Rapid prediction of high-altitude electromagnetic pulse environment based on artificial neural network
-
摘要: 高空电磁脉冲(High-altitude Electromagnetic Pulse, HEMP)幅值高、脉宽宽、覆盖范围大,对现代电子设备和电力网络构成严重威胁。为了实现对HEMP环境的快速预测,提出了一种基于人工神经网络(Artificial Neural Network, ANN)的HEMP快速预测模型,解决了传统数值计算的时效性问题,显著提高场环境计算效率及预测精度。该模型结合Karzas-Latter高频近似模型与世界地磁模型,使用Sigmoid激活函数和均方差损失函数,包含一个输入层、八个隐藏层和一个输出层。实验结果表明,该模型能在短时间内完成HEMP电场峰值的精确预测,极大缩短了计算时间,拓展了适用范围。研究成果可为HEMP风险评估及快速响应提供参考。Abstract:
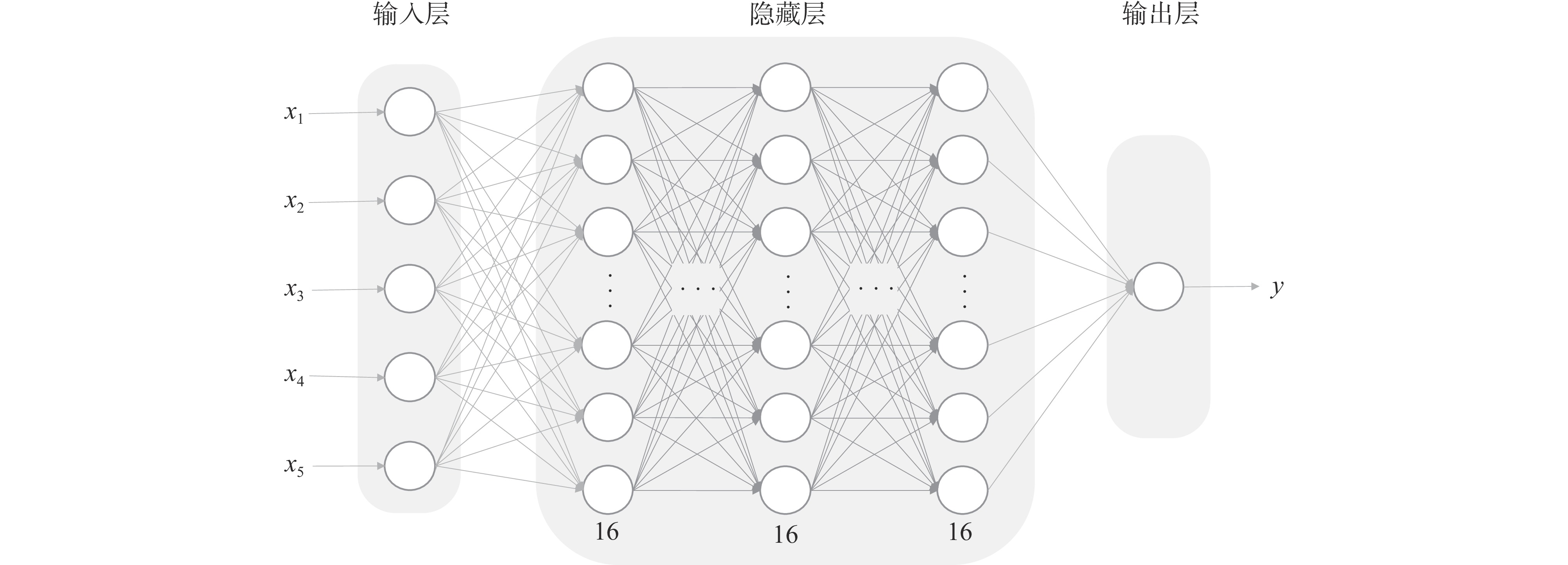
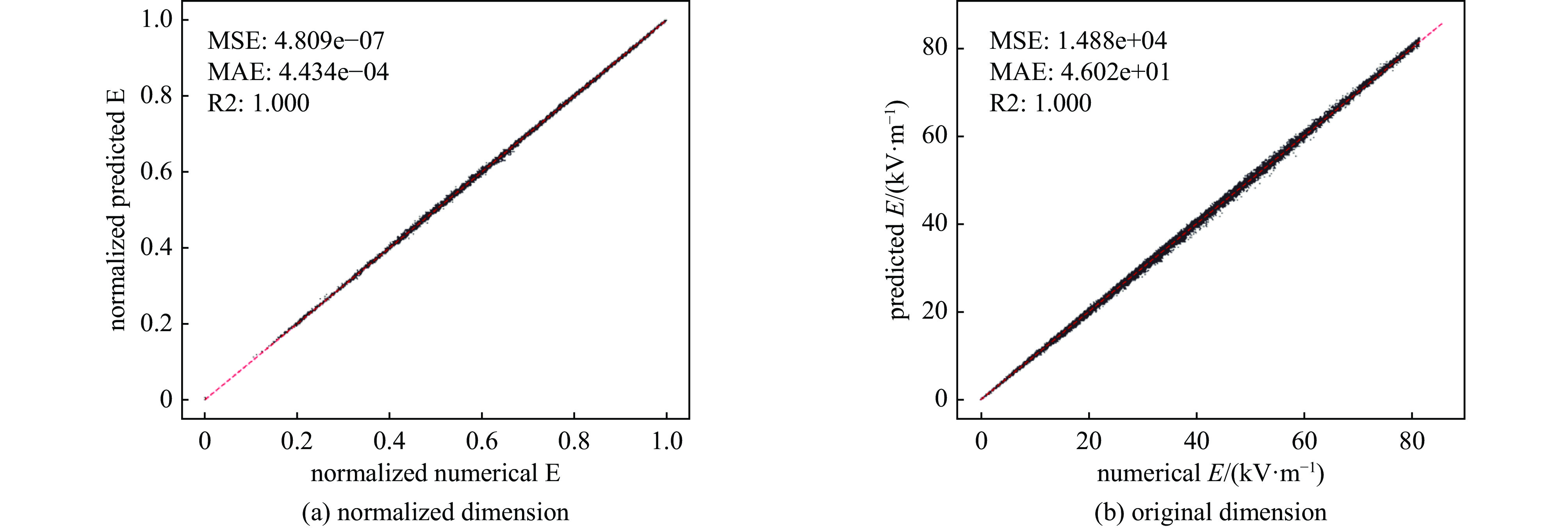
Background High-altitude electromagnetic pulse (HEMP), generated by nuclear explosions at high altitudes, is characterized by an extremely high amplitude, broad pulse width, and extensive geographic coverage. It poses a severe threat to modern electronic systems, communication infrastructures, and power grids. Accurate and efficient prediction of the HEMP environment is essential for evaluating its potential impact and formulating protective measures.Purpose Traditional numerical methods for HEMP prediction are often computationally intensive and time-consuming. This paper aims to develop a fast and accurate prediction model based on an artificial neural network (ANN) to overcome these limitations and enhance computational efficiency while maintaining prediction accuracy.Methods The proposed model integrates the Karzas–Latter high-frequency approximation model with the World Magnetic Model to establish a physical basis for HEMP simulation. A deep neural network architecture is constructed, comprising one input layer, eight hidden layers, and one output layer. The Sigmoid function is adopted as the activation function, and the mean squared error is used as the loss function during training.Results Experimental results demonstrate that the ANN-based model can accurately predict the peak electric field intensity of HEMP across a wide area within a very short computation time. Compared with conventional numerical methods, the model significantly reduces the required calculation time while achieving high predictive accuracy, making it suitable for rapid environment estimation and scenario analysis.Conclusions The developed ANN model provides an efficient and reliable tool for fast prediction of the HEMP environment. It offers substantial practical value for HEMP risk assessment, emergency response planning, and design of protection strategies for critical infrastructure. The research outcomes can serve as a valuable reference for both academic and applied disciplines concerned with electromagnetic pulse effects. -
表 1 原始数据量级
Table 1. Raw data magnitude
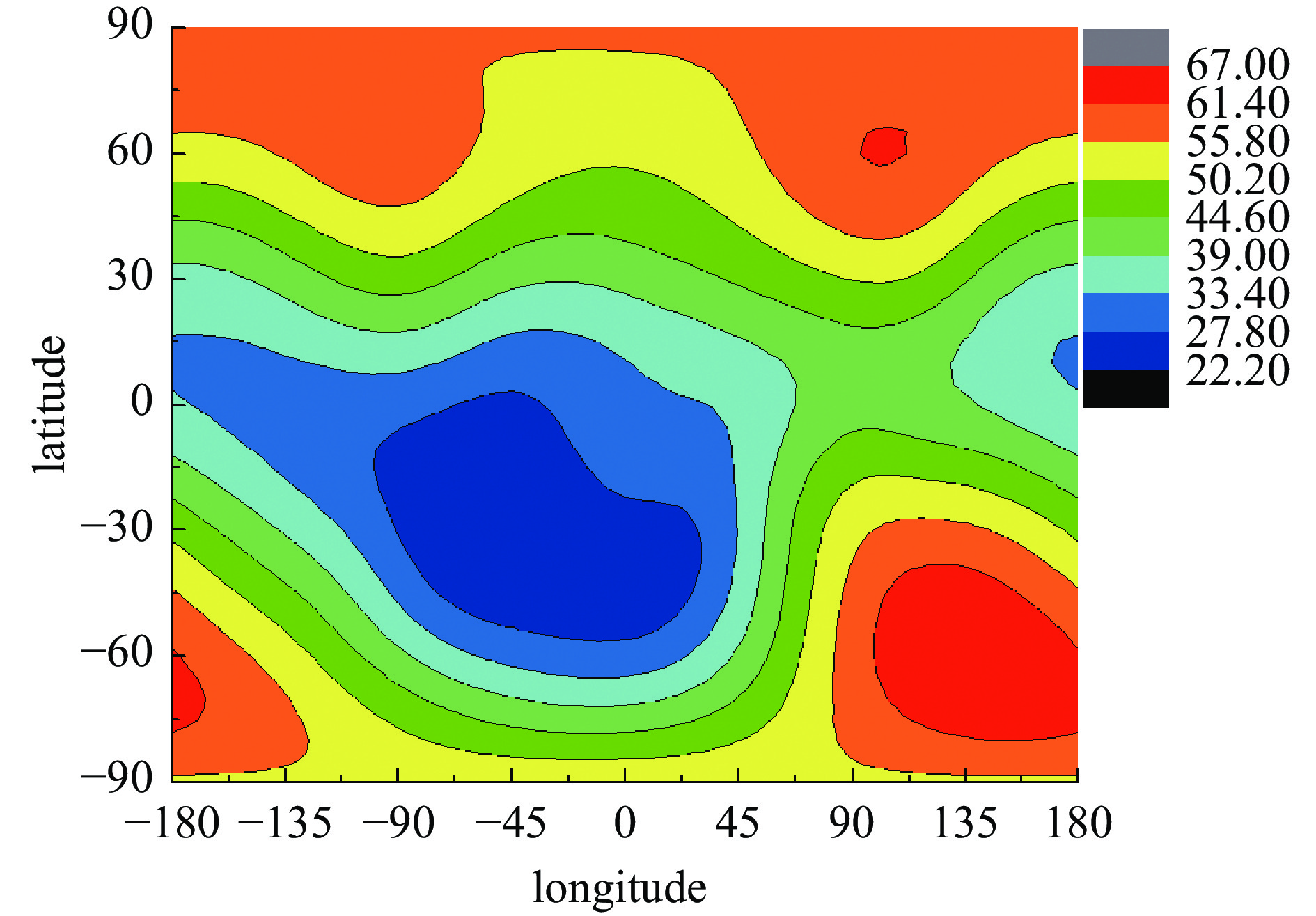
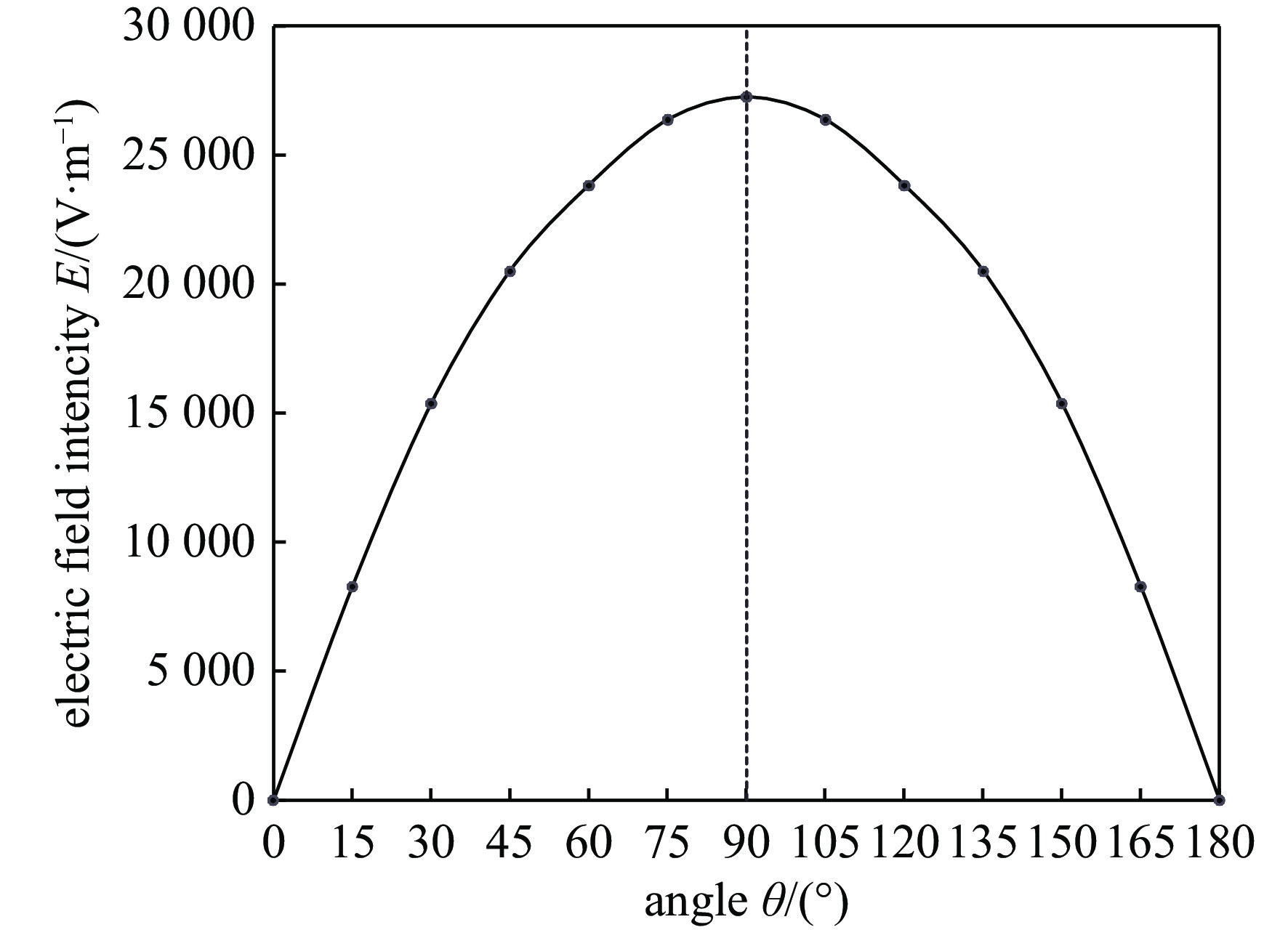
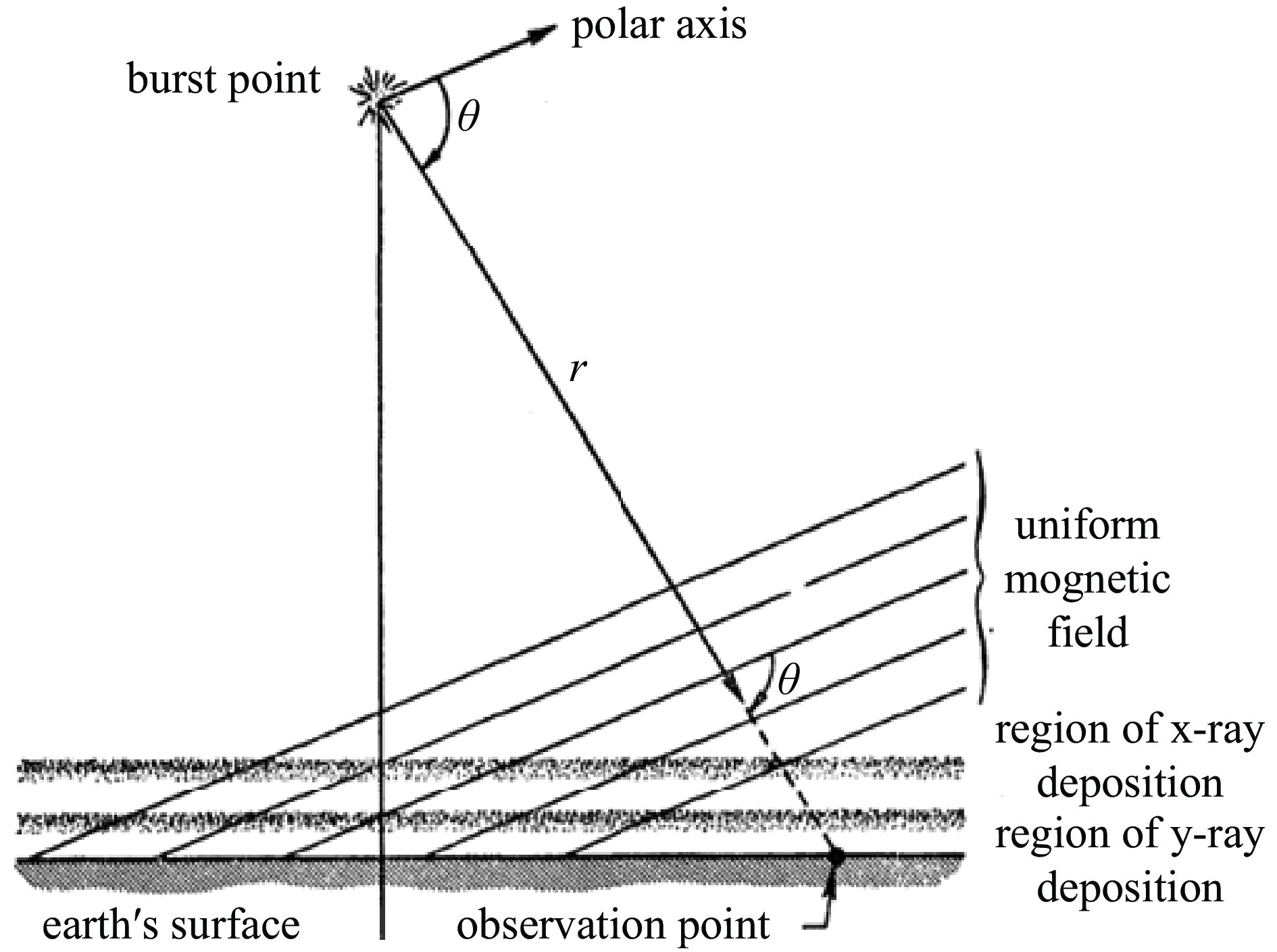
parameters Qf/kt HOB/km Bm /μT θ/(°) r/km E/(V·m−1) minimum 1 30 20 0 0 0 maximum 30000 500 70 180 2443 81751 order of magnitude 104 102 101 102 103 104 -
[1] 王建国, 牛胜利, 张殿辉, 等. 高空核爆炸效应参数手册[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 2010Wang Jianguo, Niu Shengli, Zhang Dianhui, et al. Parameter handbook of high altitude nuclear detonation effect[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 2010 [2] Wang Jianguo, Liu Li, Zuo Yinghong, et al. Research progress in numerical simulation of environmental parameters generated by the high-altitude nuclear explosions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2025, 72(3): 884-900. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2025.3530013 [3] 谢海燕. 系统级HEMP耦合分析方法研究进展[J]. 现代应用物理, 2023, 14: 020102Xie Haiyan. Research progress of system level HEMP coupling analysis methods[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2023, 14: 020102 [4] Karzas W J, Latter R. Detection of the electromagnetic radiation from nuclear explosions in space[J]. Physical Review, 1965, 137: B1369. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.137.B1369 [5] Friedman A, Cohen B I, Eng C D, et al. EMPulse, a new 3-D simulation code for EMP formation and propagation[J]. Journal of Radiation Effects: Research and Engineering, 2015, 61(18): 175-184. [6] 陈剑楠, 张茂钰, 刘利, 等. 结合MCNP的自恰近地面源区电磁脉冲数值模拟方法[J]. 现代应用物理, 2022, 13: 30503Chen Jiannan, Zhang Maoyu, Liu Li, et al. Self-consistent numerical simulation method of near ground source region electromagnetic pulse combined with MCNP[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2022, 13: 30503 [7] Dong Ning, Xie Yanzhao. On the self-consistent simulation of high-altitude electromagnetic pulse[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2022, 69(9): 2074-2082. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2022.3193586 [8] 王锦锦, 程引会, 聂鑫, 等. 基于机器学习的高空电磁脉冲环境快速计算方法[J]. 计算机科学, 2023, 50: 220500046Wang Jinjin, Cheng Yinhui, Nie Xin, et al. Fast calculation method of high-altitude electromagnetic pulse environment based on machine learning[J]. Computer Science, 2023, 50: 220500046 [9] 乔海亮, 谢海燕, 刘钰. 基于人工神经网络的HEMP-E1环境快速预测模型[J]. 现代应用物理, 2025, 16: 011318Qiao Hailiang, Xie Haiyan, Liu Yu. A fast prediction model for HEMP-E1 environment based on artificial neural network[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2025, 16: 011318 [10] Li Ya, Wang Jianguo, Zuo Yinghong, et al. Simulation of high altitude nuclear electromagnetic pulse using a modified model of scattered gamma[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2020, 67(12): 2474-2480. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2020.3031320 [11] 王建国. 核爆炸早中期电磁脉冲产生的数值模拟方法[J]. 电波科学学报, 2024, 39(5): 787-796Wang Jianguo. Numerical simulation method of early-time and intermediate-time electromagnetic pulses generated by nuclear explosions[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2024, 39(5): 787-796 [12] Chulliat A, Brown W, Alken P. The US/UK world magnetic model for 2020-2025[R]. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), 2020. [13] Goodfellow I, Bengio Y, Courville A. Deep learning[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2016. [14] LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436-444. doi: 10.1038/nature14539 [15] Rumelhart D E, Hinton G E, Williams R J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors[J]. Nature, 1986, 323(6088): 533-536. doi: 10.1038/323533a0 [16] 贾怀勤. 应用统计[M]. 北京: 对外经济贸易大学出版社, 2005Jia Huaiqin. Applied statistics[M]. Beijing: University of International Business and Economics Press, 2005 [17] Li Ya, Liu Li, Wang Jianguo, et al. Numerical simulation of the intermediate-time high-altitude electromagnetic pulse[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2022, 64(5): 1423-1430. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2022.3179676 [18] 王建国. 高空核爆炸磁流体动力学电磁脉冲[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2024, 36: 073001Wang Jianguo. Magnetohydrodynamic electromagnetic pulse produced by high altitude nuclear explosion[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2024, 36: 073001 [19] Han Feng, Wang Jianguo, Peng Guoliang, et al. physics-informed multiresolution wavelet neural network method for solving partial differential equations[DB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2508.07546, 2025. -




 下载:
下载: