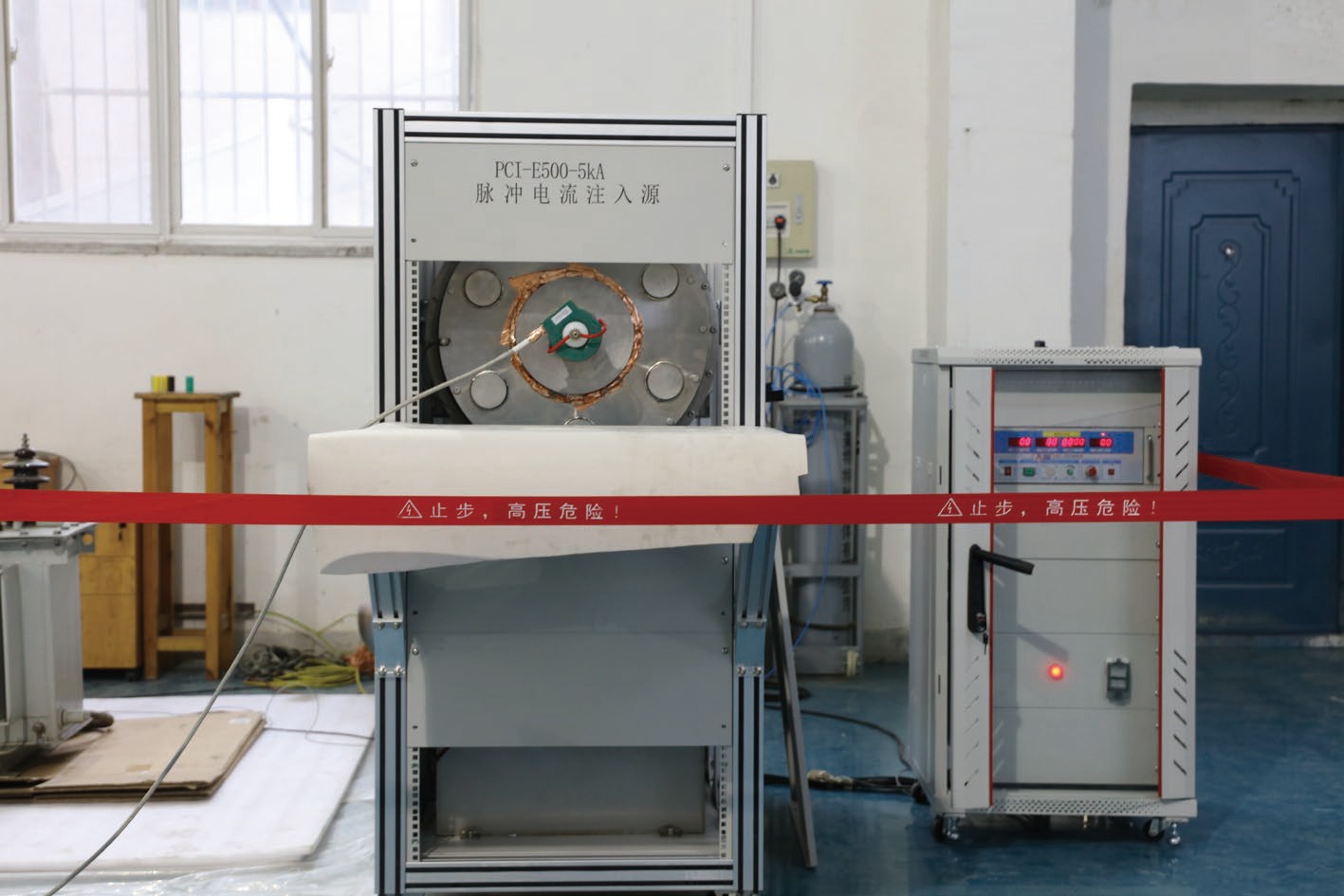
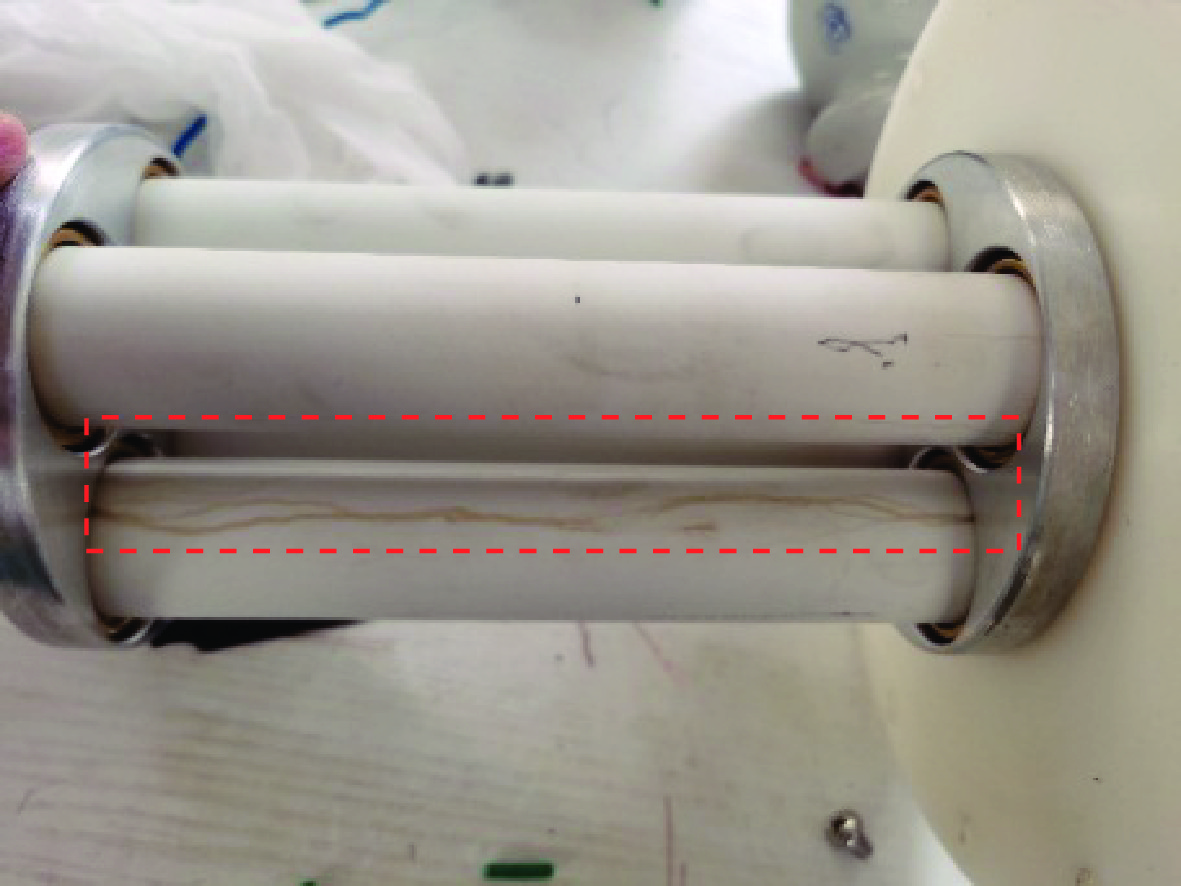
Method and platform design of HEMP interference loading in power equipment under operation state
-
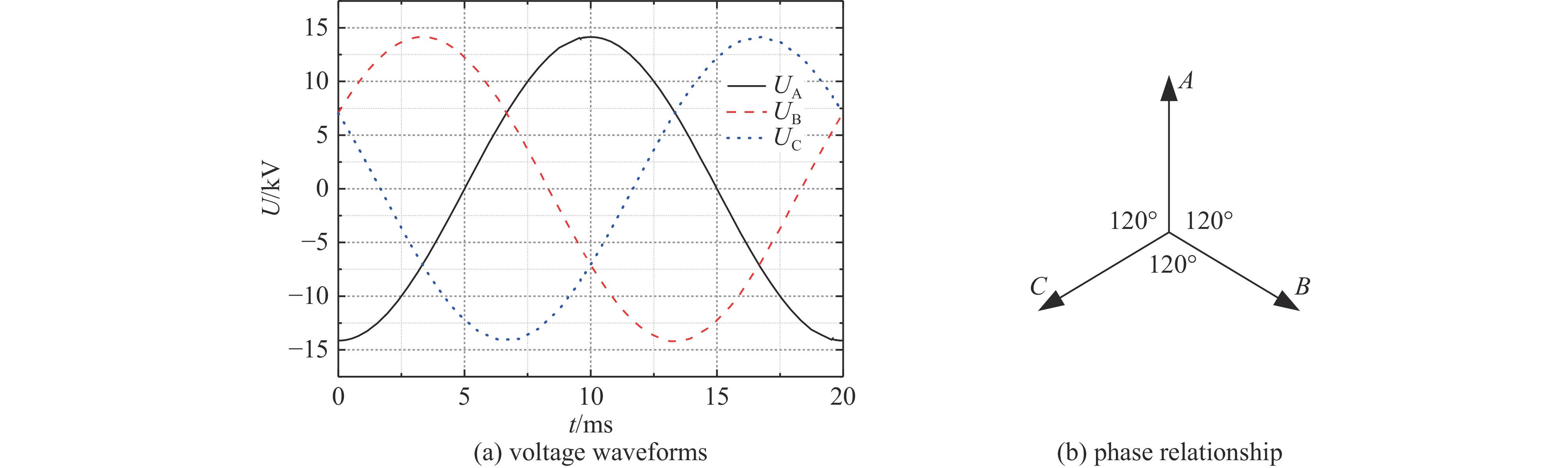
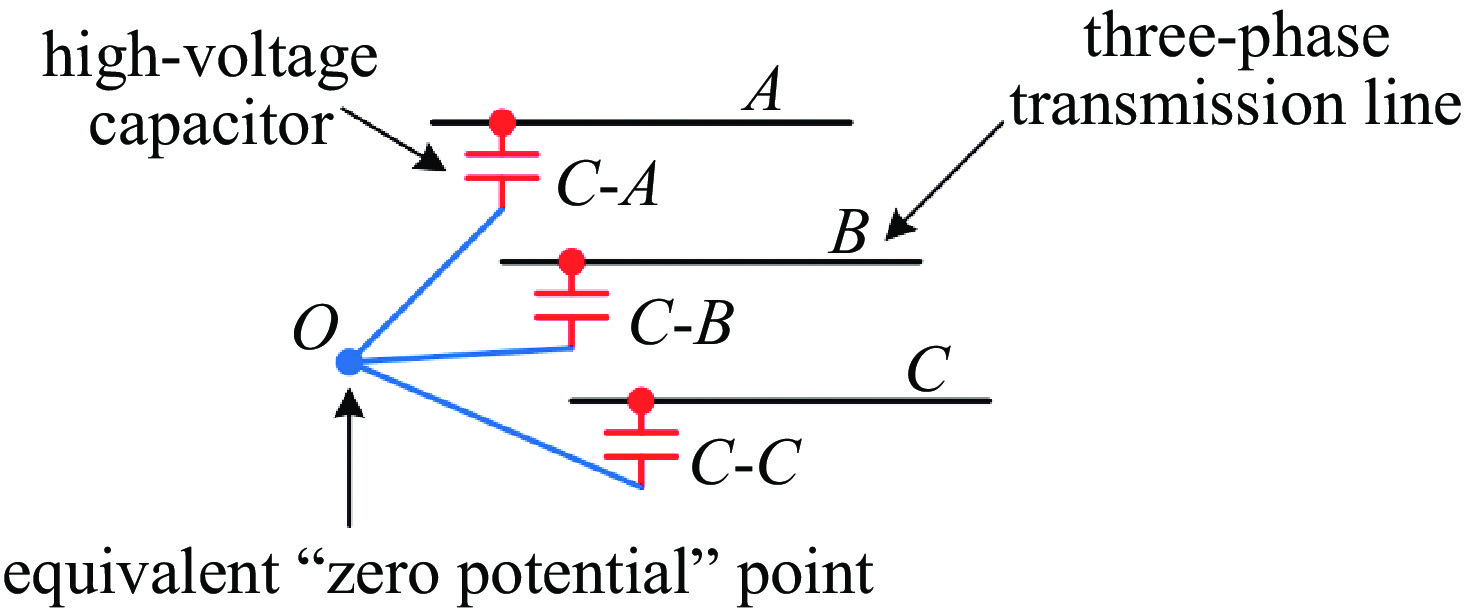
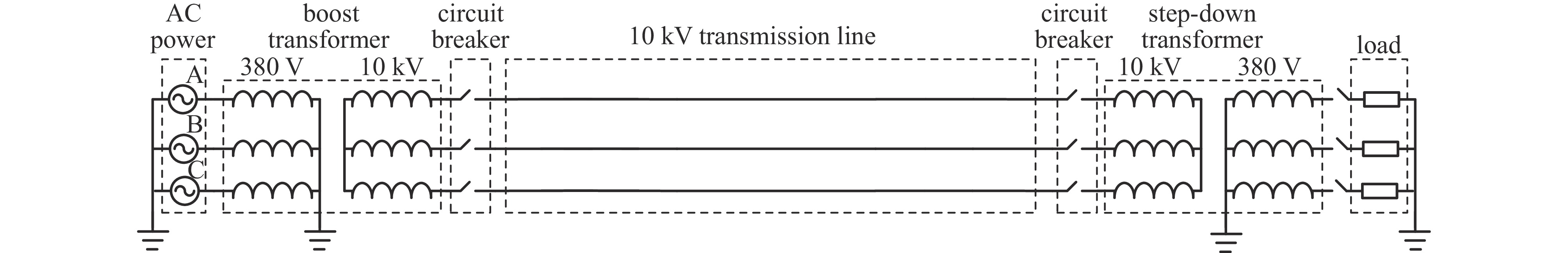
摘要: 电力设备端口特性差异大,注入波形畸变严重,耦合效率低,且其工作电压高,加电状态下开展试验,易引发试验系统故障。目前国内外尚无成熟的电力设备HEMP效应试验方法和试验平台。研究了电力系统与HEMP电流注入试验系统间相互作用的物理过程,提出了基于等效“零电位”的脉冲干扰加载方法,解决了脉冲源内部电路绝缘耐压与功率容量无法承受工频高电压的问题,同时实现了纳秒脉冲在毫秒级工频信号上的相位可控加载与脉冲源输出与电力设备的高效耦合。该方法便于更贴近真实工况下获取待测电力设备的强电磁脉冲效应现象与阈值数据。Abstract:
Background Power equipment ports exhibit significant variations in characteristics, resulting in severe waveform distortion and low coupling efficiency, especially when operating at high voltages. Traditional testing methodologies in powered states present risks of system failures, complicating the evaluation of equipment resilience under such conditions. Notably, there is a lack of established testing methods or platforms for assessing the effects of high-altitude electromagnetic pulse (HEMP) on power equipment, both domestically and internationally.Purpose This study aims to explore the physical interactions between power systems and HEMP current injection test systems, ultimately developing a novel testing method to evaluate the impact of HEMP on power equipment safely and effectively.Methods We propose a pulse disturbance loading method predicated on an equivalent "zero potential," which addresses significant limitations related to insulation withstand voltage and power capacity in existing pulse sources that struggle with power frequency voltages. The method allows for phase-controllable loading of nanosecond pulses onto millisecond-level power frequency signals. This approach enhances the coupling efficiency between the pulse source output and the power equipment, facilitating accurate measurements.Results The implementation of this novel loading method successfully captures strong electromagnetic pulse phenomena and establishes threshold data for power equipment, simulating conditions closely aligned with real operational scenarios. This advancement significantly improves the reliability of test results in understanding equipment behavior under HEMP exposure.Conclusions The developed pulse disturbance loading method offers a promising solution for evaluating the effects of HEMP on power equipment, addressing previously encountered challenges in testing. This research contributes to the establishment of reliable testing protocols for assessing the resilience of power systems against HEMP threats, ultimately enhancing the safety and robustness of critical infrastructure. -
表 1 典型电力设备端口特性
Table 1. Typical power equipment port characteristics
type technical parameters insulator open circuit in normal state; approximate short circuit after flashover or breakdown lightning arrester high resistance in normal state; low resistance after operation, with a nonlinear region transformer and winding distinct high-frequency response characteristics, presence of insulation breakdown;
coupling between three-phase windings表 2 固定监测点主要测量设备
Table 2. Main measuring equipment for fixed monitoring points
number equipment technical parameters 1 voltage divider AC withstand voltage: 400 kV; division ratio: 10000 /1; bandwidth: DC~16 MHz;
minimum measurable rise time: 18.75 ns2 current probe maximum measurable current: 5 kA; sensor coefficient: 0.01; bandwidth: 5 Hz~70 MHz;
minimum measurable rise time: 5ns3 digital oscilloscope channel count: greater than 2 channels; bandwidth: DC~1 GHz; maximum sampling rate: 5 GS/s 表 3 不同电力设备耦合波形FSV评价结果
Table 3. Evaluation results of coupled waveforms FSV for different power equipment
equipment under test transformers/% insulators/% arresters/% cables/% FSV 5.8 1.3 1.7 4.4 -
[1] 毛从光, 程引会, 谢彦召. 高空电磁脉冲技术基础[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019: 1-21Mao Congguang, Cheng Yinhui, Xie Yanzhao. High altitude electromagnetic pulse technology foundation[M]. Beijing, China: Science Press, 2019: 1-21 [2] D. V. 吉里, R. 霍德, F. 萨巴思. 电子系统高功率电磁效应[M]. 毛从光, 杜传报, 秦锋, 译. 北京: 科学出版社, 2022: 20-100Giri D V, Hoad R, Sabath F. High-power electromagnetic effects on electronic systems[M]. Mao Congguang, Du Chuanbao, Qin Feng, Trans. Beijing: Science Press, 2022: 20-100 [3] 秦锋, 陈伟, 毛从光, 等. 电力系统高空电磁脉冲效应研究综述[J]. 现代应用物理, 2023, 14: 030102Qin Feng, Chen Wei, Mao Congguang, et al. Review of high altitude electromagnetic pulse effects on power system[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2023, 14: 030102 [4] Wilson C. High altitude electromagnetic pulse (HEMP) and high power microwave (HPM) devices: threat assessments[R]. RL32544, 2004. [5] 陈宇浩, 谢彦召, 刘民周, 等. 高空电磁脉冲作用下电力系统主要效应模式分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2019, 31: 070007 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.190184Chen Yuhao, Xie Yanzhao, Liu Minzhou, et al. Analysis of high-altitude electromagnetic effect models on power system[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2019, 31: 070007 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.190184 [6] 秦锋, 王旭桐, 陈伟, 等. 高空电磁脉冲作用下配电变压器瞬态响应与失效机理[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43(17): 6924-6932Qin Feng, Wang Xutong, Chen Wei, et al. Transient response and failure mechanism of distribution transformer under high-altitude electromagnetic pulse[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43(17): 6924-6932 [7] 秦锋, 王旭桐, 陈伟, 等. 强电磁脉冲下线路绝缘子闪络特性试验研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023, 38(13): 3640-3650. (Qin Feng, Wang Xutong, Chen Wei, et al. Study on the flashover of line insulators under strong electromagnetic pulses[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2023, 38(13): 3640-3650).Du Chuanbao, Mao Congguang, Cui Zhitong, et al. Vulnerability analysis of very high frequency wireless communication system due to high altitude electromagnetic pulse[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2022, 13: 020505 [8] 樊冉阳, 李斯盟, 秦锋, 等. HEMP损伤作用下油纸绝缘工频局放特性[J]. 现代应用物理, 2024, 15: 061206Fan Ranyang, Li Simeng, Qin Feng, et al. Partial discharge characteristics of oil-paper insulation at working frequency under HEMP impact[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2024, 15: 061206 [9] 秦锋, 陈伟, 王旭桐, 等. 强电磁脉冲下金属氧化物避雷器瞬态响应特性[J]. 高电压技术, 2022, 48(8): 3326-3333Qin Feng, Chen Wei, Wang Xutong, et al. Transient response characteristics of metal oxide arrester under strong electromagnetic pulse[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2022, 48(8): 3326-3333 [10] Cui Zhitong, Grassi F, Pignari S A, et al. Pulsed current injection setup and procedure to reproduce intense transient electromagnetic disturbances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2018, 60(6): 2065-2068. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2017.2789206 [11] 李斯盟, 杨帆, 秦锋, 等. 纳秒脉冲电压下油浸纸局部尖端缺陷击穿特性及损伤规律[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42(14): 5326-5337Li Simeng, Yang Fan, Qin Feng, et al. Breakdown characteristics and damage law of localized tip defect on oil-immersed paper under nanosecond pulse voltage[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42(14): 5326-5337 [12] Savage E, Gilbert J, Radasky W. The early-time (E1) high-altitude electromagnetic pulse (HEMP) and its impact on the U. S. power grid[R]. Meta-R-320, 2010. [13] 秦锋. 早期高空电磁脉冲作用下油浸式配电变压器效应与失效机理[D]. 西安: 西北核技术研究所, 2024: 6Qin Feng. Effects and failure mechanisms of oil-immersed distribution transformers under early-time high-altitude electromagnetic pulse[D]. Xi’an: Northwest Institute of Nuclear Technology, 2024: 6 [14] 何金良, 赵伟. 现代电气工程师实用手册[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2014: 102-150He Jinliang, Zhao Wei. Practical handbook for modern electrical engineers[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2014: 102-150 [15] Tesche F M, Barnes P R. The HEMP response of an overhead power distribution line[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 1989, 4(3): 1937-1944. doi: 10.1109/61.32693 [16] 马良, 程引会, 郭景海. 高空电磁脉冲标准波形参数的时域确定方法[J]. 现代应用物理, 2022, 13: 020503 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2022.020503Ma Liang, Cheng Yinhui, Guo Jinghai, et al. Time domain method for determining standard waveform parameters of high altitude electromagnetic pulse[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2022, 13: 020503 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2022.020503 [17] IEC 61000-2-10, Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)-part 2-10: environment-description of hemp environment- conducted disturbance[S]. [18] 刘政, 黑东炜, 毛从光, 等. 架空线缆高空电磁脉冲传导环境参数的计算与分析[J]. 现代应用物理, 2021, 12: 020504Liu Zheng, Hei Dongwei, Mao Congguang, et al. Calculation and analysis of conducted parameters of elevated lines under high-altitude electromagnetic pulse[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2021, 12: 020504 [19] Shi Lihua, Zhang Xiang, Sun Zheng, et al. An overview of the HEMP research in China[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2013, 55(3): 422-430. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2013.2242080 [20] 崔志同, 陈伟, 董亚运, 等. GJB151B CS115的电路仿真分析(一)——校准设备指标需求分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2022, 34: 023002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.210406Cui Zhitong, Chen Wei, Dong Yayun, et al. Circuit Simulation of GJB151B CS115 part I: the analysis of calibration equipment indicators[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2022, 34: 023002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.210406 [21] 崔志同. HEMP脉冲电流注入的仿真与实验研究[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2020: 6Cui Zhitong. Simulation and experimental research on HEMP pulsed current injection[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2020: 6 [22] Wang Jianguo, Liu Li, Zuo Yinghong, et al. Research progress in numerical simulation of environmental parameters generated by the high-altitude nuclear explosions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2025, 72(3): 884-900. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2025.3530013 [23] Li Ya, Liu Li, Wang Jianguo, et al. Numerical simulation of the intermediate-time high-altitude electromagnetic pulse[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2022, 64(5): 1423-1430. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2022.3179676 [24] 王建国. 高空核爆炸磁流体动力学电磁脉冲[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2024, 36: 073001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.240105Wang Jianguo. Magnetohydrodynamic electromagnetic pulse produced by high altitude nuclear explosion[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2024, 36: 073001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.240105 [25] Xie Haiyan, Wang Jianguo. Research progress in computational methods for system-level coupling of electromagnetic pulse[J]. IEEE Access, 2025, 13: 22259-22269. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3536787 [26] Xie Haiyan, Li Yong, Qiao Hailiang, et al. Empirical formula of effective coupling length for transmission lines illuminated by E1 HEMP[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2016, 58(2): 581-587. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2016.2518243 [27] Xie Haiyan, Wang Jianguo, Fan Ruyu, et al. A hybrid FDTD-SPICE method for transmission lines excited by a nonuniform incident wave[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2009, 51(3): 811-817. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2009.2020913 -




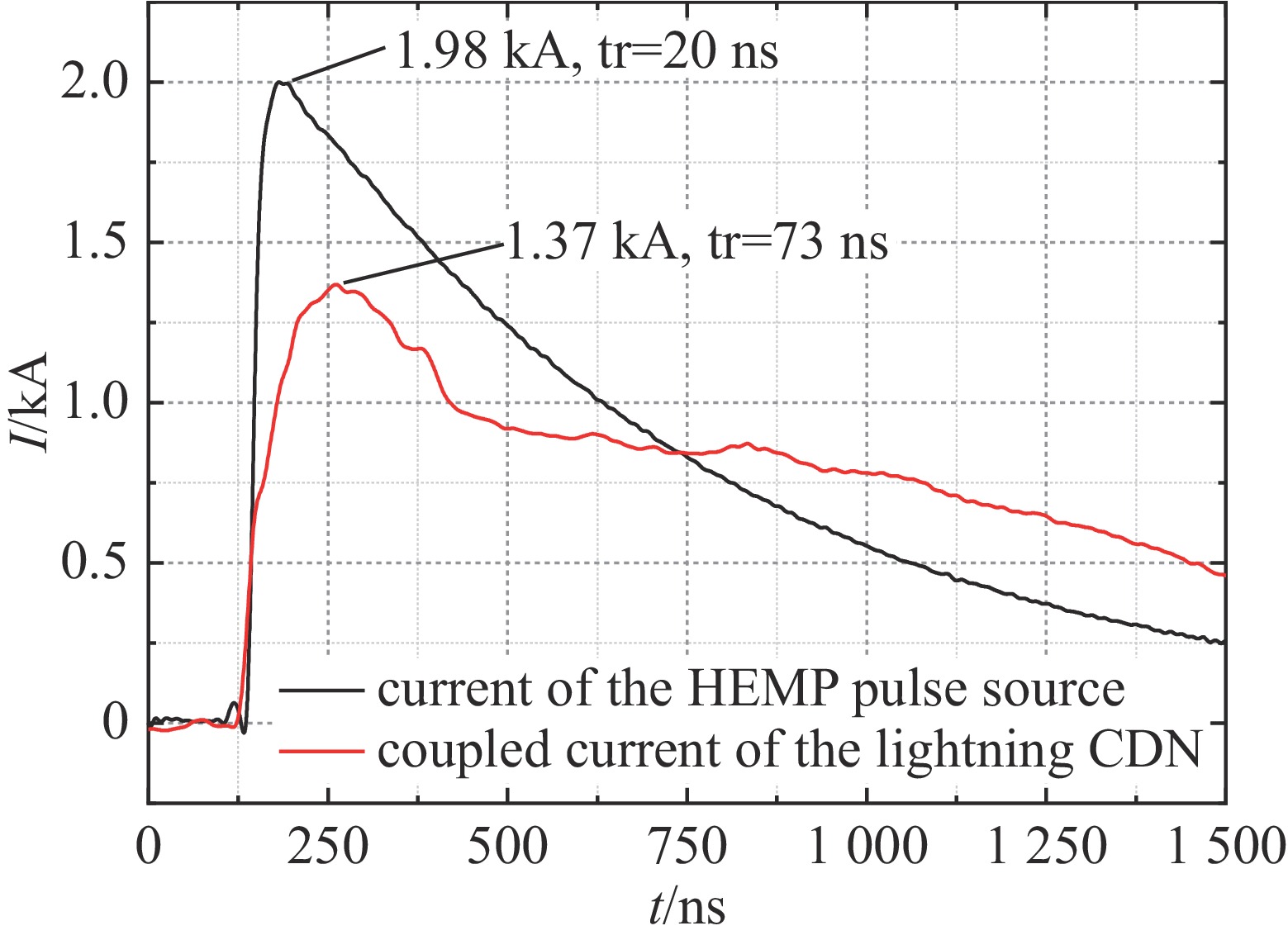
 下载:
下载: