Monte Carlo simulation of the γ-radiation dose field from fission products
-
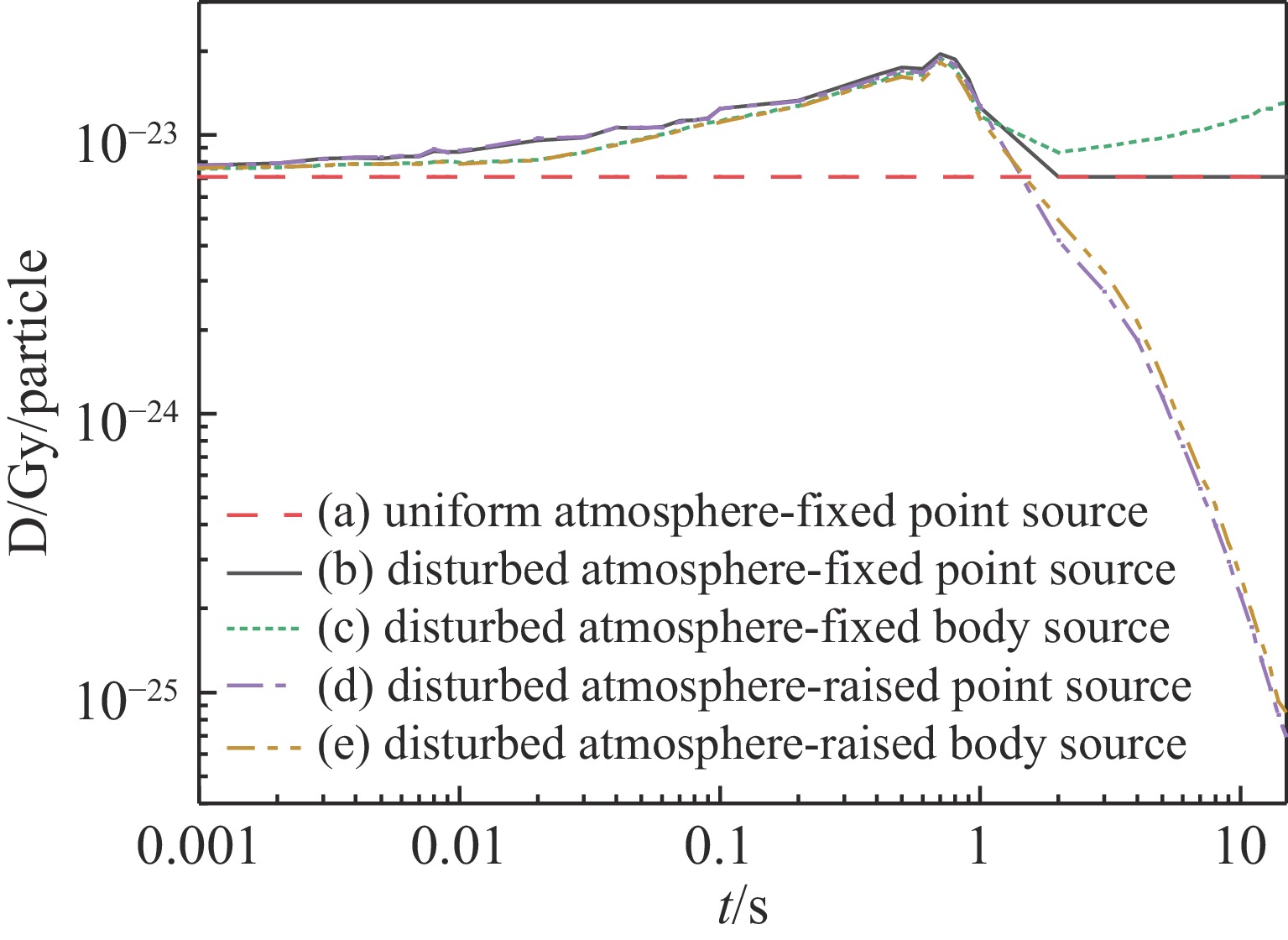
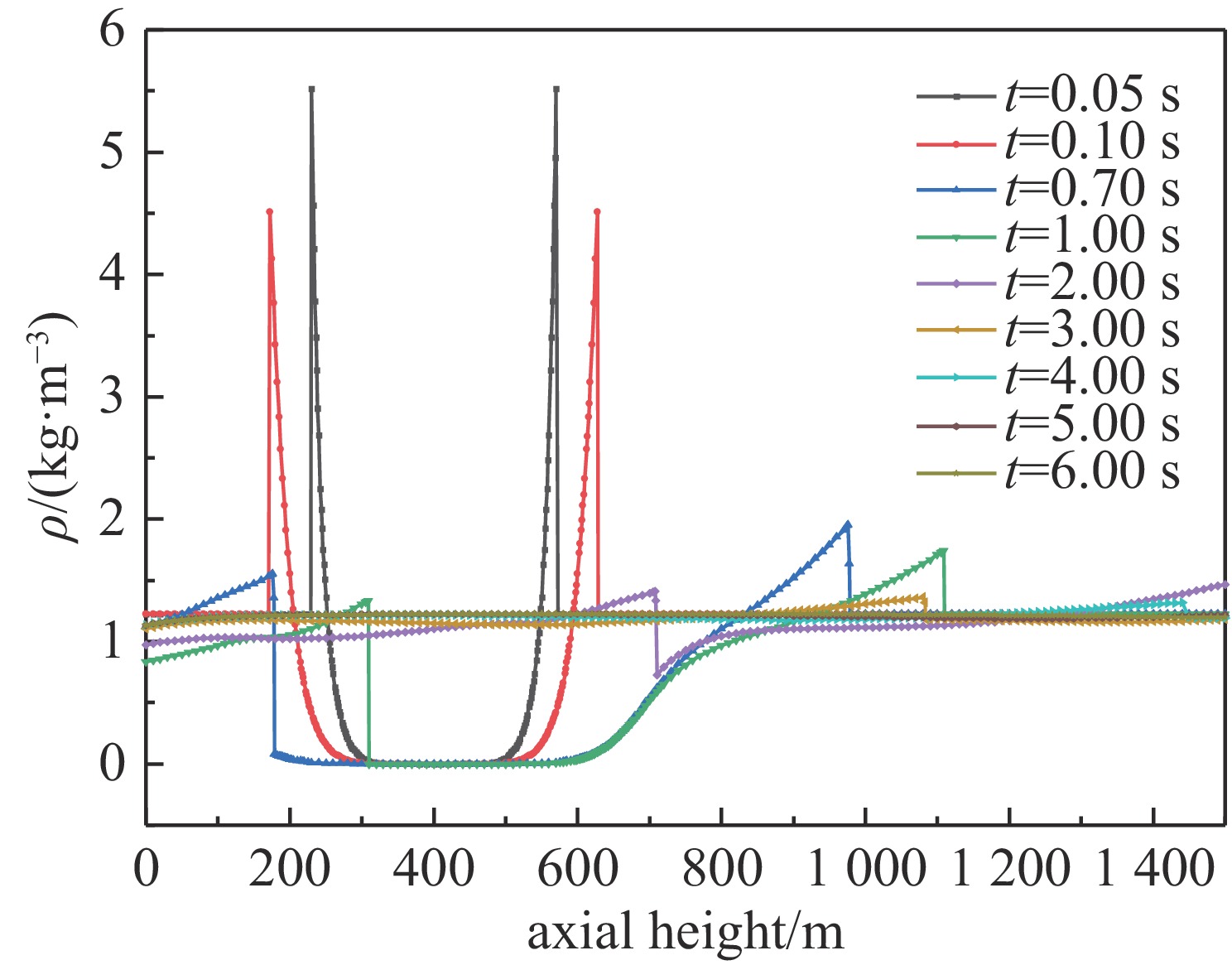
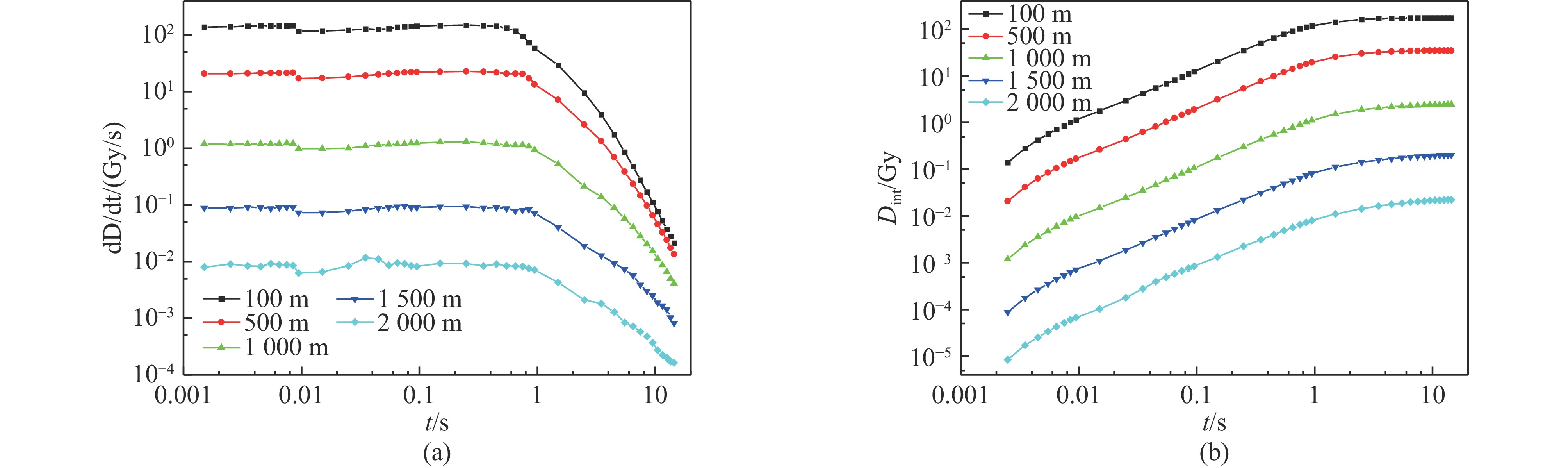
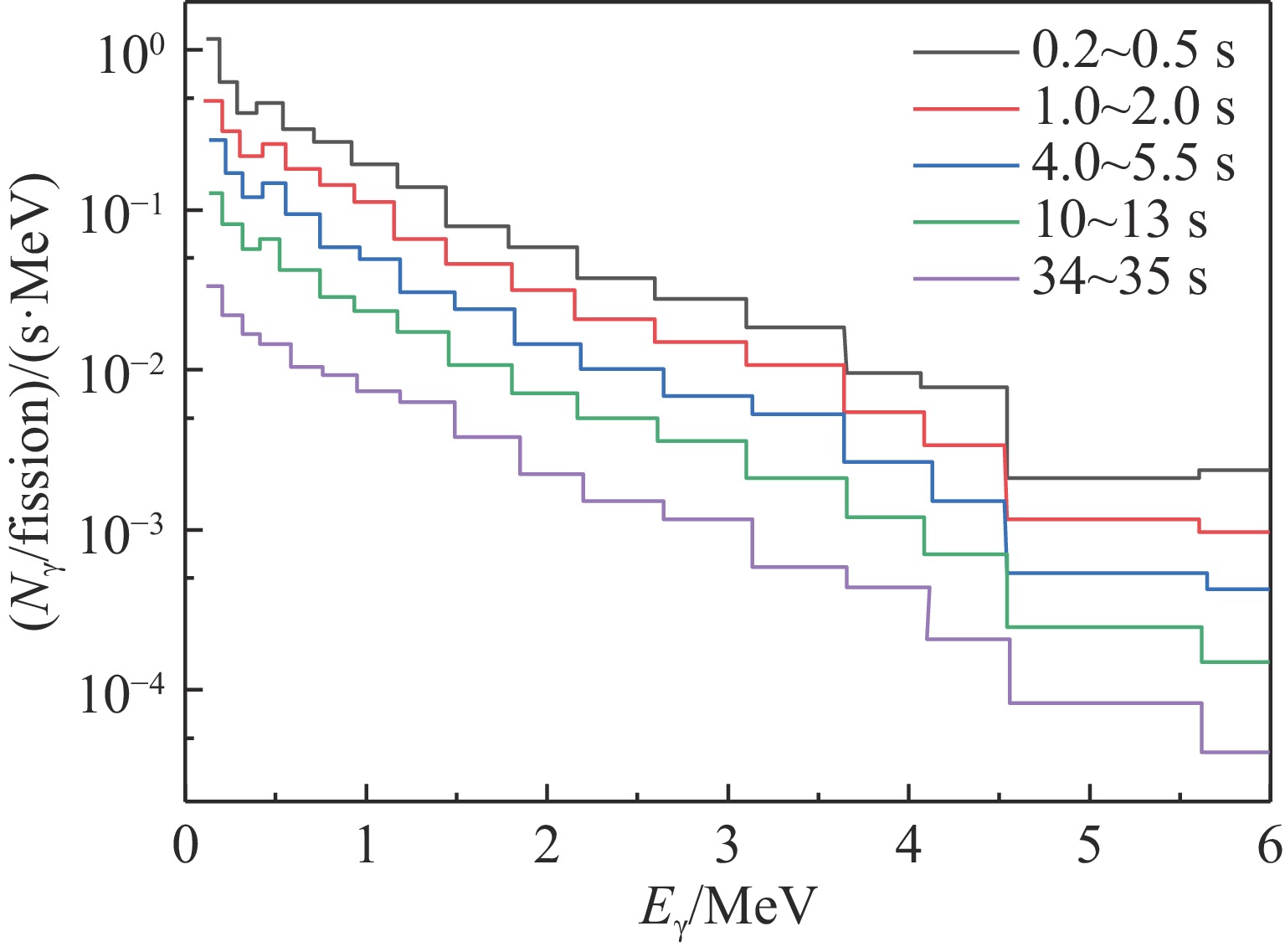
摘要: 针对随时间变化的裂变产物γ体源在冲击波扰动形成的非均匀大气中的输运问题,采用冲击波流场演化的LAMBR理论计算方法构建冲击波扰动下大气密度分布计算模型,基于辐射输运的时间离散理论,发展了用于计算裂变产物γ辐射场参数的瞬态变步长蒙特卡罗模拟方法,并开展了空旷地面条件下235U裂变产物γ辐射环境场流体力学增强效应的模拟计算。计算结果表明,建立的裂变产物γ辐射变步长多时间步MC模拟方法能够反映出冲击波扰动大气密度场对裂变产物γ辐射环境的流体力学增强效应,与静态大气模型相比,流体力学增强效应可使部分位置的总剂量增强2~3倍。Abstract:
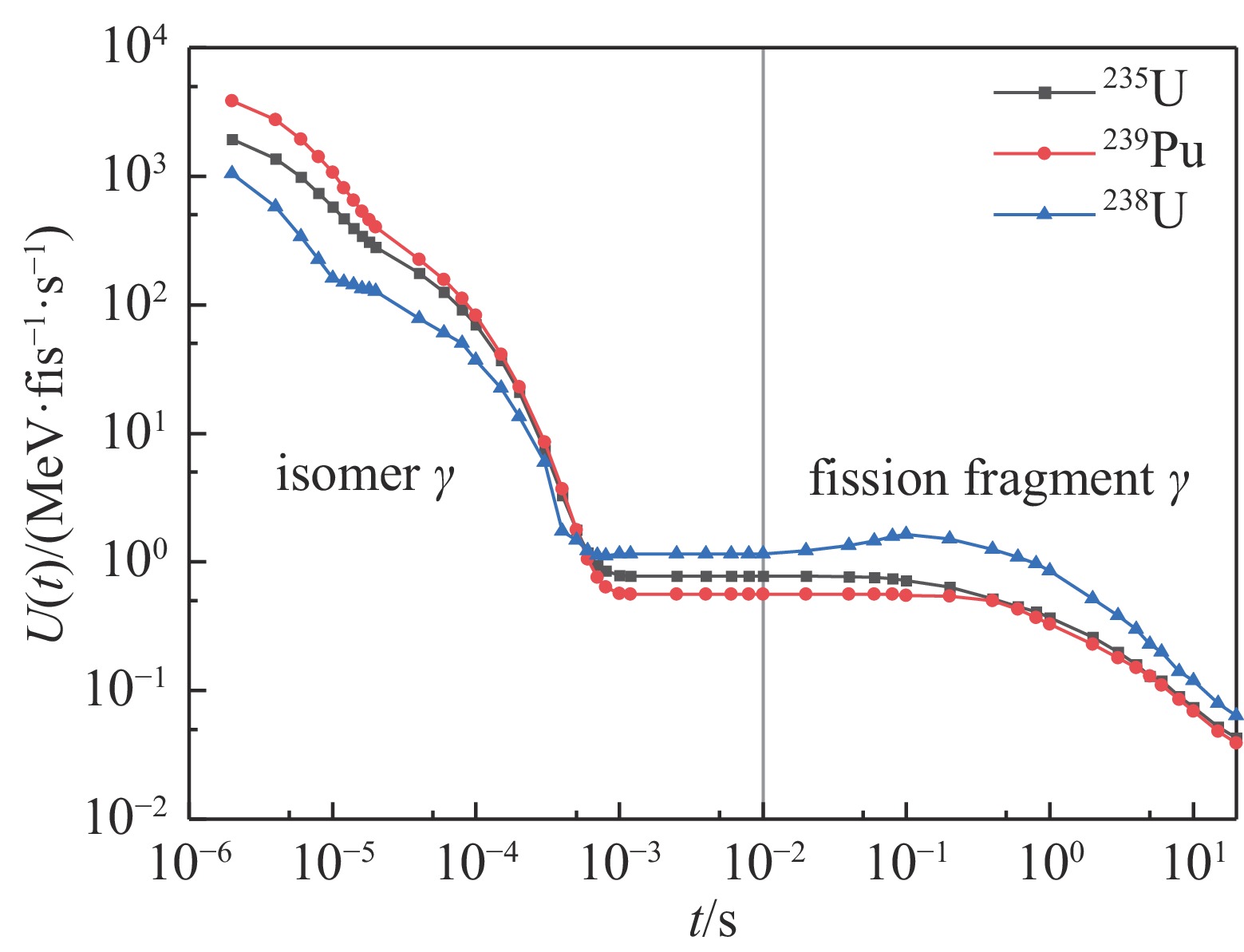
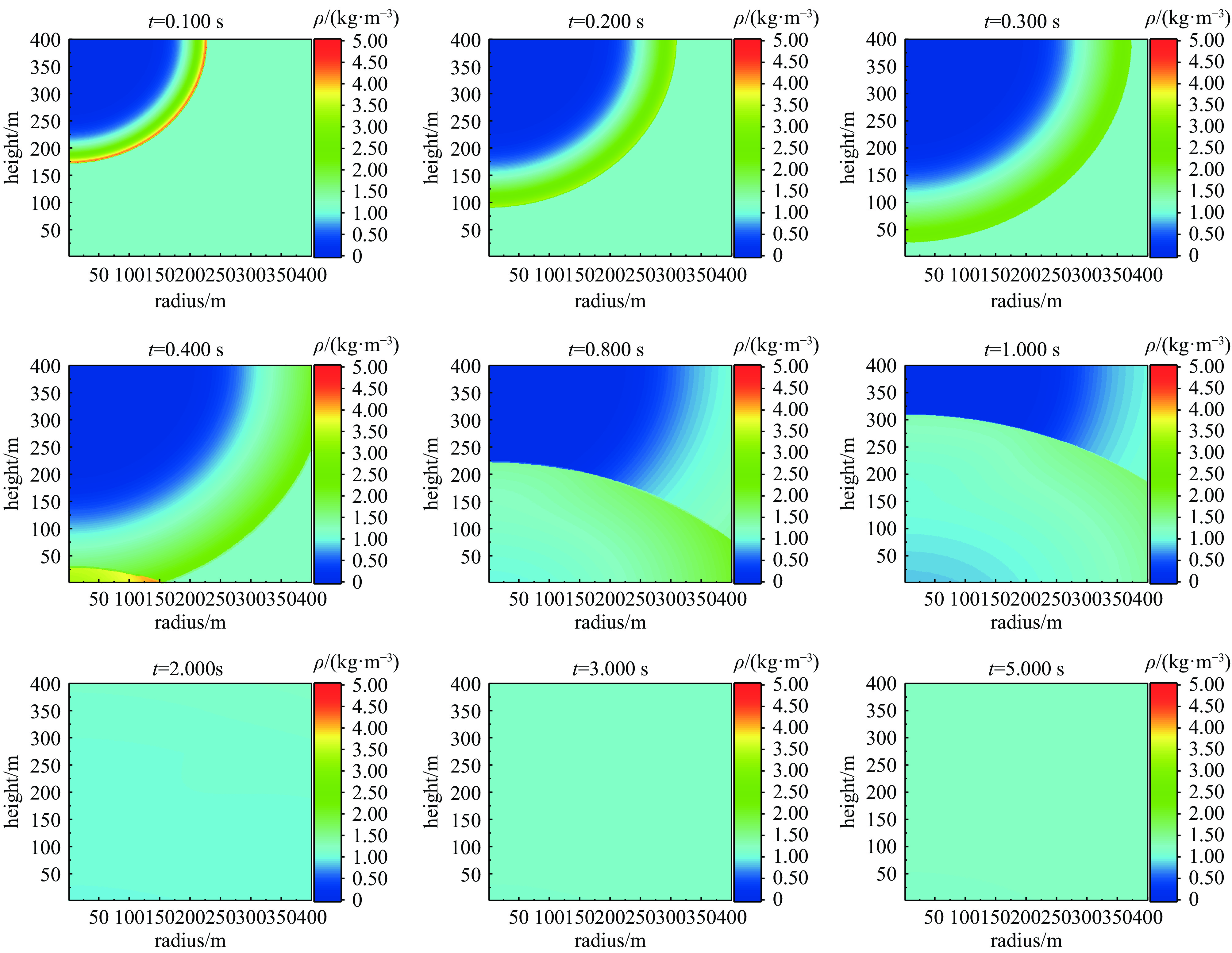
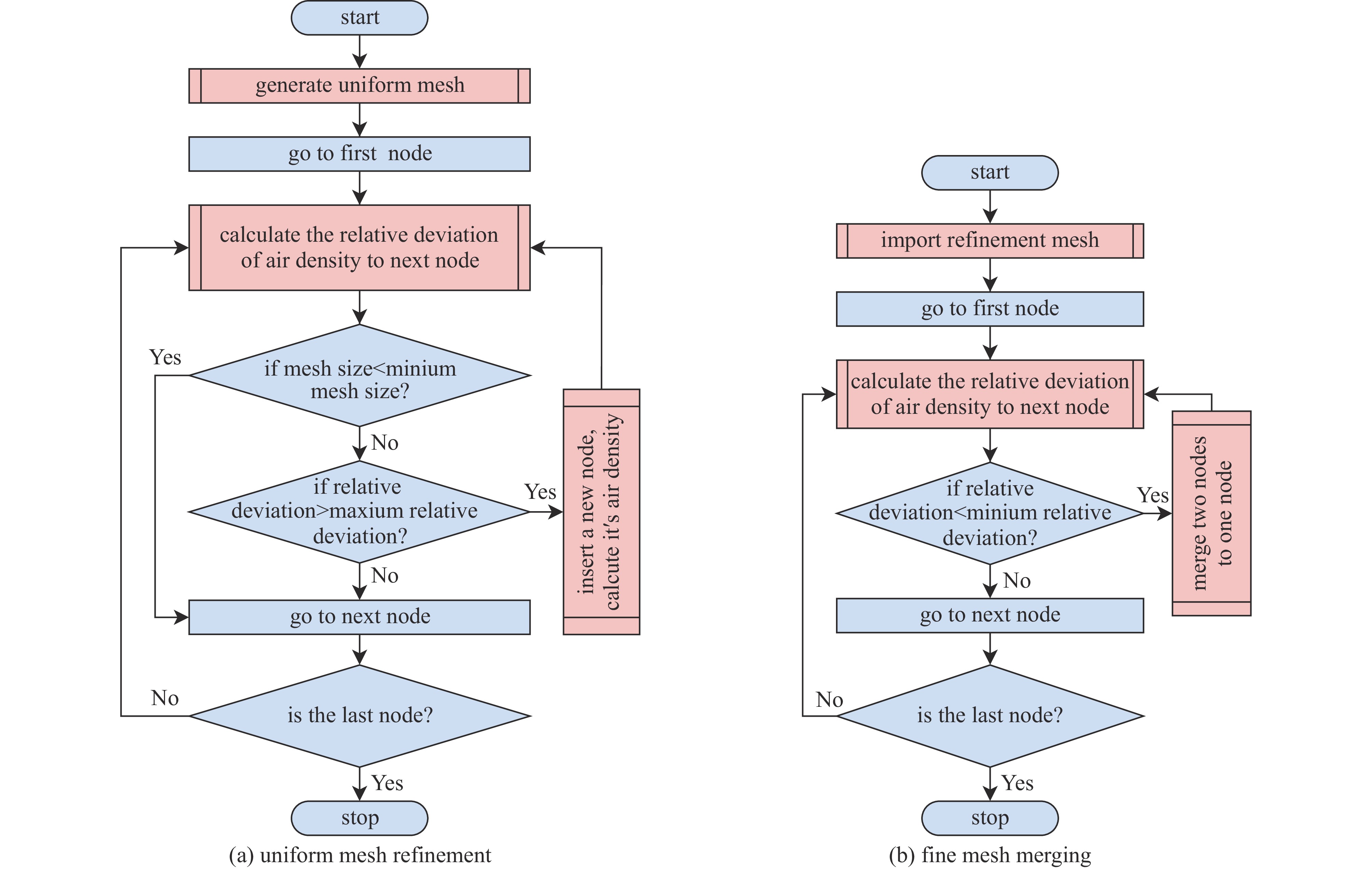
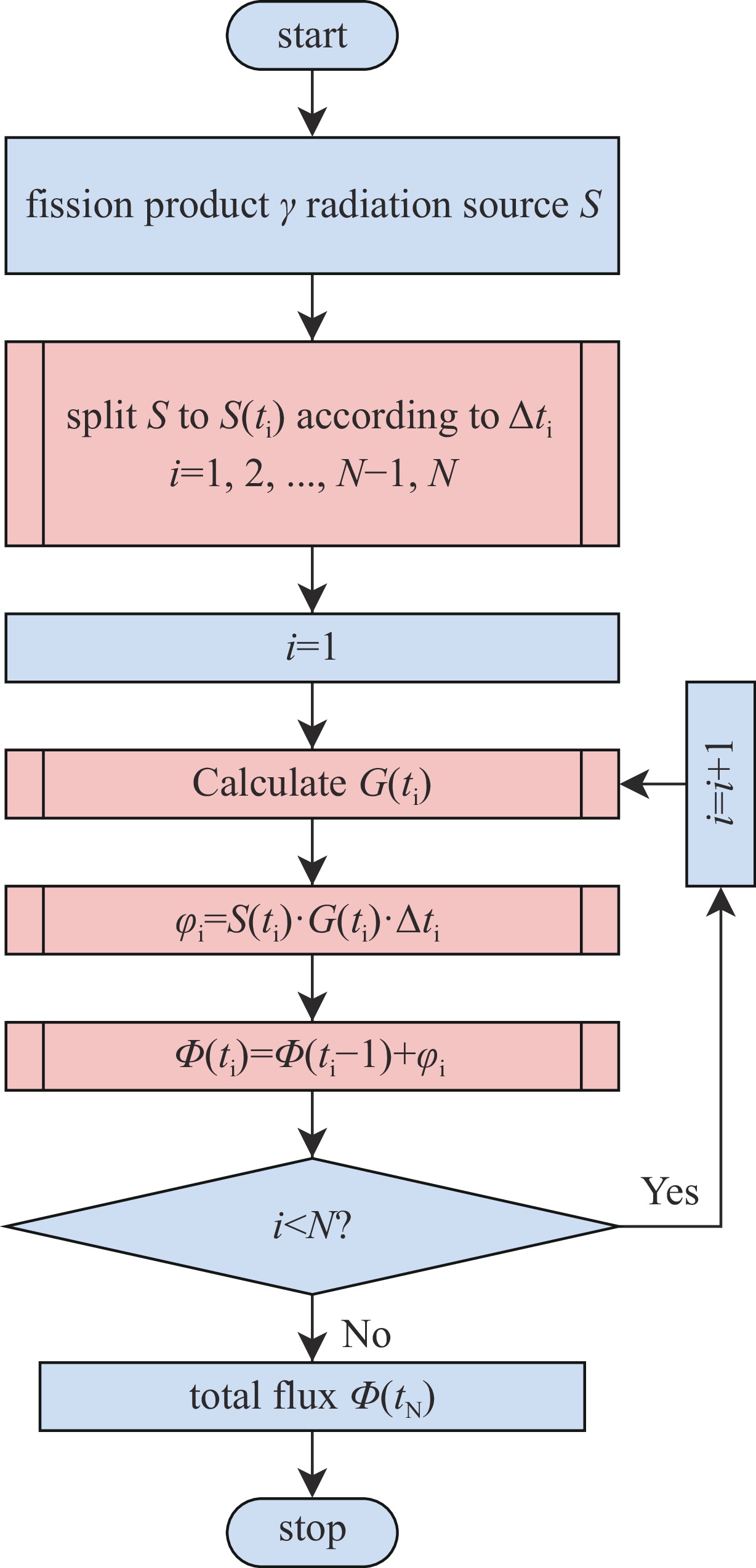
Background Extreme nuclear events typically generate intense explosions and release radioactive fission products. Fission product γ, emitted during radioactive decay of fission products, can affect radiation dose fields for 10−5 to 15 seconds. During this period, the source intensity, spectrum, and spatial distribution exhibit significant temporal variations. Concurrently, shock-waves induce complex atmospheric density changes, creating hydrodynamic enhancement effects.Purpose This study aims to develop a computational model for simulating time-varying fission product γ transport in non-uniform atmospheres perturbed by shock-waves, specifically quantifying the hydrodynamic enhancement effect on γ radiation dose fields.Methods A computational model for atmospheric density distribution was constructed using the LAMBR theory for shock-wave flow-field evolution. Based on radiation transport time-discrete theory, a transient variable-time-step Monte Carlo (MC) method was developed using the PHEN particle transport code.Results A validation via 20 kt TNT-equivalent detonation simulations at 400 m altitude was conducted to evaluate the hydrodynamic enhancement effect of fission product γ of 235U. The results demonstrate that, compared to a uniform atmospheric model, the hydrodynamic enhancement effect can amplify the γ dose by 2-3 times at some locations.Conclusions The proposed transient variable-time-step Monte Carlo simulation method can effectively capture the hydrodynamic enhancement effect of the shock wave-perturbed atmospheric density field on the fission product γ radiation fields. -
表 1 半径500 m的等效空腔对裂变产物γ辐射传播的影响
Table 1. Effect of equivalent cavity with a radius of 500 m on γ radiation propagation of fission products
ground range/m Dc/(10−24 Gy/particle) RSD/% Du/(10−24 Gy/particle) RSD/% Dc/Du cavity model uniform atmospheric model 100 28.7 1.4 4.69 3.8 6.11 300 24.7 1.5 3.94 4.7 6.26 500 18.8 1.5 3.11 3.3 6.03 700 12.8 1.5 2.17 3.7 5.93 900 8.23 2.0 1.36 3.5 6.05 1000 5.88 1.6 1.07 4.6 5.50 1200 3.35 2.1 0.618 6.6 5.43 1500 1.41 3.5 0.247 6.1 5.72 表 2 高度400m威力20ktTNT当量爆炸裂变产物源的极半径、赤道半径及中心高度
Table 2. The polar radius, equatorial radius and height of the fission product with explosion geight of 400m and power of 20ktTNT Equivalent
time/s polar radius/m equatorial raidus/m height/m time/s polar radius/m equatorial raidus/m height/m 0.001 26.589 26.589 400.005 0.400 134.157 153.864 408.868 0.002 34.182 34.182 400.010 0.500 138.050 162.659 412.442 0.003 41.438 41.438 400.015 0.600 141.853 171.237 416.497 0.004 48.352 48.354 400.020 0.700 145.568 179.597 421.010 0.005 54.921 54.923 400.025 0.800 149.194 187.738 425.956 0.006 61.141 61.143 400.031 0.900 152.730 195.659 431.311 0.007 67.006 67.009 400.036 1.000 156.177 203.359 437.053 0.008 72.514 72.517 400.041 2.000 185.671 268.007 510.433 0.009 77.659 77.663 400.046 3.000 205.976 309.561 596.145 0.010 82.438 82.442 400.051 4.000 217.808 329.289 674.347 0.020 117.042 116.990 400.099 5.000 230.135 347.923 764.869 0.030 118.987 119.448 400.222 6.000 242.753 367.006 844.379 0.040 119.413 120.417 400.354 7.000 254.535 384.827 912.429 0.050 119.838 121.383 400.492 8.000 265.382 401.215 974.151 0.060 120.262 122.348 400.636 9.000 275.463 416.464 1032.285 0.070 120.685 123.310 400.786 10.000 284.968 430.822 1088.199 0.080 121.107 124.270 400.942 11.000 294.002 444.480 1142.567 0.090 121.529 125.228 401.104 12.000 302.657 457.573 1195.753 0.100 121.949 126.184 401.271 13.000 310.917 470.058 1248.006 0.200 126.107 135.626 403.259 14.000 319.045 482.171 1297.545 0.300 130.176 144.853 405.799 14.900 327.117 492.861 1324.902 -
[1] 乔登江. 核爆炸物理概论(上册)[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2003Qiao Dengjiang. General principles to the physics of nuclear burst (Vol. 1)[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2003 [2] 刘利, 牛胜利, 朱金辉, 等. 临近空间核爆炸碎片云运动特征与规律研究[J]. 核技术, 2022, 45: 100503 doi: 10.11889/j.0253-3219.2022.hjs.45.100503Liu Li, Niu Shengli, Zhu Jinhui, et al. Motion characteristics and laws of the debris from a near-space nuclear detonation[J]. Nuclear Techniques, 2022, 45: 100503 doi: 10.11889/j.0253-3219.2022.hjs.45.100503 [3] Leipunskii O I. Gamma-radiation of an atomic explosion[R]. United States Atomic Energy Commission, 1959. [4] 朱金辉, 李夏至, 左应红, 等. 不同大气密度条件下近地面γ射线输运的几何相似理论研究[J]. 现代应用物理, 2024, 15: 060202Zhu Jinhui, Li Xiazhi, Zuo Yinghong, et al. Similarity theory of near-ground gamma-ray transport under different atmospheric density[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2024, 15: 060202 [5] Marshall J D, Wells M B. The effect of cutoff energy on monte carlo calculated Gamma-ray dose rates in air[R]. 1966. [6] 朱金辉, 陶应龙, 卓俊, 等. 模块化粒子输运程序包PHEN的开发与应用[J]. 现代应用物理, 2018, 9: 030203 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2018.030203Zhu Jinhui, Tao Yinglong, Zhuo Jun, et al. Development and application of modular particle transportation PHEN package[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2018, 9: 030203 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2018.030203 [7] 邓力, 李刚. 粒子输运问题的蒙特卡罗模拟方法与应用(上册)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019Deng Li, Li Gang. Monte Carlo simulated methods and applications for particle transport problems[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019 [8] 马天予, 金永杰. 基于Boltzmann输运方程的SPECT系统解析建模方法[J]. 高能物理与核物理, 2006, 30(8): 806-811 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-3052.2006.08.022Ma Tianyu, Jin Yongjie. Analytical system modeling method for SPECT based on the boltzmann transport equation[J]. High Energy Physics and Nuclear Physics, 2006, 30(8): 806-811 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-3052.2006.08.022 [9] Boman E, Tervo J, Vauhkonen M. Modelling the transport of ionizing radiation using the finite element method[J]. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2005, 50(2): 265-280. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/50/2/006 [10] 杜书华. 输运问题的计算机模拟[M]. 长沙: 湖南科学技术出版社, 1989Du Shuhua. Computer simulation of transport problems[M]. Changsha: Hunan Science & Technology Press, 1989 [11] 裴鹿成, 张孝泽. 蒙特卡罗方法及其在粒子输运问题中的应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1980Pei Lucheng, Zhang Xiaoze. Monte Carlo method and application in particle transport problem[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1980 [12] 黄祖洽, 丁鄂江. 输运理论[M]. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008Huang Zuqia, Ding Ejiang. Transport theory[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Science Press, 2008 [13] 顾樵. 数学物理方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012Gu Qiao. Mathematical methods for physics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012 [14] Davison B, Sykes J B. Neutron transport theory[M]. Science Press, 1960. [15] 乔登江. 核爆炸物理概论(下册)[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2003Qiao Dengjiang. General principles to the physics of nuclear burst (Vol 2)[M]. Beijing: National Defense and Industry Press, 2003 [16] Norment H G. DELFIC: department of defense fallout prediction system. Volume I - Fundamentals[R]. Bedford: Atmospheric Science Associates, 1979. [17] 王建国, 牛胜利, 张殿辉, 等. 高空核爆炸效应参数手册[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 2010Wang Jianguo, Niu Shengli, Zhang Dianhui, et al. The parameter manual book of high-altitude nuclear explosion effects[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 2010 [18] Wang Jianguo, Liu Li, Zuo Yinghong, et al. Research progress in numerical simulation of environmental parameters generated by the high-altitude nuclear explosions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2025, 72(3): 884-900. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2025.3530013 [19] Engle L B, Fisher P C. Energy and time dependence of delayed gammas from fission[R]. Los Alamos Scientific Lab. , 1961. [20] Fisher P C, Engle L B. Delayed gammas from fast-neutron fission of Th232, U233, U235, U238, and Pu239[J]. Physical Review Journals Archive, 1964, 134(4B): B796-B816. [21] Walton R B, Sund R E. Delay gamma rays between 2 and 80 μsec after U235 (n, f) and Pu239 (n, f)[J]. Physical Review Journals Archive, 1969, 178: 1894. [22] Walton R B, Sund R E. Delayed gamma rays from fission[R]. 1966. [23] Ehrhardt L, Boutillier J, Magnan P, et al. Evaluation of overpressure prediction models for air blast above the triple point[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 311: 176-185. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.02.051 [24] Xu Weizheng, Wu Weiguo, Lin Yongshui. Numerical method and simplified analytical model for predicting the blast load in a partially confined chamber[J]. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 2018, 76(2): 284-314. [25] Bewick B, Flood I, Chen Z. A neural-network model-based engineering tool for blast wall protection of structures[J]. International Journal of Protective Structures, 2011, 2(2): 159-176. doi: 10.1260/2041-4196.2.2.159 [26] Armaghani D J, Hasanipanah M, Mahdiyar A, et al. Airblast prediction through a hybrid genetic algorithm-ANN model[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2018, 29(9): 619-629. doi: 10.1007/s00521-016-2598-8 [27] Chan P C, Klein H H. A study of blast effects inside an enclosure[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 1994, 116(3): 450-455. doi: 10.1115/1.2910297 [28] Kong B, Lee K, Lee S, et al. Indoor propagation and assessment of blast waves from weapons using the alternative image theory[J]. Shock Waves, 2016, 26(2): 75-85. doi: 10.1007/s00193-015-0581-4 [29] Needham C E. Blast waves[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2010. [30] 贾雷明, 王澍霏, 田宙. 爆炸冲击波反射流场的理论计算方法[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39: 064201 doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0167Jia Leiming, Wang Shufei, Tian Zhou. A theoretical method for the calculation of flow field behind blast reflected waves[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39: 064201 doi: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0167 [31] Shang Peng, Huang Liuxing, Zhu Jinhui, et al. Development and application of particle transport Monte Carlo simulation modeling toolkit[C]//2022 4th International Conference on Modeling, Simulation, Optimization and Algorithm. 2023: 012040. [32] Shang P, Huang L, Zuo Y, et al. Adaptive modeling approach of gamma ray transport within the influence of blast wave[C]//The 16th National Symposium on Monte Carlo Method and Its Application. 2023. [33] 朱金辉, 左应红, 刘利, 等. 蒙特卡罗方法在核爆辐射环境模拟中的应用与发展[J]. 现代应用物理, 2023, 14: 030104Zhu Jinhui, Zuo Yinghong, Liu Li, et al. Application and development of Monte Carlo method in simulation of nuclear explosion radiation environments[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2023, 14: 030104 [34] 史涛. 蒙特卡罗粒子输运问题中的减方差方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国工程物理研究院, 2018Shi Tao. Monte Carlo particle transport variance reduction method[D]. Beijing: China Academy of Engineering Physics, 2018 [35] 左应红, 牛胜利, 商鹏, 等. 权窗减方差方法在γ射线长距离输运模拟中的应用[J]. 现代应用物理, 2020, 11: 010205 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2020.010205Zuo Yinghong, Niu Shengli, Shang Peng, et al. Weight window variance reduction method for simulating long distance γ-ray transport[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2020, 11: 010205 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2020.010205 [36] 刘利, 左应红, 牛胜利, 等. 中子及次级γ在高空长距离蒙特卡罗输运模拟中的减方差方法[J]. 现代应用物理, 2022, 13: 010202Liu Li, Zuo Yinghong, Niu Shengli, et al. A varaince reduction method for simulating the long-distance transport of neutrons and secondary γ in high-altitude atmosphere by Monte Carlo method[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2022, 13: 010202 [37] 刘利, 左应红, 牛胜利, 等. 全局减方差方法在大空间γ辐射场计算中的应用[J]. 核技术, 2024, 47: 020602Liu Li, Zuo Yinghong, Niu Shengli, et al. Application of global variance reduction methods for the calculation of γ radiation field in a large space[J]. Nuclear Techniques, 2024, 47: 020602 -




 下载:
下载: