Irradiation dose rate assessment of CRDM sealing coil in small reactor
-
摘要: 提出了一种小型反应堆控制棒驱动机构(CRDM)密封线圈辐照剂量率的评估方法,阐明了剂量率计算中所考虑的辐射源项与计算模型,并给出了剂量率分析结果。计算表明:小堆正常运行期间CRDM密封线圈处辐照剂量率为4.1 Gy·h−1,主要源自冷却剂中N-16衰变产生的高能γ射线。冷却剂中裂变产物与活化腐蚀产物,以及堆芯裂变中子和γ射线的贡献可忽略。Abstract:
Background In small integrated reactors, the control rod drive mechanism (CRDM) is located within a high-intensity radiation field. The sealing coil of the CRDM may experience performance degradation due to intense irradiation, making accurate dose rate assessment essential for predicting maintenance cycles.Purpose This study aims to evaluate the irradiation dose rate at the CRDM sealing coil in a small reactor during normal operation, identifying the main contributors to the dose rate.Methods Radiation source terms including core fission neutrons and photons, fission and activated corrosion products in the primary coolant, and activation product N-16 were calculated. Computational models were developed using Monte Carlo methods for photon transport and point-kernel integration for dose rate evaluation. Conservative assumptions were applied to coolant density and source distribution.Results The total dose rate at the CRDM sealing coil was found to be 4.1 Gy·h−1. N-16, produced via neutron activation in the coolant, was the dominant contributor, accounting for nearly the entire dose. Contributions from fission products, activated corrosion products, and core fission photons were negligible (less than 1%).Conclusions The irradiation dose rate at the CRDM sealing coil is primarily due to N-16 decay gamma rays, with the majority originating from coolant within a 1.5-meter thick region centered around the dose point. These results provide a basis for predicting coil lifespan and planning replacement intervals.-
Key words:
- sealing coil /
- dose rate assessment /
- N-16 /
- small integrated reactors /
- control rod drive mechanism
-
表 1 堆芯主要参数
Table 1. Main core parameters
thermal power/MWt active core height/cm number of fuel assembly core pressure/MPa coolant average temperature/℃ 200 210 208 8 256 表 2 堆芯不同典型位置的N-16源强
Table 2. N-16 source strength at different core locations
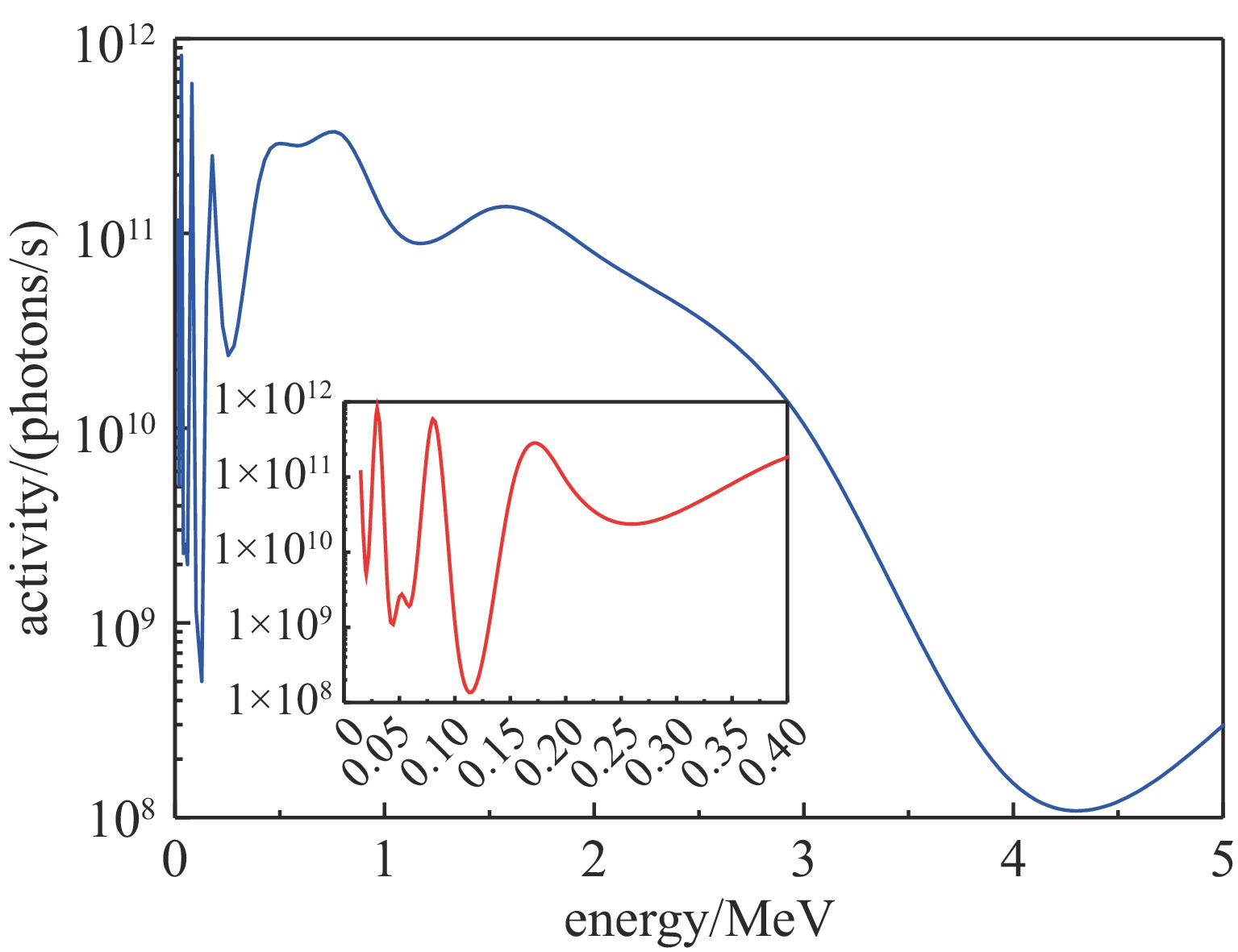
height above core/m coolant transit time/s source strength/(Bq·cm−3) 0.0 0.0 9.7×106 0.5 1.8 8.1×106 1.0 3.5 6.9×106 1.5 5.3 5.8×106 2.0 7.1 4.9×106 2.5 8.8 4.1×106 3.0 10.6 3.5×106 3.5 12.4 2.9×106 4.0 14.1 2.5×106 4.5 15.9 2.1×106 5.0 17.7 1.7×106 5.5 19.4 1.5×106 5.7 20.4 1.3×106 6.0 21.2 1.2×106 6.5 22.9 1.0×106 7.0 24.7 8.7×105 7.5 26.5 7.4×105 表 3 堆芯裂变中光子所致的剂量率
Table 3. Dose rates from fission neutrons and gamma rays in reactor core
No. particle type dose rate/(mGy·h−1) 1 Neutrons ~0.0 2 secondary gamma rays 5.5 3 gamma rays 2.5 total 8.0 表 4 不同位置的N-16源对剂量率的贡献情况
Table 4. Contribution of N-16 sources at different locations to dose rate
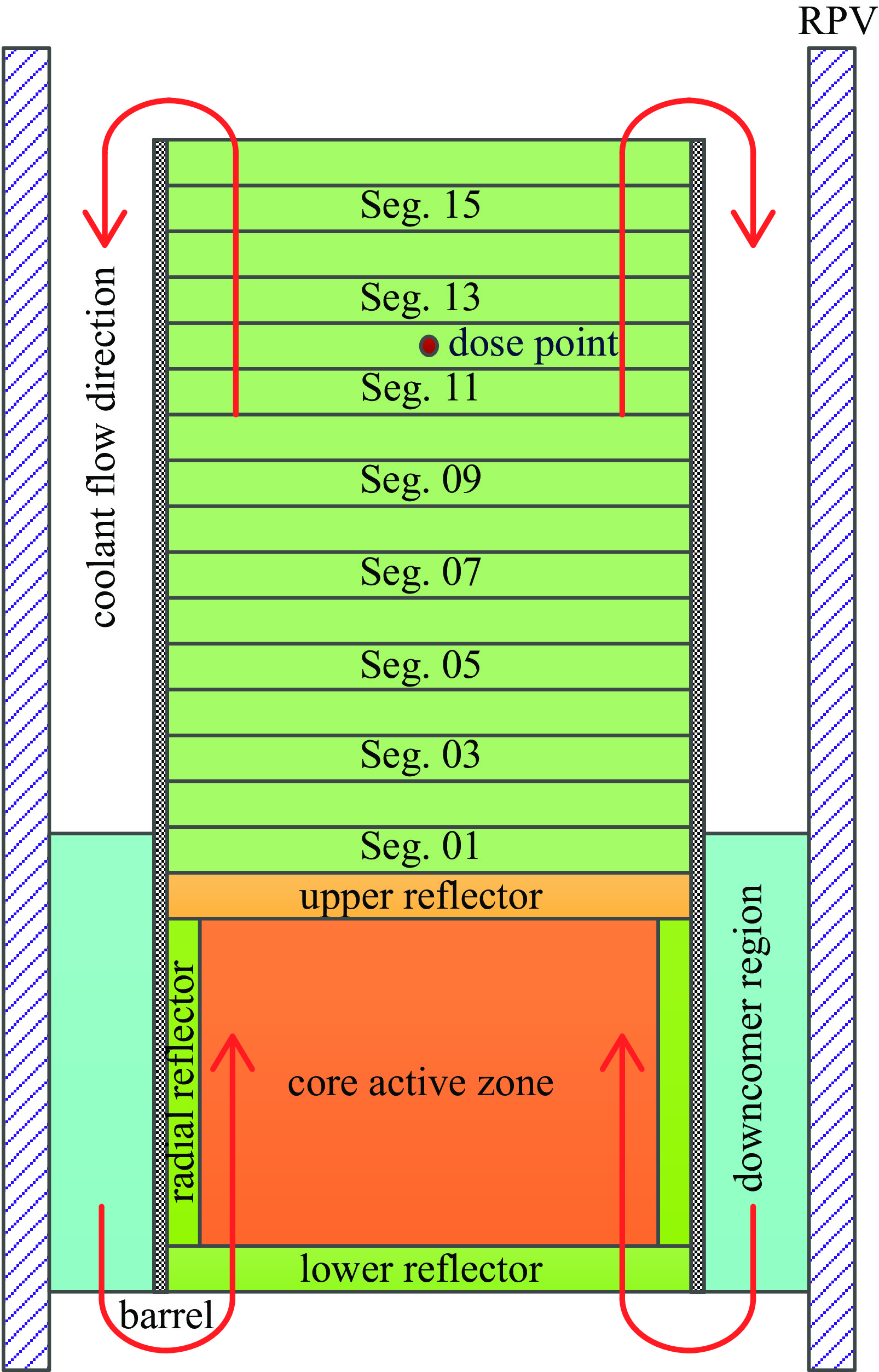
segment No. height region above core/m dose rate/(mGy·h−1) contribution fraction/% Seg. 01 0.0~0.5 1.7×10−2 0.0 Seg. 02 0.5~1.0 4.4×10−2 0.0 Seg. 03 1.0~1.5 1.1×10−1 0.0 Seg. 04 1.5~2.0 3.0×10−1 0.0 Seg. 05 2.0~2.5 8.2×10−1 0.0 Seg. 06 2.5~3.0 2.2×10+0 0.1 Seg. 07 3.0~3.5 6.3×10+0 0.2 Seg. 08 3.5~4.0 1.8×10+1 0.4 Seg. 09 4.0~4.5 5.5×10+1 1.3 Seg. 10 4.5~5.0 1.8×10+2 4.3 Seg. 11 5.0~5.5 6.5×10+2 15.9 Seg. 12 5.5~5.7 1.4×10+3 33.6 Seg. 13 5.7~6.0 1.1×10+3 27.2 Seg. 14 6.0~6.5 5.6×10+2 13.7 Seg. 15 6.5~7.0 1.1×10+2 2.6 Seg. 16 7.0~7.5 2.3×10+1 0.6 / total 4.1×10+3 100 -
[1] 张作义, 张亚军, 贾海军. 低温核供热堆关键技术[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 2023Zhang Zuoyi, Zhang Yajun, Jia Haijun. Key technologies of low-temperature nuclear heating reactors[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University Press, 2023 [2] 谢弗. 核反应堆屏蔽工程学[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 1983Schaeffer N M. Reactor shielding for nuclear engineers[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 1983 [3] 苏耿华, 石秀安, 蔡德昌, 等. 瞬发和缓发γ射线对堆内构件释热率影响的研究[J]. 核科学与工程, 2012, 32(2): 150-155 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0918.2012.02.009Su Genghua, Shi Xiuan, Cai Dechang, et al. Study on the influence of prompt fission γ-ray and delayed γ-ray on reactor internals heating rate[J]. Nuclear Science and Engineering, 2012, 32(2): 150-155 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0918.2012.02.009 [4] 包鹏飞, 苏耿华, 谭世杰. 压水堆内钴靶件的辐射释热率计算[J]. 现代应用物理, 2020, 11: 020203 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2020.020203Bao Pengfei, Su Genghua, Tan Shijie. Calculation of heating rate of cobalt target in pressurized water reactor[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2020, 11: 020203 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2020.020203 [5] 唐邵华, 吕炜枫, 熊军, 等. 主回路裂变产物源项计算程序CPFP的开发[J]. 核动力工程, 2018, 39(4): 33-38Tang Shaohua, Lyu Weifeng, Xiong Jun, et al. Development of calculation code CPFP for fission product in primary loop of pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant[J]. Nuclear Power Engineering, 2018, 39(4): 33-38 [6] 陈志宏. 主回路冷却剂源项计算[R]. 深证中广核工程设计有限公司, 2024Chen Zhihong. Primary loop coolant source term calculation[R]. China Nuclear Power Design Co. , Ltd (Shenzhen), 2024 [7] ANSI/ANS 18.1-2016, Radioactive source term for normal operation of light water reactors[S]. [8] 潘自强, 程建平. 电离辐射防护和辐射源安全[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 2007Pan Ziqiang, Cheng Jianping. Ionizing radiation protection and safety of radiation sources[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 2007 [9] 陈志宏. 主回路N-16源项计算[R]. 深证中广核工程设计有限公司, 2022Chen Zhihong. Primary loop coolant N-16 source term calculation[R]. China Nuclear Power Design Co. , Ltd (Shenzhen), 2022 [10] 韩静茹, 陈义学, 石生春, 等. 基于离散纵标法与蒙特卡罗方法的三维耦合程序开发[J]. 核科学与工程, 2012, 32(2): 160-164 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0918.2012.02.011Han Jingru, Chen Yixue, Shi Shengchun, et al. Development of three dimensional coupled code system based on discrete ordinates and Monte Carlo method[J]. Nuclear Science and Engineering, 2012, 32(2): 160-164 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0918.2012.02.011 [11] 郑征, 王梦琪, 黎辉, 等. 三维离散纵标-蒙特卡罗耦合方法在核电厂堆腔漏束计算中的应用[J]. 计算物理, 2016, 33(5): 599-605 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-246X.2016.05.012Zheng Zheng, Wang Mengqi, Li Hui, et al. 3D discrete ordinates-monte Carlo coupling method for nuclear power plant cavity streaming calculation[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2016, 33(5): 599-605 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-246X.2016.05.012 [12] 黎辉, 王梦琪, 郑征. CAP1400核电厂堆腔辐射漏束屏蔽设计研究[J]. 核科学与工程, 2021, 41(2): 230-235 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0918.2021.02.005Li Hui, Wang Mengqi, Zheng Zheng. The shielding design of cavity radiation streaming for CAP1400 nuclear power plant[J]. Nuclear Science and Engineering, 2021, 41(2): 230-235 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0918.2021.02.005 [13] 黄倩倩, 唐邵华, 杨寿海. MC-MC耦合计算方法在核电厂中子屏蔽设计中的应用[J]. 辐射防护, 2019, 39(4): 309-313Huang Qianqian, Tang Shaohua, Yang Shouhai. Application of MC-MC coupled method in neutron shielding analysis of NPP[J]. Radiation Protection, 2019, 39(4): 309-313 [14] ICRP. Conversion coefficients for radiological protection quantities for external radiation exposures[R]. ICRP, 2010. -




 下载:
下载: