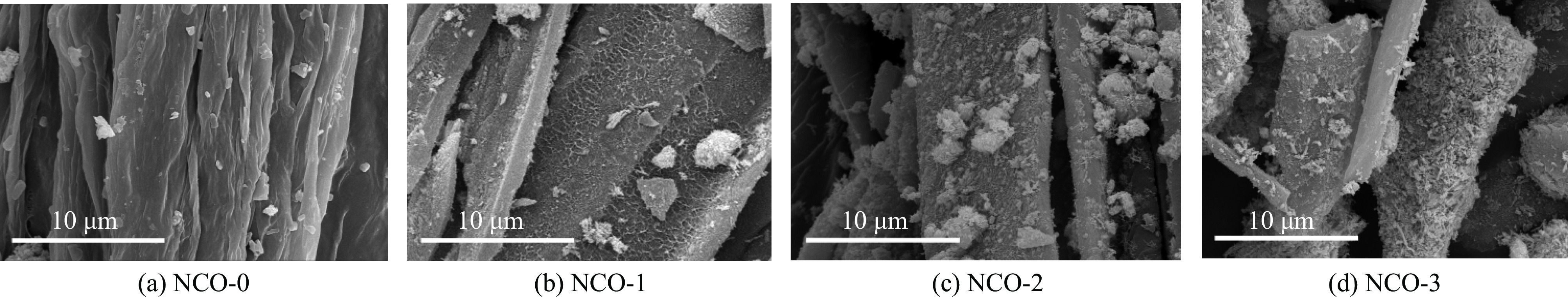
Based on loofah-derived NiCo2O4/C composites for high-performance microwave absorption
-
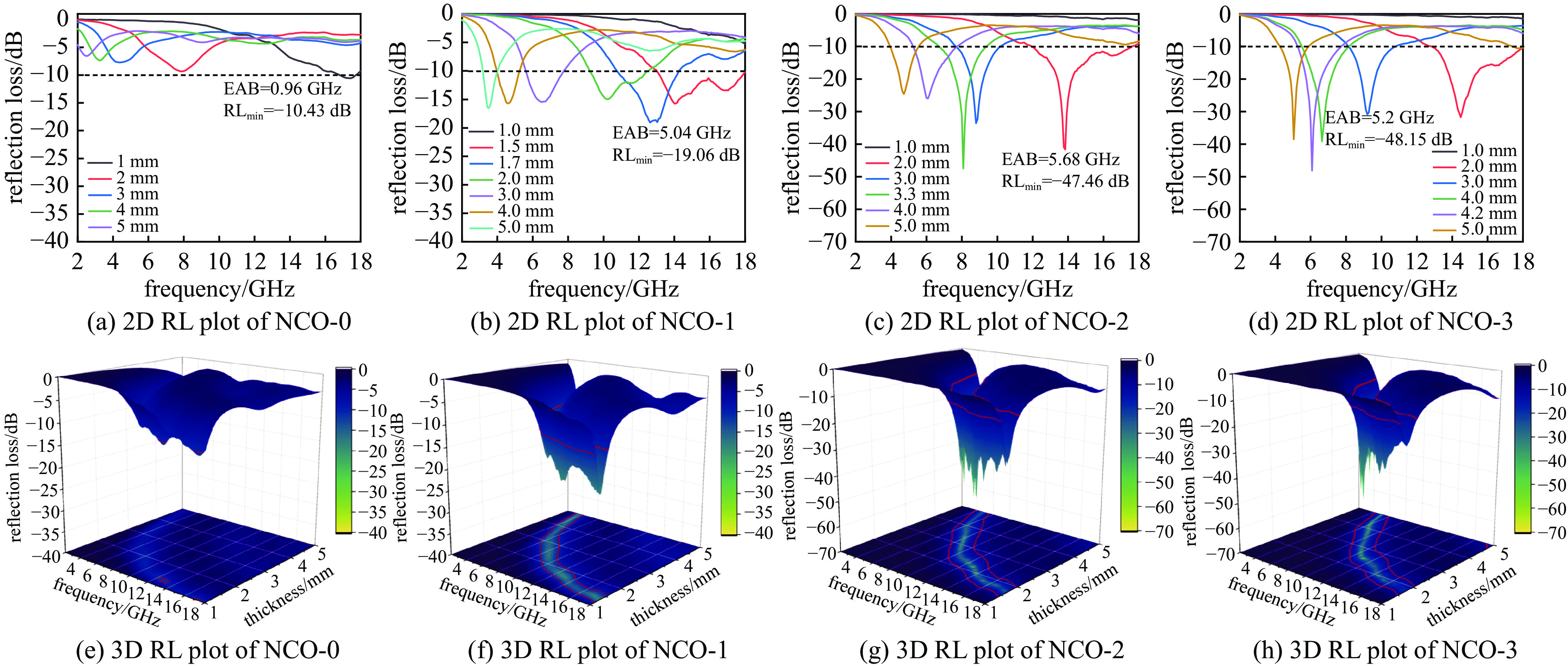
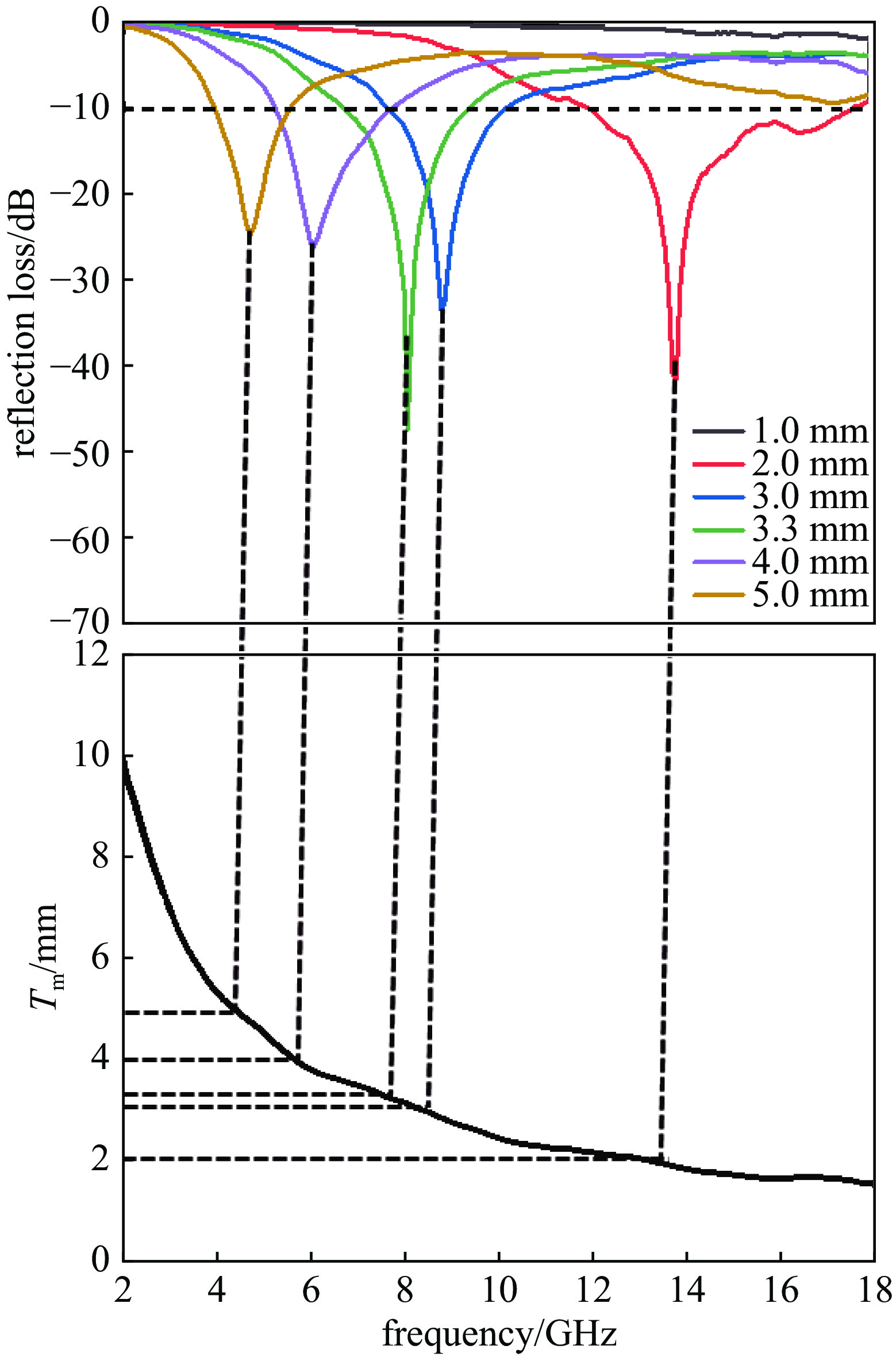
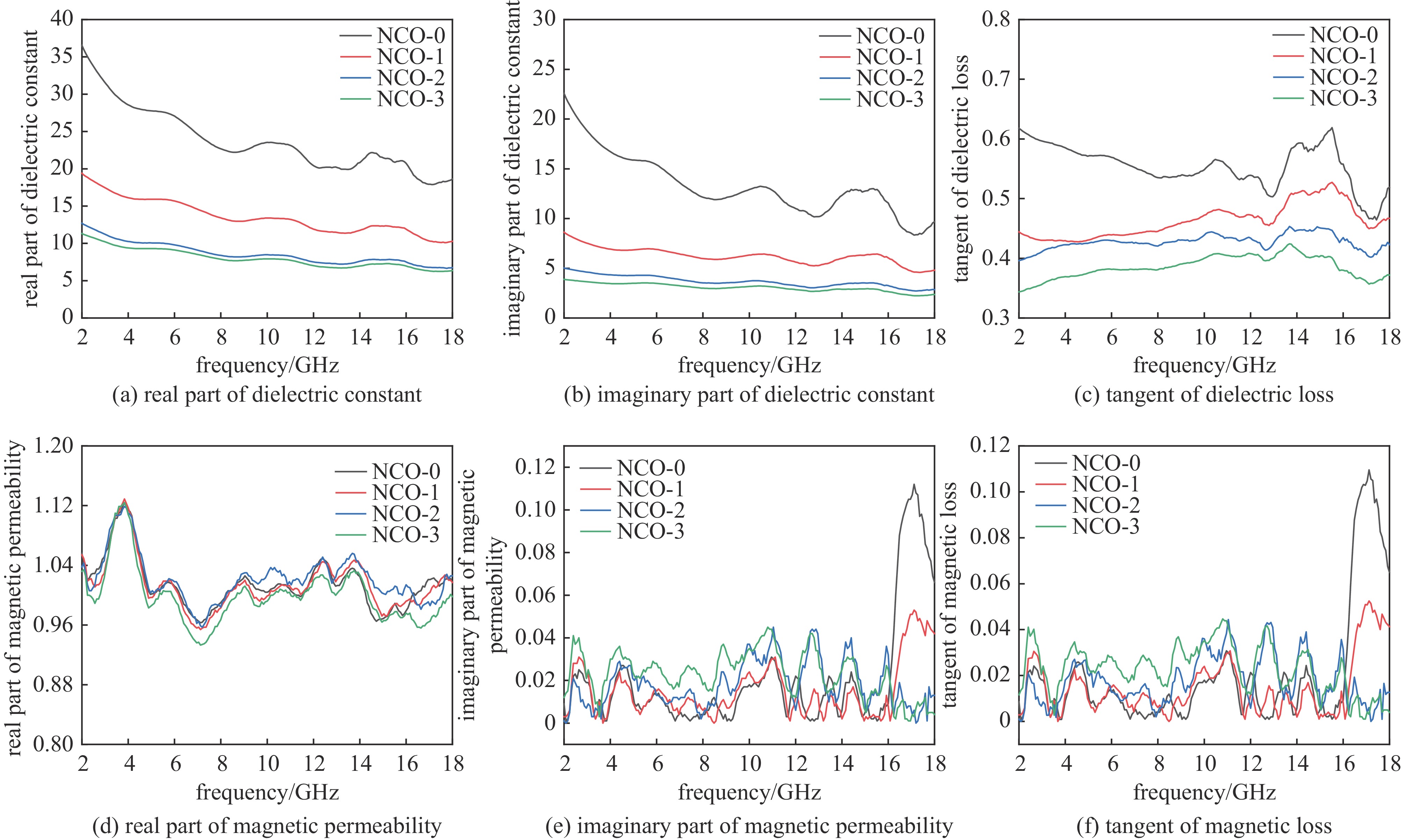
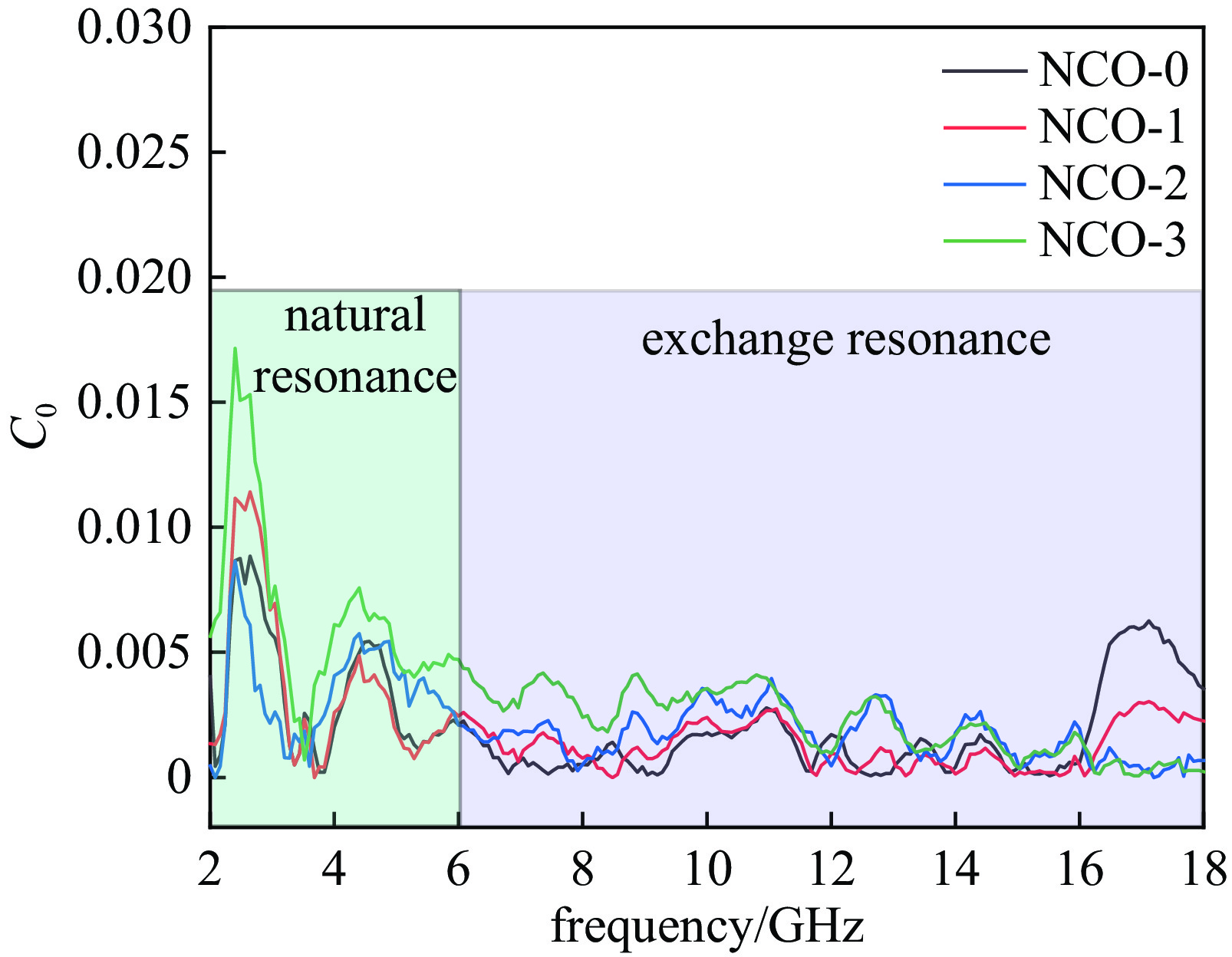
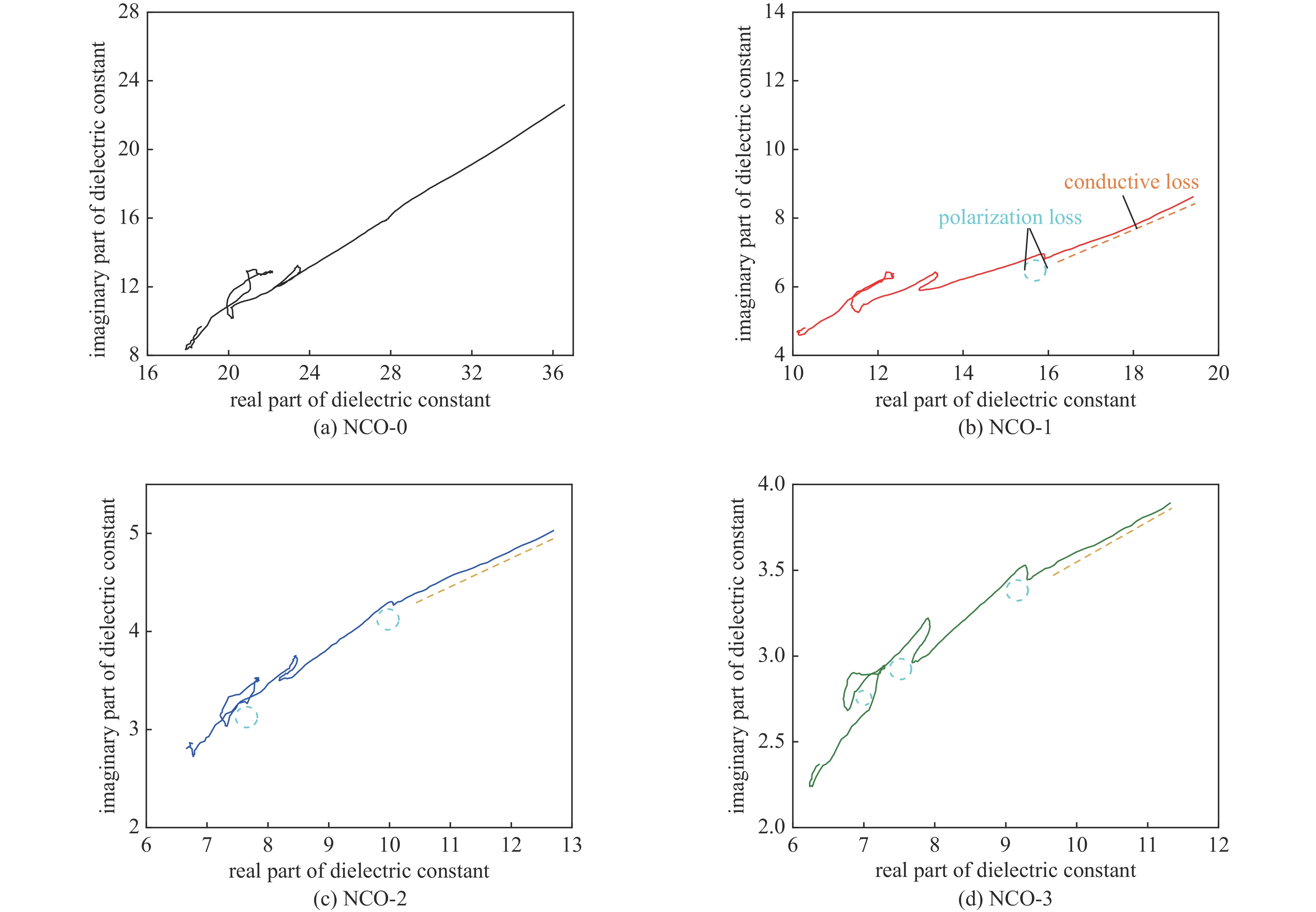
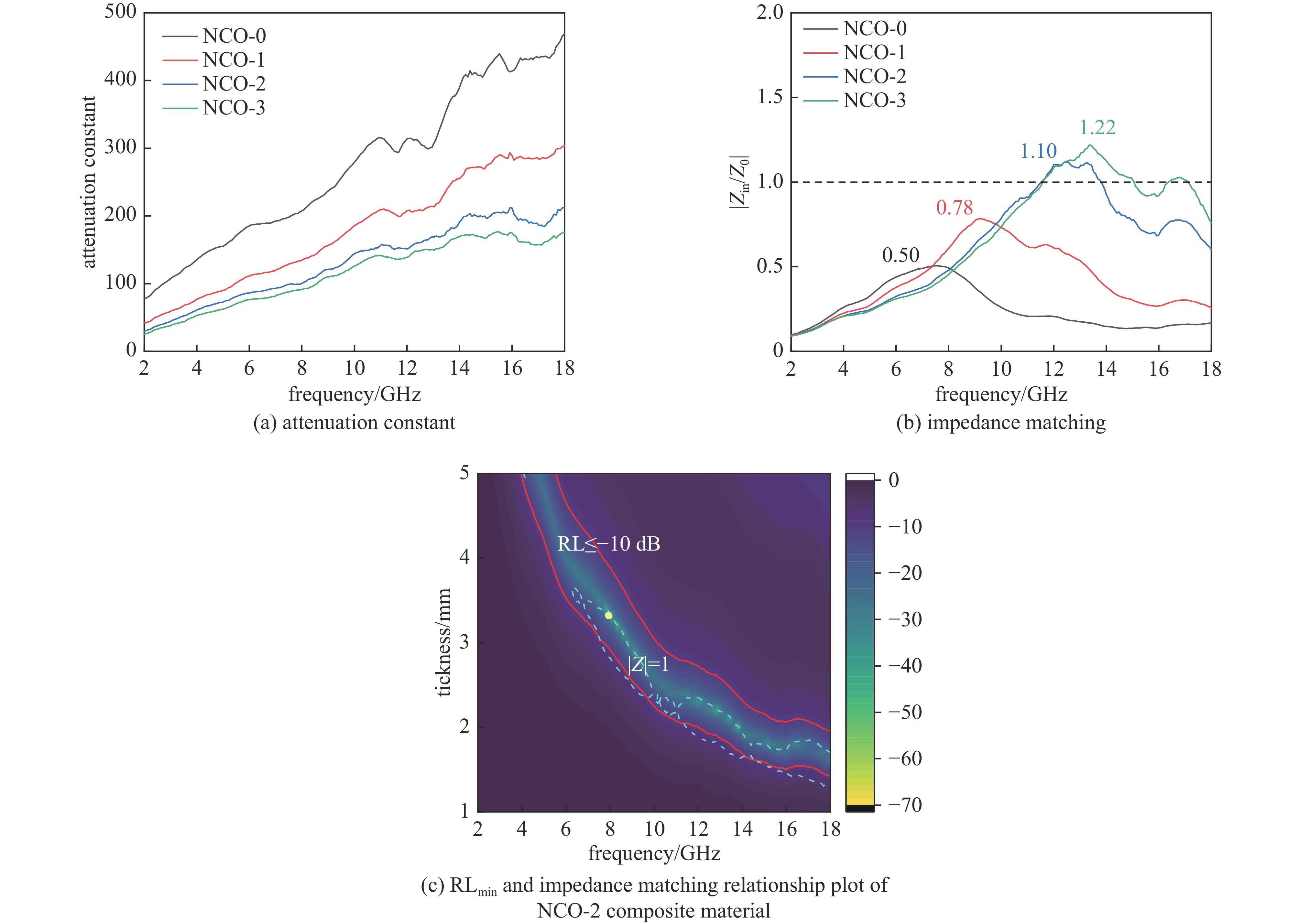
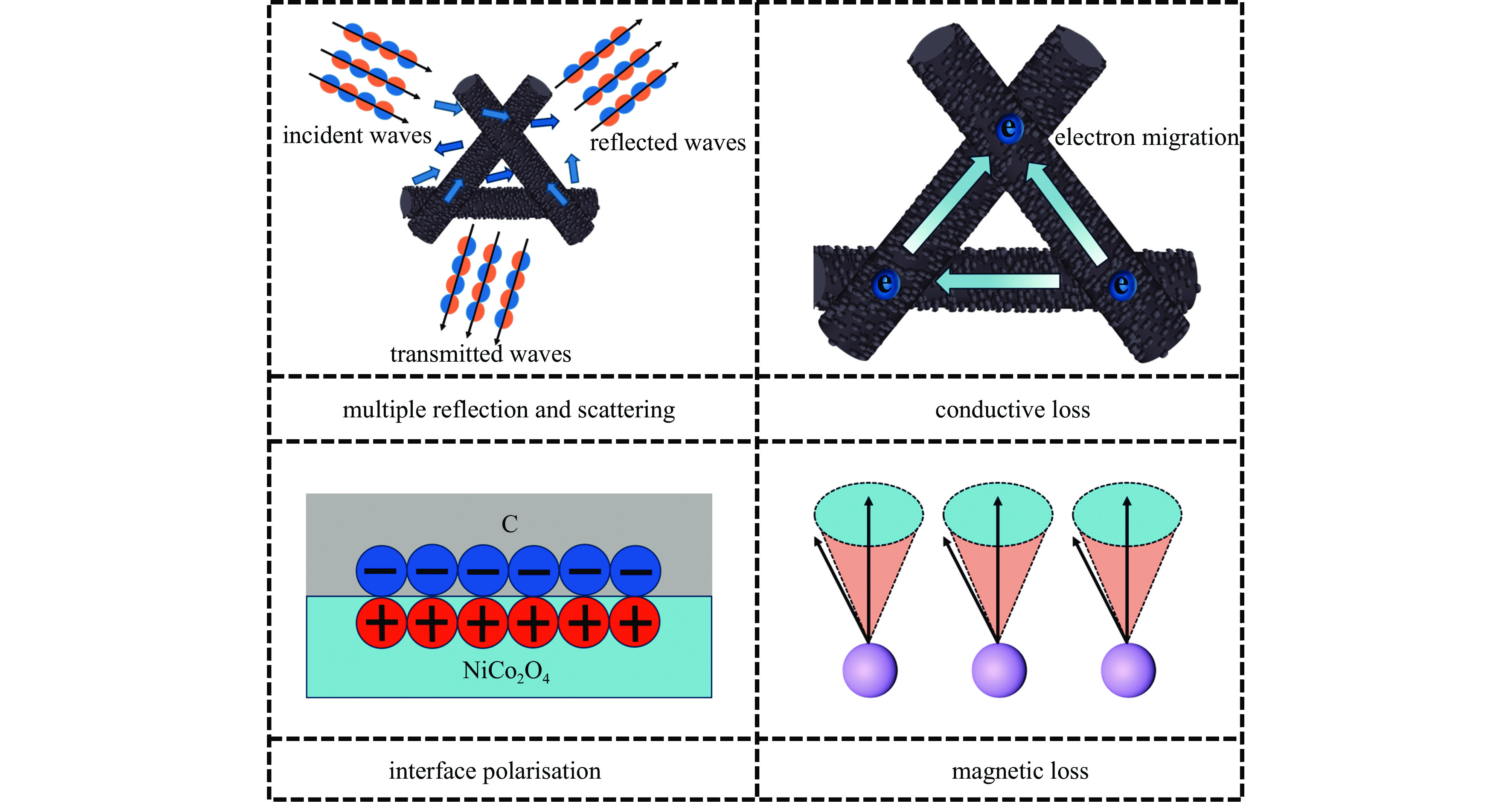
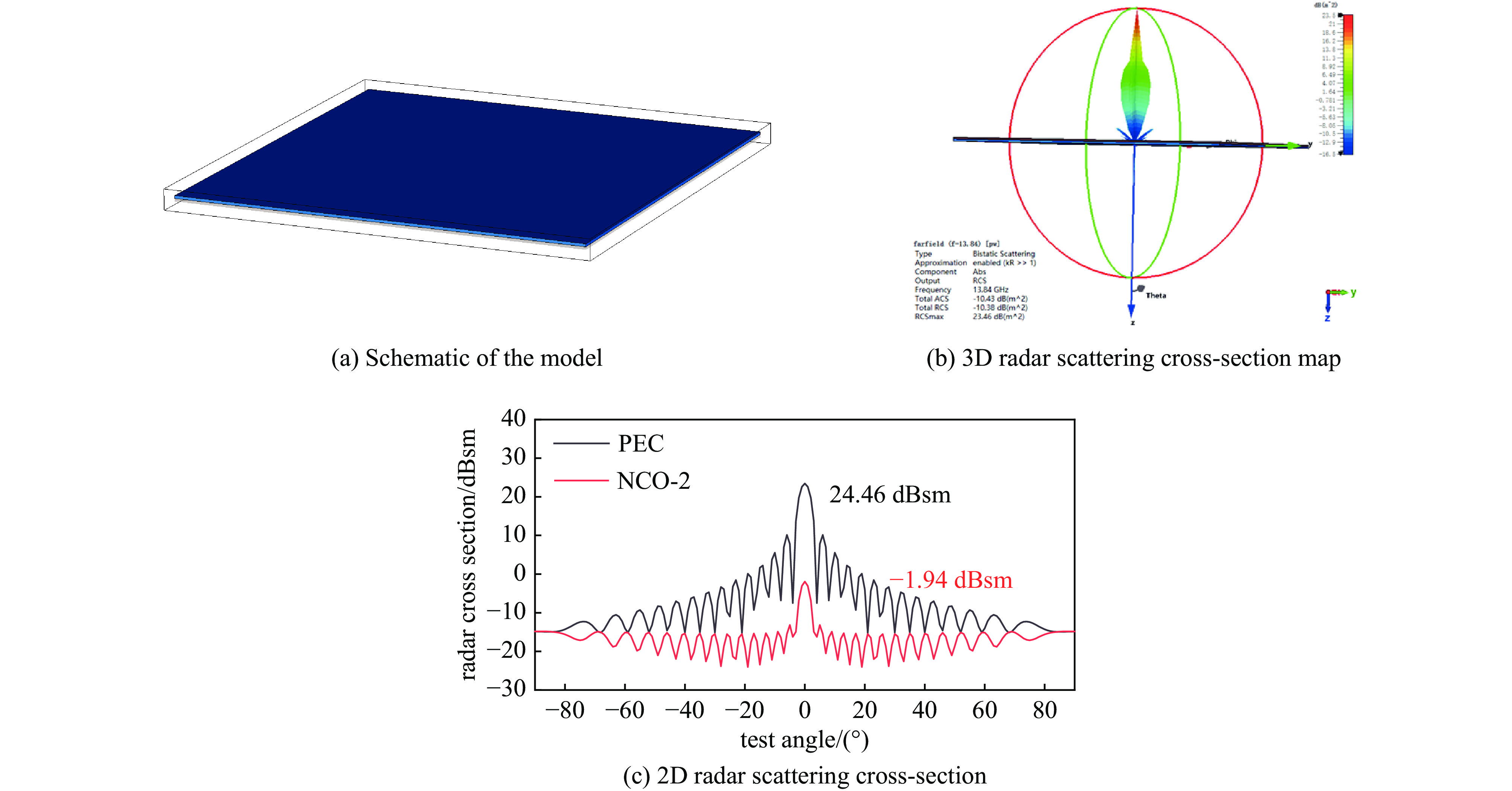
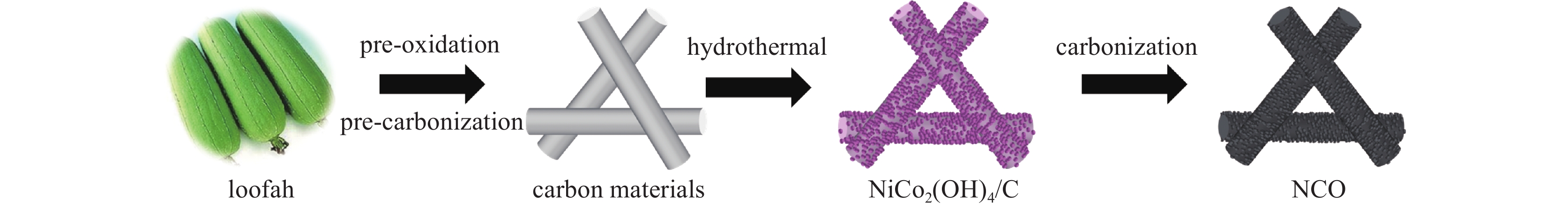
摘要: 日益增长的电磁辐射对电子设备、人体健康、环境等造成了严重的危害。从生物质衍生的碳基材料,由于高孔隙率、低密度、介电损耗强、来源广泛、成本低廉等优点被认为具有极强的电磁吸收潜力。基于此,本研究以丝瓜作为碳前驱体,引入NiCo2O4磁性粒子,制备了NiCo2O4/C电磁波吸收材料(NCO)。NiCo2O4粒子的引入,不仅增强了复合材料的磁损耗性能,还调节了介电性能,优化了阻抗匹配。由于独特的网状结构以及界面极化、电导损耗、磁损耗等损耗机制的协同作用,NiCo2O4/C复合材料获得了良好的电磁波吸收特性,其最强反射损耗为−47.46 dB,最宽吸收频带为5.68 GHz(12−17.68 GHz),几乎覆盖整个Ku波段。此外,本研究还通过雷达散射截面面积(Radar scattering cross section, RCS)仿真,证明了NCO-2复合材料具有一定的实际应用价值。这项工作为开发绿色可持续的高性能生物质衍生碳基复合材料提供了理论和实验基础。
-
关键词:
- 生物质材料 /
- NiCo2O4磁性粒子 /
- 介电损耗 /
- 磁损耗 /
- 电磁波吸收
Abstract:Background The increasing electromagnetic radiation poses a serious hazard to electronic devices, human health, and the environment. Carbon-based materials derived from biomass are considered to have excellent electromagnetic absorption potential due to their high porosity, low density, strong dielectric loss, wide range of sources and low cost.Purpose This study aims to analyze the electromagnetic wave absorption characteristics of biomass-derived carbon-based materials.Methods This study is based on hydrothermal and carbonization processes, using loofah as the carbon precursor, and introducing NiCo2O4 magnetic particles to prepare NiCo2O4/C (NCO) electromagnetic wave absorbing material, with its actual wave-absorbing performance verified through COMSOL simulation software.Results The introduction of NiCo2O4 particles not only enhanced the magnetic loss properties of the composites, but also regulated the dielectric properties and optimized the impedance matching. Due to the unique mesh structure and the synergistic effect of interfacial polarization, conductive loss, magnetic loss and other loss mechanisms, the NiCo2O4/C composites obtain good electromagnetic wave absorption properties, with the strongest reflection loss of −47.46 dB, and the widest absorption band of 5.68 GHz (12−17.68 GHz), which covers almost the whole Ku-band. In addition, the study also demonstrated that NCO-2 composites have some practical applications through RCS simulations.Conclusions The synergistic effect of dielectric and magnetic properties can significantly modulate the dielectric properties of composites, optimize impedance matching, and enhance loss mechanisms, thereby achieving excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance. The work provides a theoretical and experimental basis for the development of green and sustainable high-performance biomass-derived carbon-based composites. -
表 1 NCO-2 复合材料的微波吸收特性与近期文献报道的代表性生物质衍生 EMW吸收材料的微波吸收特性的比较。
Table 1. Comparison of microwave absorption properties of NCO-2 composites with those of representative biomass-derived EMW absorbing materials recently reported in the literature
EMW
absorption materialsEAB
(GHz)RLmin
(dB)Tickness
(mm)Ratio
(wt%)References MoS2@C 3.7(8.5-12.2) −45.8 2.63 20% [8] BCN 4.16(13.84-18) −54.24 1.4 45% [12] PCF 5.52(12.48-18) −46.95 1.72 10% [13] NiCo2S4/C 5.26(9.22-14.48) −64.74 2.05 50% [14] MDBC 5.52(11.68-17.2) −47.06 1.8 30% [15] NCO-2 5.68(12-17.68) −47.46 2.0 35% This study -
[1] Wu Nannan, Hu Qian, Wei Renbo, et al. Review on the electromagnetic interference shielding properties of carbon based materials and their novel composites: Recent progress, challenges and prospects[J]. Carbon, 2021, 176: 88-105. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2021.01.124 [2] Li Qi, Zhang Zheng, Qi Luping, et al. Toward the application of high frequency electromagnetic wave absorption by carbon nanostructures[J]. Advanced Science, 2019, 6: 1801057. doi: 10.1002/advs.201801057 [3] Gai Lixue, Zhao Honghong, Wang Fengyuan, et al. Advances in core—shell engineering of carbon-based composites for electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Nano Research, 2022, 15(10): 9410-9439. doi: 10.1007/s12274-022-4695-6 [4] Huang Xinmeng, Liu Xuehua, Jia Zirui, et al. Synthesis of 3D cerium oxide/porous carbon for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 2021, 4(4): 1398-1412. doi: 10.1007/s42114-021-00304-2 [5] Zhang Feng, Jia Zirui, Zhou Jixi, et al. Metal-organic framework-derived carbon nanotubes for broadband electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 450: 138205. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.138205 [6] Cheng Yuanjing, Sun Xianxian, Yang Shuang, et al. Multifunctional elastic rGO hybrid aerogels for microwave absorption, infrared stealth and heat insulation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 452: 139376. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.139376 [7] Xiang Lele, Darboe A K, Luo Zhihong, et al. Constructing two-dimensional/two-dimensional reduced graphene oxide/MoX2 (X = Se and S) van der Waals heterojunctions: a combined composition modulation and interface engineering strategy for microwave absorption[J]. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 2023, 6: 215. doi: 10.1007/s42114-023-00793-3 [8] Zhao Jia, Gu Zhe, Zhang Qingguo. Stacking MoS2 flower-like microspheres on pomelo peels-derived porous carbon nanosheets for high-efficient X-band electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Nano Research, 2024, 17(3): 1607-1615. doi: 10.1007/s12274-023-6090-3 [9] Lan Xiaolin, Wang Ran, Liu Wenbo, et al. Multicomponent synergistic flower-like FeS/hollow C fiber for tunable and efficient microwave absorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 485: 149238. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2024.149238 [10] Shen Laifa, Che Qian, Li Hongsen, et al. Mesoporous NiCo2O4 nanowire arrays grown on carbon textiles as binder-free flexible electrodes for energy storage[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2014, 24(18): 2630-2637. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201303138 [11] Liu Chenyu, Lin Zhan, Chen Chao, et al. Porous C/Ni composites derived from fluid coke for ultra-wide bandwidth electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 366: 415-422. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.082 [12] Mou Pengpeng, Zhao Jinchuan, Wang Guizhen, et al. BCN nanosheets derived from coconut shells with outstanding microwave absorption and thermal conductive properties[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 437: 135285. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.135285 [13] Cheng Tingting, Guo Yuying, Xie Yuxin, et al. Customizing the structure and chemical composition of ultralight carbon foams for superior microwave absorption performance[J]. Carbon, 2023, 206: 181-191. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2023.02.052 [14] Dong Shun, Hu Peitao, Li Xiutao, et al. NiCo2S4 nanosheets on 3D wood-derived carbon for microwave absorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 398: 125588. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.125588 [15] Huang Xiangbin, Wang Yanting, Lou Zhichao, et al. Porous, magnetic carbon derived from bamboo for microwave absorption[J]. Carbon, 2023, 209: 118005. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2023.118005 [16] Wang Lei, Huang Mengqiu, Yu Xuefeng, et al. MOF-derived Ni1−xCox@carbon with tunable nano–microstructure as lightweight and highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorber[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2020, 12: 150. doi: 10.1007/s40820-020-00488-0 [17] Cui Liru, Wang Yahui, Han Xijiang, et al. Phenolic resin reinforcement: a new strategy for hollow NiCo@C microboxes against electromagnetic pollution[J]. Carbon, 2021, 174: 673-682. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.10.070 [18] Zhou Panpan, Zhang Jing, Song Zhi, et al. Defect engineering in N-doped OMC for lightweight and high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Journal of Materiomics, 2024, 10(1): 190-199. doi: 10.1016/j.jmat.2023.05.008 [19] Wang Yanli, Wang Guangsheng, Zhang Xiaojuan, et al. Porous carbon polyhedrons coupled with bimetallic CoNi alloys for frequency selective wave absorption at ultralow filler loading[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2022, 103: 34-41. [20] Lan Di, Qin Ming, Liu Jiaolong, et al. Novel binary cobalt nickel oxide hollowed-out spheres for electromagnetic absorption applications[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 382: 122797. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122797 [21] Zhang Hongxia, Shi Chuan, Jia Zirui, et al. FeNi nanoparticles embedded reduced graphene/nitrogen-doped carbon composites towards the ultra-wideband electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 584: 382-394. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.09.122 [22] Liu Yue, Liu Xuehua, E Xinyu, et al. Synthesis of MnxOy@C hybrid composites for optimal electromagnetic wave absorption capacity and wideband absorption[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2022, 103: 157-164. [23] Wu Nannan, Liu Chang, Xu Dongmei, et al. Ultrathin high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers with facilely fabricated hierarchical porous Co/C crabapples[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2019, 7(6): 1659-1669. doi: 10.1039/C8TC04984J [24] Du Hanying, Ren Jiaqi, Zhang Wenchao, et al. Ni nanoparticles in situ embedment in 3D ordered macro-/mesoporous carbon framework as efficient microwave absorption and infrared stealth materials[J]. Carbon, 2023, 204: 325-335. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2022.12.051 [25] Chang Ming, Jia Zirui, He Shuangqiao, et al. Two-dimensional interface engineering of NiS/MoS2/Ti3C2Tx heterostructures for promoting electromagnetic wave absorption capability[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2021, 225: 109306. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109306 [26] Su Qiang, He Yunfei, Liu Dongdong, et al. Facile fabrication of graphene/g-C3N4 for electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Nano Research, 2024, 17(3): 1687-1698. doi: 10.1007/s12274-023-6231-z [27] Wang Jiayao, Wang Yiqun, Jiang Rui, et al. Self-assembly of submillimeter porous structure on metal-organic framework to construct heterogeneous interface for controlling microwave absorption[J]. Materials Today Physics, 2023, 35: 101126. doi: 10.1016/j.mtphys.2023.101126 [28] Cheng Jie, Jiang Haojie, Cai Lei, et al. Porous N-doped C/VB-group VS2 composites derived from perishable garbage to synergistically solve the environmental and electromagnetic pollution[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 457: 141208. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.141208 -




 下载:
下载: