Research on reactor component activation and dose calculation
-
摘要: 放射性源项调查是反应堆退役制订方案、估算费用和进度以及作好辐射防护和应急准备的重要依据。反应堆构件在中子辐照过程中由于中子活化反应会产生大量的放射性核素,其产生的衰变光子是反应堆退役过程中工作人员面临辐射剂量的主要来源。采用蒙特卡罗粒子输运程序(cosRMC、MCNP)和活化计算程序(DEPTH、ALARA)相结合的方法计算反应堆构件在运行一定时间后产生的放射性核素核子数密度、活度和几个主要构件的辐射剂量率。对比通过两个不同活化程序计算得到的计算结果,相对偏差在可接受范围内,表明了cosRMC的活化计算和剂量率计算功能应用于反应堆退役分析的可靠性和准确性。Abstract:
Background The investigation of radioactive source terms serves as a critical basis for formulating reactor decommissioning plans, estimating costs and schedules, and ensuring adequate radiation protection and emergency preparedness.Purpose During neutron irradiation, reactor components undergo neutron activation reactions that generate significant quantities of radionuclides. The decay photons emitted by these nuclides constitute the primary source of radiation exposure for personnel during reactor decommissioning.Methods A combined approach using Monte Carlo particle transport programs (cosRMC, MCNP) and activation calculation programs (DEPTH, ALARA) was employed to calculate the nuclide atom density, activity, and radiation dose rates for key components after a specified operational period.Results Comparing results from the two activation programs shows relative deviations within acceptable limits,Conclusions demonstrating the reliability and accuracy of cosRMC’s activation calculations and dose rate assessment capabilities for reactor decommissioning analysis.-
Key words:
- reactor decommissioning /
- cosRMC /
- ALARA /
- activation calculation /
- dose calculation
-
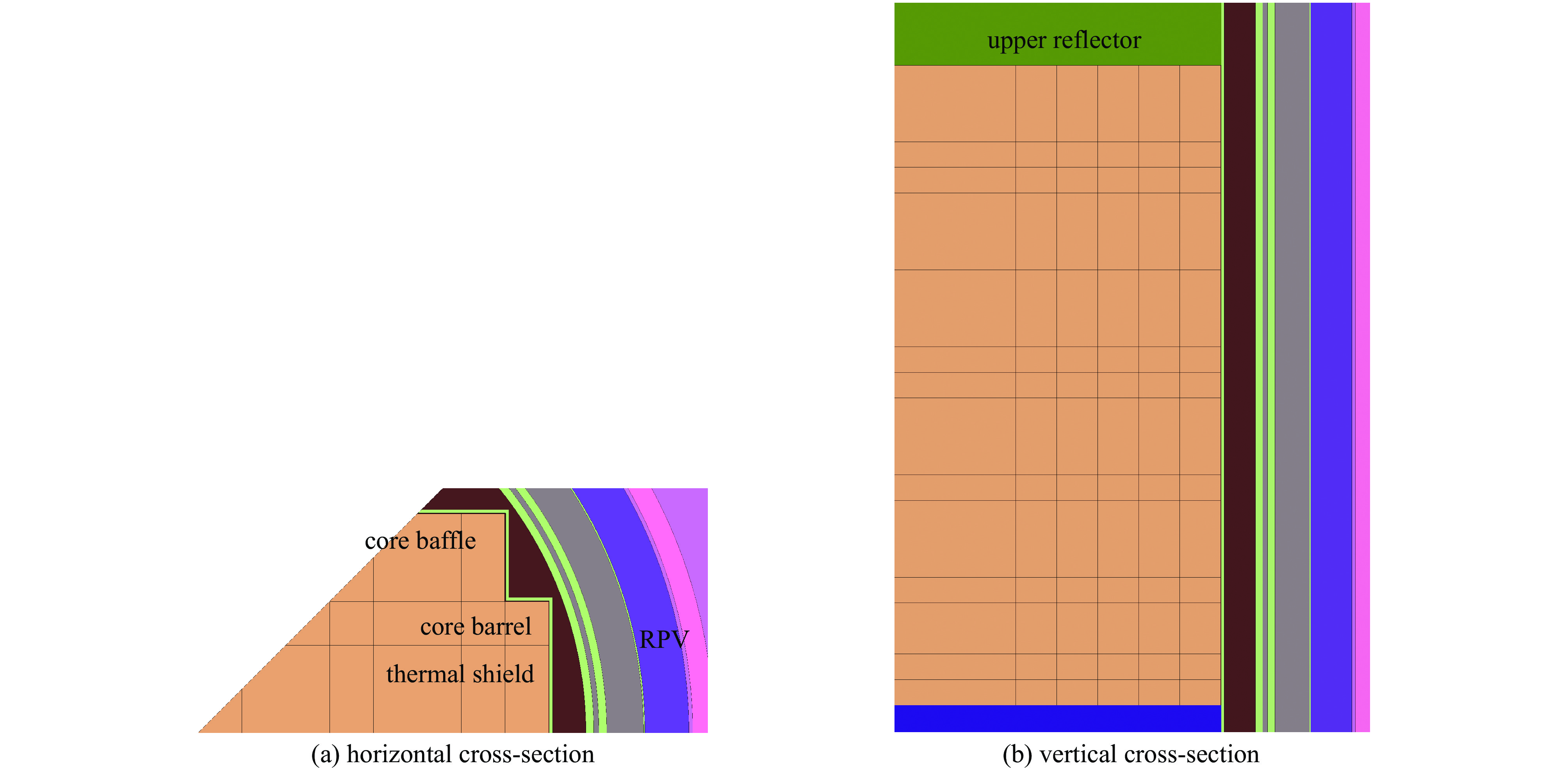
表 1 NUREG/CR-
6115 模型结构参数Table 1. Structural parameters of NUREG/CR-
6115 structure inner radius/cm outer radius/cm height/cm materials upper reflector \ \ 32.865 306.7 ℃ water + steel lower reflector \ \ 13.97 280 ℃ water + steel core baffle \ \ 382.115 SS-304 stainless steel by-pass flow \ 190.185 382.115 293.3 ℃ boron water core barrel 190.185 193.995 382.115 SS-304 stainless steel inner inlet water gap 193.995 196.535 382.115 280 ℃ boron water thermal shield 196.535 200.345 382.115 SS-304 stainless steel outer inlet water gap 200.345 218.440 382.115 280 ℃ boron water RPV Liner 218.440 219.075 382.115 SS-304 stainless steel RPV 219.075 240.665 382.115 SA-302B stainless steel 注:“\”表示不适用。 表 2 重要核素产额
Table 2. Yield of important nuclides
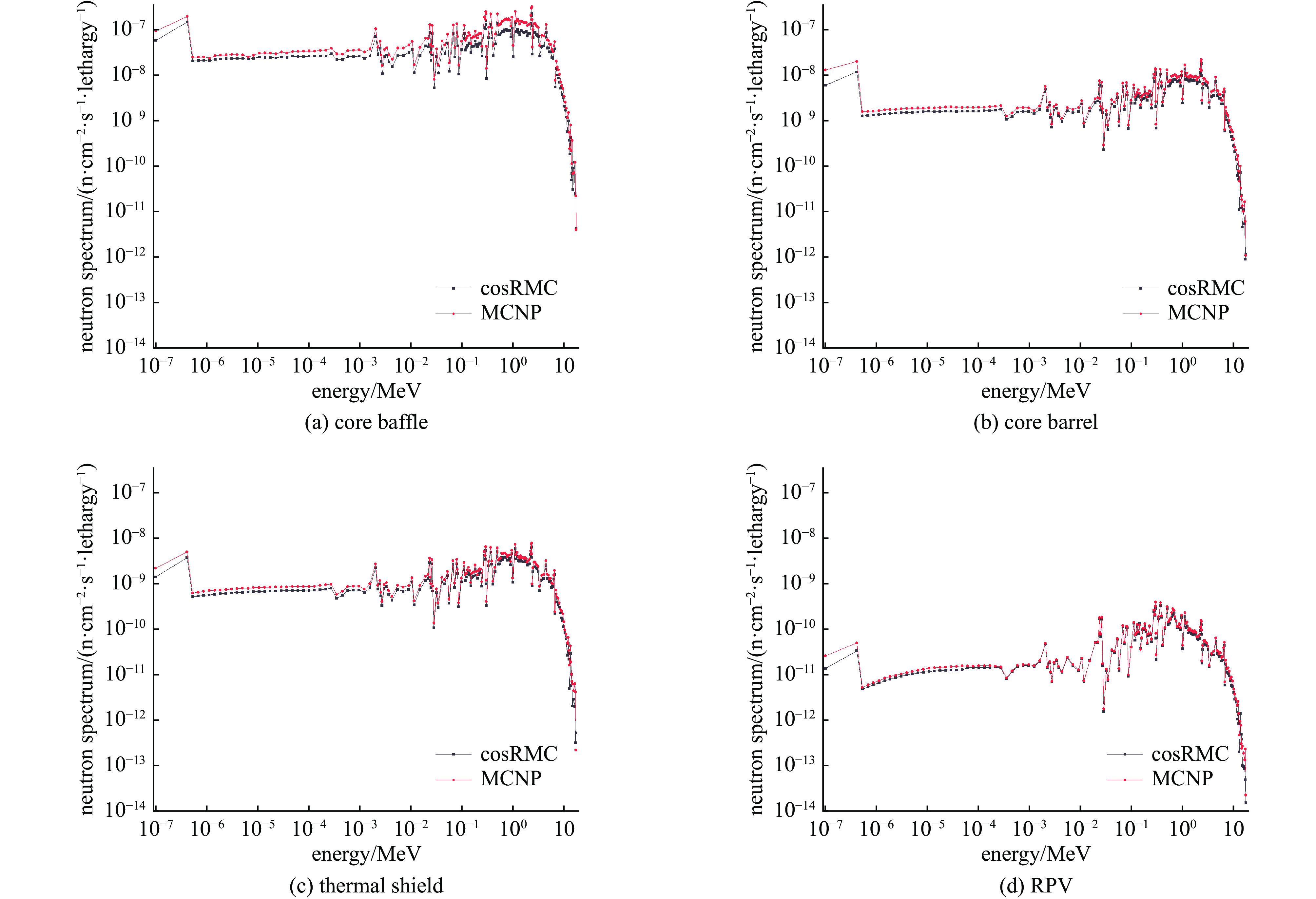
structure nuclides atom density/cm−3 |relative error|/% ALARA DEPTH core baffle 60Co 2.0926E+16 2.1057E+16 0.6278 51Cr 8.6670E+17 8.6683E+17 0.0148 55Fe 6.3342E+18 6.3550E+18 0.3280 59Fe 3.0794E+16 3.0802E+16 0.0268 54Mn 2.4371E+17 2.4416E+17 0.1826 48Sc 2.0590E+09 2.0673E+09 0.4039 65Zn 2.5127E+09 2.5267E+09 0.5573 core barrel 60Co 9.9192E+14 9.9564E+14 0.3751 51Cr 8.2801E+16 8.2817E+16 0.0197 55Fe 5.9648E+17 5.9844E+17 0.3283 59Fe 2.6898E+15 2.6903E+15 0.0188 54Mn 2.1917E+16 2.1957E+16 0.1864 48Sc 2.3200E+07 2.3296E+07 0.4123 65Zn 1.8511E+06 1.8616E+06 0.5649 thermal shield 60Co 3.6517E+14 3.6648E+14 0.3583 51Cr 2.1479E+16 2.1483E+16 0.0193 55Fe 1.5670E+17 1.5722E+17 0.3310 59Fe 7.4995E+14 7.5010E+14 0.0203 54Mn 8.0167E+15 8.0314E+15 0.1831 48Sc 2.4734E+06 2.4843E+06 0.4421 65Zn 3.9769E+04 4.0424E+04 1.6461 RPV 51Cr 6.5003E+11 6.5016E+11 0.0201 55Fe 2.3698E+15 2.3776E+15 0.3272 54Mn 2.7002E+14 2.7051E+14 0.1818 表 3 四个目标栅元的停堆剂量率
Table 3. Shutdown dose rate of the four target grid cells
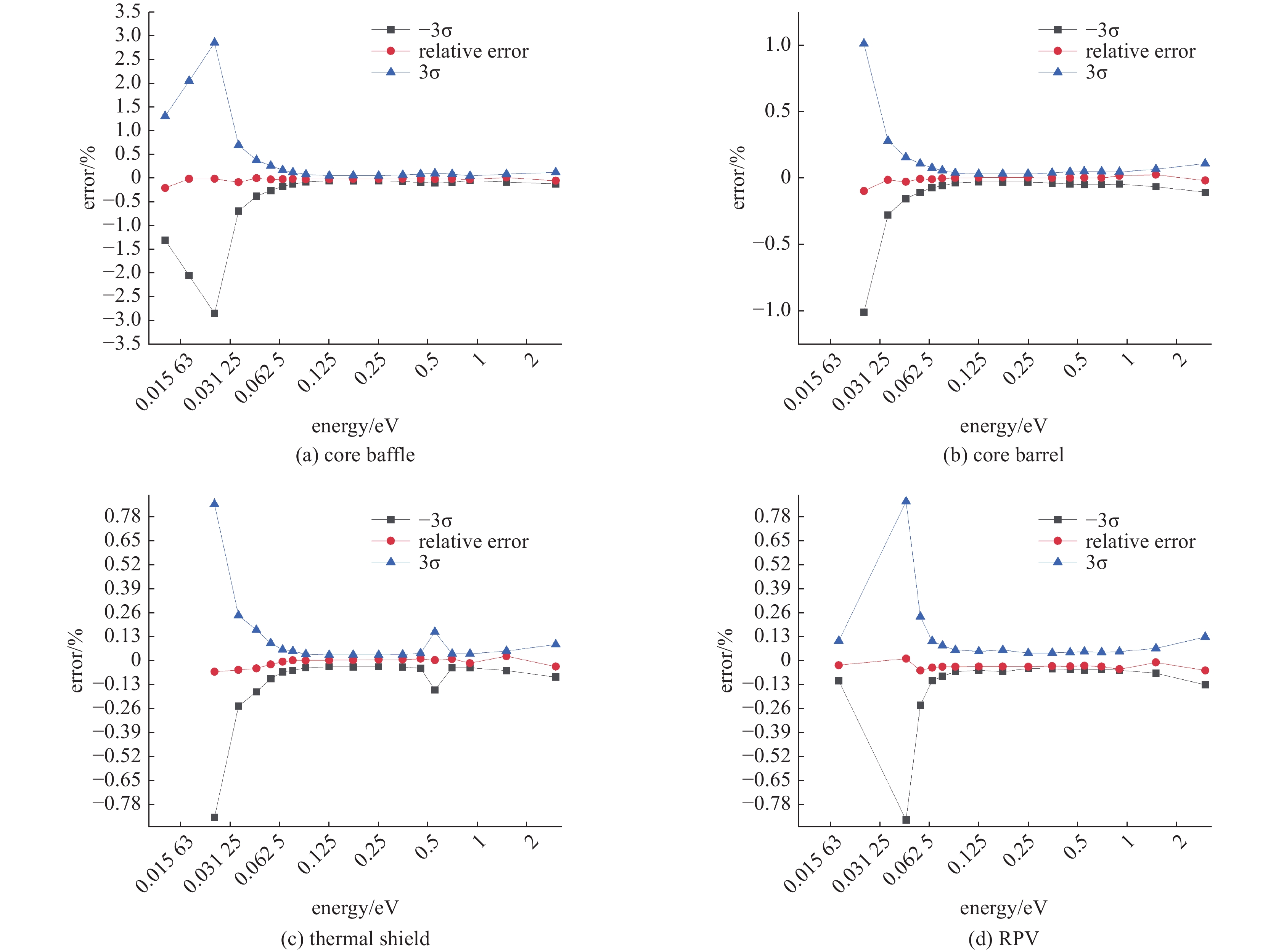
structure dose rate/(Sv/hr) relative error/% −3σ/% 3σ/% ALARA DEPTH core baffle 6.1679E+00 6.2696E+00 − 1.6489 − 3.6347 3.6347 core barrel 3.9238E+00 3.8921E+00 0.8079 − 3.3881 3.3881 thermal shield 1.1709E+00 1.1652E+00 0.4868 − 3.3986 3.3986 RPV 1.6995E-01 1.7454E-01 − 2.7008 − 4.9815 4.9815 -
[1] Bleynat S, Dulla S, Pancotti F, et al. Hybrid Monte Carlo/deterministic activation calculation to support the decommissioning of PWRs: validation against data from the thermal shield of the Enrico Fermi NPP[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2023, 181: 109527. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2022.109527 [2] 冯建, 王凯, 邱立青, 等. 反应堆污染部件放射性存留量估算方法[J]. 科技视界, 2018(7): 102-103Feng Jian, Wang Kai, Qiu Liqing, et al. A method for estimating the radioactive inventory of the contaminated parts in reactors[J]. Science & Technology Vision, 2018(7): 102-103 [3] 邢宏传, 周荣生, 徐济鋆. 退役核设施放射性存留量估算方法研究[J]. 核动力工程, 2005, 26(6): 544-547,571Xing Hongchuan, Zhou Rongsheng, Xu Jiyun. Study of estimating method for residual radioactive on decommissioning nuclear establishment[J]. Nuclear Power Engineering, 2005, 26(6): 544-547,571 [4] 郭武仁, 林晓玲, 郑宁宁. 反应堆退役压力容器放射性活度估算方法[J]. 核动力工程, 2011, 32(4): 114-117Guo Wuren, Lin Xiaoling, Zheng Ningning. Method for estimation of activity in decommissioned nuclear reactor pressure vessel[J]. Nuclear Power Engineering, 2011, 32(4): 114-117 [5] 楼吉洁, 杨波, 毕光文, 等. 小型压水堆无硼堆芯高精度数值模拟验证研究[J]. 现代应用物理, 2024, 15: 010402Lou Jijie, Yang Bo, Bi Guangwen, et al. High-precision numerical simulation and verification of soluble boron-free core in small pressurized water reactors[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2024, 15: 010402 [6] 罗上庚. 核设施退役中几个值得重视的问题[J]. 辐射防护, 2002, 22(3): 129-134,139Luo Shanggeng. Some noticeable issues of decommissioning of nuclear facilities[J]. Radiation Protection, 2002, 22(3): 129-134,139 [7] 张显, 刘仕倡, 强胜龙, 等. 蒙特卡罗全局权窗和均匀裂变源方法在全堆临界计算中的应用研究[J]. 原子能科学技术, 2021, 55(s1): 66-72Zhang Xian, Liu Shichang, Qiang Shenglong, et al. Application of Monte Carlo global weight window and uniform fission site methods in full core criticality calculation[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2021, 55(s1): 66-72 [8] 李锐, 张显, 刘仕倡, 等. 蒙特卡罗粒子输运程序cosRMC的深穿透屏蔽计算研究[J]. 原子能科学技术, 2021, 55(s1): 82-87Li Rui, Zhang Xian, Liu Shichang, et al. Research on deep penetration shielding calculation using Monte Carlo particle transport code cosRMC[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2021, 55(s1): 82-87 [9] 张宽, 宋婧, 陈珍平, 等. 蒙特卡罗粒子输运计算网格计数方法研究[J]. 核科学与工程, 2016, 36(2): 200-204Zhang Kuan, Song Jing, Chen Zhenping, et al. Mesh tally method study for Monte Carlo particles transport simulation[J]. Nuclear Science and Engineering, 2016, 36(2): 200-204 [10] 刘扬, 林晓玲, 蔡琦. 核动力装置活化构件放射性存留量计算及影响因素分析[J]. 核动力工程, 2011, 32(4): 118-121Liu Yang, Lin Xiaoling, Cai Qi. Calculation of radioactive inventory of activated parts for nuclear power unit and analysis of influence factors[J]. Nuclear Power Engineering, 2011, 32(4): 118-121 [11] 王小胡, 胡一非, 李江波, 等. 退役反应堆放射性活化源项计算[J]. 原子能科学技术, 2014, 48(5): 893-897Wang Xiaohu, Hu Yifei, Li Jiangbo, et al. Calculation of radioactive activated source term for decommissioned reactor[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2014, 48(5): 893-897 [12] Hoogenboom J E, Martin W R, Petrovic B. Monte Carlo performance benchmark for detailed power density calculation in a full size reactor core[J]. Ann Arbor, 2011. [13] 佘顶, 王侃, 余纲林. 堆用蒙卡程序燃耗计算功能开发[J]. 核动力工程, 2012, 33(3): 1-5,11She Ding, Wang Kan, Yu Ganglin. Development of burnup calculation function in reactor Monte Carlo code RMC[J]. Nuclear Power Engineering, 2012, 33(3): 1-5,11 [14] 苑旭东, 马辉强, 陈珍平, 等. 基于R2S方法的反应堆结构材料活化剂量计算研究[J]. 核动力工程, 2021, 42(5): 103-109Yuan Xudong, Ma Huiqiang, Chen Zhenping, et al. Study on activation-induced dose calculation of reactor structural materials[J]. Nuclear Power Engineering, 2021, 42(5): 103-109 [15] 于虓, 张竞宇, 于珑选, 等. 基于运输和活化程序耦合的停堆剂量率计算[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2024, 45(12): 2384-2390Yu Xiao, Zhang Jingyu, Yu Longxuan, et al. Shutdown dose rate calculation using transport and activation program coupling[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2024, 45(12): 2384-2390 [16] Wang Kan, Li Zeguang, She Ding, et al. RMC–a Monte Carlo code for reactor core analysis[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2015, 82: 121-129. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2014.08.048 [17] 苏耿华, 包鹏飞, 韩嵩, 等. 核电厂反应堆构件的退役活化源项计算[J]. 核动力工程, 2016, 37(5): 167-170Su Genghua, Bao Pengfei, Han Song, et al. Calculation of activation source terms of reactor components for decommissioned nuclear power plant[J]. Nuclear Power Engineering, 2016, 37(5): 167-170 -




 下载:
下载: