Influence of space-charge-effect on beam quality in the low-energy superconducting Linac
-
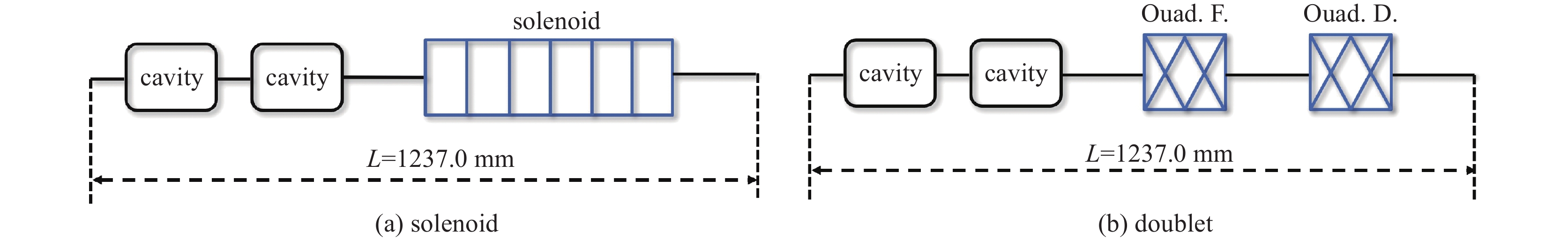
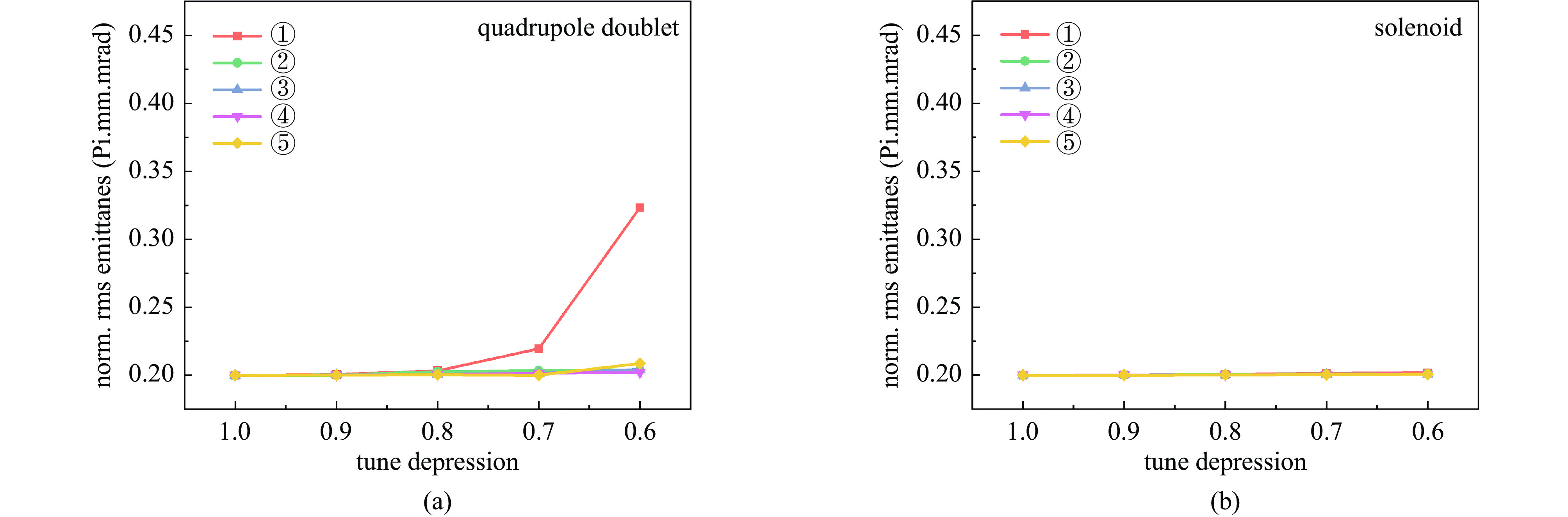
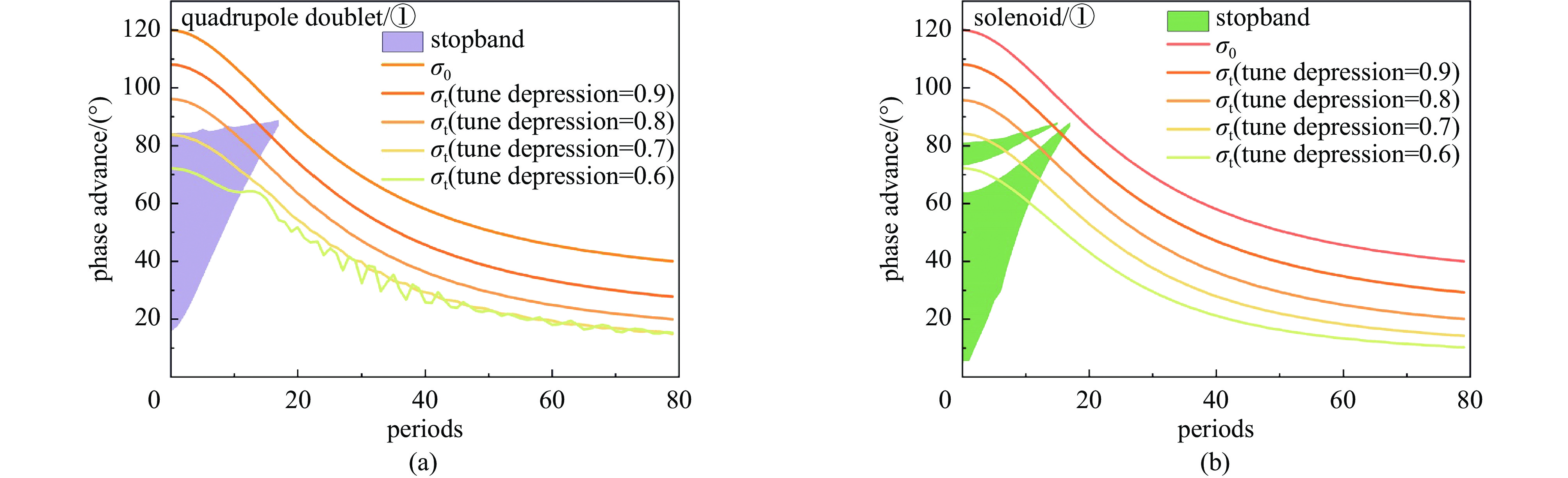
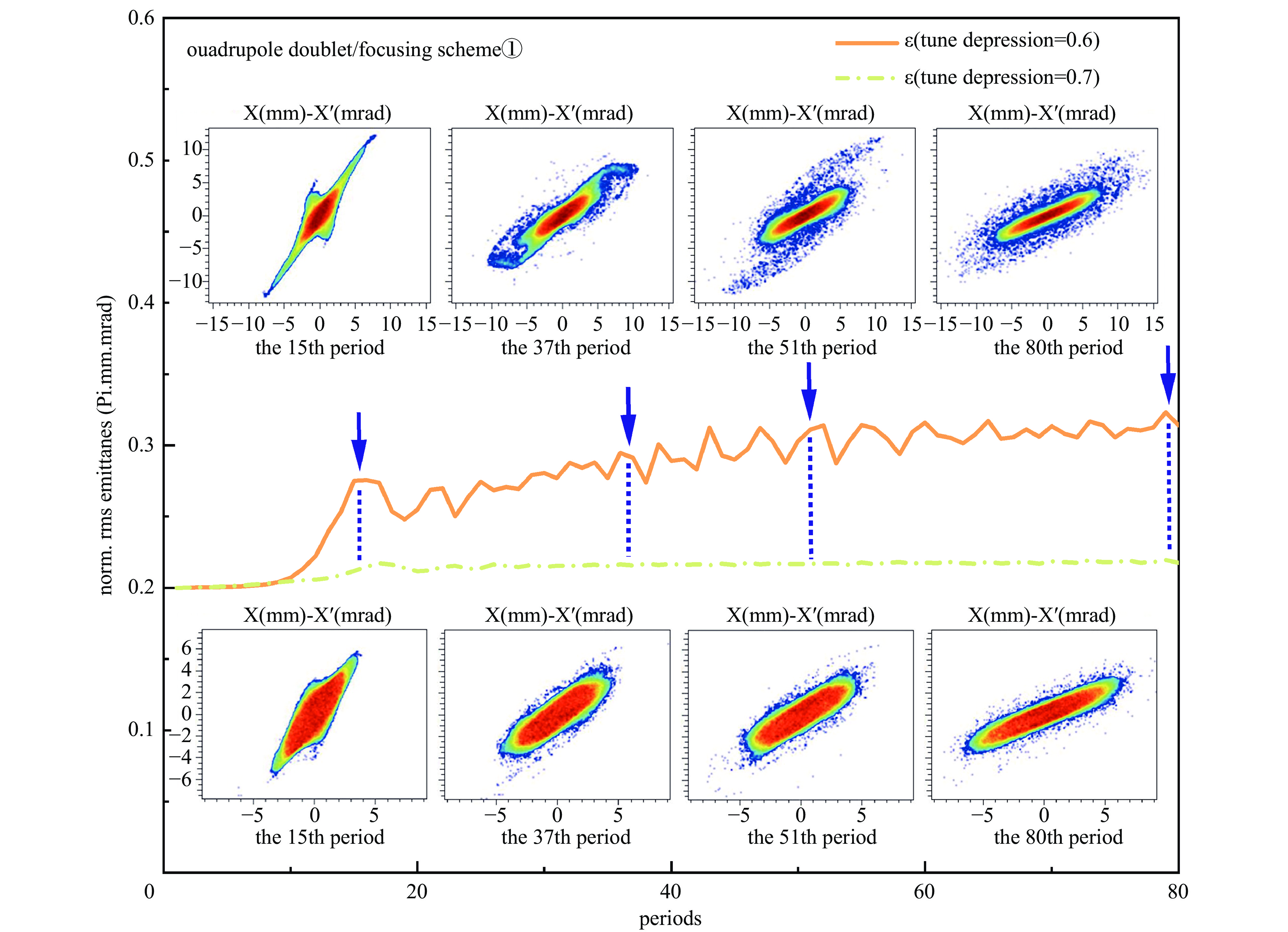
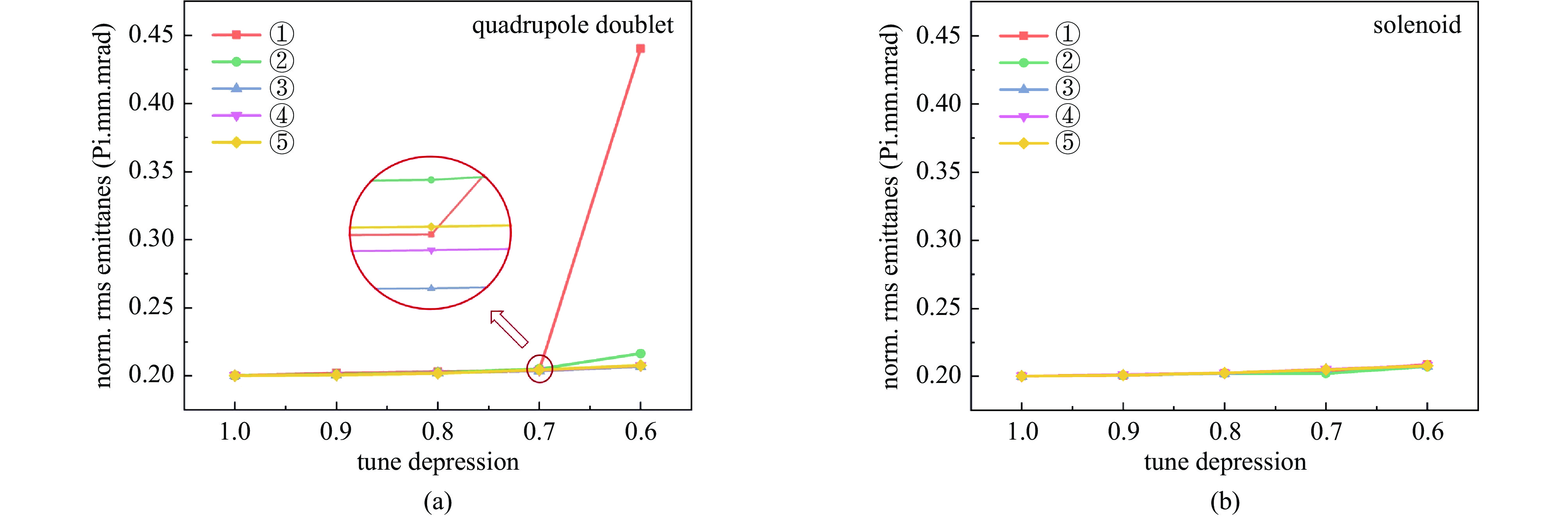
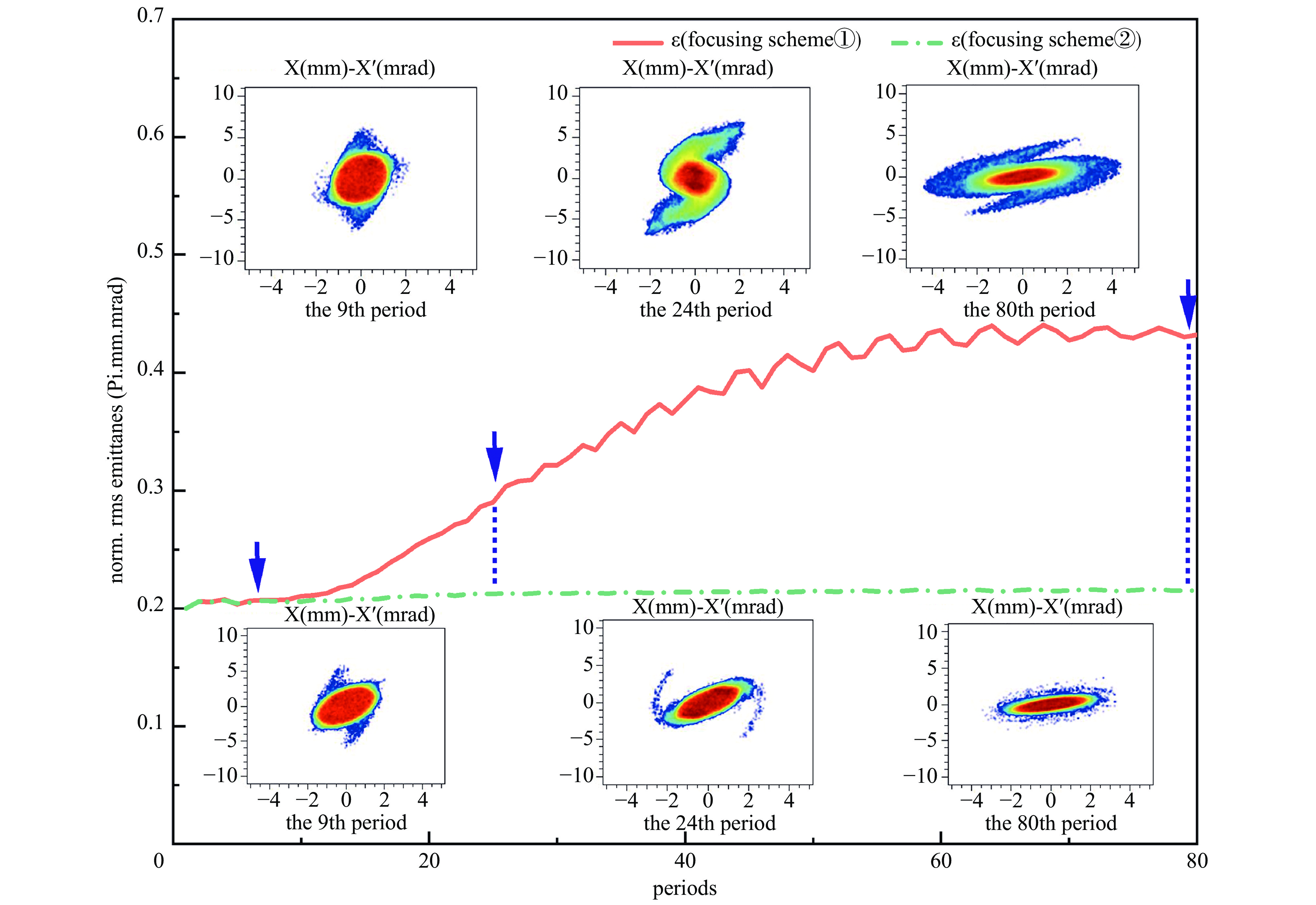
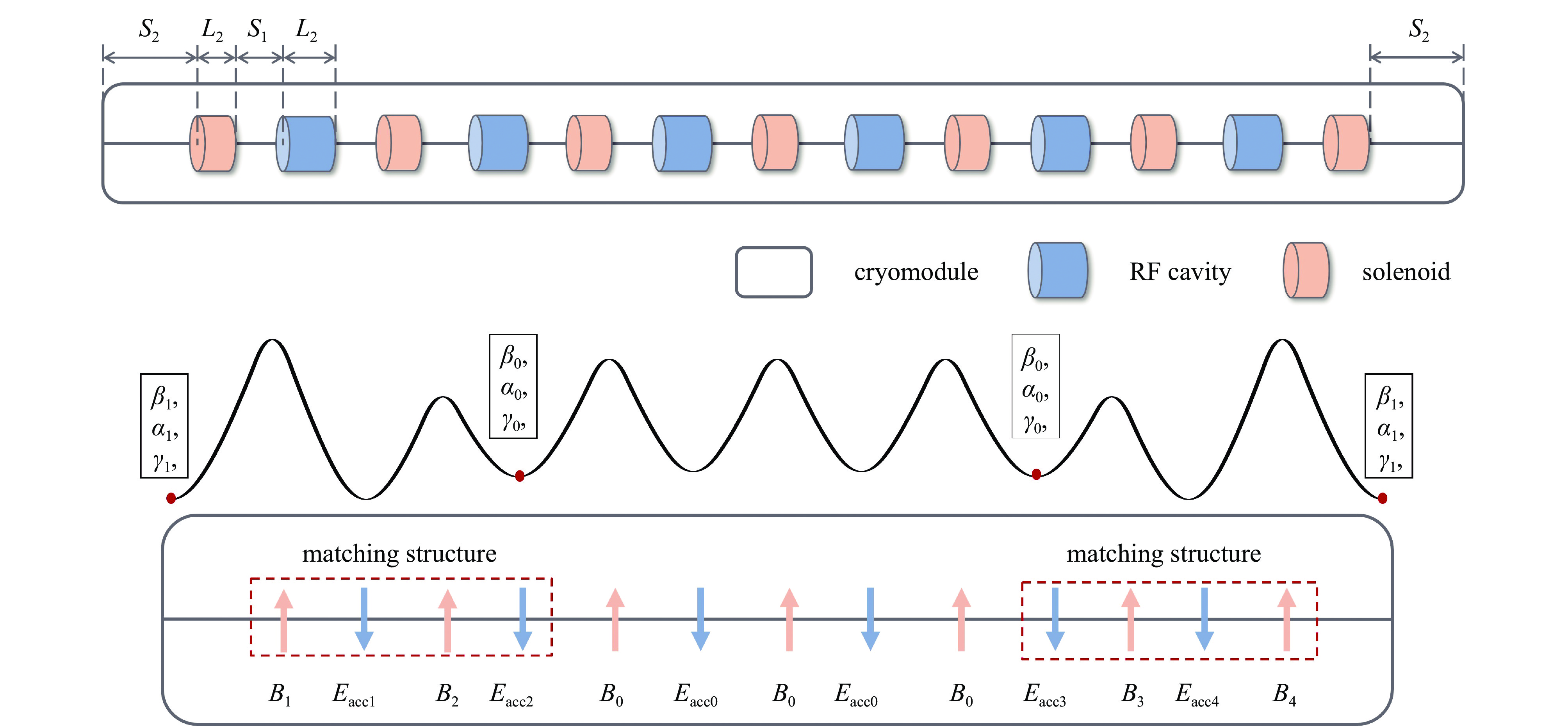
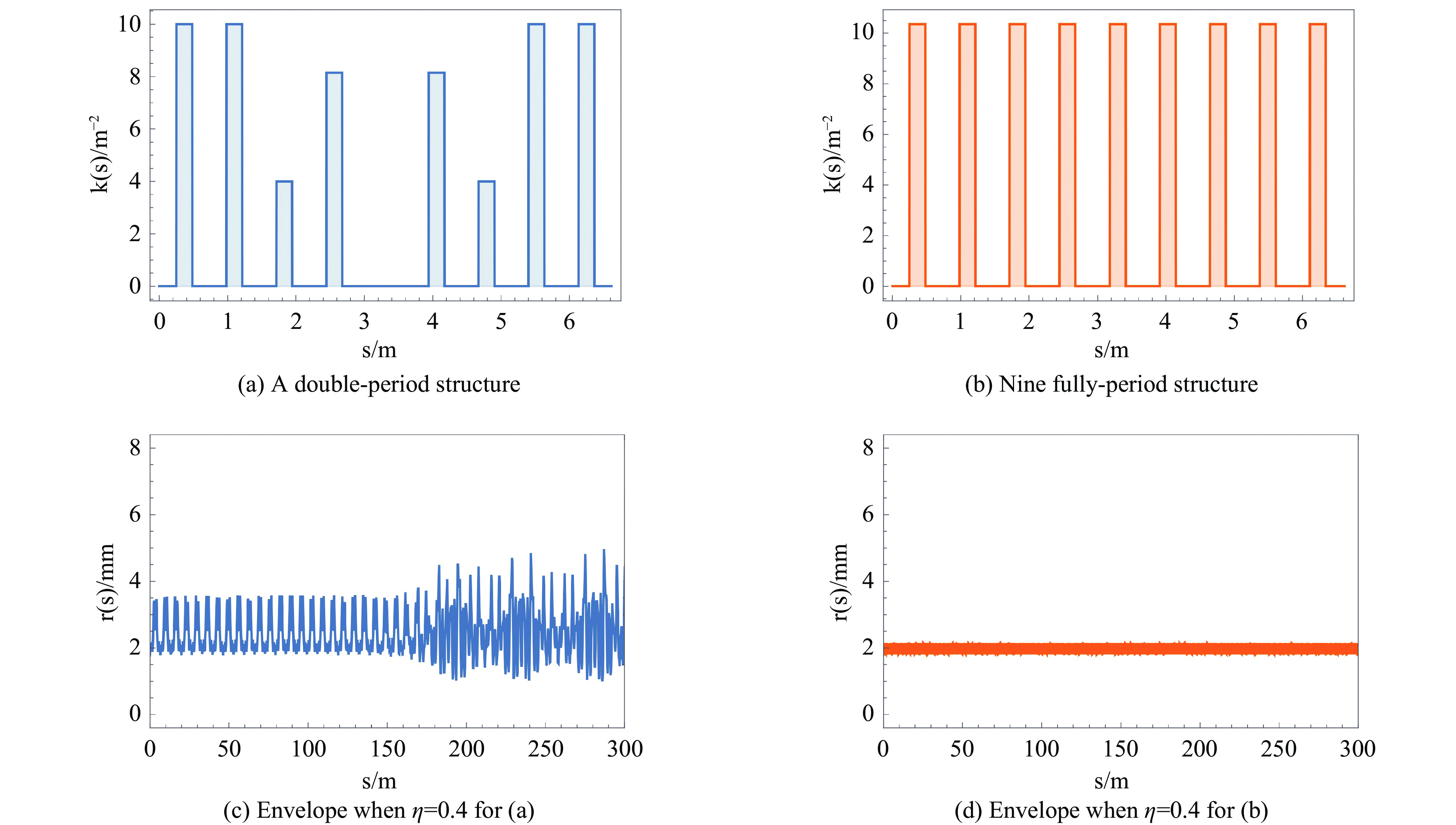
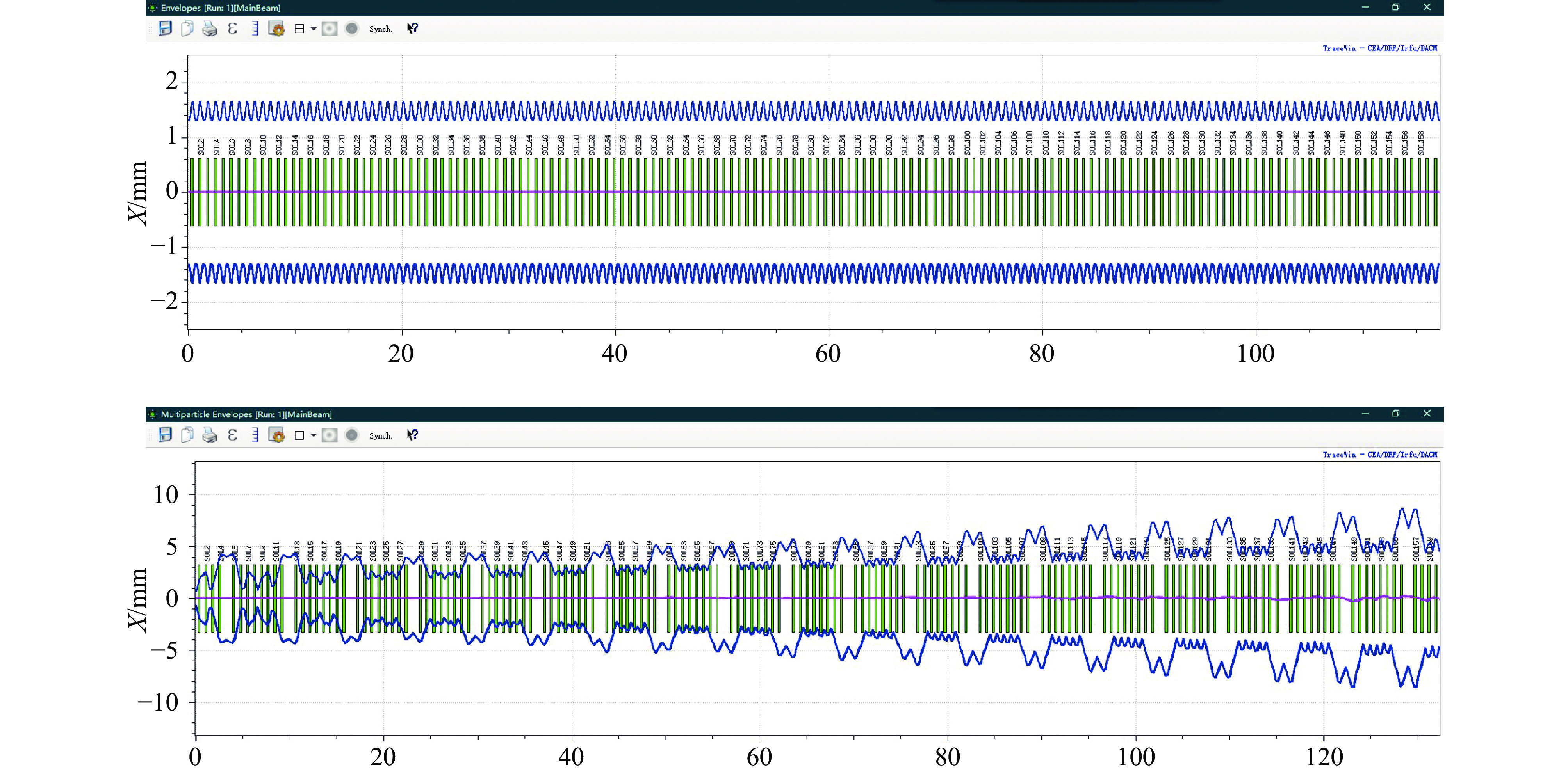
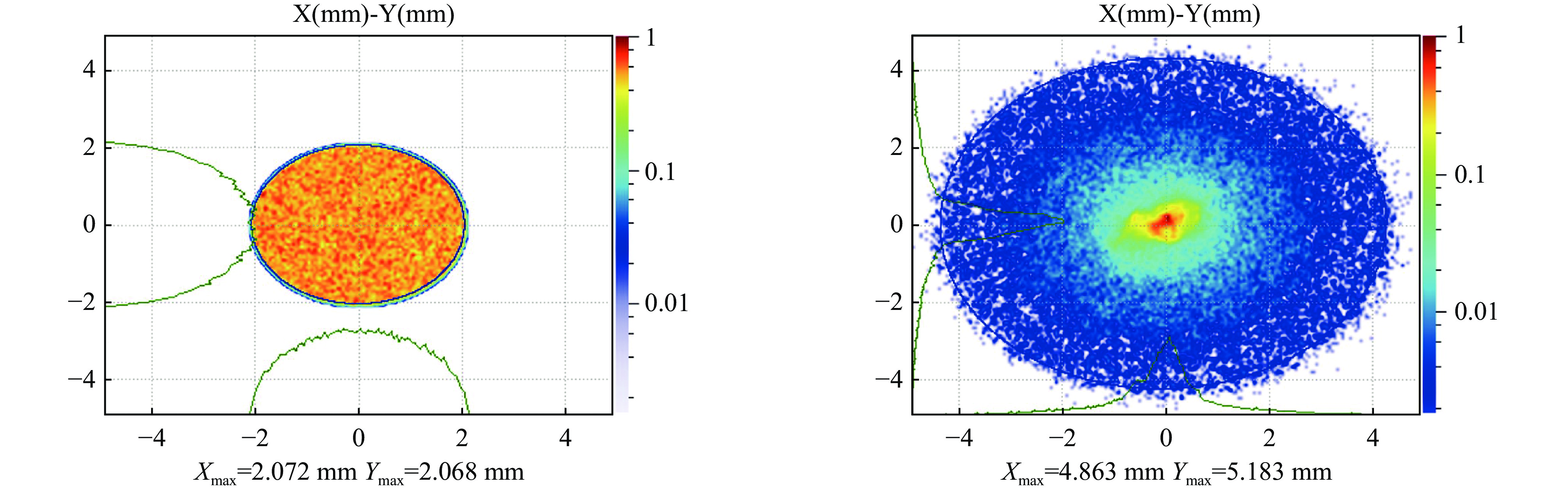
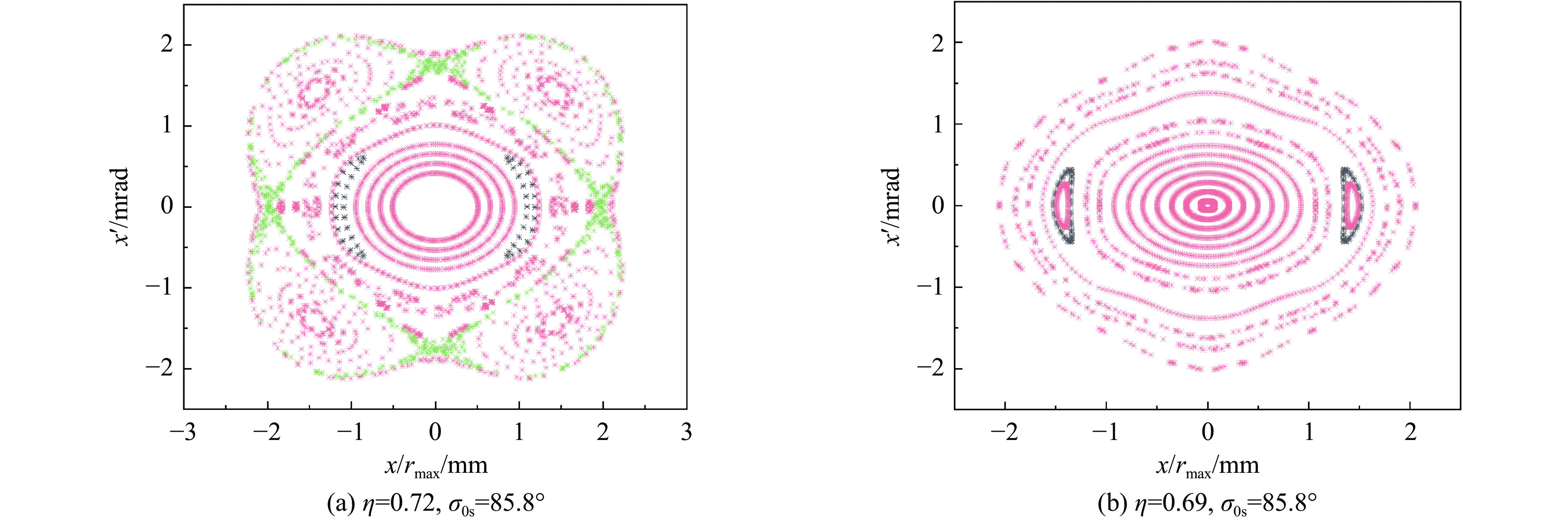
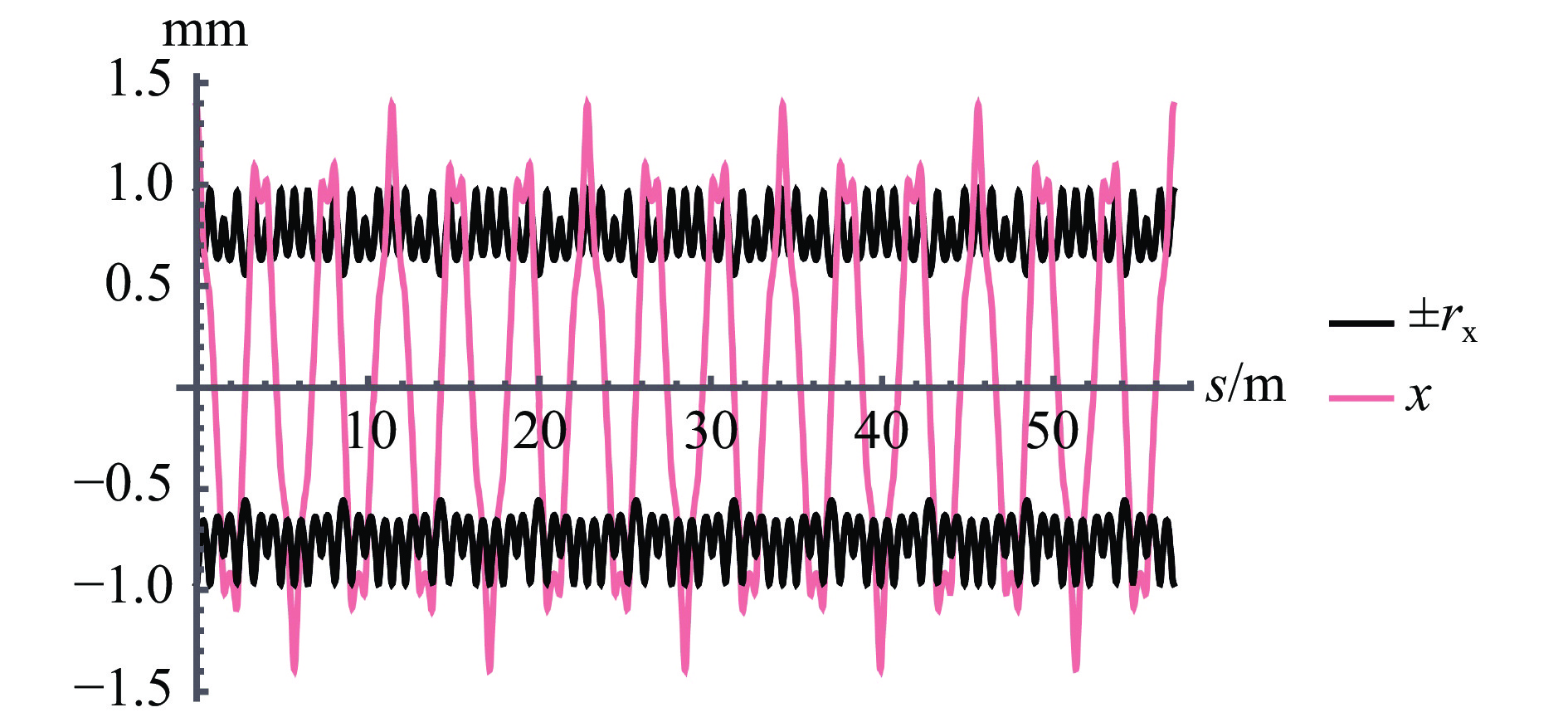
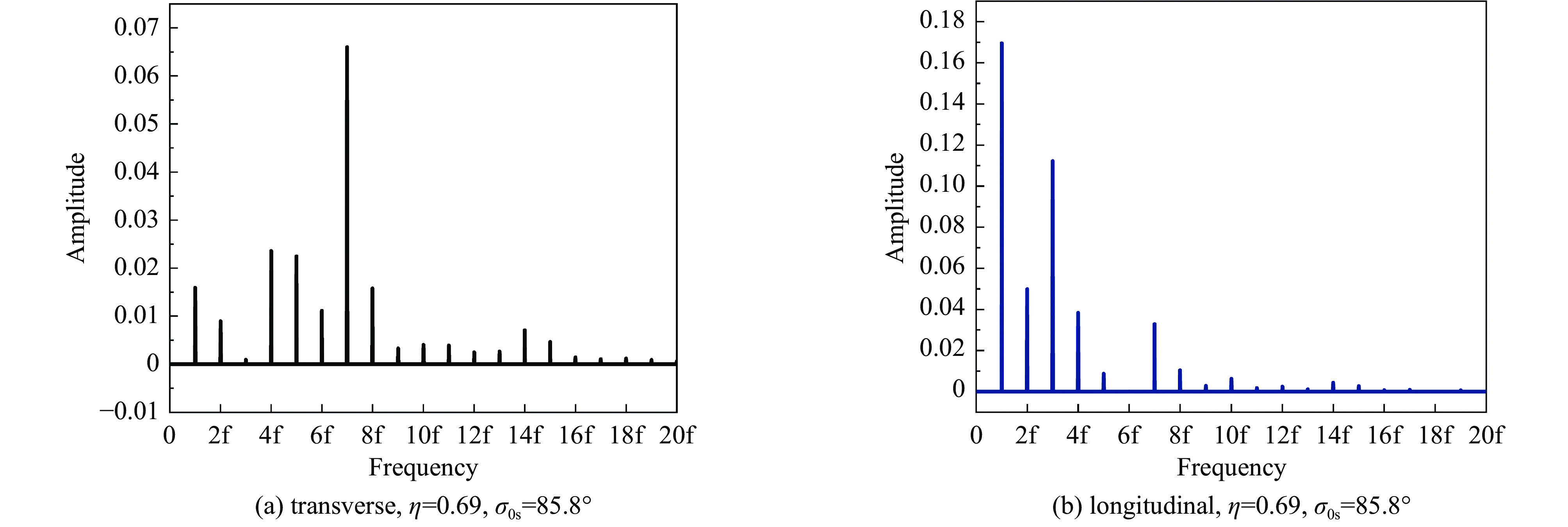
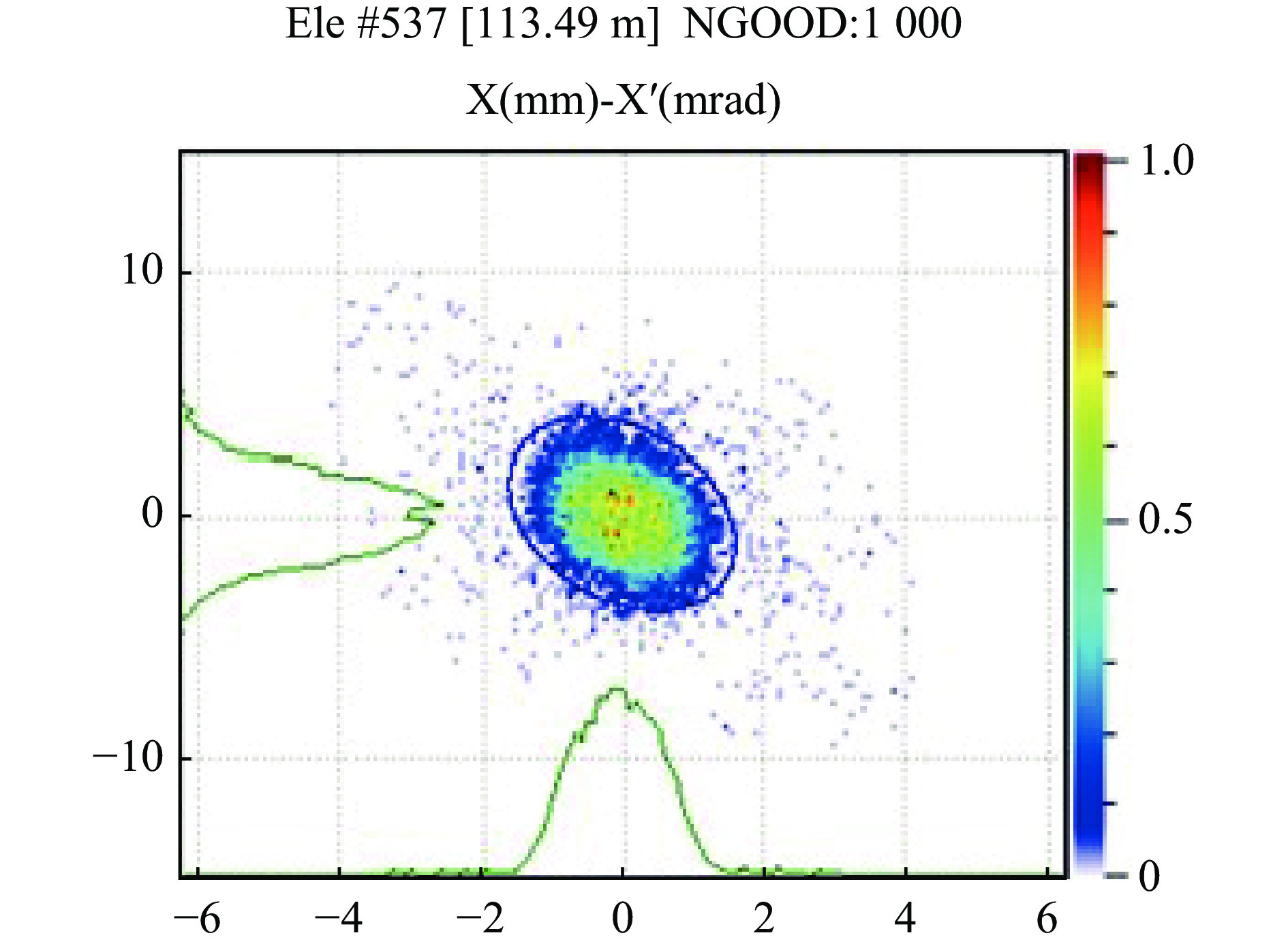
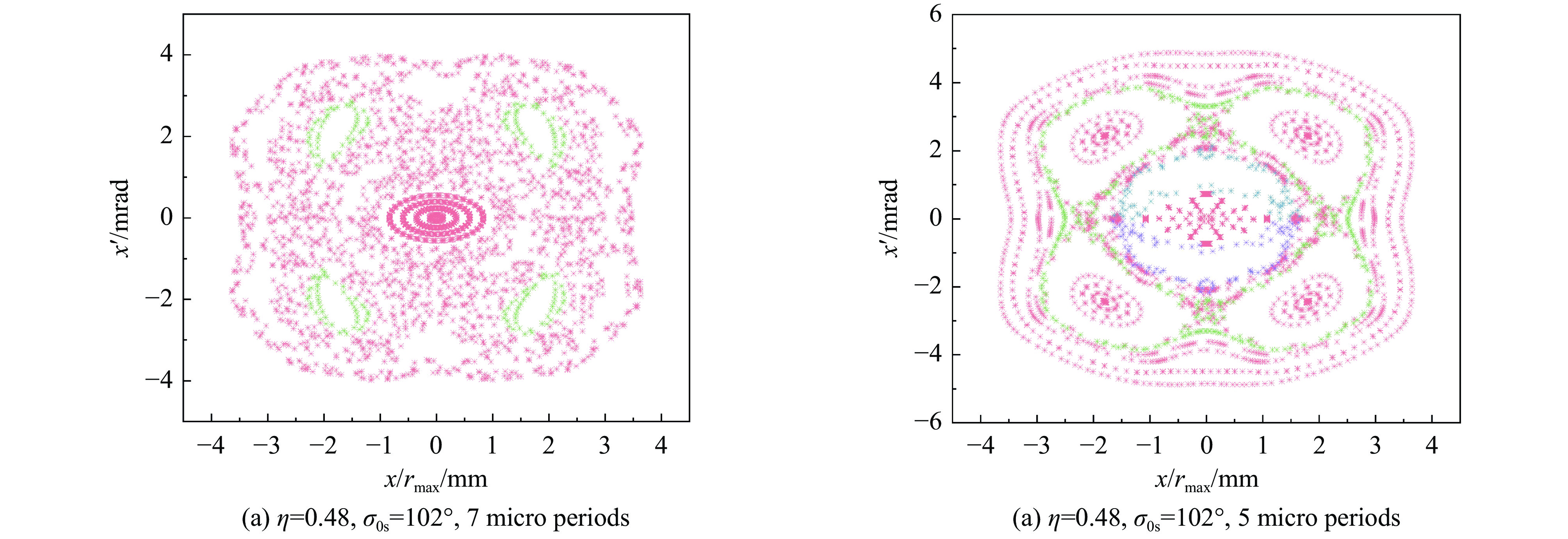
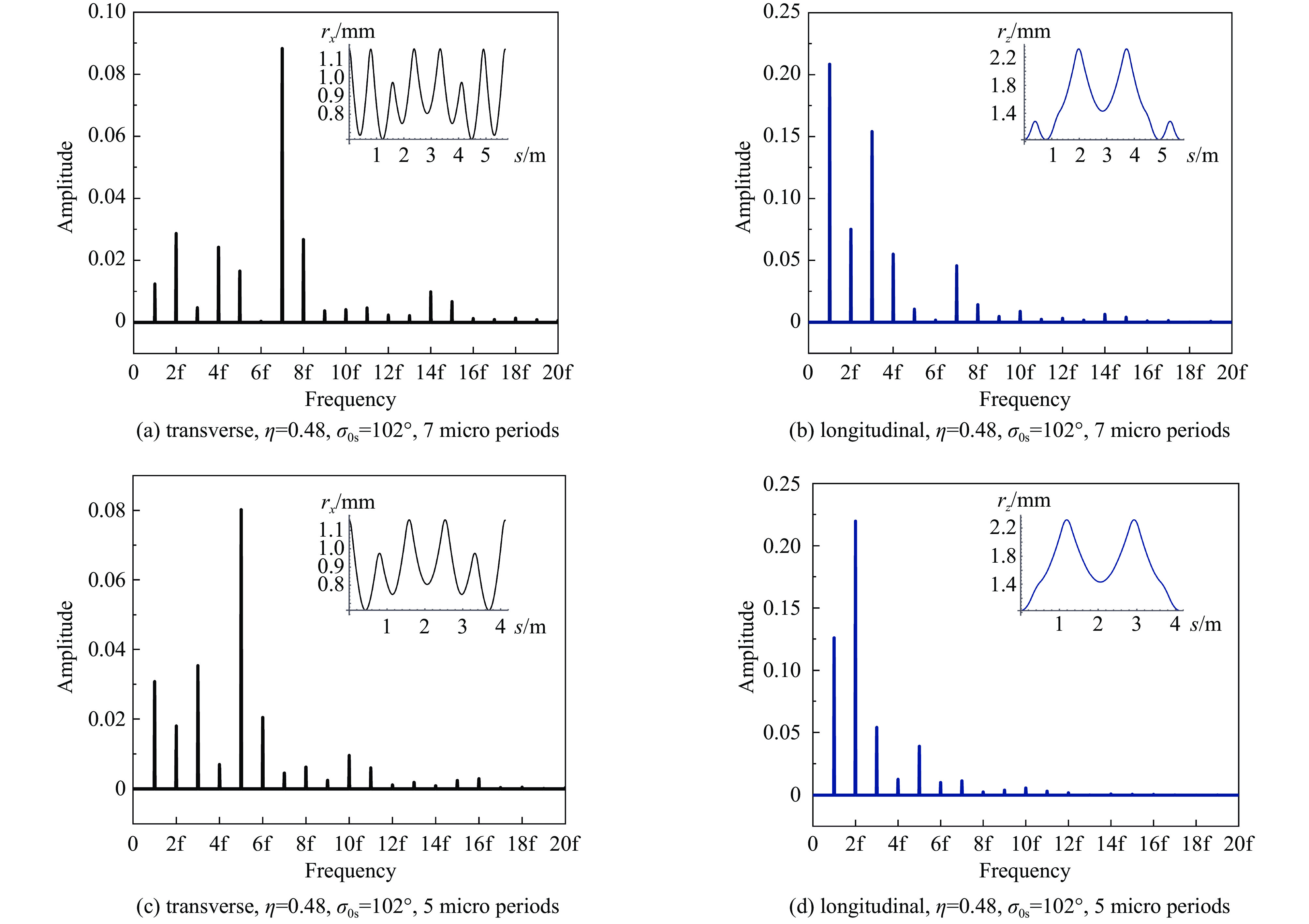
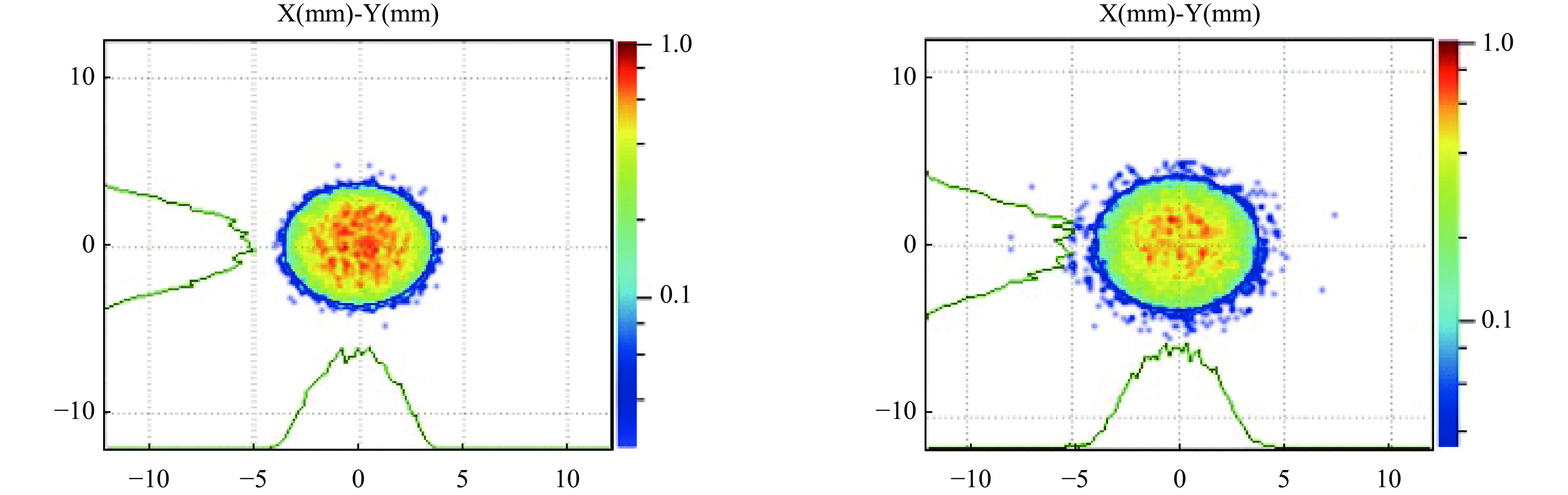
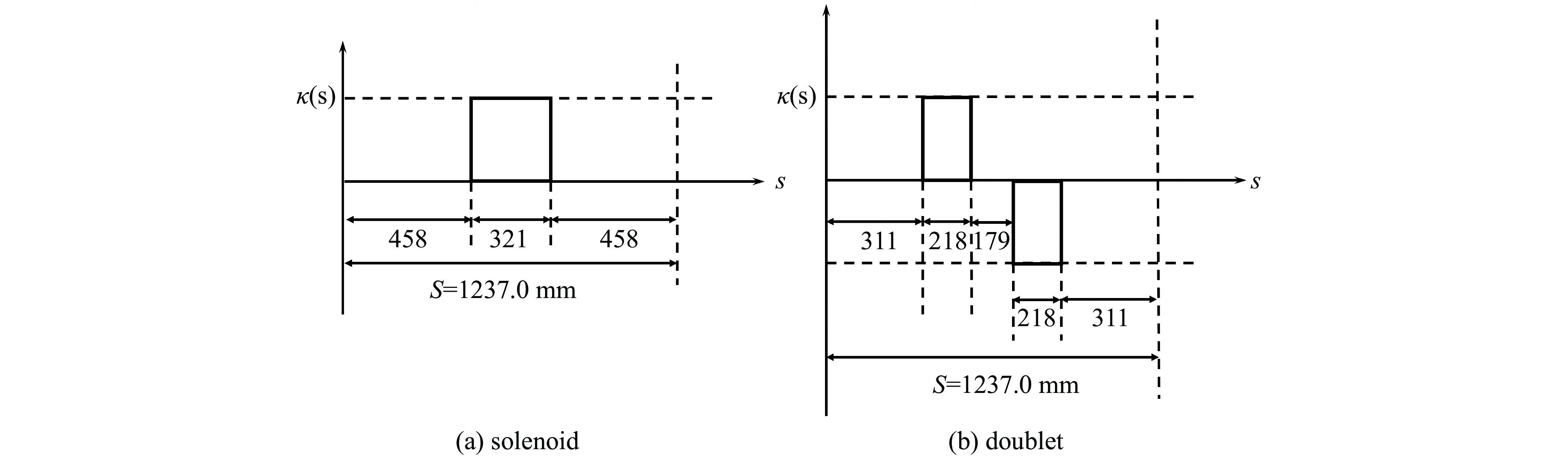
摘要: 本文通过理论建模与数值模拟相结合,系统探究了在低能超导质子直线加速器内,加速过程中聚焦参数动态演化对空间电荷主导型包络不稳定性的影响机制,创新性地揭示了低能段双周期聚焦结构与束晕产生的内在关联。基于Vlasov-Poisson方程二阶偶模展开,构建了理论模型,设计零流强周期相移(σ0)局部突破90°的多种演化方案,全面探究了不同聚焦方案下,局部突破90°对束流品质的影响,并用多粒子模拟软件对低能、归一化均方根发射度0.2~0.4 π·mm·mrad的质子束进行了多粒子模拟验证;针对双周期聚焦结构特征,设计了相应的聚焦结构与束流匹配方案,通过粒子-束核模型对比分析了准周期与双周期结构的束晕形成机制差异,定量分析了纵向包络对横向束晕的耦合作用。研究结果表明,当空间电荷效应较弱(对应于较高的调谐因子η,η=带电流周期相移σ/零流强周期相移σ0)时,σ0可突破90°而不导致束流品质恶化;反之,当空间电荷效应较强(低η值)时,σ0的突破会激发共振并导致束流发射度显著增长,且这一效应在双组合四极透镜聚焦结构中尤为显著。二维/三维模型均证实,即便每个聚焦单元的σ0<90°,双周期结构仍会引发束流包络的不稳定性。二维模型研究结果显示,相较于准周期结构,双周期结构更易产生束晕现象,其中2∶1共振仍是束晕形成的主要原因。采用三维模型进一步研究纵向因素的影响时发现,三维束团纵向尺寸的变化会显著改变束核电荷密度分布,这一现象成为束晕形成的新机制。此外,高阶共振也在很大程度上促进了束晕的形成。研究还揭示了小周期结构数(N)与共振概率呈负相关关系。Abstract:
Background Envelope instabilities and halo formation are critical challenges limiting beam quality in space-charge-dominated beams of low-energy superconducting proton linear accelerators. The dynamic evolution of focusing parameters during acceleration and the intrinsic role of double-period focusing structures in the low-energy region in these phenomena remain insufficiently explored.Purpose This study aims to systematically investigate the influence of dynamically evolving focusing parameters on envelope instabilities, reveal the relationship between double-period focusing structures and halo formation, and achieve localized breakthroughs of the zero-current phase advance σ0 beyond 90° while optimizing beam quality.Methods A theoretical model was established via the second-order even-mode expansion of the Vlasov–Poisson equations. Multiple evolution schemes were designed, and multi-particle simulations were performed on low-energy proton beams (normalized RMS emittance: 0.2–0.4 π·mm·mrad). The particle–core model was used to compare halo formation mechanisms between quasi-periodic and double-period structures, with two-dimensional and three-dimensional models verifying key findings.Results For weak space-charge effects (high η), σ0 can exceed 90° without degrading beam quality; strong space-charge effects (low η) induce resonances and emittance growth, especially in doublet structures. Double-period structures cause envelope instability even with σ0 < 90° per cell, being more prone to halo formation via the 2∶1 resonance. Longitudinal beam size variations alter core charge density (a new halo mechanism), and higher-order resonances contribute significantly. The number of short-period cells (N) correlates inversely with resonance probability.Conclusions Dynamic focusing parameters and double-period structures strongly affect envelope instabilities and halo formation. The 2∶1 resonance and longitudinal-transverse coupling are key halo mechanisms. σ0 breakthrough beyond 90° is feasible under weak space-charge conditions, and increasing N reduces resonance risk. These findings provide theoretical and numerical support for beam quality optimization in low-energy superconducting proton linac. -
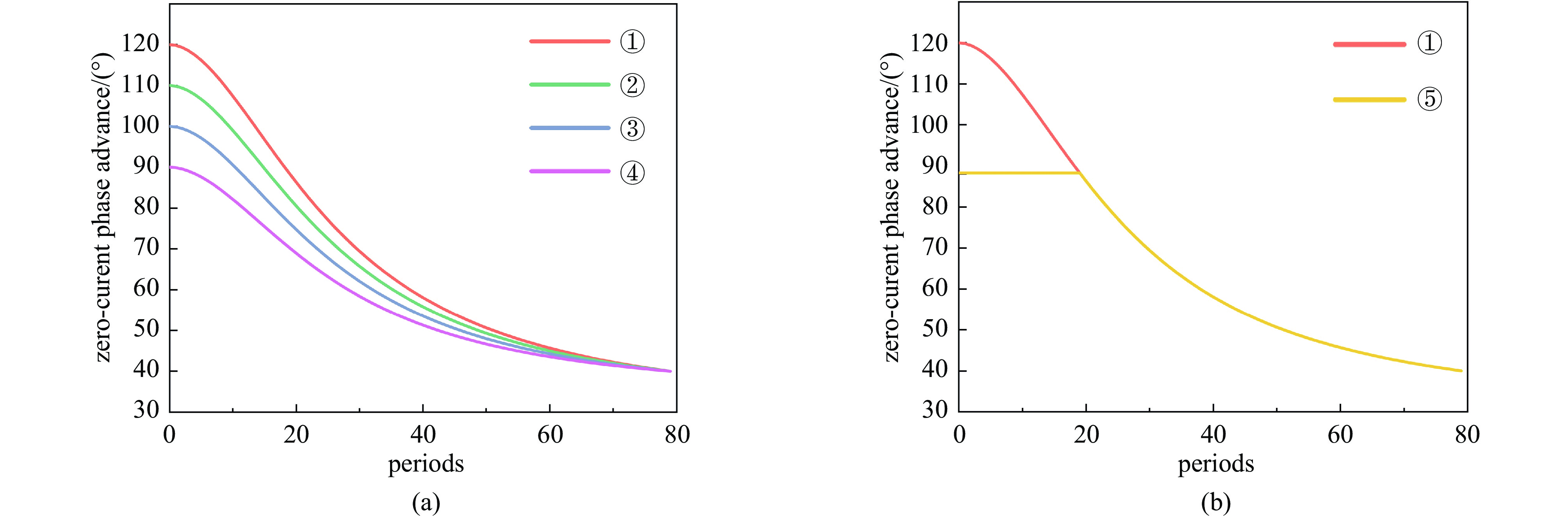
表 1 σ0的具体参数
Table 1. The specific parameters of logistic functions for σ0
Scheme Max σ0 (°) Min σ0 (°) A1 A2 x0 p ① 120 40 120 29.8312 26.3333 1.87755 ② 110 40 110 31.1023 26.3333 1.87755 ③ 100 40 100 32.3734 26.3333 1.87755 ④ 90 40 90 33.6445 26.3333 1.87755 -
[1] Neutron Sciences Directorate[EB/OL]. http://neutrons.ornl.gov/media/pubs/. [2] Neutrino Factory[EB/OL]. http://www.nu.to.infn.it/Neutrino_Factory/. [3] 袁建东, 马力祯, 何源, 等. 超导直线加速器准直方案设计[J]. 北京测绘, 2019, 33(3): 285-290Yuan Jiandong, Ma Lizhen, He Yuan, et al. Design of alignment scheme for superconducting linear accelerator[J]. Beijing Surveying and Mapping, 2019, 33(3): 285-290 [4] Jeon D O. Classification of space-charge resonances and instabilities in high-intensity linear accelerators[J]. Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 2018, 72(12): 1523-1530. doi: 10.3938/jkps.72.1523 [5] Lund S M, Bukh B. Stability properties of the transverse envelope equations describing intense ion beam transport[J]. Physical Review Special Topics - Accelerators and Beams, 2004, 7: 024801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.7.024801 [6] Ikegami M. Particle–core analysis of beam halo formation in anisotropic beams[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 1999, 435(3): 284-296. [7] Cheon Y L, Moon S H, Chung M, et al. Analysis on the stop band of fourth-order resonance in high-intensity linear accelerators[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2020, 27: 063105. doi: 10.1063/5.0004651 [8] Jeon D O. Experimental evidence of space charge driven resonances in high intensity linear accelerators[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2016, 19: 010101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.19.010101 [9] Groening L, Barth W, Bayer W, et al. Experimental evidence of the 90° stop band in the GSI UNILAC[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 102: 234801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.234801 [10] Wangler T P, Allen C K, Chan K C D, et al. Beam-halo in mismatched proton beams[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2004, 519(1/2): 425-431. [11] 孙纪磊, 阮玉芳, 肖帅, 等. 强流质子加速器束流剖面分布及束晕测量系统设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2011, 23(01Sun Jilei, Ruan Yufang, Xiao Shuai, et al. Design of beam profile and halo measurement system for high-intensity RFQ accelerator[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2011, 23 [12] Li Zhihui, Cheng Peng, Geng Huiping, et al. Physics design of an accelerator for an accelerator-driven subcritical system[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2013, 16: 080101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.16.080101 [13] Wangler T P, Crandall K R, Ryne R, et al. Particle-core model for transverse dynamics of beam halo[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 1998, 1: 084201. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.1.084201 [14] Wang T S F. Particle-core study of halo dynamics in periodic-focusing channels[J]. Physical Review E, 2000, 61(1): 855-861. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.61.855 [15] Hofmann I, Laslett L J, Smith L, et al. Stability of the Kapchinskij-Vladimirskij (K-V) distribution in long periodic transport systems[J]. Particle Accelerators, 1983, 13: 145-178. [16] Chernin D. Evolution of RMS beam envelopes in transport systems with linear X-Y coupling[J]. Particle Accelerators, 1988, 24: 29-44. [17] Struckmeier J, Reiser M. Theoretical studies of envelope oscillations and instabilities of mismatched intense charged-particle beams in periodic focusing channels[J]. Particle Accelerators, 1984, 14: 227-260. [18] Li Chao, Qin Qing. Space charge induced beam instability in periodic focusing channel[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2015, 22: 023108. doi: 10.1063/1.4908546 [19] Liu Yudong, Huang Liangsheng, Wang Sheng, et al. Impedances and beam instability in RCS/CSNS[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(2): 465-470. doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132502.0465 [20] Hofmann I. Stability of anisotropic beams with space charge[J]. Physical Review E, 1998, 57(4): 4713-4724. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.57.4713 [21] 刘伟, 颜学庆, 郭之虞, 等. BNCT中子源用RFQ加速器[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2007, 19(10): 1731-1734Liu Wei, Yan Xueqing, Guo Zhiyu, et al. RFQ accelerator used as neutron source for BNCT[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2007, 19(10): 1731-1734 [22] Gluckstern R L. Analytic model for halo formation in high current ion linacs[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1994, 73(9): 1247-1250. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.73.1247 [23] Qiang Ji, Ryne R D. Beam halo studies using a three-dimensional particle-core model[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2000, 3: 064201. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.3.064201 [24] Wan Xinmiao, Ren Zhiqiang, Liao Wenlong, et al. Beam halo studies of double-periodic focusing structures at the low-energy end of superconducting linac[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2025, 1070: 170017. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2024.170017 -




 下载:
下载: