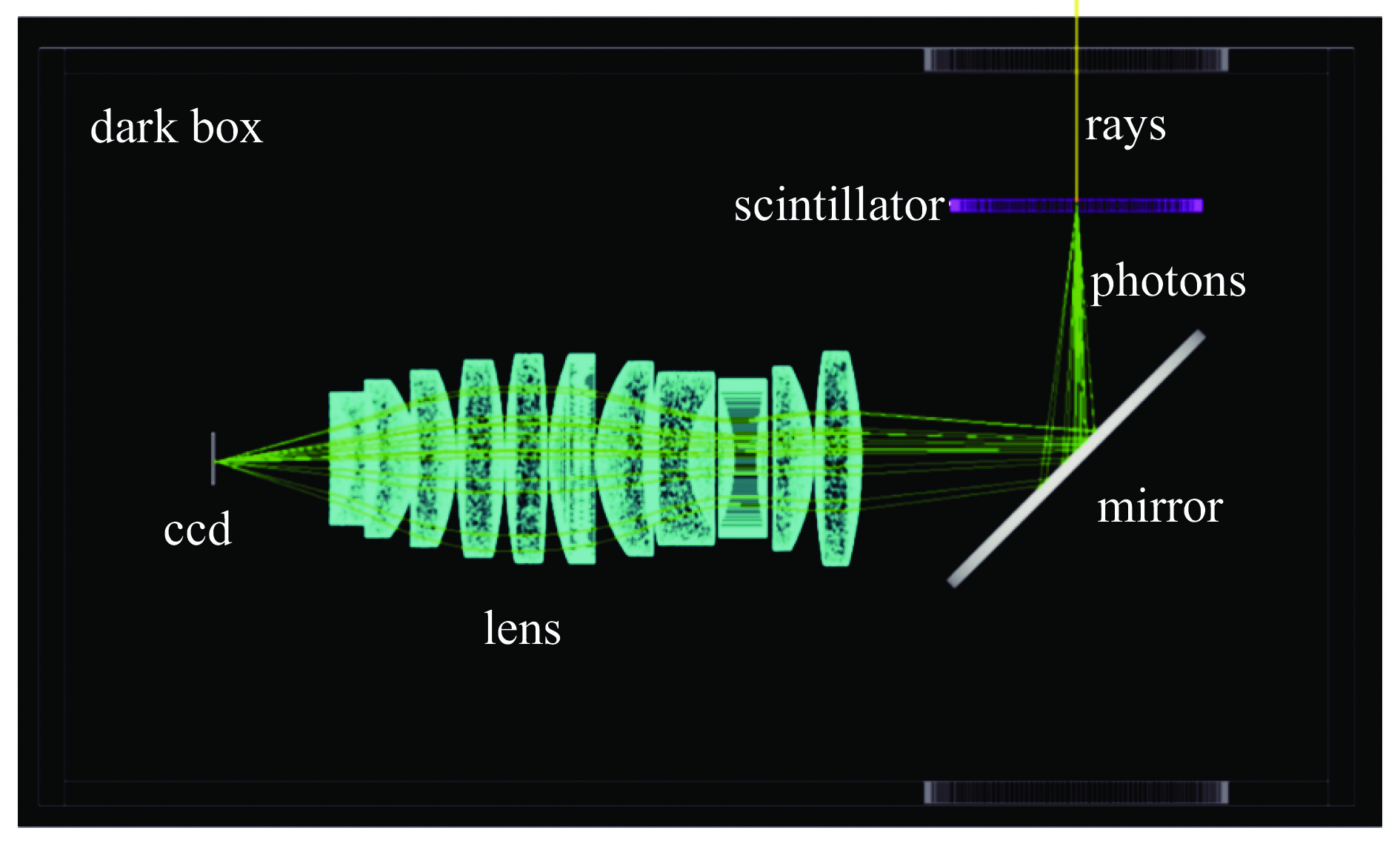
components model identifier specifications function scintillator plastic scintillator EJ262 EJ262-1 ϕ124 mm×5 mm,front and back surfaces are polished with roughness Ra=0.2 μm, the side surface is ground image conversion EJ262-2 ϕ124 mm×5 mm,front and back surfaces are polished with roughness Ra=0.2 μm, the side surface is ground, black paint is applied to non-optical surfaces inorganic scintillator LYSO: Ce LYSO-1 ϕ124 mm×5 mm,front and back surfaces are polished with roughness Ra=20 nm LYSO-2 ϕ124 mm×5 mm,front and back surfaces are polished with roughness Ra=20 nm, black paint is applied to non-optical surfaces imaging module Integrated optical imaging module —— field of view: ϕ120 mm
image size: ϕ22 mm
spatial resolution: 5 lp/mmoptical imaging and light shielding camera Scientific ICCD camera —— pixels:2 048×2 048
data range:16 bit
dynamic range:10 000
spatial resolution:28.5 lp/mmimage selection, enhancement and recording 表 3 实验配置
Table 3. experimental configuration
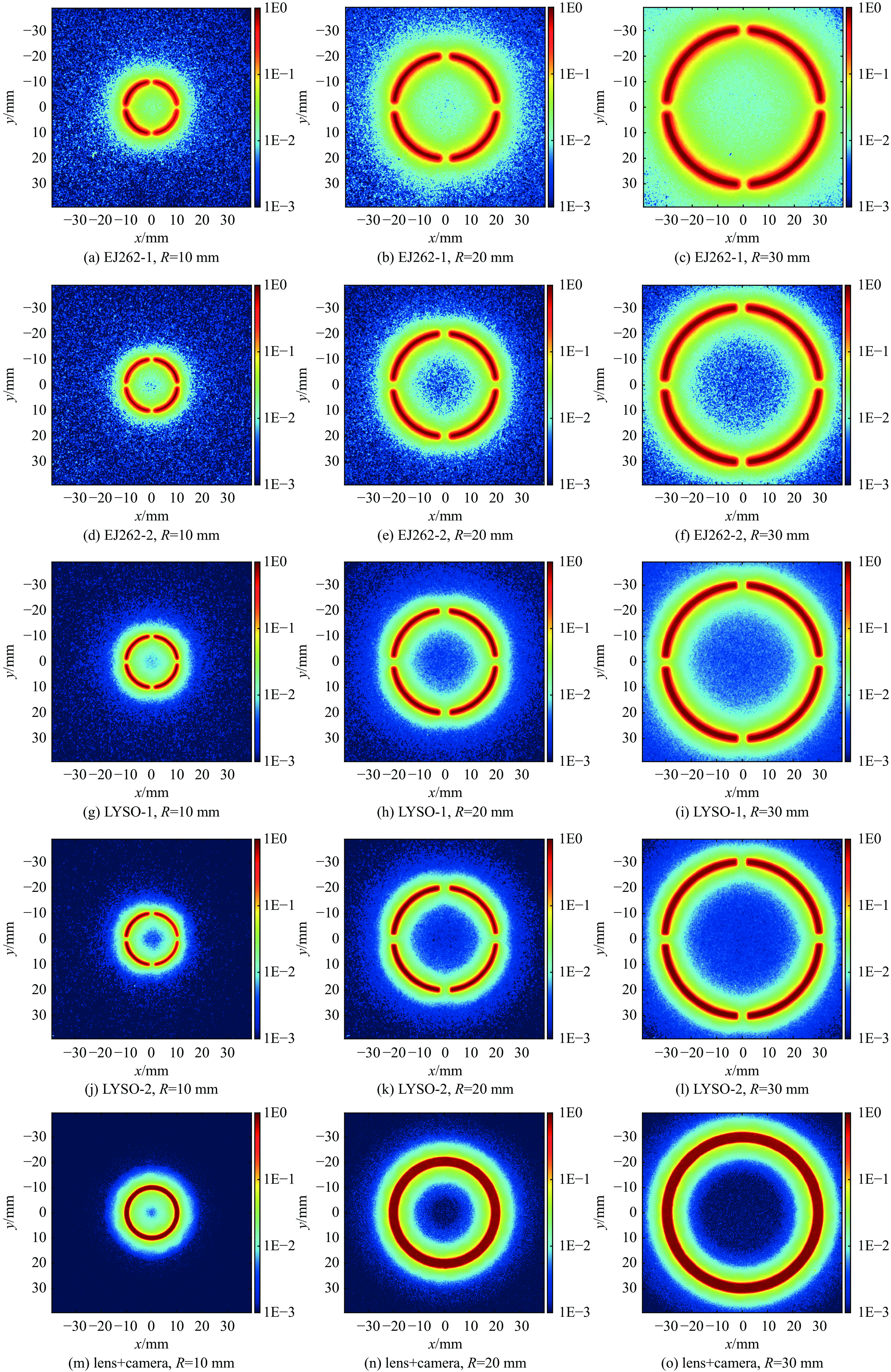
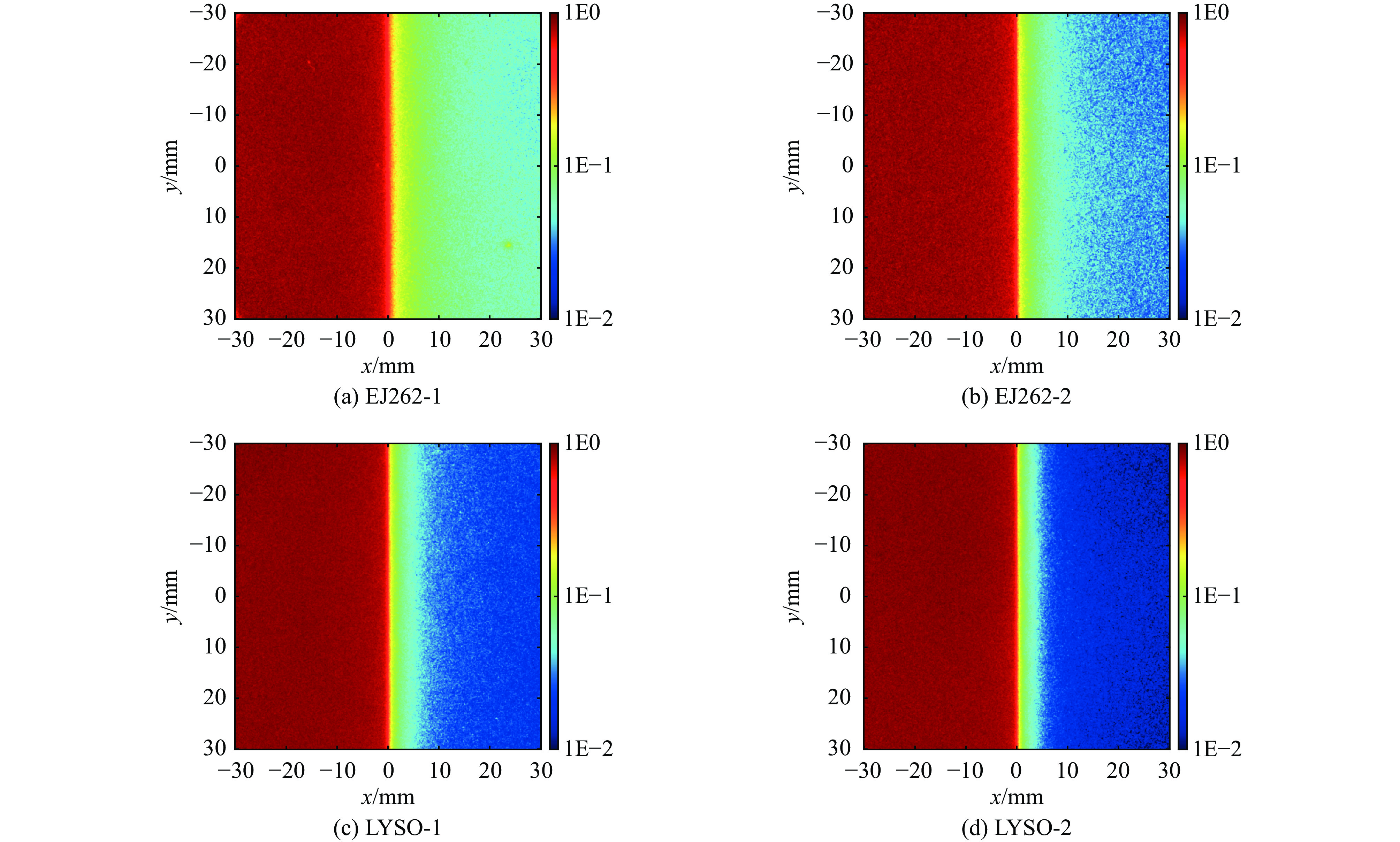
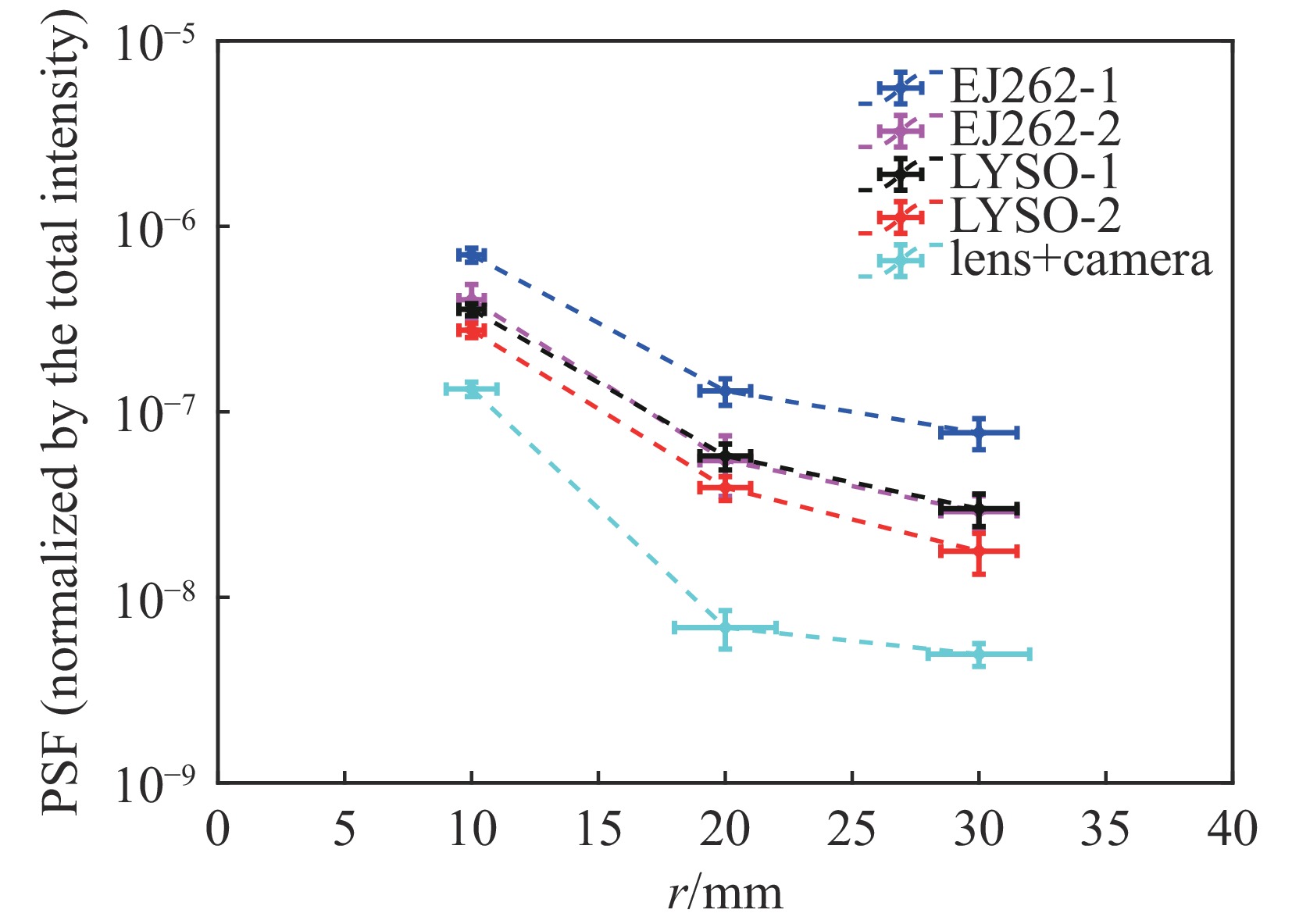
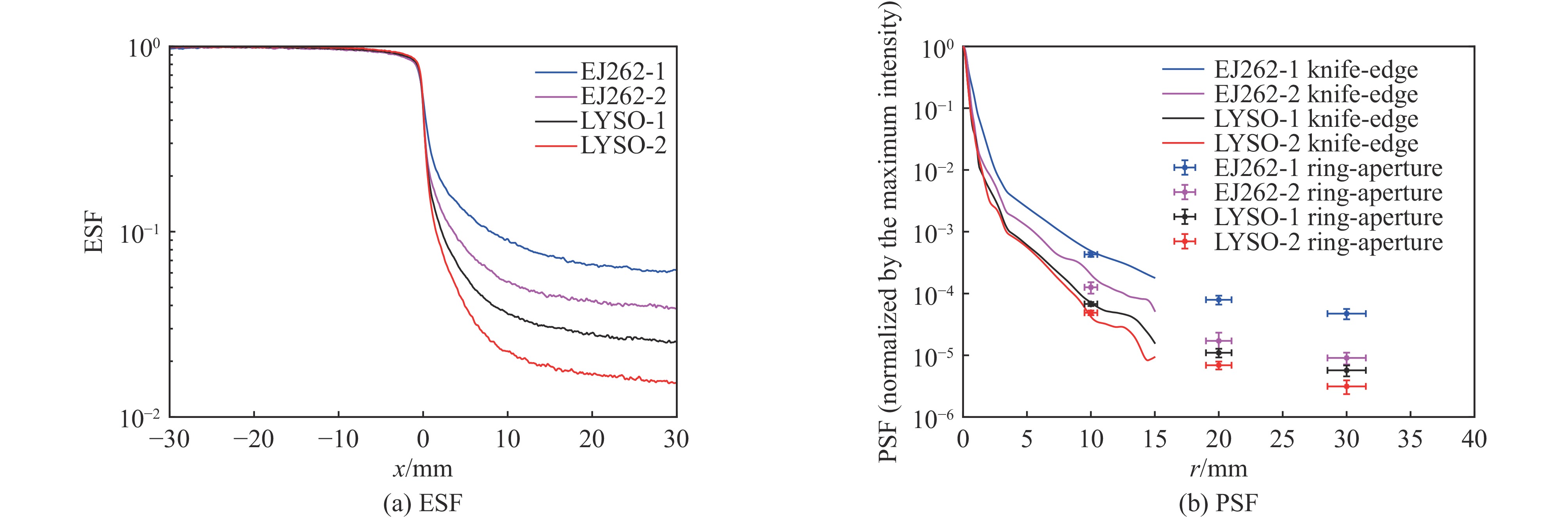
source component to be tested collimator purpose pulsed X-ray generator Scintillator + lens + camera ring-aperture 1#、2#、3# measure the low-frequency components of PSF excited by X rays tungsten sharp edge measure PSF excited by X rays tungsten plate Measure the radiation background in the X-ray field —— Measure the flat-field image pulsed uniform visible light source lens + camera ring mask 1#、2#、3# measure the low-frequency components of the PSF of lens and camera —— measure the flat-field image 表 4 PSF在不同距离r处的实测值
Table 4. Measured values of PSF at different distances
source component to be tested HPSF(r), normalized by total intensity r=10.0 mm r=20.0 mm r=30.0 mm pulsed X-ray generator EJ262-1+lens+camera 7.02E-7 (1±9%) 1.30E-7 (1±16%) 7.72E-8 (1±19%) EJ262-2 (blackening)+lens+camera 4.02E-7 (1±21%) 5.46E-8 (1±36%) 2.90E-8 (1±22%) LYSO-1+ lens+camera 3.57E-7 (1±8%) 5.79E-8 (1±16%) 3.00E-8 (1±20%) LYSO-2 (blackening)+ lens+camera 2.76E-7 (1±9%) 3.90E-8 (1±15%) 1.77E-8 (1±25%) pulsed uniform visible light source lens+camera 1.33E-7 (1±9%) 6.87E-9 (1±23%) 4.94E-9 (1±14%) Note: the confidence factor for uncertainty is k=1. 表 5 模拟计算条件
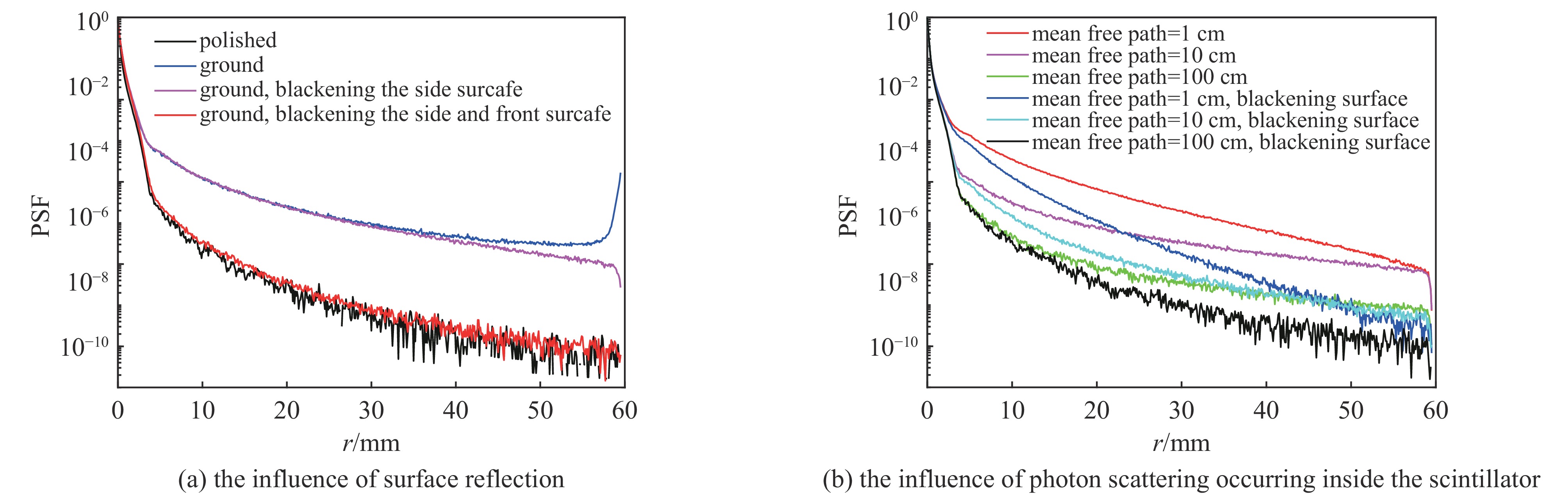
Table 5. Simulation conditions
number research subject front surface back surface side surcafe Geant4 physics list related
to optical photons1 the influence of specular reflection polished polished polished scintillation
boundary
absorption2 the influence of diffuse reflection ground ground ground 3 the influence of lateral dispersion ground ground ground+ black paint 4 the influence of diffuse reflection occurring on the side ground+ black paint ground ground+ black paint 5 the influence of internal scattering polished polished ground+ black paint scintillation
boundary
absorption
a custom scattering processpolished+ black paint polished ground+ black paint -
[1] Merrill F E, Bower D, Buckles R, et al. The neutron imaging diagnostic at NIF (invited)[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2012, 83: 10D317. doi: 10.1063/1.4739242 [2] Volegov P L, Danly C R, Fittinghoff D N, et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction of neutron, Gamma-ray, and X-ray sources using spherical harmonic decomposition[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2017, 122: 175901. doi: 10.1063/1.4986652 [3] Birge N W, Geppert-Kleinrath V, Danly C R, et al. Fast neutron imaging and tomography at NIF[R]. New Mexico: Los Alamos, 2022. [4] 余波, 苏明, 黄天晅, 等. 基于神光Ⅲ主机装置的中子半影锥成像系统设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2013, 25(10): 2604-2610 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132510.2604Yu Bo, Su Ming, Huang Tianxuan, et al. Design of diagnostic system for neutron penumbral imaging based on Shenguang-Ⅲ facility[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(10): 2604-2610 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132510.2604 [5] 李忠良, 张栩彬, 严明飞, 等. 一种环孔编码成像空间移变评估方法[J]. 现代应用物理, 2025, 16: 020204Li Zhongliang, Zhang Xubin, Yan Mingfei, et al. A spatial shift-variant evaluation method for coded ring-aperture imaging[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2025, 16: 020204 [6] Fittinghoff D N, Bower D E, Hollaway J R, et al. One-dimensional neutron imager for the Sandia Z facility[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2008, 79: 10E530. doi: 10.1063/1.2988819 [7] Ricketts S A, Mangan M A, Volegov P, et al. Neutron source reconstruction using a generalized expectation–maximization algorithm on one-dimensional neutron images from the Z facility[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2024, 95: 033501. doi: 10.1063/5.0176152 [8] 邱孟通, 吕敏, 王奎禄, 等. Z-pinch X射线时间分辨多幅图像诊断系统[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2003, 15(1): 101-104Qiu Mengtong, Lv Min, Wang Kuilu, et al. Time resolved X-ray image diagnostic system for Z-pinch[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2003, 15(1): 101-104 [9] 杨建伦, 李正宏, 徐荣昆, 等. Z-pinch内爆等离子体时空分辨诊断技术[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2007, 19(2): 234-240Yang Jianlun, Li Zhenghong, Xu Rongkun, et al. Time-space-resolved diagnostic technique for Z-pinch plasma investigation[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2007, 19(2): 234-240 [10] 温树槐, 丁永坤. 激光惯性约束聚变诊断学[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2012Wen Shuhuai, Ding Yongkun. Laser inertial confinement fusion diagnostics[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2012 [11] Ekdahl C, Abeyta E O, Caudill L, et al. First beam at DARHT-II[C]//Proceedings of the 2003 Particle Accelerator Conference. 2003: 558-562. [12] Zepeda-Alarcon E, Clayton J H, Haines T J, et al. Advancing radiographic capabilities for future Cygnus experiments[R]. Las Vegas: Nevada National Security Site/Mission Support and Test Services LLC, 2022. [13] 刘军, 张绚, 刘进, 等. 高能闪光照相中网栅相机的性能分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2016, 28: 024003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201628.024003Liu Jun, Zhang Xuan, Liu Jin, et al. Performance analysis of anti-scatter grid camera in high energy flash radiography[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2016, 28: 024003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201628.024003 [14] 徐畅, 董鹏举, 仵可, 等. X射线荧光测量光敏炸药面密度的数值模拟[J]. 现代应用物理, 2025, 16: 020205Xu Chang, Dong Pengju, Wu Ke, et al. Numerical simulation of areal density measurement of light-initiated high explosive based on X-ray fluorescence[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2025, 16: 020205 [15] Wallace M S, Neilsen A, Dutra E C. High-fidelity dynamic neutron imaging and radiography for subcritical experiments and other applications[R]. Las Vega: Nevada National Security Site/Mission Support and Test Services LLC, 2022. [16] 张翱, 孙世峰, 张翔铭, 等. 双端读出提高快中子探测器时间分辨率方法的研究[J]. 现代应用物理, 2024, 15: 050201Zhang Ao, Sun Shifeng, Zhang Xiangming, et al. Temporal resolution optimization of fast neutron detector using dual-ended readout method[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2024, 15: 050201 [17] Smalley D, Baker S, Phillips D, et al. Scintillator evaluations: long-range blur[R]. Washington: Nevada National Site/National Security Technologies, LLC, 2016. [18] Smalley D, Baker S, Baldonado B, et al. Image restoration of high-energy X-ray radiography with a scintillator blur model[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2020, 968: 163910. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2020.163910 [19] Wilke M D, Batha S H, Bradley P A, et al. The national ignition facility neutron imaging system[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2008, 79: 10E529. doi: 10.1063/1.2987984 -




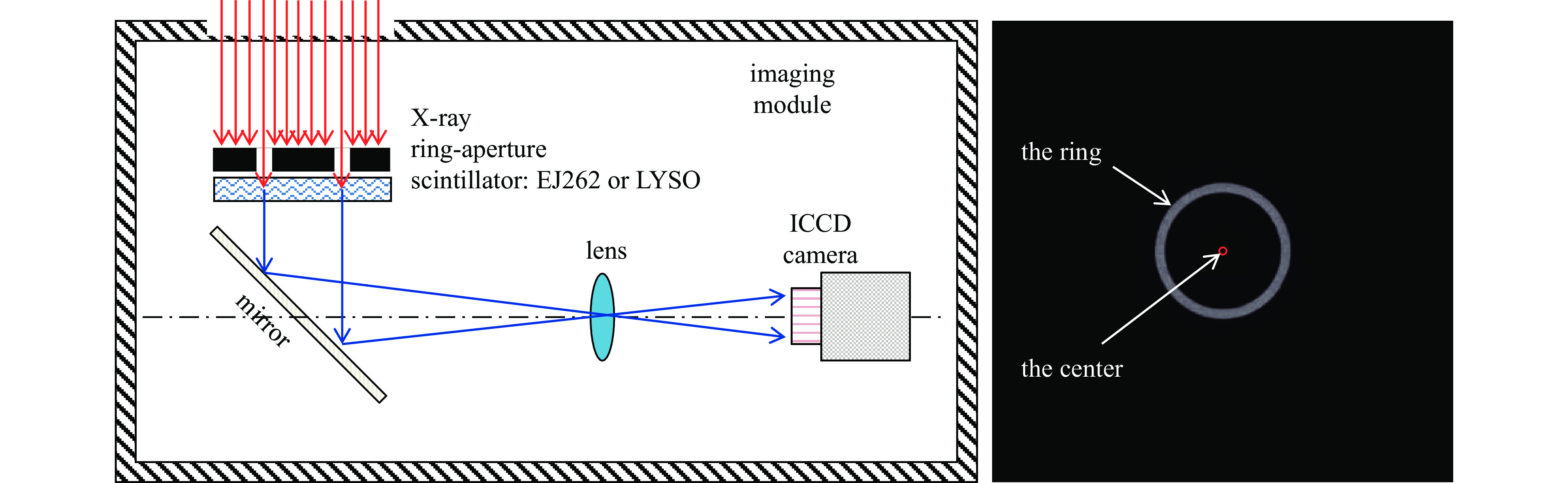
 下载:
下载: