Intelligent algorithm for predicting light radiation damage areas and inverting source parameters in nuclear explosion
-
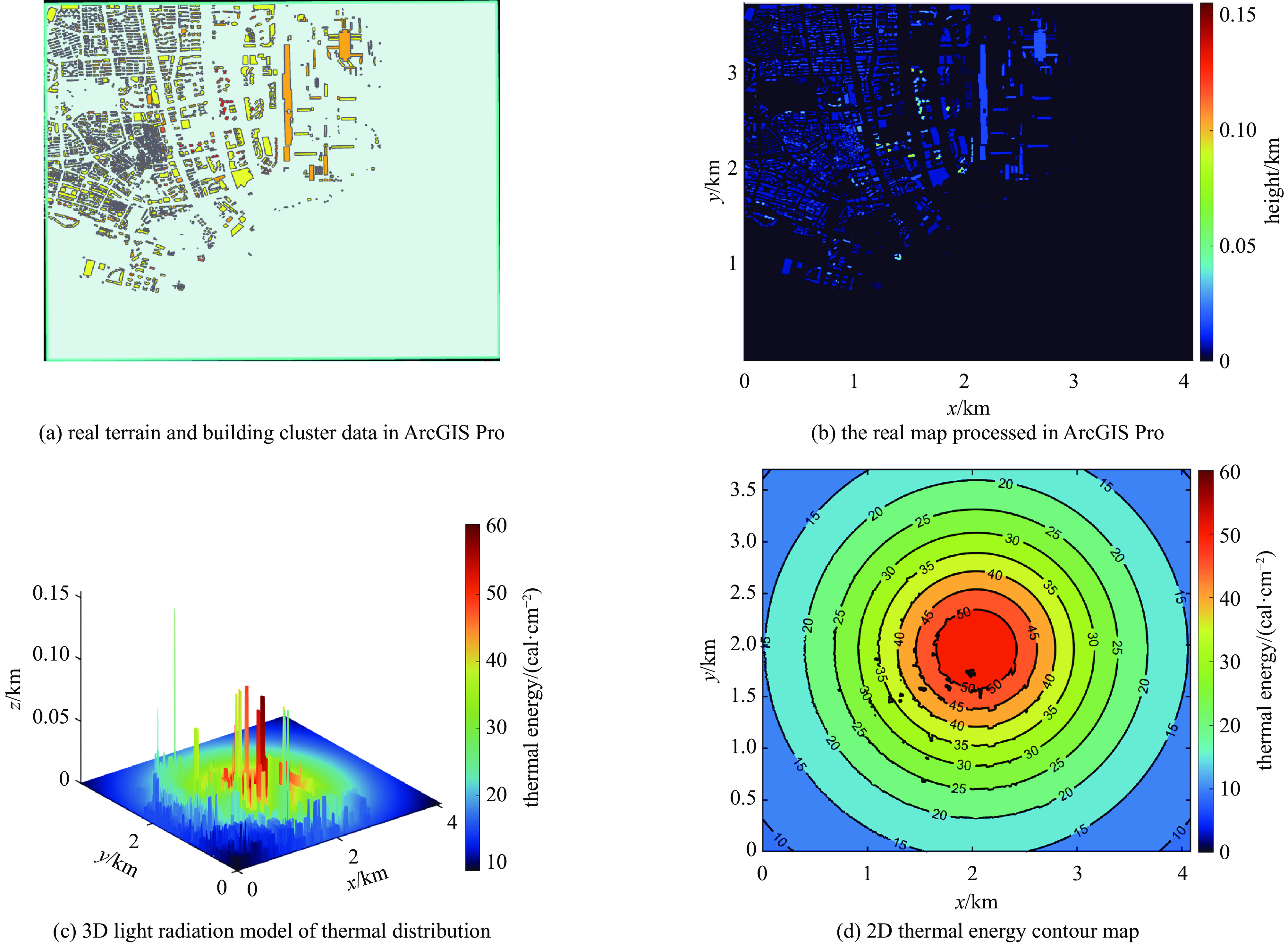
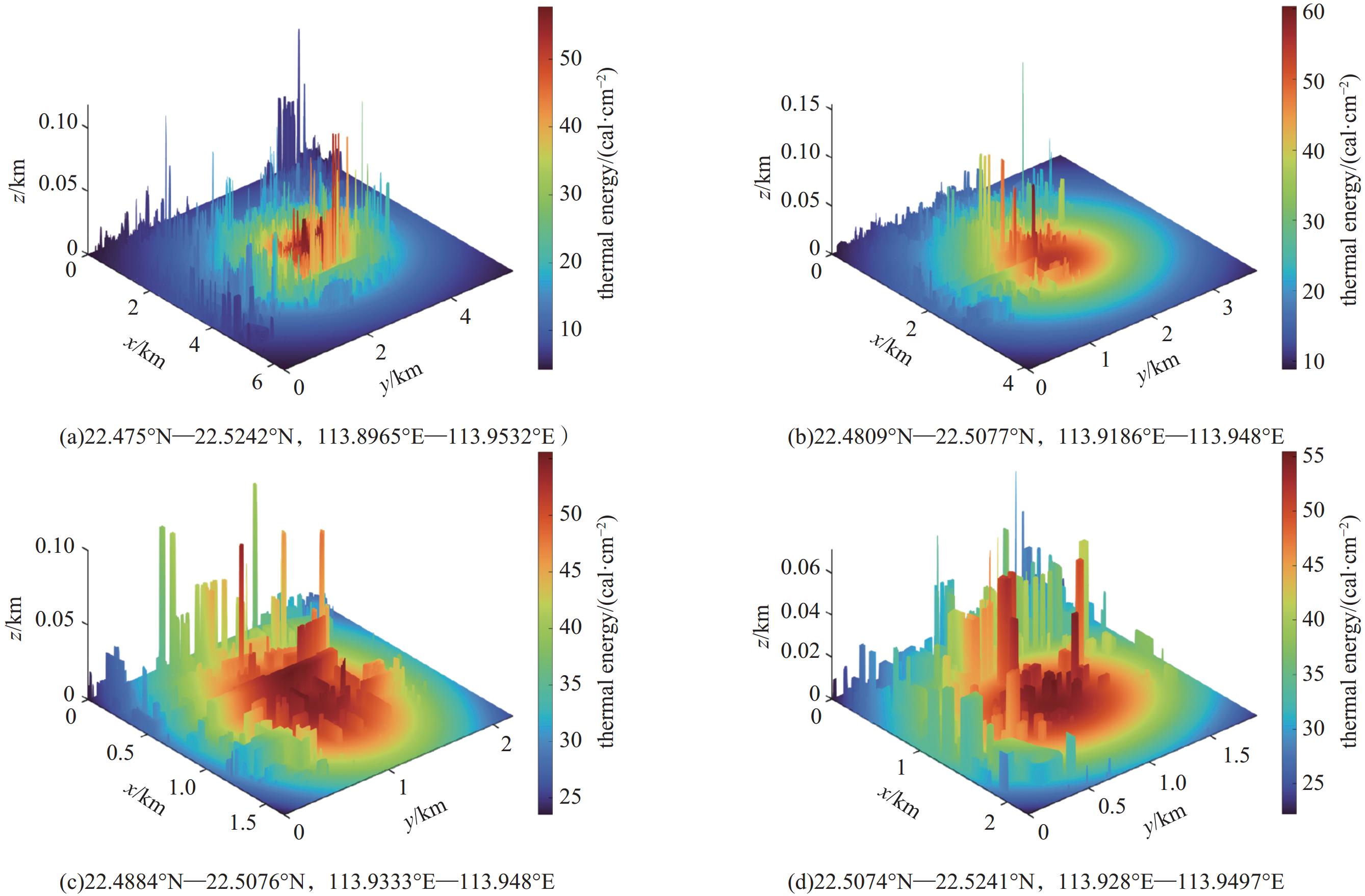
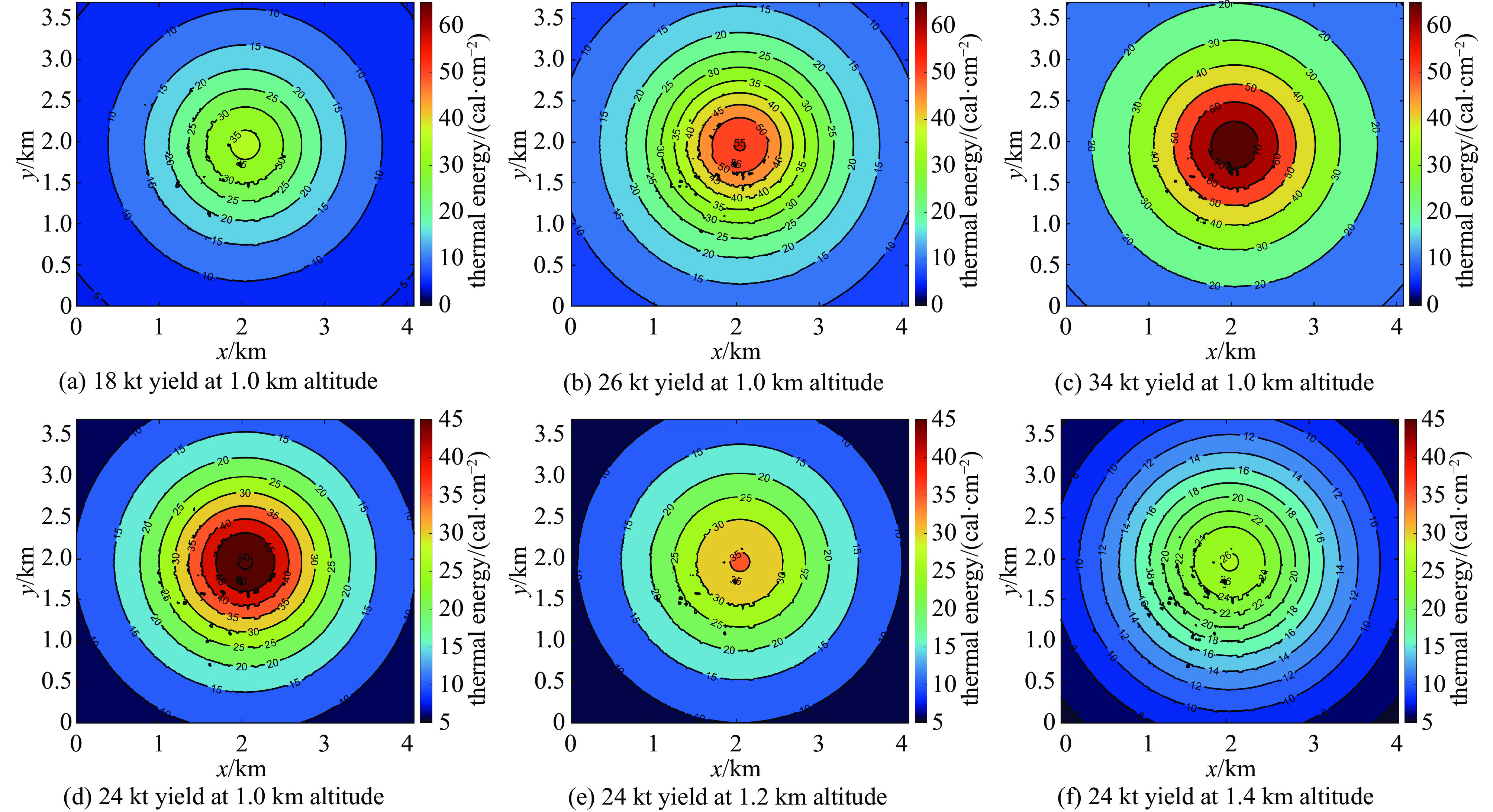
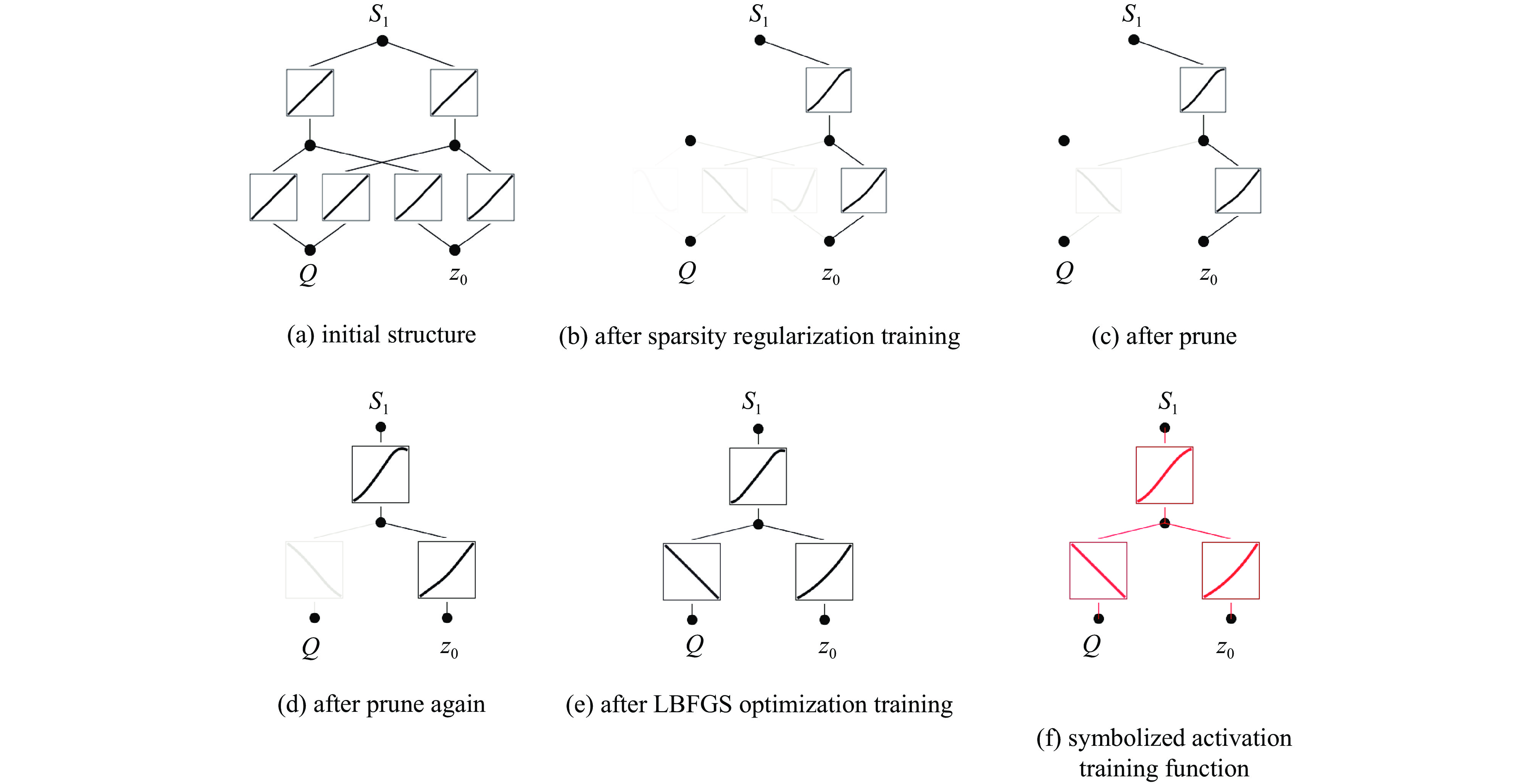
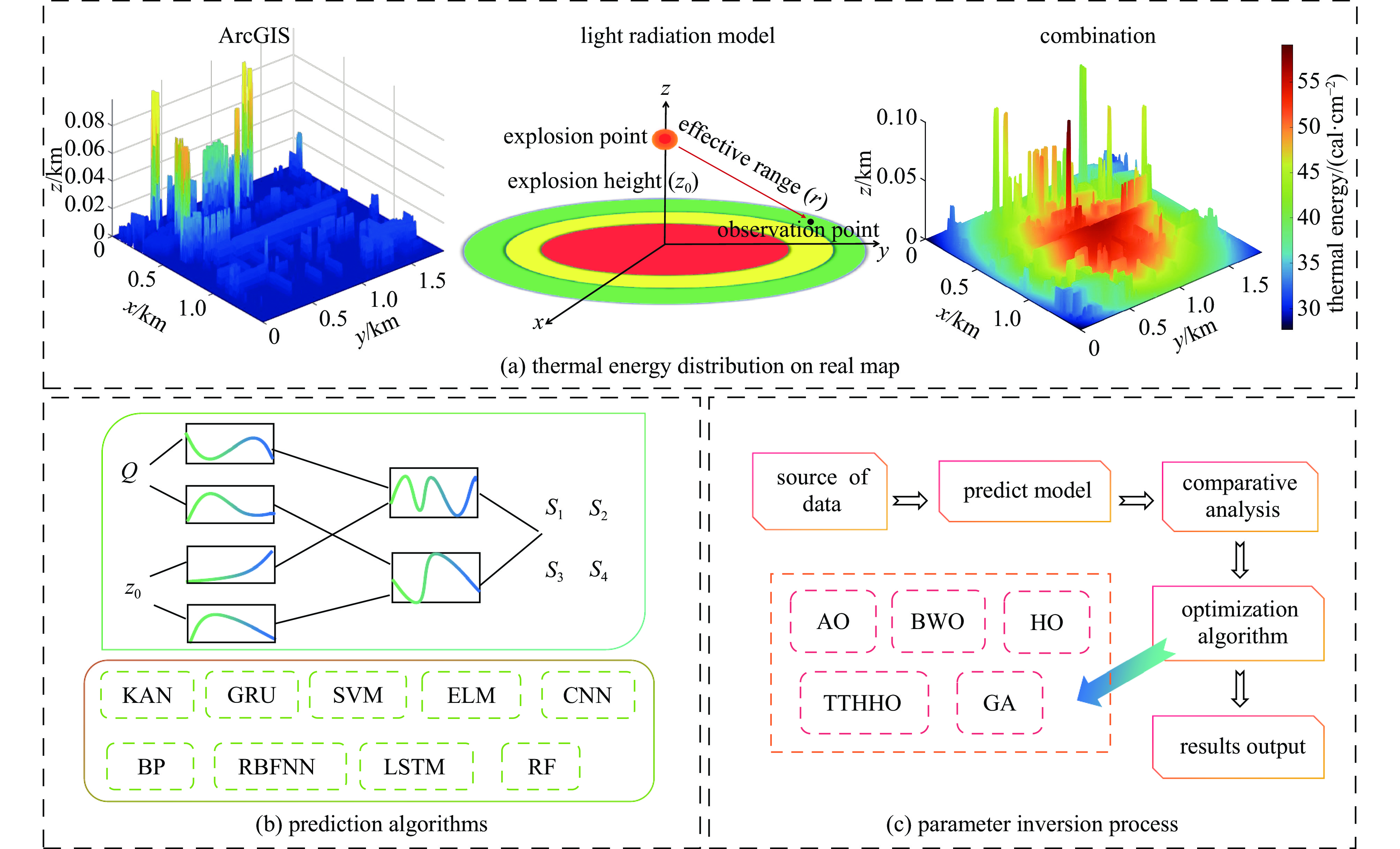
摘要: 光辐射是核爆炸能量耗散的主要形式,对生态环境和人类社会具有深远影响。研究其特性、传播规律和能量分布,可为核爆炸毁伤效应评估与防护提供重要依据。引入Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KAN),构建了可解释的核爆炸光辐射损伤面积预测模型,同时采用多种优化算法反演出核爆炸的源项参数。首先,基于核爆炸火球理论构建光辐射模型,结合ArcGIS Pro软件实现真实地图下光辐射的热能分布,并根据生物的烧伤伤情分级标准生成爆炸当量、爆炸高度与损伤面积之间的数据集。其次,利用KAN网络进行数据集预测,凭借其独特的可解释性优势获得显式预测公式。再次,采用门控循环单元、极限学习机和随机森林等8种算法对比预测结果,评估KAN的性能。最后,构建核爆炸光辐射模型损失函数,通过多种优化算法获得爆炸当量、爆炸高度和爆心位置等源项信息。本研究实现了对核爆炸光辐射损伤效应的快速预测和精准反演,有助于提高应急响应效率并辅助防护决策。
-
关键词:
- 光辐射 /
- ArcGIS Pro /
- Kolmogorov-Arnold网络 /
- 参数反演 /
- 机器学习
Abstract:Background Light radiation, the primary mode of energy dissipation in nuclear explosions, profoundly impacts both the ecological environment and human society. A thorough understanding of its characteristics, propagation dynamics, and energy distribution is therefore essential for evaluating and protecting against nuclear explosion damage effects.Purpose This study introduces the Kolmogorov-Arnold network (KAN) to construct an interpretable model for predicting the area of light radiation damage. The model utilizes multiple optimization algorithms to invert key source term parameters, namely the explosion yield, height of explosion, and explosion location.Methods Based on the theory of nuclear explosion fireballs, a light radiation model was developed and integrated with ArcGIS Pro software to visualize thermal energy distribution on real-world maps. A dataset correlating explosion yield and height with damage area was then generated, quantified according to established standards for biological burn injuries. The KAN was trained on this dataset, leveraging its unique advantage of providing explicit, interpretable formulas for prediction. To validate its efficacy, the KAN's performance was benchmarked against eight other algorithms, including Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU), Extreme Learning Machine (ELM), and Random Forest (RF). A loss function was constructed for the radiation model to facilitate the inversion of source term parameters via multiple optimization algorithms.Results The results demonstrate that the KAN model achieves high prediction accuracy while yielding an interpretable formula for the damage area. Furthermore, both the genetic algorithm and the Hippopotamus optimization algorithm successfully inverted the nuclear source term parameters with high fidelity.Conclusions This methodology facilitates both the rapid prediction of damage effects and the accurate inversion of source parameters, thereby enhancing emergency response efficiency and aiding in strategic protective decision-making.-
Key words:
- light radiation /
- ArcGIS Pro /
- Kolmogorov-Arnold network /
- parameter inversion /
- machine learning
-
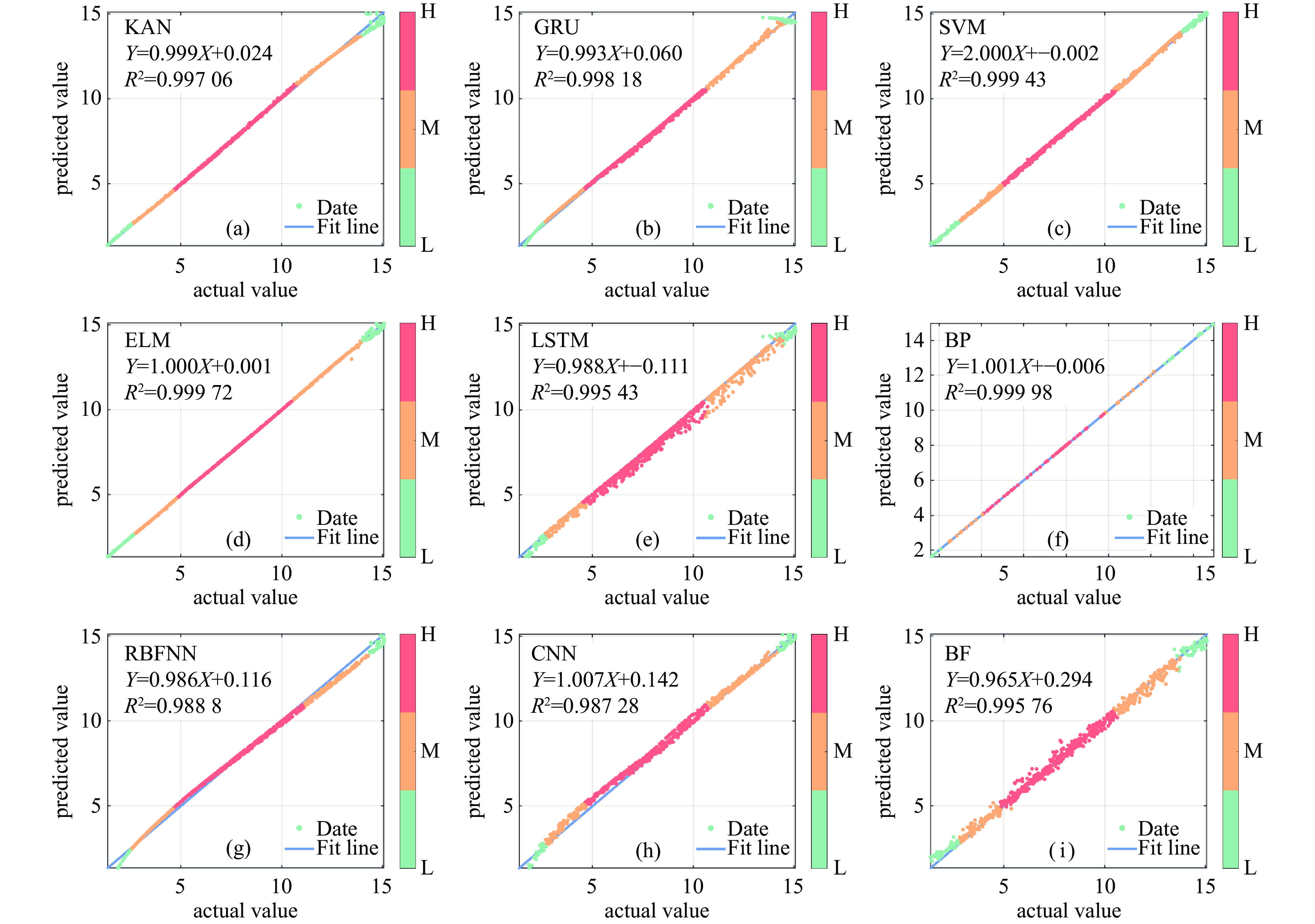
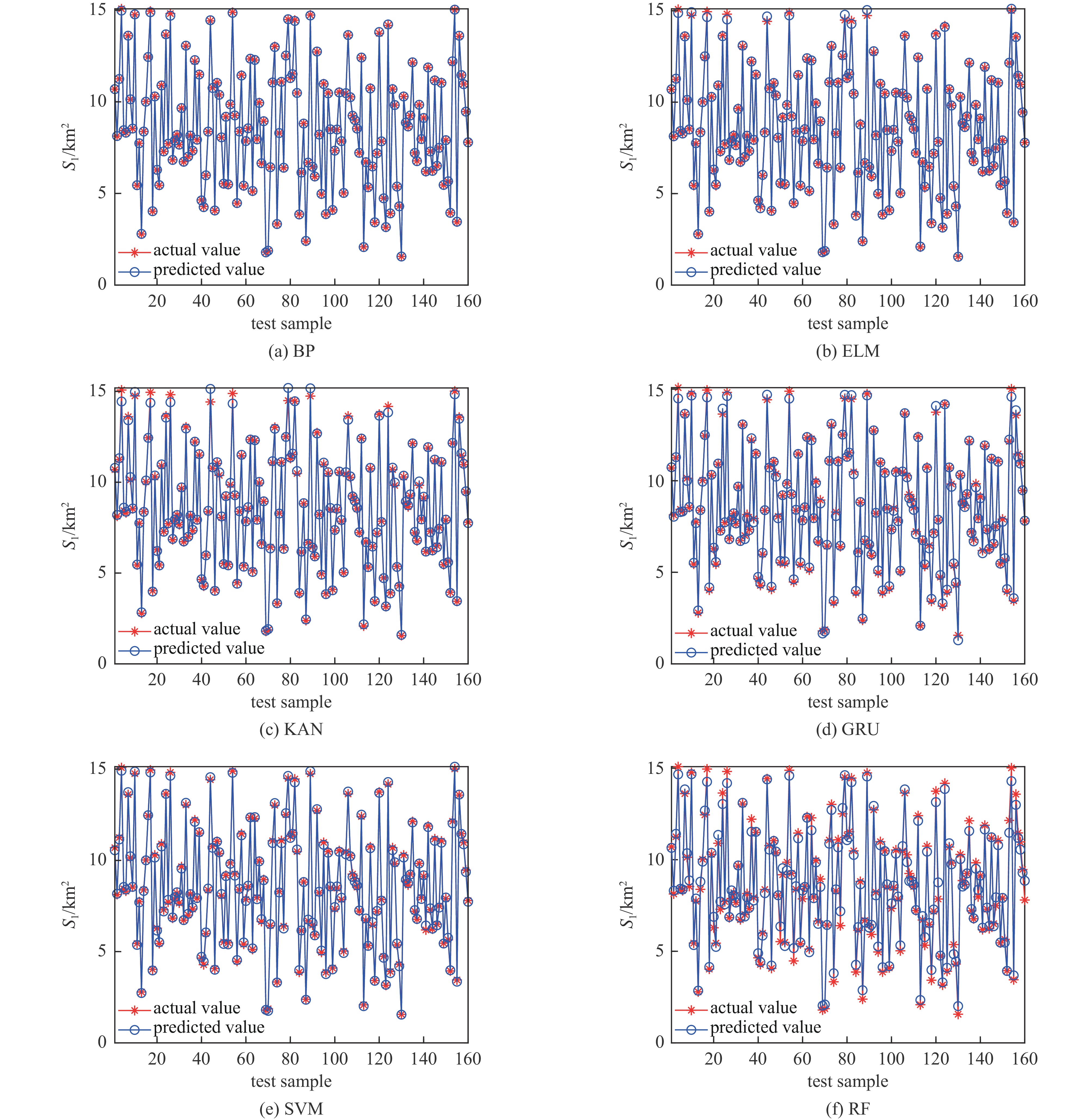
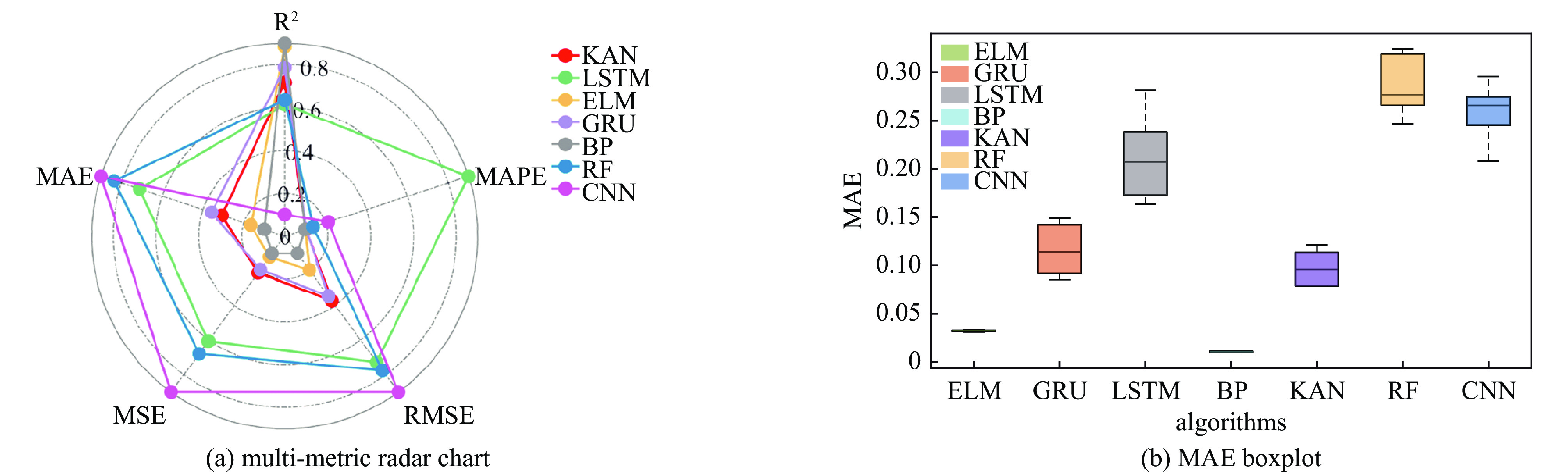
表 1 不同机器学习模型对轻度损伤面积分布预测指标
Table 1. Performance metrics of machine learning models for mild burn area distribution prediction
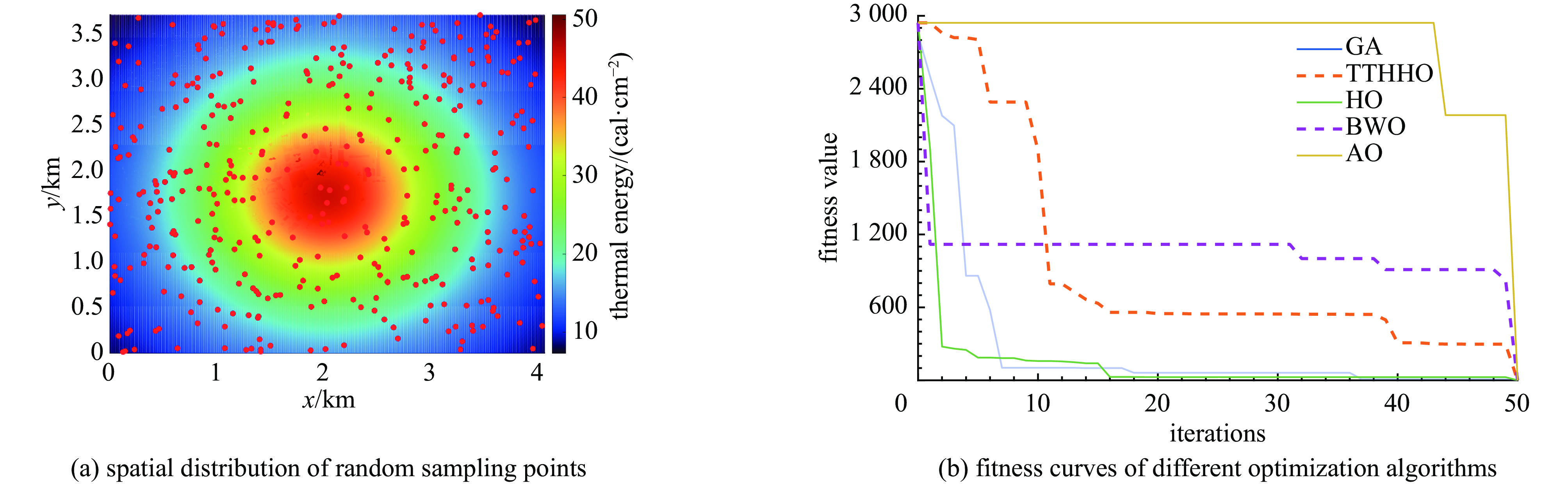
prediction algorithm MAE MSE RMSE MAPE KAN 0.078509 0.020217 0.14219 0.0011629 GRU 0.094142 0.017032 0.13051 0.0016689 SVM 0.080676 0.0084754 0.092062 0.0108 ELM 0.032639 0.0040316 0.063495 0.00024225 LSTM 0.20743 0.090121 0.3002 0.33317 BP 0.01153 0.00042322 0.020572 2.3645E-06 RBFNN 0.21585 0.084455 0.29061 0.0046114 CNN 0.2678 0.14225 0.37716 0.047087 RF 0.24701 0.1031 0.32109 0.016381 表 2 不同优化算法反演的爆炸源项参数
Table 2. Inverted explosion source parameters by different optimization algorithms
optimization
algorithmsnuclear explosion
yield Q/ktnuclear explosion
height z0/kmx-axis coordinate of
explosion point/kmy-axis coordinate of
explosion point/kmReal 30 1.2 2.0396 1.7349 AO 36.5698 1.4291 2.0681 1.8919 BWO 25.6759 1.05075 2.02041 1.74864 HO 30.7551 1.2296 2.0309 1.7362 TTHHO 32.691 1.30716 2.01174 1.72705 GA 30.50 1.22 2.04 1.74 -
[1] Batcher R T. The consequences of an Indo-Pakistani nuclear war[J]. International Studies Review, 2004, 6(4): 135-162. doi: 10.1111/j.1521-9488.2004.00453.x [2] Marrs R E, Moss W C, Whitlock B. Thermal radiation from nuclear detonations in urban environments[R]. Livermore: Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), 2007. [3] 王建国, 牛胜利, 张殿辉, 等. 高空核爆炸效应参数手册[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 2010Wang Jianguo, Niu Shengli, Zhang Dianhui, et al. The parameter manual book of high-altitude nuclear explosion effects[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 2010 [4] Jung H, Shim W. Calculation of thermal fluence from extremely high-energy emission in air[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2015, 62(3): 1395-1398. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2015.2421891 [5] Abdil-Hasan J. Analysis of thermal energy distribution from low yield nuclear explosions[J]. Modern Applied Science, 2017, 11(8): 1-6. doi: 10.5539/mas.v11n8p1 [6] Brode H L. Fireball phenomenology[M]. Santa Monica: The Rand Corporation, 1964: 1-46. [7] Brode H L, Hillendahl R W, Landshoff R K. Thermal radiation phenomena. volume 5: radiation hydrodynamics of high temperature air[R]. Sunnyvale: The Lockheed Missiles and Space Company, 1967: 1-81. [8] Hoerlin H. United States high-altitude test experiences[R]. Los Alamos: Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory, 1976: LA-6405. [9] Hoerlin H. Artificial aurora and upper atmospheric shock produced by teak[R]. Los Alamos: Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory, 1961. [10] Glasstone S. The effects of nuclear weapons[M]. Washington: Atomic Energy Commission, 1962: 1-100. [11] Bethe H A. Theory of the fireball[R]. Los Alamos: Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL), 1964. [12] Bethe H A. The fireball in air[J]. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 1965, 5(1): 9-12. doi: 10.1016/0022-4073(65)90027-0 [13] Peery T, Walli K. Physical modeling of nuclear detonations in dirsig[C]//2013 IEEE Applied Imagery Pattern Recognition Workshop (AIPR). 2013: 1-12. [14] 乔登江. 核爆炸火球物理[J]. 物理学进展, 1983, 3(2): 236-267 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0542.1983.02.004Qiao Dengjiang. The physics of fireball[J]. Progress in Physics., 1983, 3(2): 236-267 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0542.1983.02.004 [15] 乔登江. 核爆炸物理概论[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 1988: 1-201Qiao Dengjiang. Introduction to nuclear explosion physics[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 1988: 1-201 [16] 陈健华, 王心正, 谢龙生, 等. 均匀大气中的强爆炸一维辐射流体力学数值解[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 1981, 1(2): 37-49 doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(1981)02-0037-13Chen Jianhua, Wang Xinzheng, Xie Longsheng, et al. An one-dimensional radiation hydrodynamic numerical solution for a strong explosion in uniform atmosphere[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 1981, 1(2): 37-49 doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(1981)02-0037-13 [17] Wang Jianguo, Liu Li, Zuo Yinghong, et al. Research progress in numerical simulation of environmental parameters generated by the high-altitude nuclear explosions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2025, 72(3): 884-900. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2025.3530013 [18] 吴健辉, 杨坤涛, 张南洋生. 核爆炸光辐射探测系统分析[J]. 光电工程, 2008, 35(9): 45-49 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2008.09.010Wu Jianhui, Yang Kuntao, Zhang Nanyangsheng. Analysis of the ray radiation detection system for nuclear explosion[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2008, 35(9): 45-49 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2008.09.010 [19] 吴健辉. 核爆炸光辐射特性及探测技术的理论与实验研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2009Wu Jianhui. Study on theory and experiment of the characteristics and detection technology of nuclear explosion radiation[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2009 [20] 张欣, 王博宇, 李君, 等. 核爆炸光热辐射研究进展[J]. 现代应用物理, 2025, 16: 020101Zhang Xin, Wang Boyu, Li Jun, et al. Research progress of nuclear explosion photo thermal radiation[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2025, 16: 020101 [21] 王学栋, 朱金辉, 左应红, 等. 复杂地形对核爆炸瞬发中子辐射场的影响[J]. 现代应用物理, 2023, 14: 030202Wang Xuedong, Zhu Jinhui, Zuo Yinghong, et al. Influence of complex terrain on prompt neutron radiation field of nuclear detonation[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2023, 14: 030202 [22] Xiong Chen, Li Qiangsheng, Lu Xinzheng. Automated regional seismic damage assessment of buildings using an unmanned aerial vehicle and a convolutional neural network[J]. Automation in Construction, 2020, 109: 102994. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2019.102994 [23] Wang Yixing, Yue Qingrui, Lu Xinzheng, et al. Digital twin approach for enhancing urban resilience: a cycle between virtual space and the real world[J]. Resilient Cities and Structures, 2024, 3(2): 34-45. doi: 10.1016/j.rcns.2024.06.002 [24] 许鹏, 刘梦雅, 范新峰, 等. 人工智能算法在核应急中的应用综述[J]. 火箭军工程大学学报, 2024, 38(3): 104-110Xu Peng, Liu Mengya, Fan Xinfeng, et al. Overview of application of artificial intelligence algorithms in nuclear emergency[J]. Journal of Rocket Force University of Engineering, 2024, 38(3): 104-110 [25] 乔海亮, 谢海燕, 刘钰. 基于人工神经网络的HEMP-E1环境快速预测模型[J]. 现代应用物理, 2025, 16: 011318 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.202501011Qiao Hailiang, Xie Haiyan, Liu Yu. A fast prediction model for HEMP-E1 environment based on artificial neural network[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2025, 16: 011318 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.202501011 [26] 赵静宜. 人工智能在高能物理领域的应用: 探索未知的利器[J]. 现代应用物理, 2025, 16: 011306Zhao Jingyi. Application of artificial intelligence in high-energy physics: a powerful tool for exploring the unknown[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2025, 16: 011306 [27] 郑炀. 基于数据同化核爆炸放射性沾染预测方法研究[D]. 北京: 军事科学院, 2023Zheng Yang. Prediction method of radioactive contamination in nuclear explosion based on data assimilation[D]. Beijing: Academy of Military Science, 2023 [28] Wang Bing, Chen Bingzhen, Zhao Jinsong. The real-time estimation of hazardous gas dispersion by the integration of gas detectors, neural network and gas dispersion models[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 300: 433-442. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.07.028 [29] Ma Denglong, Zhang Zaoxiao. Contaminant dispersion prediction and source estimation with integrated Gaussian-machine learning network model for point source emission in atmosphere[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 311: 237-245. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.03.022 [30] Wang Rongxiao, Chen Bin, Qiu Sihang, et al. Hazardous source estimation using an artificial neural network, particle swarm optimization and a simulated annealing algorithm[J]. Atmosphere, 2018, 9(4): 119. doi: 10.3390/atmos9040119 [31] Vaca-Rubio C J, Blanco L, Pereira R, et al. Kolmogorov-Arnold networks (KANs) for time series analysis[DB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2405.08790, 2024. [32] Bozorgasl Z, Chen Hao. Wav-KAN: wavelet Kolmogorov-Arnold networks[DB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2405.12832, 2024. [33] 李晓菲, 李帆, 尹禄高, 等. 低空核爆炸环境效应模拟研究[J]. 强度与环境, 2022, 49(5): 48-55Li Xiaofei, Li Fan, Yin Lugao, et al. Simulation study on low-altitude nuclear explosion environment effect[J]. Structure & Environment Engineering, 2022, 49(5): 48-55 [34] 王东. 基于大气透射率和海表发射率的红外测量海表温度修正方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2020Wang Dong. Study on the correction method of infrared sea surface temperature measurement based on atmospheric transmittance and sea surface emissivity[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2020 [35] 韩小祥, 李君, 张欣, 等. 核爆炸光辐射能量分布的模拟仿真研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2024, 36: 076003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.230406Han Xiaoxiang, Li Jun, Zhang Xin, et al. Simulation research on energy distribution of light radiation from nuclear explosion[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2024, 36: 076003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.230406 [36] Kaul D C, Dolatshahi F, Egbert S D, et al. The development and testing of the air transport of radiation code version 6 (ATR6)[R]. DNA-TR-91-237, 1992. [37] Liu Hao, Lei Jin, Ren Zhongzhou. From complexity to clarity: Kolmogorov-Arnold networks in nuclear binding energy prediction[DB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2407.20737, 2024. [38] Cheon M. Kolmogorov-Arnold network for satellite image classification in remote sensing[DB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2406.00600, 2024. [39] Amiri M H, Mehrabi Hashjin N, Montazeri M, et al. Hippopotamus optimization algorithm: a novel nature-inspired optimization algorithm[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14: 5032. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54910-3 [40] Wang Hongbin, Binti Mansor N N, Mokhlis H B. Novel hybrid optimization technique for solar photovoltaic output prediction using improved hippopotamus algorithm[J]. Applied Sciences, 2024, 14: 7803. doi: 10.3390/app14177803 [41] 武益民, 张成良, 张焕雄. 基于河马算法优化BP神经网络的库坡变形预测研究[J/OL]. 水利水电技术(中英文), 2025: 1-23. (2025-03-17)[2025-04-09]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/10.1746.tv.20250315.1157.006.Wu Yimin, Zhang Chengliang, Zhang Huanxiong. Study on slope deformation prediction using BP neural network optimized by Hippo Algorithm[J/OL]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2025: 1-23. (2025-03-17)[2025-04-09]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/10.1746.tv.20250315.1157.006. -




 下载:
下载: