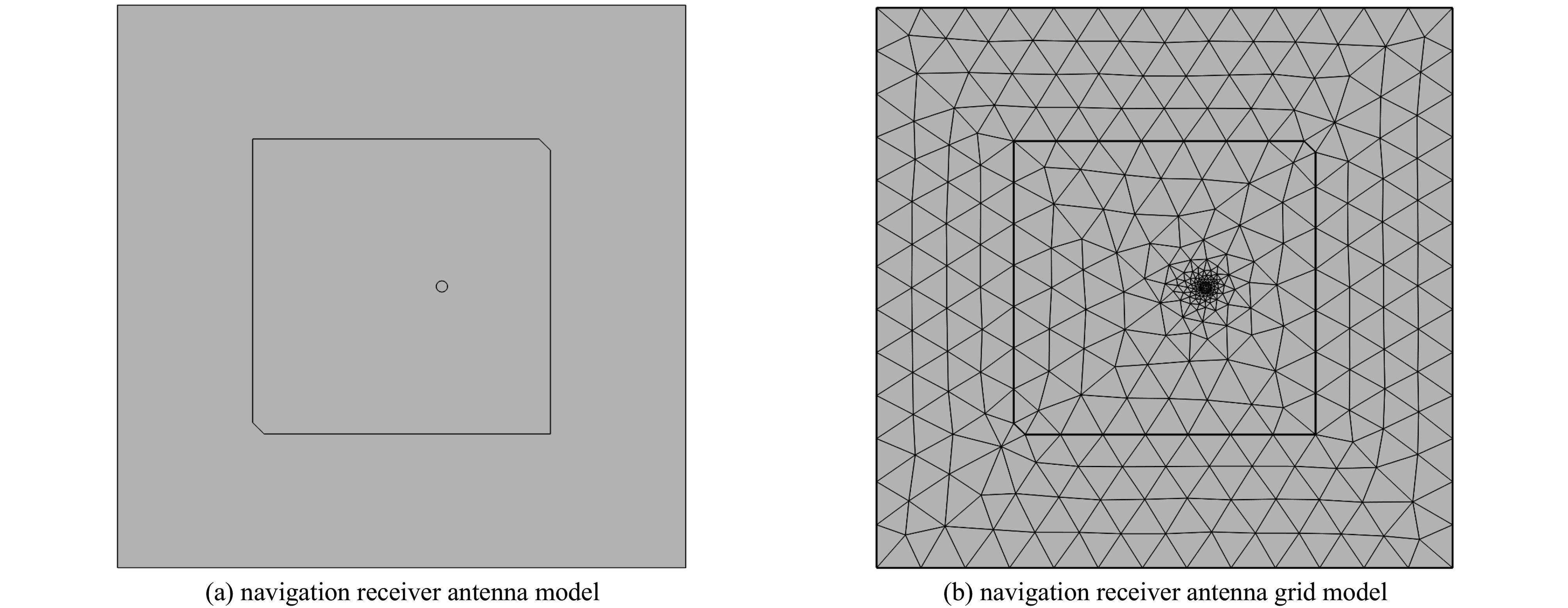
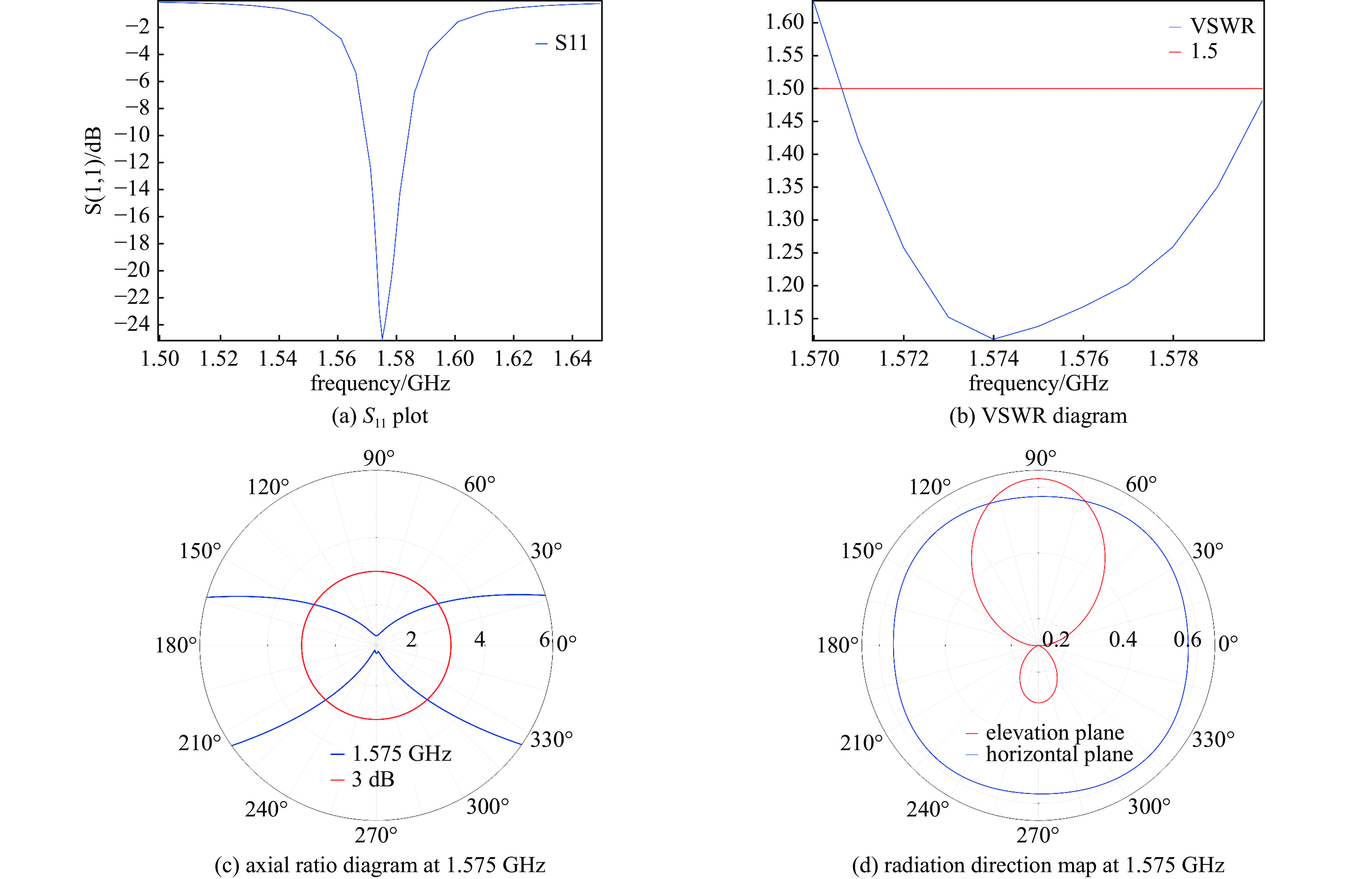
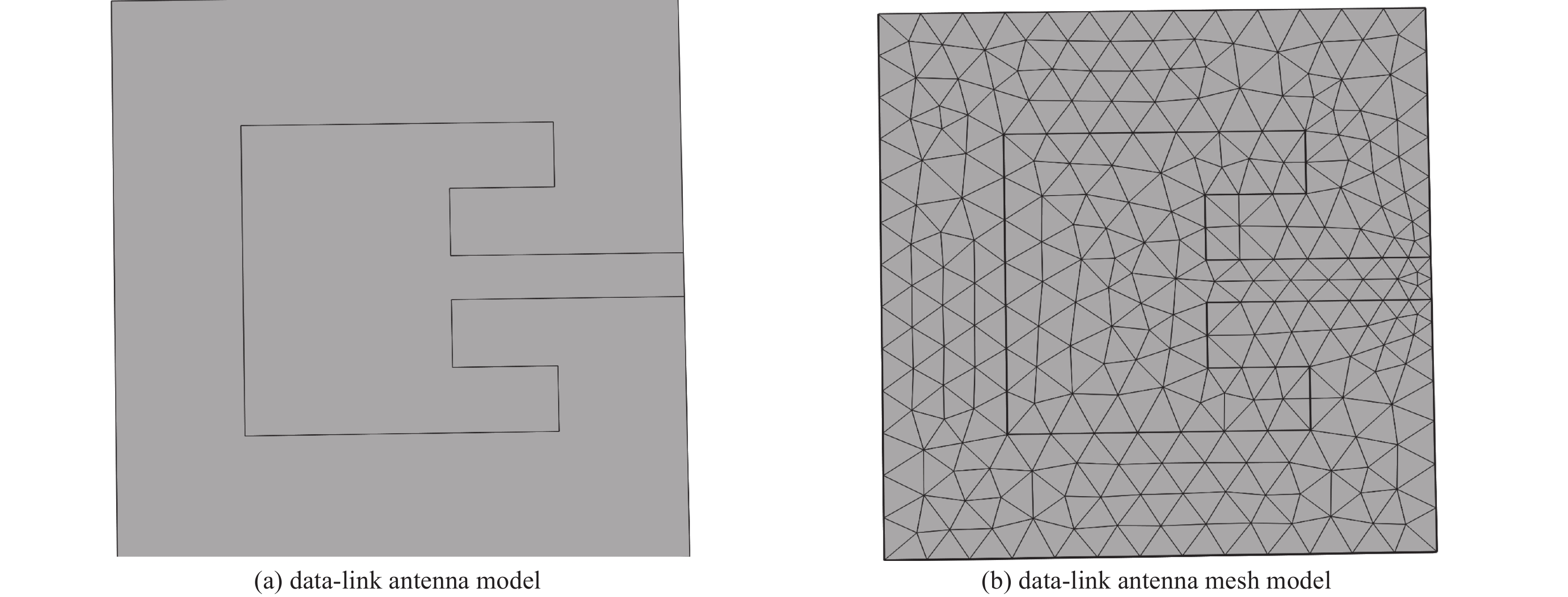
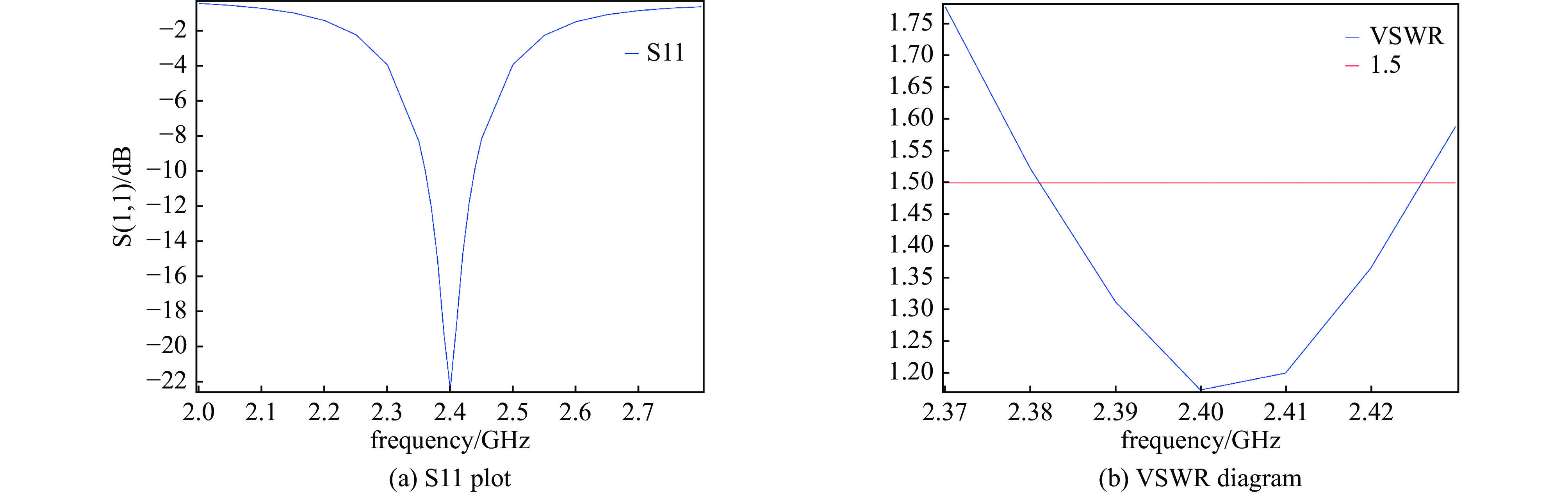
Simulation study of coupling response of aerial vehicle antennas under high power-microwave radiation
-
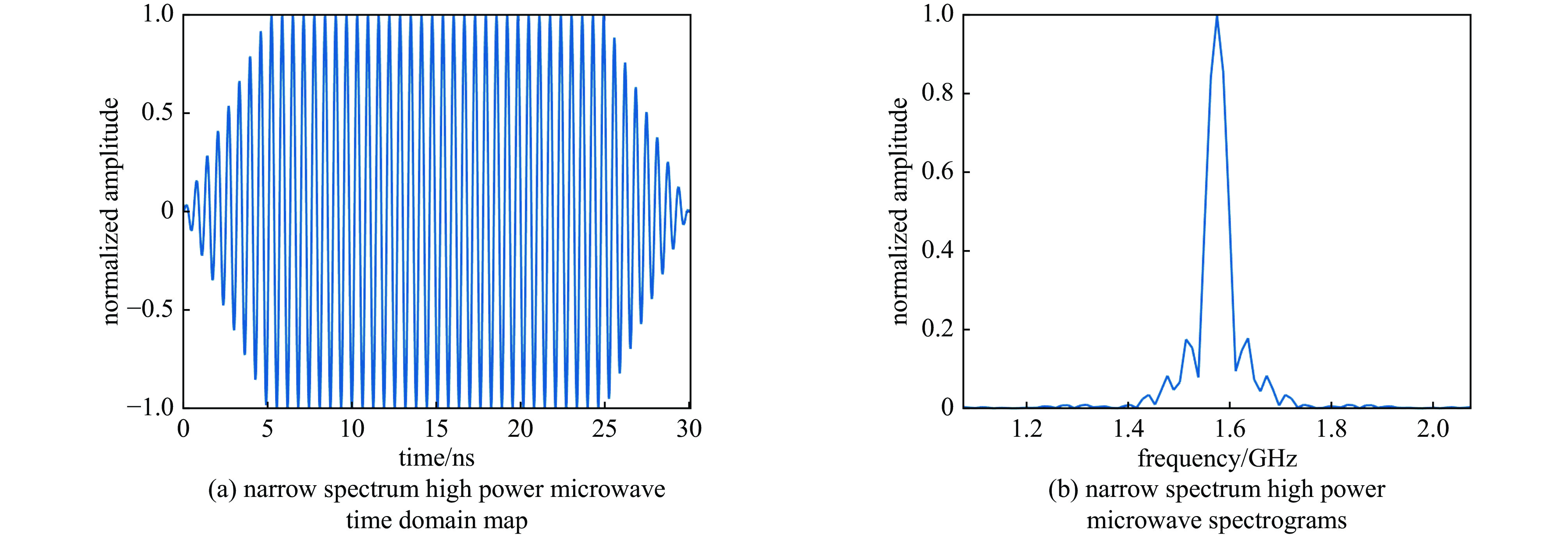
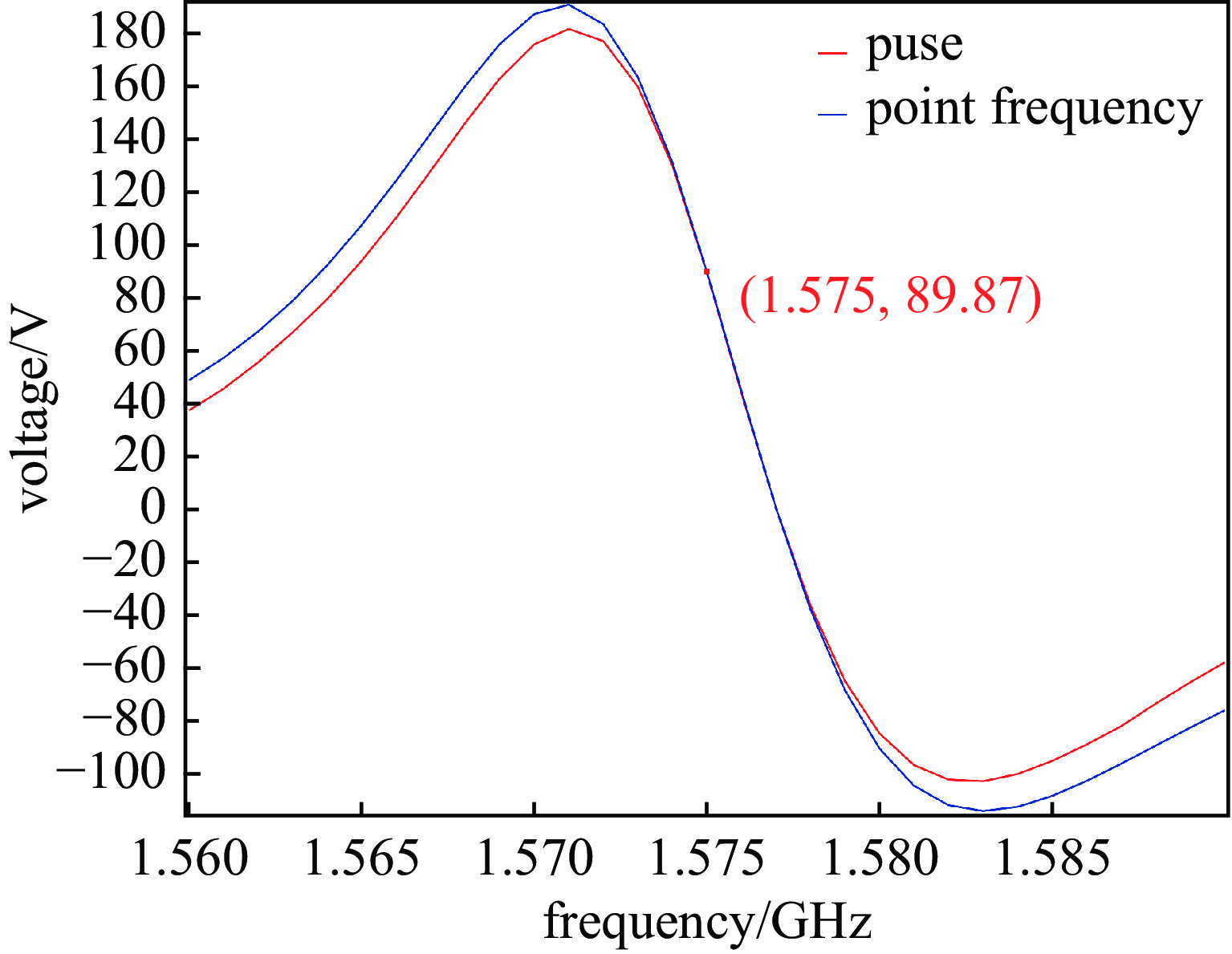
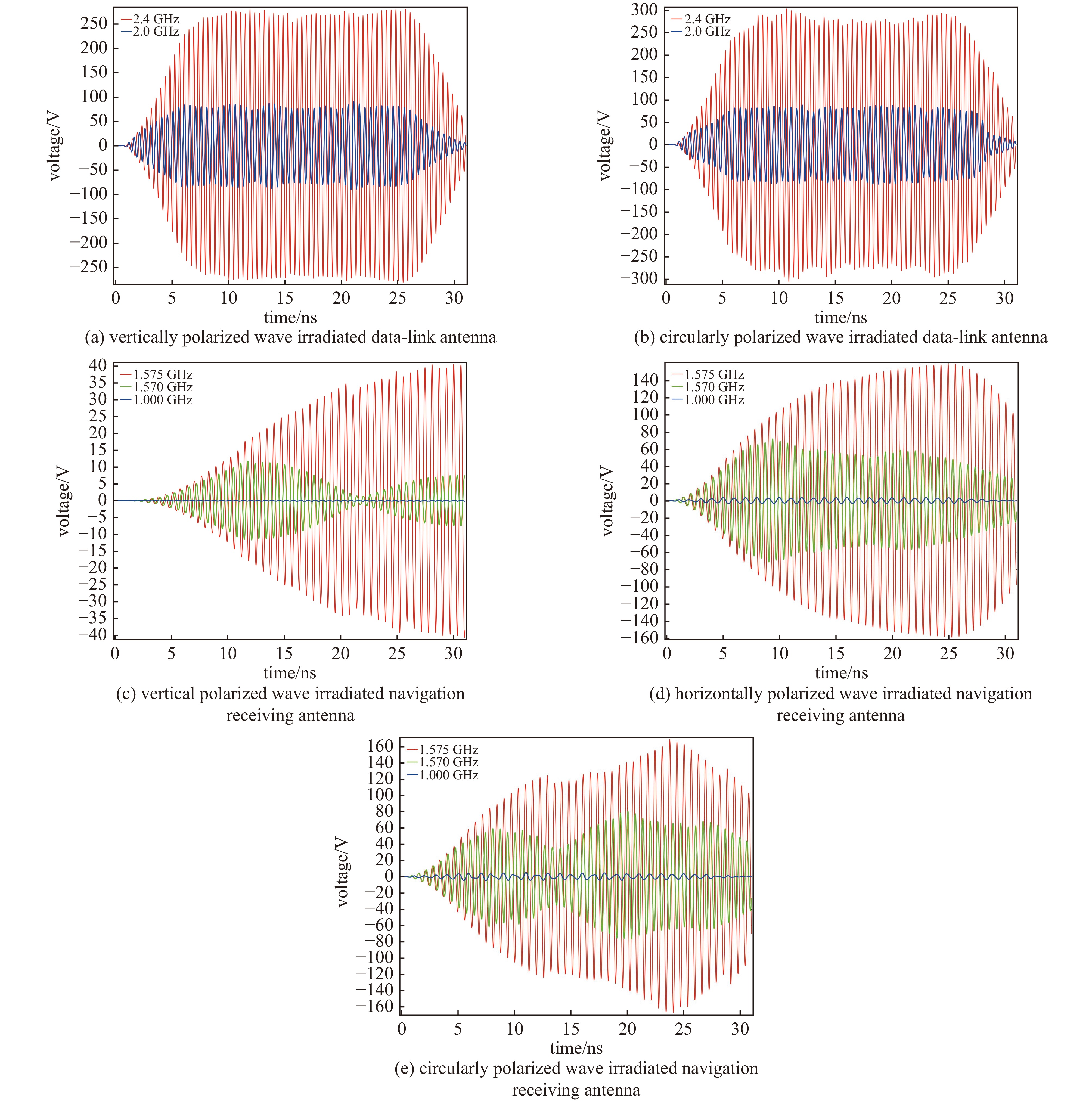
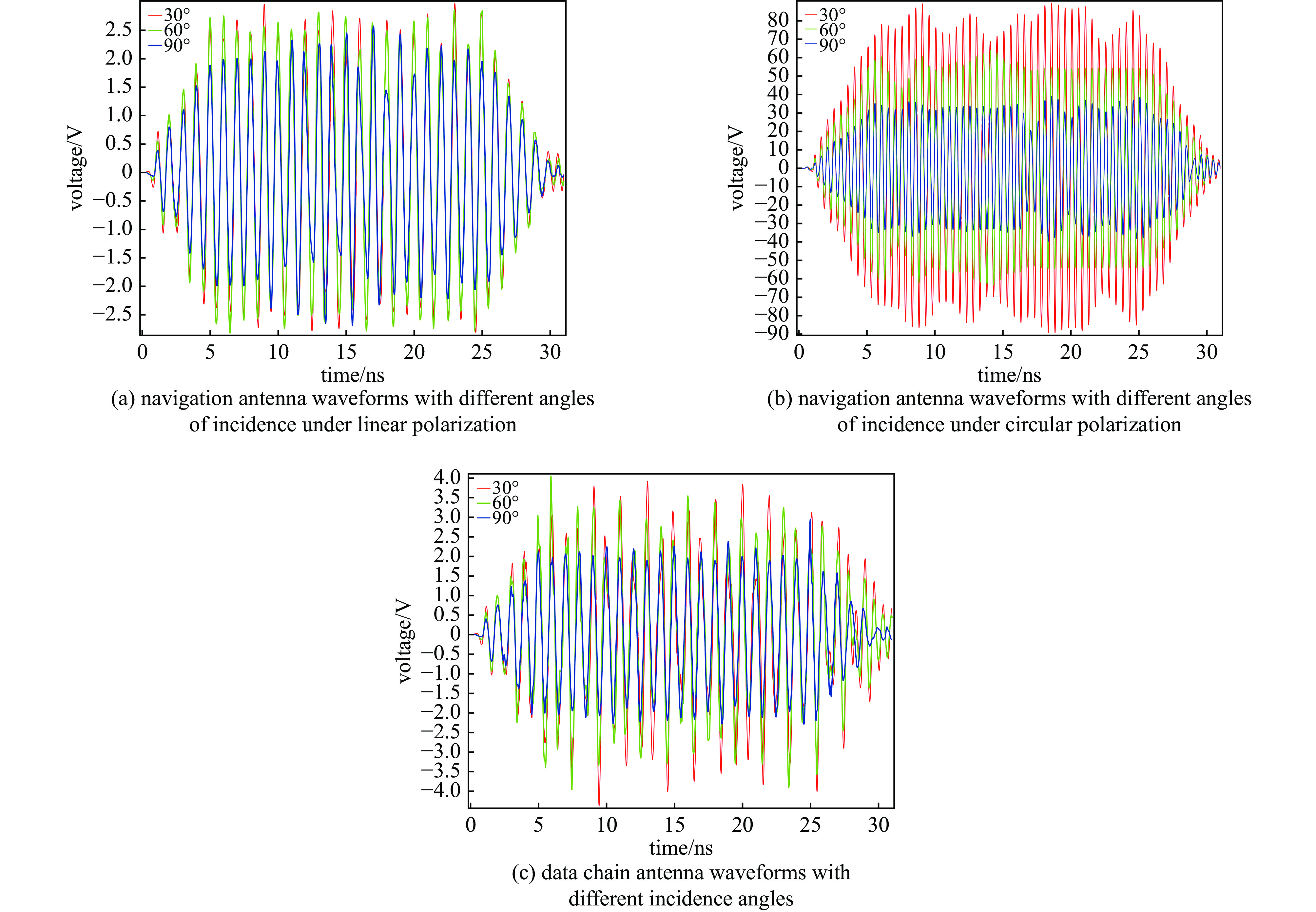
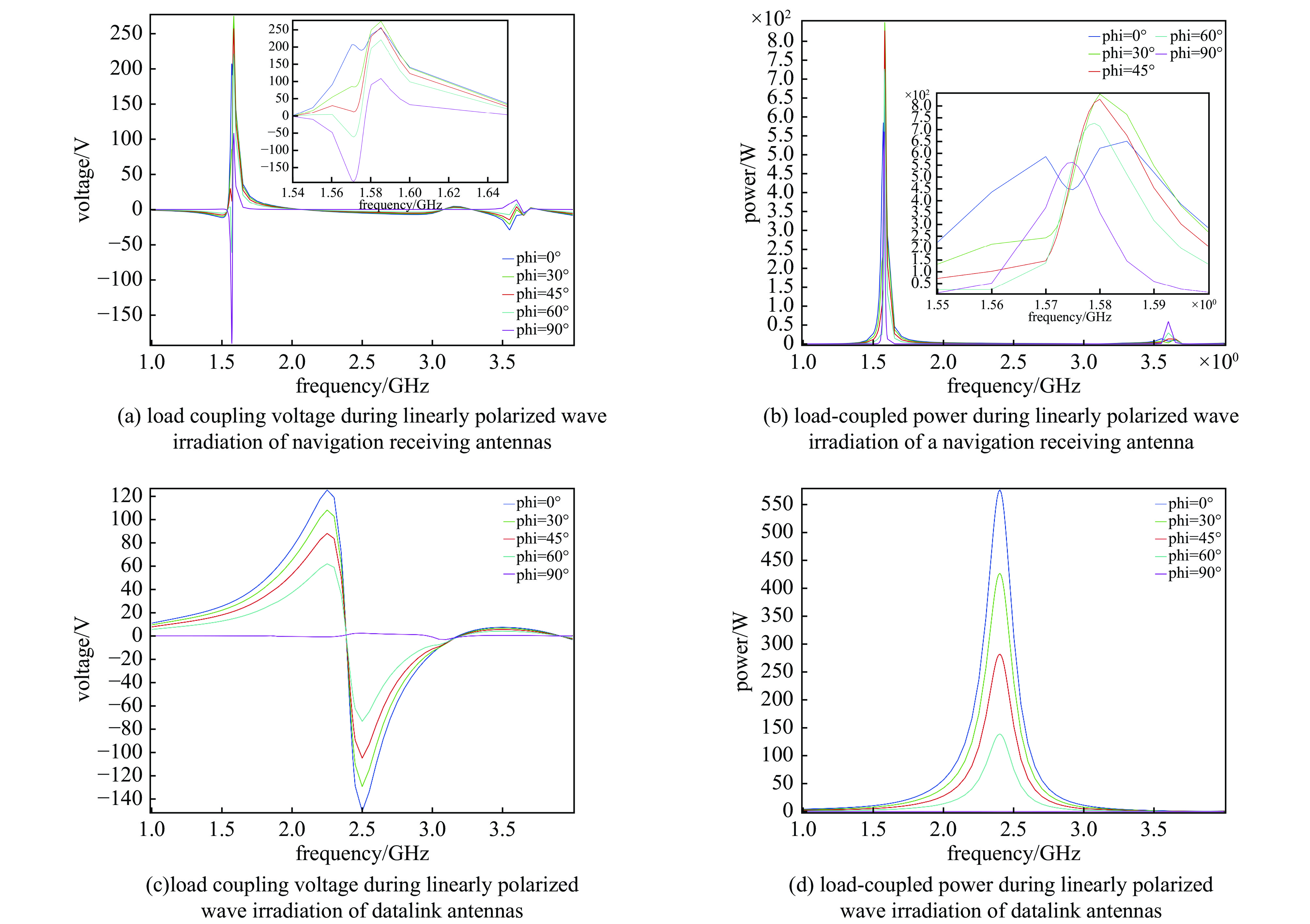
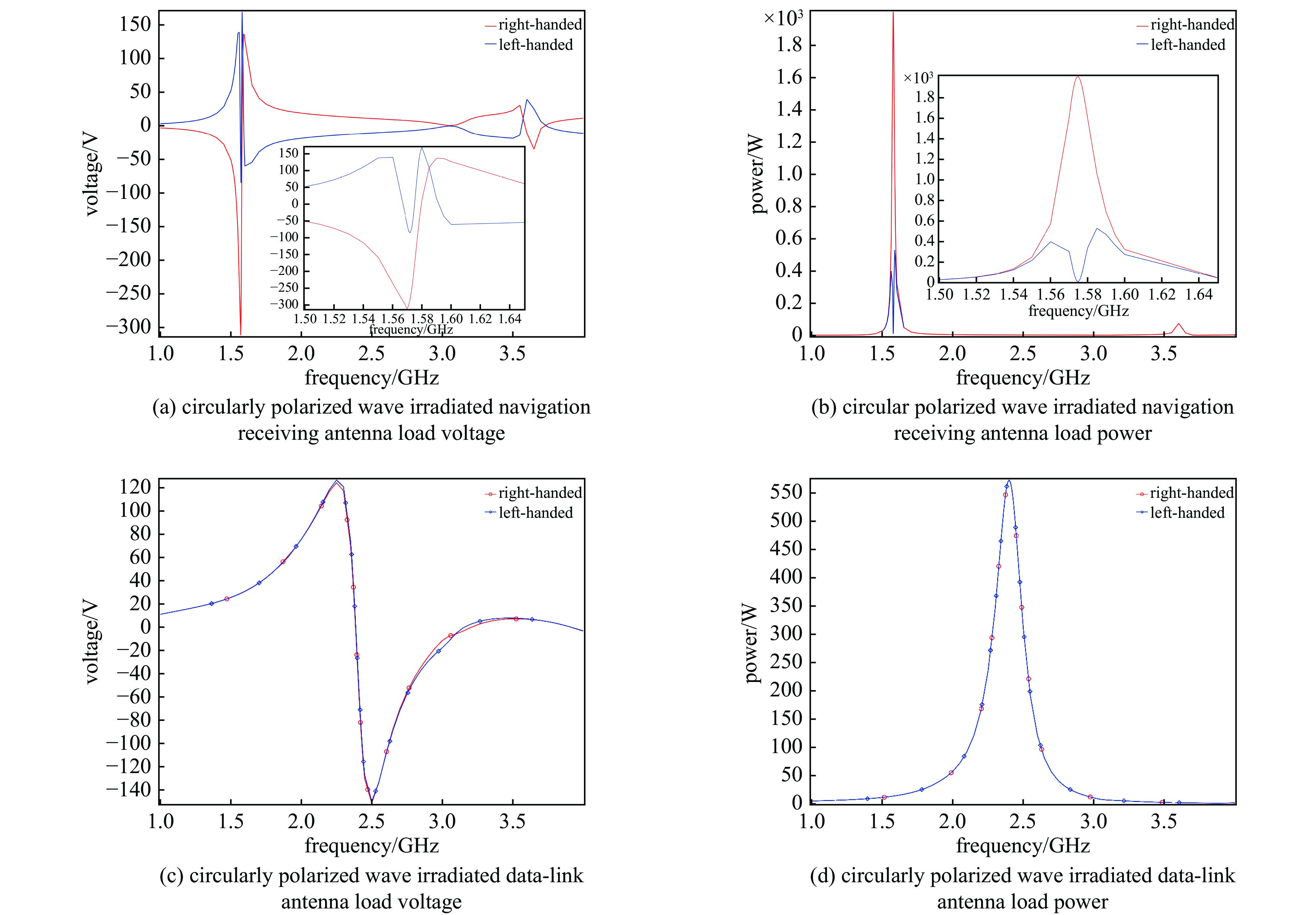
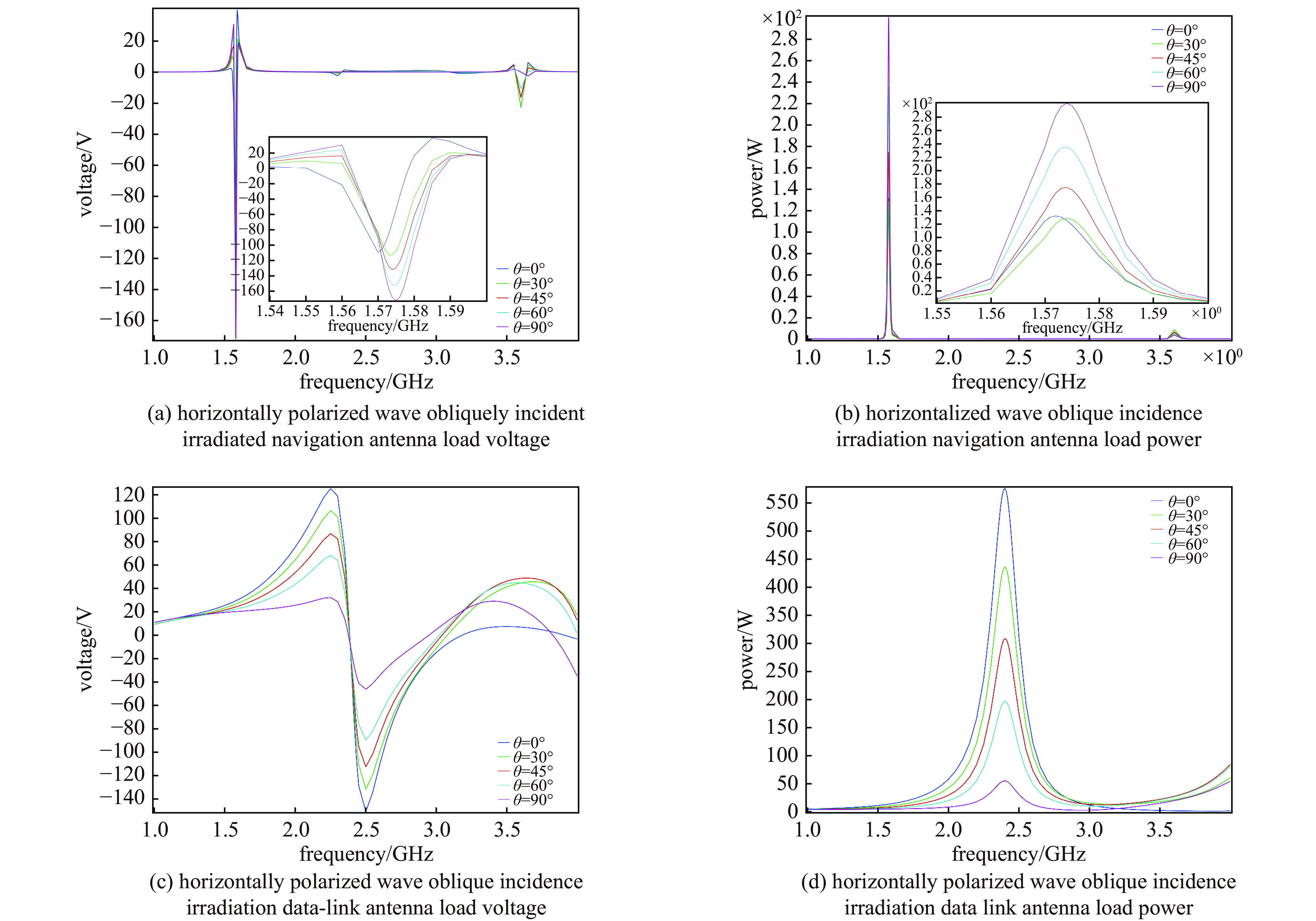
摘要: 无人机蜂群与低空经济的发展凸显了高功率微波(HPM)攻防技术的战略价值。本研究针对无人机导航天线和数据链天线,基于COMSOL构建三维电磁耦合模型,通过场-路协同仿真分析其在HPM辐照下的时频响应特性。结果表明:导航天线在带内及邻近频段无论线极化或圆极化激励,均出现上升沿展宽、下降沿“截断”等波形失真,因其等效为窄带移相网络,在“宽带”脉冲激励下引发强烈色散,导致时域波形畸变;而数据链天线在各类激励下波形保持完整,因其幅频与相频响应平坦,色散弱。频域结果显示,两类天线最大耦合电压偏移于中心频点,最大功率位于中心频点。导航天线对右旋圆极化响应最强,但频偏时出现左旋耦合增强现象;数据链天线对各类极化响应相近,呈极化不敏感性。研究认为,天线的极化类型与频率选择性通过内在色散机制主导HPM耦合过程,决定能量响应与波形完整性,建议构建“前端滤波—瞬态抑制—系统冗余”的多层级防护体系,提升无人机电磁韧性。本研究可为无人机的反制与防护提供一定提供理论支撑。Abstract:
Background The development of drone swarms and the low-altitude economy has highlighted the strategic importance of high-power microwave attack and defense technologies.Purpose This study aims to analyze the time-frequency response characteristics of drone navigation antennas and data link antennas under HPM irradiation.Methods A three-dimensional electromagnetic coupling model was constructed based on COMSOL, and field-circuit co-simulation was employed to investigate the antennas’ responses to HPM exposure across different polarization types and frequency bands.Results The results show that the navigation antenna, equivalent to a narrowband phase-shifting network, exhibits waveform distortions such as rising-edge broadening and falling-edge “truncation” under in-band and adjacent broadband pulse excitation due to strong dispersion. In contrast, the data link antenna maintains waveform integrity under various excitations owing to its flat amplitude-frequency and phase-frequency responses with weak dispersion. In the frequency domain, both antennas exhibit maximum coupled voltage at frequencies offset from the center, while the peak power occurs at the center frequency. The navigation antenna responds most strongly to right-hand circular polarization but shows enhanced left-hand coupling at frequency offsets. The data link antenna demonstrates similar responses to all polarizations, indicating polarization insensitivity.Conclusions The polarization type and frequency selectivity of antennas dominate the HPM coupling process through intrinsic dispersion mechanisms, determining energy response and waveform integrity. A multi-level protection system incorporating “front-end filtering—transient suppression—system redundancy” is recommended to enhance the electromagnetic resilience of drones. This study provides theoretical support for the countermeasures and protection of drones. -
表 1 不同距离对应的场强
Table 1. Field strength corresponding to different distances
launch power/GW antenna gain/dB distance/km E/(kV·m−1) 3 40 1 30 3 40 2 15 3 40 3 10 3 40 4 7.5 3 40 5 6 -
[1] 令钧溥, 王蕾, 皮明瑶, 等. 美国反无人机高功率微波技术研究现状及启示[J]. 国防科技, 2023, 44(3): 74-80Ling Junpu, Wang Lei, Pi Mingyao, et al. High-power microwave technology countering UAVs in the United States: research status and implications[J]. National Defense Technology, 2023, 44(3): 74-80 [2] 张颜颜, 陈宏, 鄢振麟, 等. 高功率微波反无人机技术[J]. 电子信息对抗技术, 2020, 35(4): 39-43Zhang Yanyan, Chen Hong, Yan Zhenlin, et al. The technology of high-power microwave anti-bee swarm drone[J]. Electronic Information Warfare Technology, 2020, 35(4): 39-43 [3] 金祖升, 施佳林, 李建轩, 等. 微波接收前端高功率微波效应实验研究[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 49(4): 146-152Jin Zusheng, Shi Jialin, Li Jianxuan, et al. Experimental study of high power microwave effects on a microwave receiver front-end[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2022, 49(4): 146-152 [4] 章勇华, 黄文华, 李平, 等. 集成电路HPM损伤机理分析[J]. 现代应用物理, 2023, 14: 020501Zhang Yonghua, Huang Wenhua, Li Ping, et al. Analysis of high power microwave damage mechanism in integrated circuits[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2023, 14: 020501 [5] 闫涛, 李平. 高电子迁移率晶体管放大器高功率微波损伤机理[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2016, 28: 103002Yan Tao, Li Ping. High power microwave damage mechanism on high electron mobility transistor amplifier[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2016, 28: 103002 [6] 袁月乾, 陈自东, 马弘舸, 等. PIN限幅器的高功率微波单脉冲效应研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2020, 32: 063003Yuan Yueqian, Chen Zidong, Ma Hongge, et al. High power microwave effect of PIN limiter induced by single pulse[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2020, 32: 063003 [7] 陈自东, 秦风, 赵景涛, 等. 高功率微波作用下限幅器尖峰泄漏特性[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2020, 32: 103014Chen Zidong, Qin Feng, Zhao Jingtao, et al. Spike leakage characteristic of limiter irradiated by high power microwave[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2020, 32: 103014 [8] 赵敏, 陈亚洲, 周星, 等. 无人机机载天线高功率微波耦合响应研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2024, 36: 033006Zhao Min, Chen Yazhou, Zhou Xing, et al. Coupling response of unmanned aerial vehicle antennas under high-power microwave radiation[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2024, 36: 033006 [9] 胡欣, 杨江平, 孟藏珍, 等. UWB-HPM脉冲辐照下抛物面天线耦合特性研究[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2022, 43(11): 141-146Hu Xin, Yang Jiangping, Meng Cangzhen, et al. Study on coupling characteristics of parabolic antenna under UWB-HPM pulse irradiation[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2022, 43(11): 141-146 [10] 李磊, 张昕. 微带天线对高功率电磁脉冲响应的时域分析[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2014, 35(8): 1015-1021Li Lei, Zhang Xin. Time domain analysis of the response of the microstrip antenna to a high power electromagnetic pulse[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2014, 35(8): 1015-1021 [11] 段泽民, 朱博, 仇善良, 等. 螺旋天线电磁脉冲响应特性研究[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2018, 37(1): 87-90,95Duan Zemin, Zhu Bo, Qiu Shanliang, et al. Research on response characteristics of helical antenna exposed to electromagnetic pulse[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2018, 37(1): 87-90,95 [12] 胡晓, 邱扬, 田锦. 车载单极天线的电磁脉冲响应特性[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2018, 30: 033201Hu Xiao, Qiu Yang, Tian Jin. Response characteristics of vehicle monopole antenna exposed to electromagnetic pulse[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2018, 30: 033201 [13] 范宇清, 程二威, 魏明, 等. 高功率微波弹对GNSS接收机毁伤效果分析[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2020, 42(1): 37-44Fan Yuqing, Cheng Erwei, Wei Ming, et al. Analysis of damage effect of high-power microwave bomb on GNSS receiver[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(1): 37-44 [14] 王哲, 贺宇, 武丹丹, 等. 雷达接收机高功率微波效应试验研究[J]. 通信技术, 2019, 52(1): 56-61Wang Zhe, He Yu, Wu Dandan, et al. Experimental exploration on high-power microwave effect of radar receiver[J]. Communications Technology, 2019, 52(1): 56-61 [15] 沈衍, 王玉明, 陈亚洲. 无人机载SAR高功率微波效应仿真方法[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2024, 46(6): 131-140Shen Yan, Wang Yuming, Chen Yazhou. Simulation method of high-power microwave effect for UAV′s SAR[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2024, 46(6): 131-140 [16] 李巍, 李明典, 刘斌, 等. 高功率微波对引信射频前端的干扰与防护研究[J]. 航空兵器, 2022, 29(5): 100-106Li Wei, Li Mingdian, Liu Bin, et al. Research on the interference and protection of high power microwave to RF front-end of Fuze[J]. Aero Weaponry, 2022, 29(5): 100-106 [17] 陈凯柏, 高敏, 周晓东, 等. 调频连续波引信高功率微波前门耦合效应研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2020, 41(5): 881-889Chen Kaibai, Gao Min, Zhou Xiaodong, et al. Research on coupling effect of high-power microwave front-gate in FMCW Fuze[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2020, 41(5): 881-889 [18] 韩曹政, 王武斌, 赵伟, 等. 北斗/GPS导航系统抗高功率微波防护设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2024, 36: 123001Han Caozheng, Wang Wubin, Zhao Wei, et al. Protection design of BDS/GPS to resist high power microwave[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2024, 36: 123001 [19] 秦洪才, 袁成卫, 宁辉, 等. 高功率平板波导螺旋阵列天线设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33: 023002Qin Hongcai, Yuan Chengwei, Ning Hui, et al. Design of high power helical array antenna fed from planar waveguide[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 023002 [20] 孔歌星, 李相强, 张健穹, 等. X波段高功率宽频带双螺旋反射阵列天线的设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2019, 31: 093001Kong Gexing, Li Xiangqiang, Zhang Jianqiong, et al. Design of X-band high power wideband dual-helical reflectarray antenna[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2019, 31: 093001 -




 下载:
下载: