Study on characteristics of in-orbit SRAM single event upsets and their correlation with the space environment
-
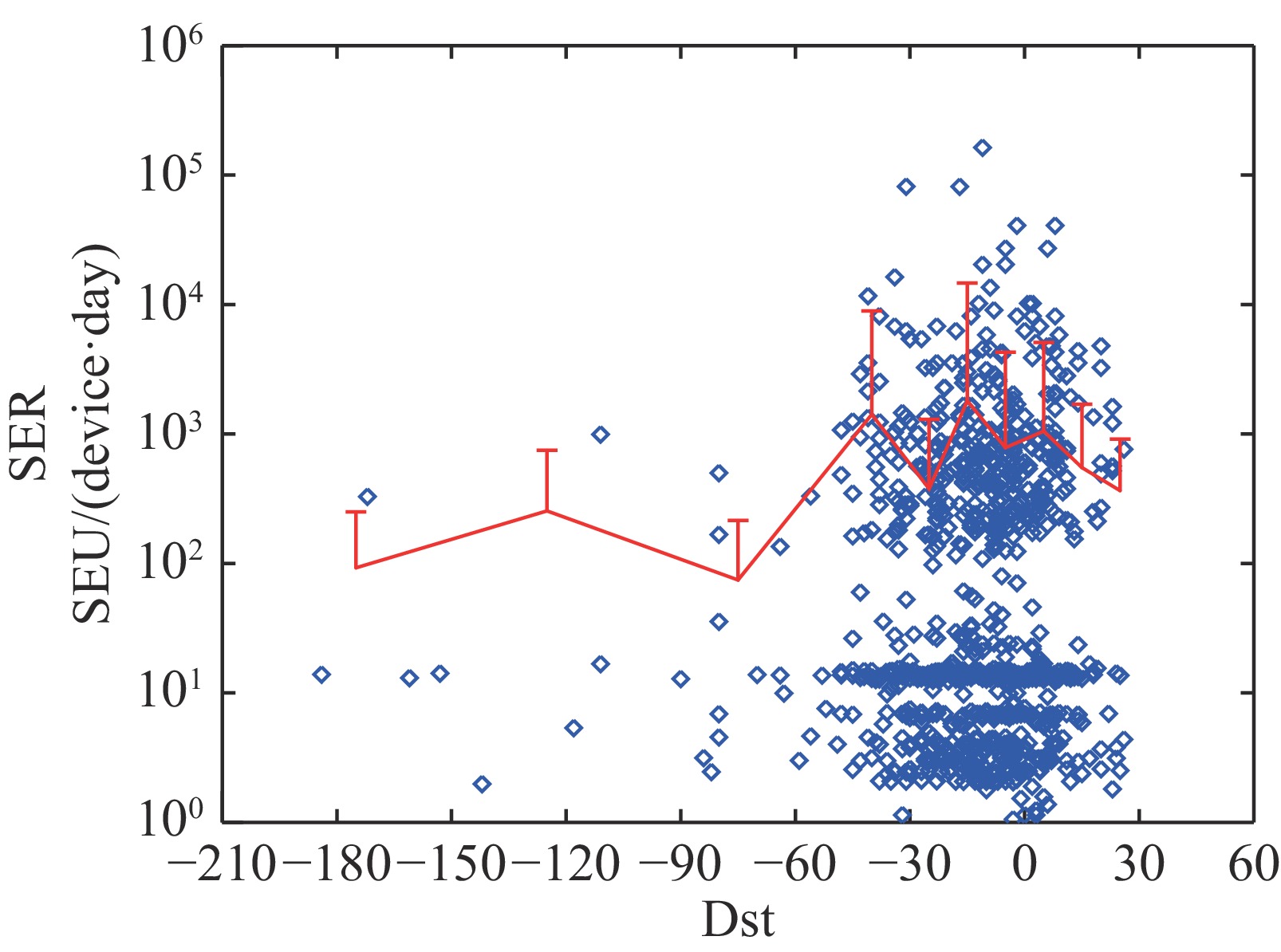
摘要: 空间辐射环境对航天电子器件的可靠性影响显著,其中单粒子翻转(Single Event Upset, SEU)是最具代表性的瞬态辐射效应之一。基于在轨静态随机存取存储器(SRAM)SEU监测数据,系统分析了SEU与空间环境参数的相关性。结果表明,97.5%的SEU事件集中发生在南大西洋异常区(SAA),并在磁壳层L≈1.24~1.25处出现峰值,其空间分布与≥10 MeV质子通量增强区高度一致。≥10 MeV质子通量与在轨软错误率(SER)呈显著幂律正相关(R≈0.73),表明高能质子是驱动SEU的主要因素。基于地面质子辐照试验截面和在轨能谱估算的理论SER与观测值在1个数量级内一致,但整体偏低,需扩展能谱范围以提高预测精度。在轨期间经历的3次小型太阳质子事件均未触发SEU,而地磁暴期间Dst指数下降伴随SER显著降低,表明地磁暴引发SAA区域质子通量衰减使得SEU发生频率降低。研究结果揭示了在轨SRAM器件SEU的空间分布规律及其驱动机理,为辐射效应建模、抗辐射设计和任务可靠性评估提供参考。Abstract:
Background The space radiation environment poses a critical threat to spacecraft electronics, with single-event upset (SEU) being one of the most representative transient radiation effects. Understanding the spatial distribution and driving mechanisms of SEUs is essential for improving radiation-hardened design and mission reliability.Purpose This study aims to systematically investigate the relationship between on-orbit SEUs and space environment parameters, and to quantify the contribution of high-energy protons to SEU occurrence.Methods On-orbit SEU monitoring data from static random-access memory (SRAM) devices were analyzed in conjunction with particle flux measurements, geomagnetic parameters, and proton energy spectra. The spatial distribution of SEUs was mapped in L-shell coordinates, and statistical correlation analysis was performed between the flux of protons at or above 10 MeV and on-orbit soft error rate (SER). Theoretical SER was calculated using ground-based proton irradiation cross sections and compared with observed values.Results A total of 97.5% of SEU events were concentrated within the South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA), with a peak at L ≈ 1.24−1.25, coinciding with enhanced the flux of protons at or above 10 MeV regions. A significant power-law correlation (R ≈ 0.73) was found between the flux of protons at or above 10 MeV and SER, confirming high-energy protons as the dominant driver of SEUs. The calculated SER agreed with observations within one order of magnitude but was systematically lower, indicating the need for extending the spectral range to improve prediction accuracy. No SEUs were detected during three minor solar proton events, while geomagnetic storms caused significant SER decreases due to proton flux depletion in the SAA.Conclusions This study systematically elucidates the spatial distribution characteristics and primary driving mechanisms of on-orbit SRAM SEUs, demonstrating that high-energy proton flux is the dominant contributor to SEU occurrence. These findings advance the understanding of space radiation effects and provide essential theoretical and experimental support for radiation effect modeling, radiation-hardened design, and mission reliability assessment. -
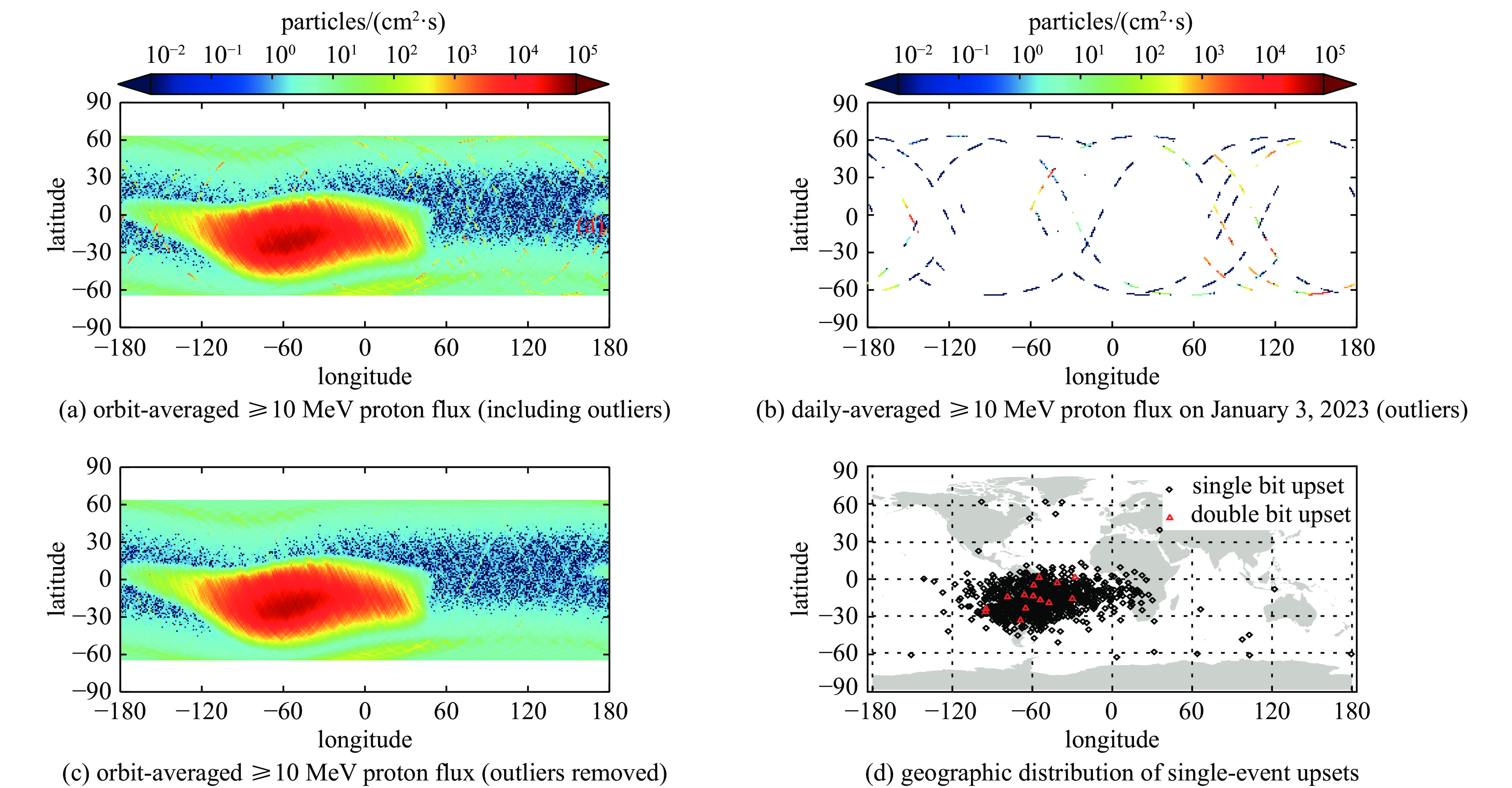
图 1 (a)轨道≥10 MeV平均质子通量(包含异常值);(b) 2023年1月3日日平均≥10 MeV质子通量(异常值);(c)轨道≥10 MeV平均质子通量(剔除异常值);(d) SEU地理分布
Figure 1. (a) Orbit-averaged ≥10 MeV proton flux (including outliers), (b) daily-averaged ≥10 MeV proton flux on January 3, 2023 (outliers), (c) orbit-averaged ≥10 MeV proton flux (outliers removed), (d) geographic distribution of single-event upsets
表 1 在轨期间(SRAM开机)经历的太阳质子事件
Table 1. Solar proton events encountered during on-orbit operation (with SRAM powered on)
No. start time (UT) maximum time (UT) proton flux/(pfu @ >10 MeV) 1 2022-08-27 11:55 2022-08-27 12:20 27 2 2023-02-25 21:10 2023-02-26 04:40 58 3 2023-03-13 07:35 2023-03-15 04:25 22 -
[1] 沈国红, 张珅毅, 王春琴, 等. HXMT轨道空间辐射环境分析[J]. 现代应用物理, 2023, 14: 010606 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2023.010606Shen Guohong, Zhang Shenyi, Wang Chunqin, et al. Analysis of space radiation exploration on hard X-Ray modulation telescope[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2023, 14: 010606 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2023.010606 [2] Aguiar Y Q D, Wrobel F, Autran J L, et al. Introduction to single-event effects[M]//De Aguiar Y Q, Wrobel F, Autran J L, et al. Single-Event Effects, from Space to Accelerator Environments: Analysis, Prediction and Hardening by Design. Cham: Springer, 2025: 29-47. [3] Duzellier S. Radiation effects on electronic devices in space[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2005, 9(1): 93-99. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2004.08.006 [4] 张艳文, 郭刚, 韩金华, 等. 质子单粒子试验技术及其应用[J]. 现代应用物理, 2024, 15: 040417Zhang Yanwen, Guo Gang, Han Jinhua, et al. Proton single event effect testing technology and its application[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2024, 15: 040417 [5] 沈志强, 刘剑利, 陈启明, 等. 300 MeV质子重离子加速器及电子器件单粒子效应试验研究[J]. 现代应用物理, 2024, 15: 040418 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2024.040418Shen Zhiqiang, Liu Jianli, Chen Qiming, et al. 300 MeV proton and heavy ion accelerator and single event effects of electronic devices[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2024, 15: 040418 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2024.040418 [6] Ma Y Q, Yu T, Xu X H, et al. Comparative study of the single-event functional interrupt (SEFI) rate in solid-state drives (SSD) through ground and on-orbit testing[J]. Space Weather, 2025, 23: e2025SW004414. doi: 10.1029/2025SW004414 [7] Leach R. Spacecraft system failures and anomalies attributed to the natural space environment[C]//Space Programs and Technologies Conference. 1995. [8] 王长河. 单粒子效应对卫星空间运行可靠性影响[J]. 半导体情报, 1998, 35(1): 1-8Wang Changhe. The influence with reliability of motional satelliteby the single -event phenomena[J]. Semiconductor Information, 1998, 35(1): 1-8 [9] Ji Xinyan, Li Yunze, Liu Guoqing, et al. A brief review of ground and flight failures of Chinese spacecraft[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2019, 107: 19-29. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2019.04.002 [10] 韩建伟, 陈睿, 李宏伟, 等. 单粒子效应及充放电效应诱发航天器故障的甄别与机理探讨[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2021, 38(3): 344-350Han Jianwei, Chen Rui, Li Hongwei, et al. The anomalies supposed to be due to the single event effects may be caused by spacecraft charging induced electrostatic discharge[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2021, 38(3): 344-350 [11] 周飞, 李强, 信太林, 等. 空间辐射环境引起在轨卫星故障分析与加固对策[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2012, 29(4): 392-396Zhou Fei, Li Qiang, Xin Tailin, et al. Analyses and countermeasures of in-orbit satellite failures caused by space radiation environment[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2012, 29(4): 392-396 [12] Harrington R C, Kauppila J S, Warren K M, et al. Estimating single-event logic cross sections in advanced technologies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2017, 64(8): 2115-2121. [13] 尚琳, 刘晓娜, 曹彩霞, 等. 低轨互联网卫星在轨单粒子翻转分析及防护措施[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2021, 38(5): 503-507Shang Lin, Liu Xiaona, Cao Caixia, et al. Analysis of in-orbit single event upset of low-Earth-orbit internet satellite and protection measures[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2021, 38(5): 503-507 [14] Mai Ziqi, Zhu Xiang, Li Hongwei, et al. Experiment study of single event functional interrupt in analog-to-digital converters using a pulsed laser[J]. Electronics, 2023, 12: 2774. doi: 10.3390/electronics12132774 [15] Chen Junchao, Lange T, Andjelkovic M, et al. Solar particle event and single event upset prediction from SRAM-based monitor and supervised machine learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2022, 10(2): 564-580. [16] Kottaras G, Sarris T, Psomoulis A, et al. A low-power, radiation-hardened single event effect rate detection system on a chip for real time monitoring of single event effects on low earth orbit satellites[C]//2022 IFIP/IEEE 30th International Conference on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI-SoC). 2022: 1-6. [17] 马英起, 朱翔, 李宏伟, 等. 空间辐射环境危害综合监测原理样机研制[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2019, 36(1): 89-94 doi: 10.12126/see.2019.01.014Ma Yingqi, Zhu Xiang, Li Hongwei, et al. Development of a space radiation hazard monitor[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2019, 36(1): 89-94 doi: 10.12126/see.2019.01.014 [18] Zhang Binquan, Zhang Shenyi, Shen Guohong, et al. Monitor of the single event upsets and linear energy transfer of space radiation on the Beidou navigation satellites[J]. Open Astronomy, 2023, 32: 20220206. doi: 10.1515/astro-2022-0206 [19] Noeldeke C, Boettcher M, Mohr U, et al. Single event upset investigations on the “Flying Laptop” satellite mission[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2021, 67(6): 2000-2009. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2020.12.032 [20] Katz S, Goldvais U, Price C. The connection between space weather and Single Event Upsets in polar low earth orbit satellites[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2021, 67(10): 3237-3249. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2021.02.007 [21] 侯建文, 张爱兵, 郑香脂, 等. FPGA单粒子翻转事件在轨探测研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2014, 35(4): 454-458Hou Jianwen, Zhang Aibing, Zheng Xiangzhi, et al. Research on in-orbit detection of SEU of FPGA[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2014, 35(4): 454-458 [22] Hansen D L, Resor S, Vermeire B, et al. Comparison of figure of merit calculations to on-orbit data[C]//2023 IEEE Radiation Effects Data Workshop (REDW) (in Conjunction with 2023 NSREC). 2023: 1-8. [23] Wrobel F, Aguiar Y, Marques C, et al. An analytical approach to calculate soft error rate induced by atmospheric neutrons[J]. Electronics, 2023, 12(1): 104. [24] He Wei, Li Jing, Zhou Yimin, et al. Study on an estimation method of on-orbit single event upset rate based on historical data[C]//2021 IEEE 4th International Conference on Electronics Technology (ICET). 2021: 1342-1346. [25] Slayman C. JEDEC standards on measurement and reporting of alpha particle and terrestrial cosmic ray induced soft errors[M]//Nicolaidis M. Soft Errors in Modern Electronic Systems. New York: Springer, 2011: 55-76. [26] 张付强, 郭刚, 覃英参, 等. 质子单粒子效应引发卫星典型轨道下SRAM在轨错误率分析[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2018, 35(4): 365-370 doi: 10.12126/j.issn.1673-1379.2018.04.010Zhang Fuqiang, Guo Gang, Qin Yingcan, et al. Prediction of proton-induced single event effect on SRAM’s in-orbit soft error rate on typical satellite orbit[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2018, 35(4): 365-370 doi: 10.12126/j.issn.1673-1379.2018.04.010 [27] 王会斌, 呼延奇, 郑悦, 等. 航天器空间辐射效应分析技术现状与思考[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2022, 39(4): 427-435 doi: 10.12126/see.2022.04.015Wang Huibin, Hu Yanqi, Zheng Yue, et al. The present situation of technologies for analysis of space radiation effects to spacecraft and some retrospection[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2022, 39(4): 427-435 doi: 10.12126/see.2022.04.015 [28] 沈国红, 常峥, 张焕新, 等. 太阳同步轨道粒子辐射效应综合探测技术[J]. 北京大学学报自然科学版, 2025, 61(2): 379-387Shen Guohong, Chang Zheng, Zhang Huanxin, et al. Comprehensive detection technology of particle radiation effects in solar synchronous orbit[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2025, 61(2): 379-387 [29] Shen Guohong, Chang Zheng, Zhang Huanxin, et al. Comprehensive detection of particle radiation effects on the orbital platform of the upper stage of the Chinese CZ-4C carrier rocket[J]. Atmosphere, 2024, 15: 705. doi: 10.3390/atmos15060705 [30] Wang Jieyi, Zhang Huanxin, Zhu Xinyu, et al. Analyzing measured evidence for inducing factors of SEU from in-flight data of NSSC-SPRECMI on OPUS CZ-4C[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2025, 72(2): 101-109. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2024.3522366 [31] Poivey C, Harboe-Sørensen R, Pinto M, et al. SEL and SEU in-flight data from memories on-board PROBA-II spacecraft[C]//2022 IEEE Radiation Effects Data Workshop (REDW) (in Conjunction with 2022 NSREC). 2022: 1-6. [32] Quinn H, Graham P, Morgan K, et al. Flight experience of the Xilinx virtex-4[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2013, 60(4): 2682-2690. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2013.2246581 [33] Pinto M, Sampaio J M, Arruda L, et al. CTTB memory test board single event effect geostationary in-flight data analysis[C]//2020 20th European Conference on Radiation and Its Effects on Components and Systems (RADECS). 2020: 1-6. [34] 国家卫星气象中心. 地磁暴强度等级[P]. 2015National Satellite Meteorological Center. Classification of geomagnetic storm intensity[P]. 2015 [35] Xu Xiaoheng, Ma Yingqi, Zhang Longlong, et al. Dynamics of proton flux in the South Atlantic anomaly during the super geomagnetic storm in May 2024[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2025, 130: e2024JA033536. doi: 10.1029/2024JA033536 [36] Zou Hong, Li Chenfang, Zong Qiugang, et al. Short-term variations of the inner radiation belt in the South Atlantic anomaly[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2015, 120(6): 4475-4486. doi: 10.1002/2015JA021312 [37] 陈洋, 邹鸿, 陈鸿飞, 等. 暴时内辐射带高能质子的损失和恢复机制探究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(7): 2344-2355 doi: 10.6038/cjg20160702Chen Yang, Zou Hong, Chen Hongfei, et al. Study on the loss and recovery mechanisms of high-energy protons in the inner radiation belt during geomagnetic storms[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(7): 2344-2355 doi: 10.6038/cjg20160702 [38] 王建国, 牛胜利, 张殿辉, 等. 高空核爆炸效应参数手册[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 2010Wang Jianguo, Niu Shengli, Zhang Dianhui, et al. The parameter manual book of high-altitude nuclear explosion effects[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 2010 [39] Wang Jianguo, Liu Li, Zuo Yinghong, et al. Research progress in numerical simulation of environmental parameters generated by the high-altitude nuclear explosions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2025, 72(3): 884-900. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2025.3530013 -




 下载:
下载: