Simulation study of neutron source for bimodal imaging target system based on low energy hgh current cyclotron
-
摘要: 无损检测方法在各领域都上发挥着重要的作用,伽马射线、热中子成像均是重要的无损检测方法,各有优劣,在许多方面上具有互补性。热中子-伽马射线双模成像将两者融合,在兼具这两类射线检测方法优点的同时,与单一射线检测相比,还具有物质识别的能力。以原子能院正在研发的18 MeV回旋加速器为设计基础,利用质子加速器驱动的中子源可同时产生中子和伽马射线这一特性,通过模拟对双模成像中子源进行研究。其中选用具有高(p, n)反应截面的铍做中子靶产生中子,为得到热中子,用聚乙烯做中子慢化体和反射体。利用热中子和伽马束流在空间上的分布不同,通过设计在不同空间取向上分别引出这两种射线,实现一靶同时得到两种射线。此外,通过在聚乙烯上对中子引出口和伽马射线引出口的设计,进一步提高热中子束流和伽马射线束流的引出效率。Abstract:
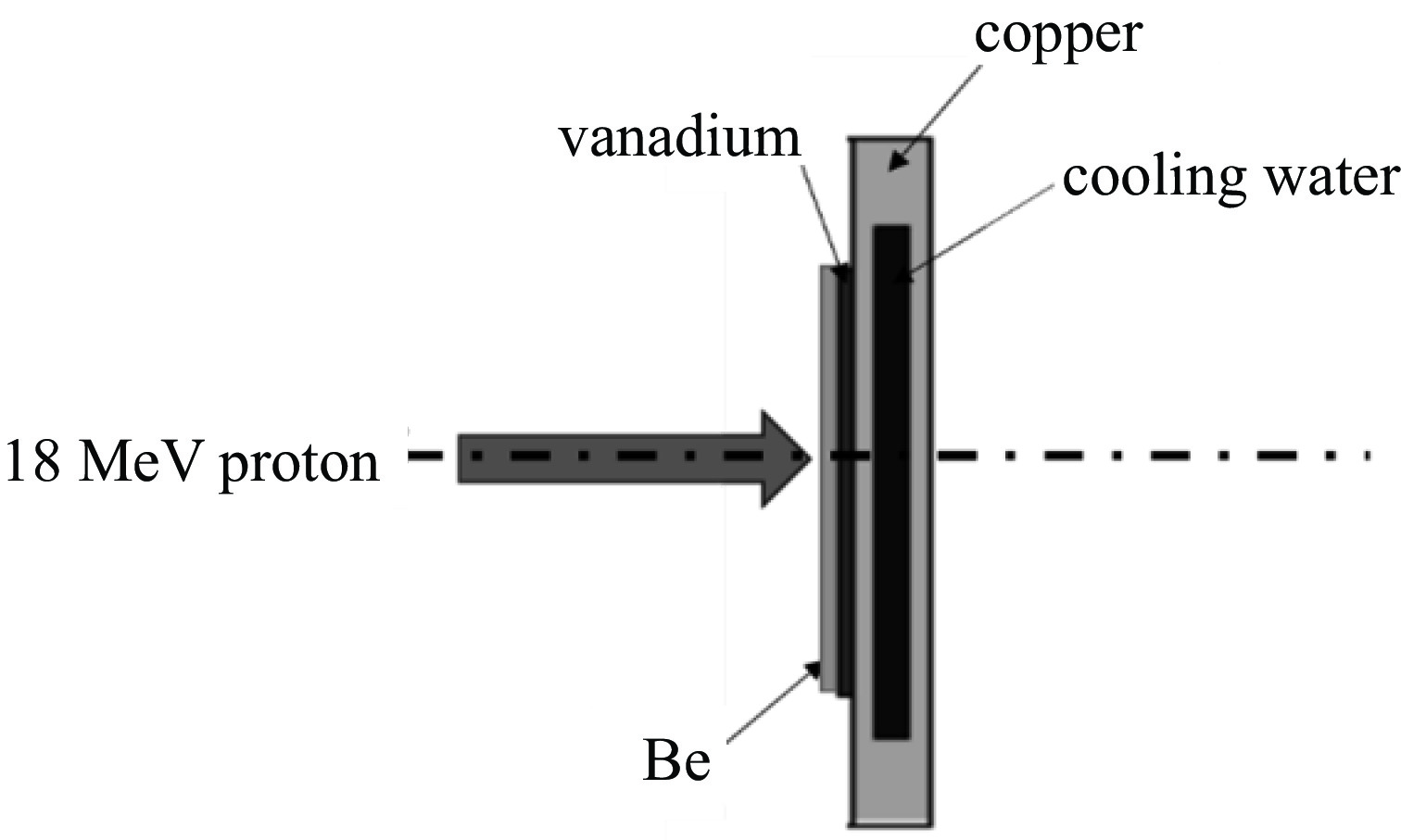
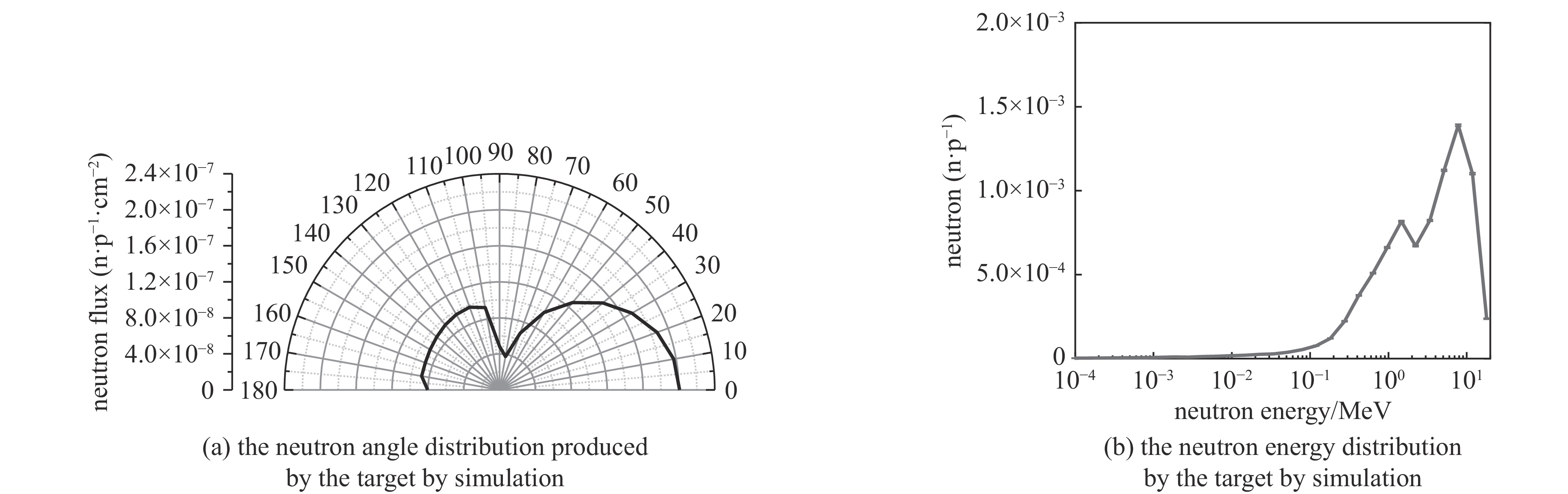
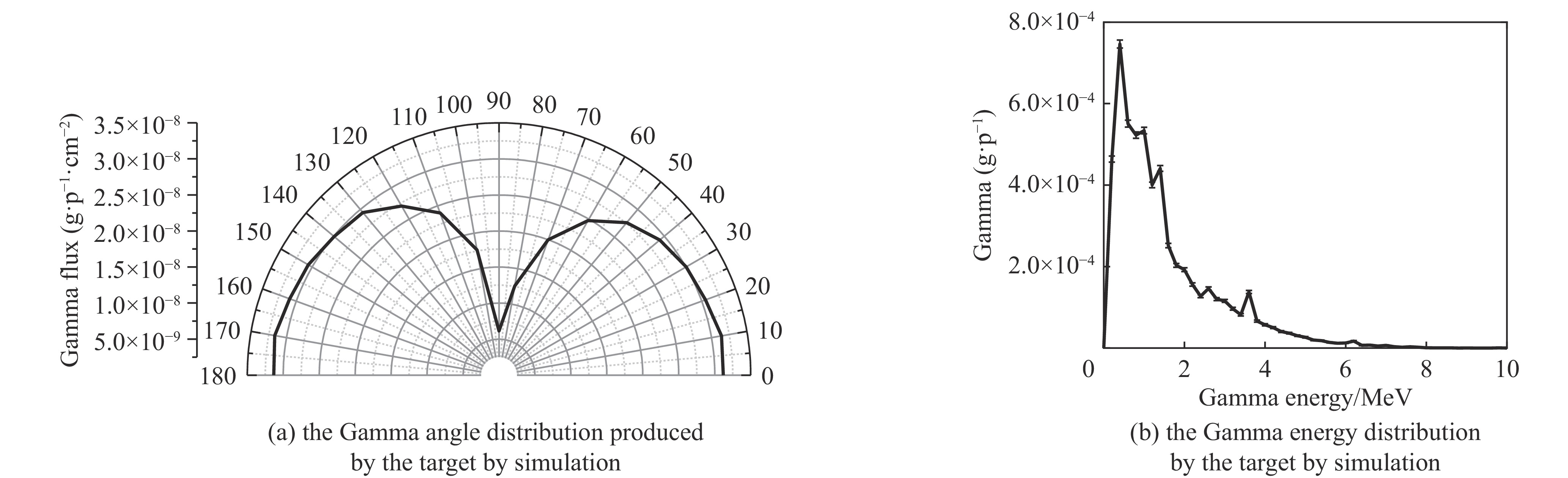
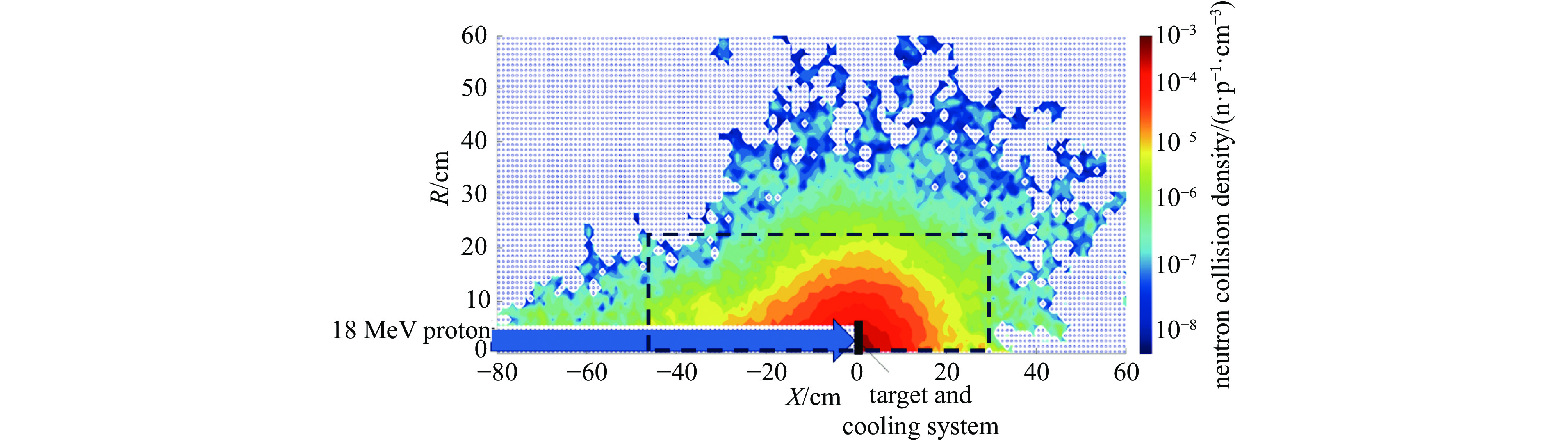
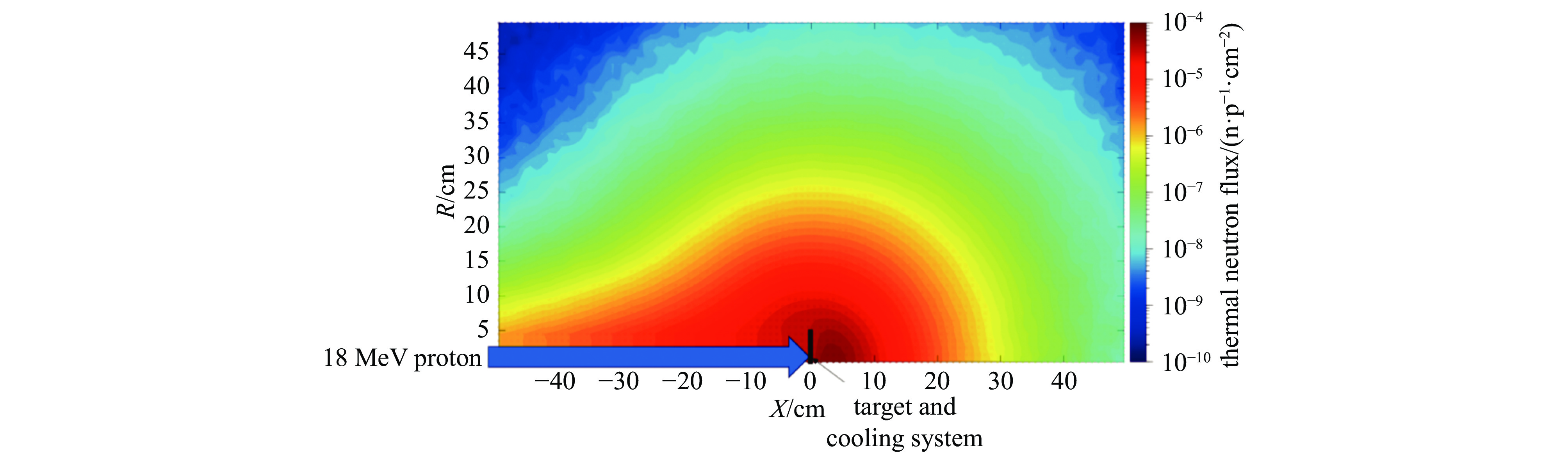
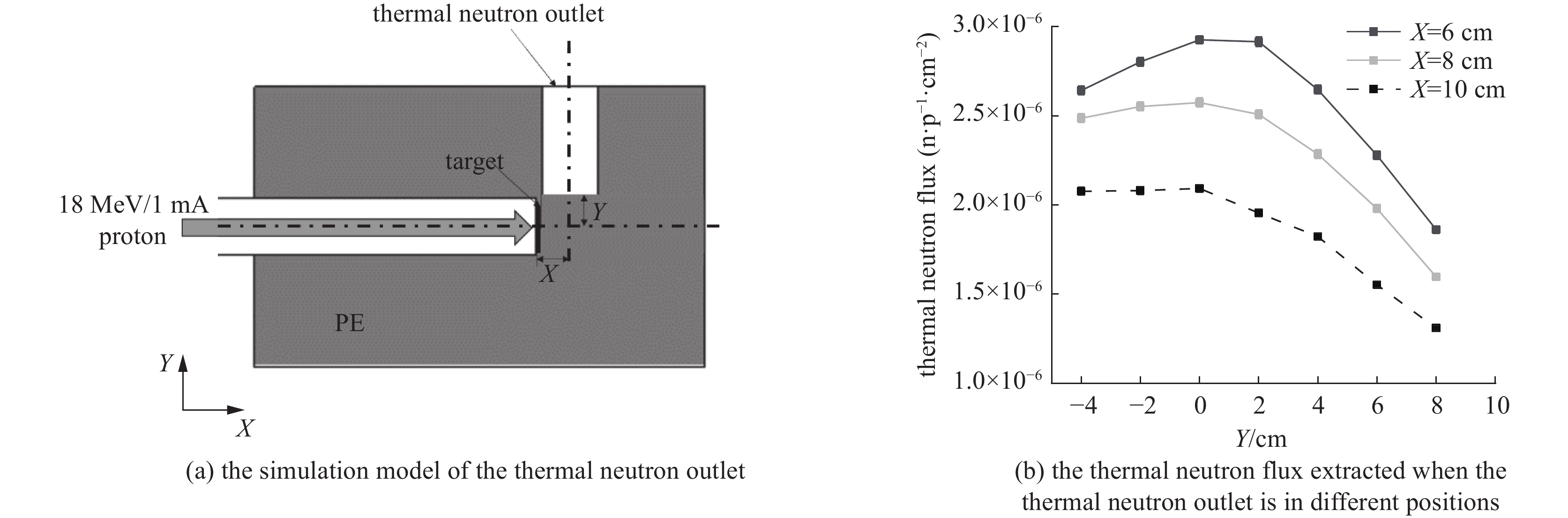
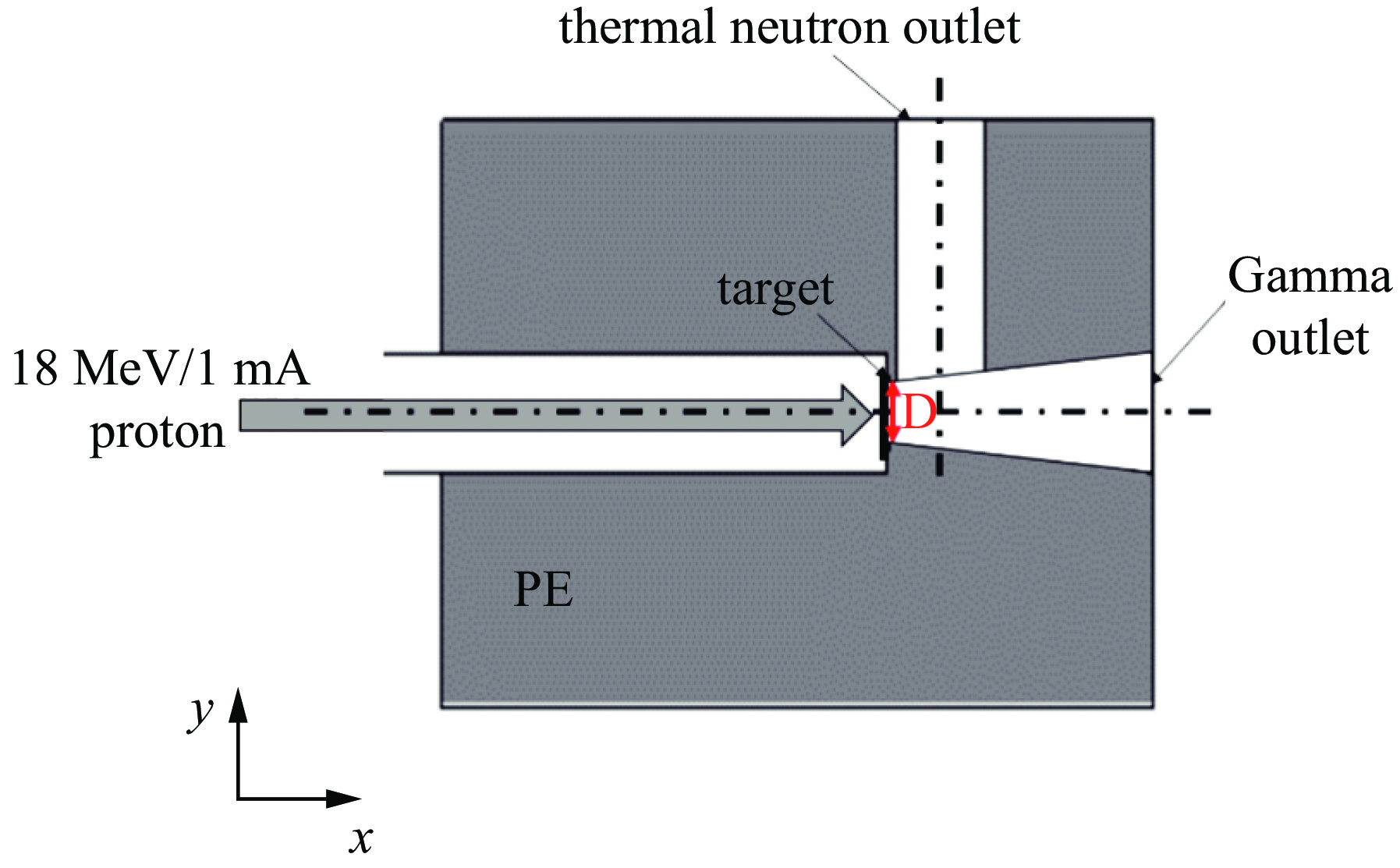
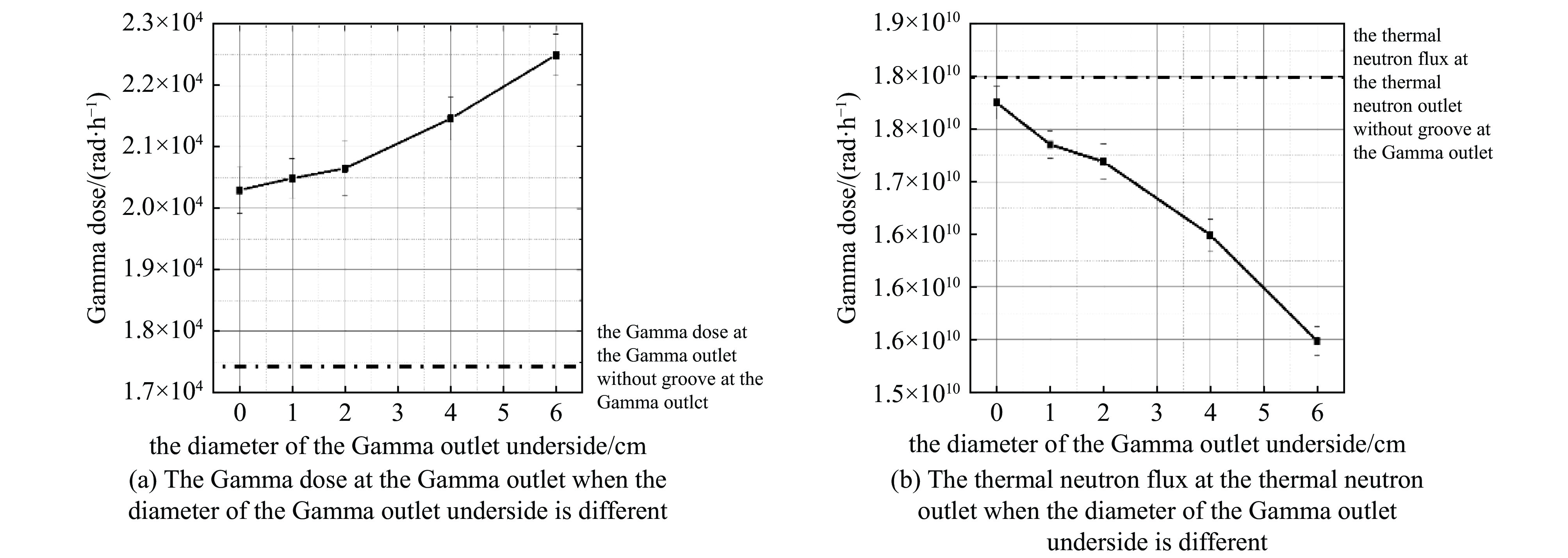
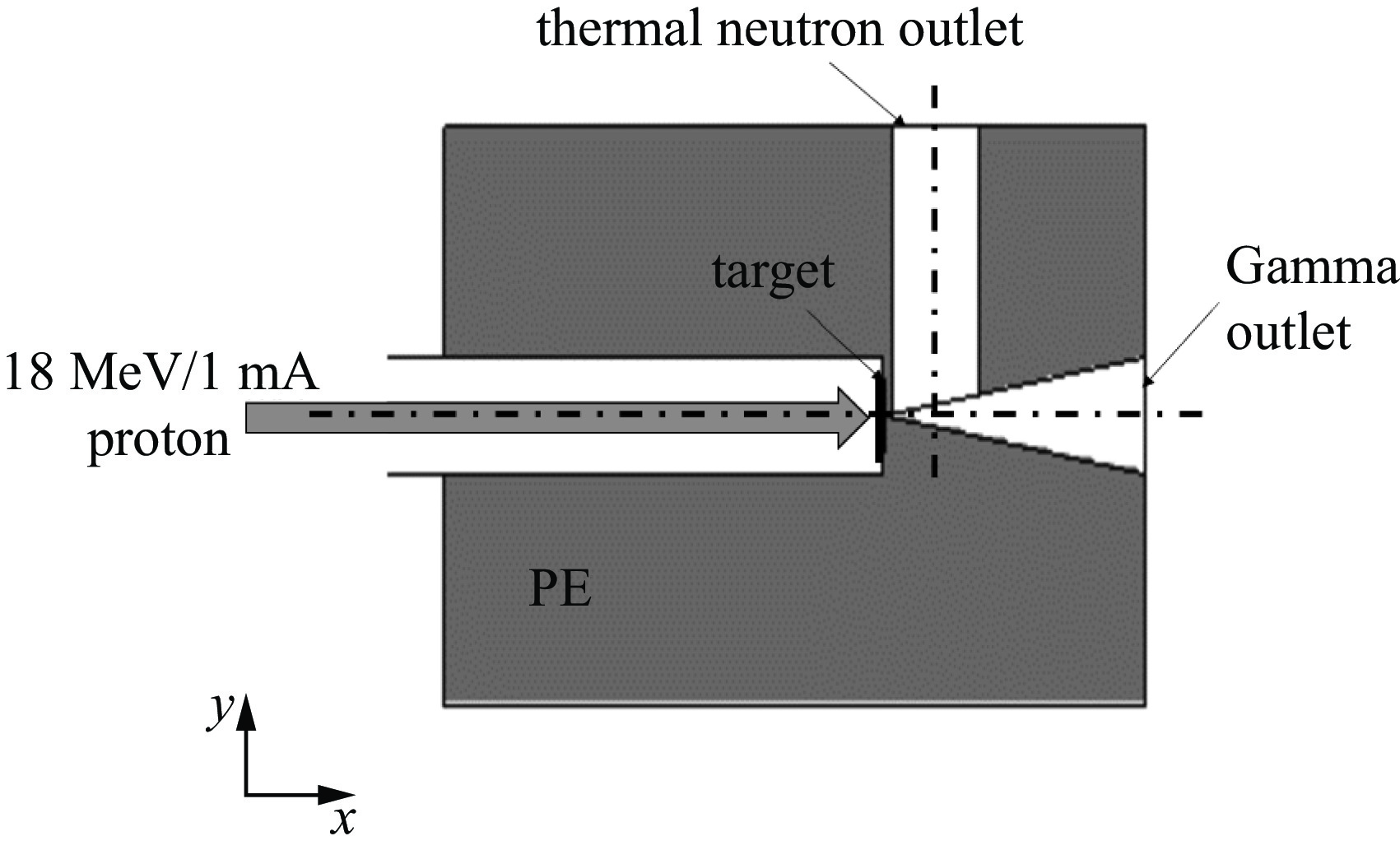
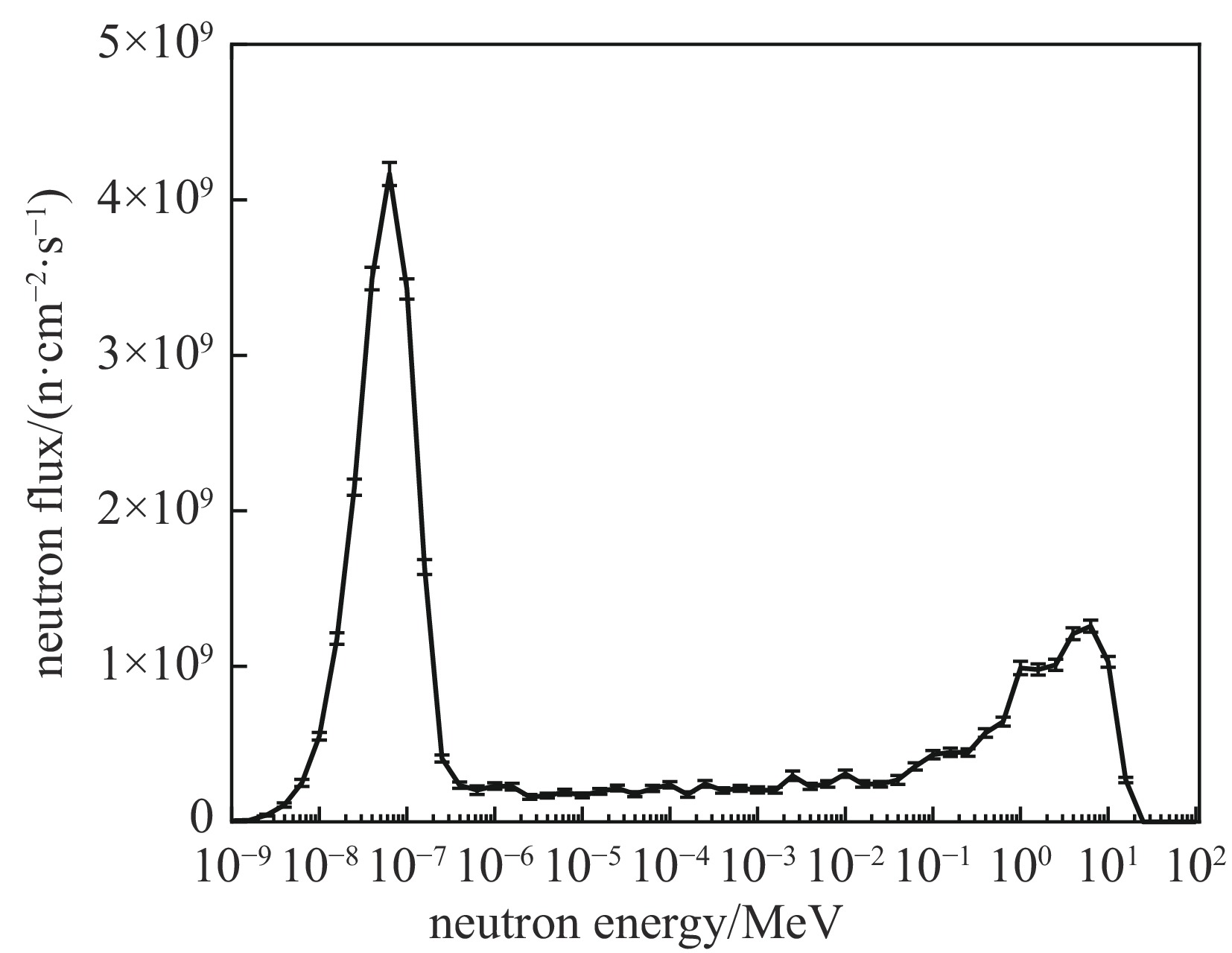
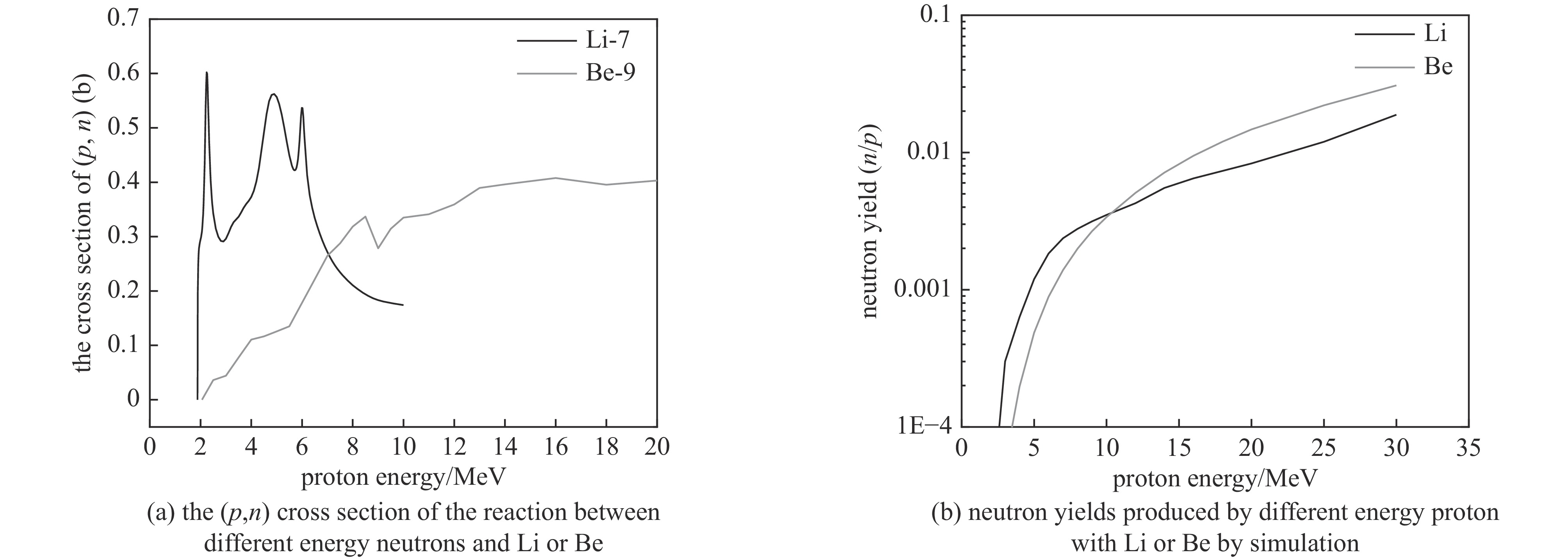
Background Gamma and thermal neutron imaging are important non-destructive testing methods, which are complementary in many aspects. The thermal neutron and Gamma bimodal imaging can combine the advantages of both. Compares with single beam imaging, the bimodal imaging has the ability to identify different substances and the sensitivity to both nuclides and elements simultaneous.Purpose Utilizing the reaction between protons and target material producing neutrons and Gamma together, based on the 18 MeV cyclotron accelerator being developed by the Institute of Atomic Energy, this paper designs a bimodal imaging neutron source by simulation.Methods Beryllium with a high (p, n) reaction cross-section is selected as the neutron target to generate neutrons. To obtain thermal neutrons with higher flux, polyethylene is used as the neutron moderator and reflector. By the different spatial distributions of thermal neutrons and Gamma, these two types of radiation are separately extracted from different directions. Besides, by designing the neutron and Gamma exits on polyethylene, high neutron flux and Gamma beams are simultaneously obtained.Results After simulation optimization, the thermal neutron flux at the thermal neutron outlet can reach 1.78×1010 n/(cm2·s) , and the gamma dose at the gamma outlet can reach 2.23×104 rad/h.Conclusions This paper design a neutron source for thermal-neutron-gamma imaging based on the 18 MeV/1 mA cyclotron accelerator. The design efficiently extracts thermal neutron flux and gamma flux from a single target, implementing a single-target-dual-source configuration.-
Key words:
- bimodal imaging /
- neutron source /
- cyclotron /
- thermal neutron /
- gamma
-
表 1 不同材料的慢化本领和减速比[22]
Table 1. The moderation ability and deceleration ratio of different materials
moderator material slowing-down power/cm−1 gear ratio (thermal neutron) water 1.53 72 polyethylene (PE) 1.84 64 heavy water 0.37 12000 graphite 0.064 170 表 2 模拟得到的18 MeV质子与铍靶反应产生的中子经过不同慢化材料后慢化体内最大热中子通量
Table 2. The max thermal neutron flux in the moderator when the neutrons produced by 18 MeV proton and Be are moderated by different moderator materials by simulation
moderator material the most thermal neutron flux in the moderator/(n/(p·cm2)) water 1.27×10−5 polyethylene (PE) 7.42×10−5 heavy water 3.87×10−5 graphite 3.19×10−5 -
[1] Anderson I S, McGreevy R L, Bilheux H Z. Neutron imaging and applications[M]. New York: Springer, 2009: 987. [2] Horn Q C, Yang S H. Morphology and spatial distribution of ZnO formed in discharged alkaline Zn/MnO2 AA cells[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2003, 150: A652. doi: 10.1149/1.1566014 [3] Tötzke C, Kardjilov N, Lenoir N, et al. What comes NeXT?—High-speed neutron tomography at ILL[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(20): 28640-28648. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.028640 [4] De Beer F C. Neutron and X-ray tomography at Necsa[J]. The Journal of the Southern African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 2008, 108: 613-620. [5] Clark T, Burca G, Boardman R, et al. Correlative X-ray and neutron tomography of root systems using cadmium fiducial markers[J]. Journal of Microscopy, 2020, 277(3): 170-178. doi: 10.1111/jmi.12831 [6] Lehmann E H, Vontobel P, Deschler-Erb E, et al. Non-invasive studies of objects from cultural heritage[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2005, 542(1/3): 68-75. [7] Banhart J, Borbély A, Dzieciol K, et al. X-ray and neutron imaging–Complementary techniques for materials science and engineering[J]. International Journal of Materials Research, 2010, 101: 1069-1079. [8] Carminati A, Kaestner A, Lehmann P, et al. Monitoring water flow in soils, using neutron and gamma tomography[J]. PSI Sci Rep, 2005, 2006: 28-29. [9] Kaestner A P, Hovind J, Boillat P, et al. Bimodal imaging at ICON using neutrons and X-rays[J]. Physics Procedia, 2017, 88: 314-321. doi: 10.1016/j.phpro.2017.06.043 [10] Fedrigo A, Marstal K, Bender Koch C, et al. Investigation of a Monturaqui Impactite by means of bi-modal X-ray and neutron tomography[J]. Journal of Imaging, 2018, 4: 72. doi: 10.3390/jimaging4050072 [11] Lehmann E H, Mannes D, Kaestner A P, et al. The XTRA option at the NEUTRA facility—more than 10 years of Bi-modal neutron and X-ray imaging at PSI[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11: 3825. doi: 10.3390/app11093825 [12] Sinha V, Srivastava A, Lee H K, et al. Performance evaluation of a combined neutron and x-ray digital imaging system[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 8694, Nondestructive Characterization for Composite Materials, Aerospace Engineering, Civil Infrastructure, and Homeland Security 2013. 2013: 86940R. [13] Mannes D, Schmid F, Frey J, et al. Combined neutron and X-ray imaging for non-invasive investigations of cultural heritage objects[J]. Physics Procedia, 2015, 69: 653-660. doi: 10.1016/j.phpro.2015.07.092 [14] LaManna J M, Hussey D S, Baltic E, et al. Neutron and X-ray Tomography (NeXT) system for simultaneous, dual modality tomography[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2017, 88: 113702. doi: 10.1063/1.4989642 [15] Tengattini A, Lenoir N, Andò E, et al. NeXT-Grenoble, the neutron and X-ray tomograph in Grenoble[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2020, 968: 163939. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2020.163939 [16] 丁大钊, 叶春堂, 赵志祥. 中子物理学: 原理、方法与应用[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 2001Ding Dazhao, Ye Chuntang, Zhao Zhixiang. Neutron physics[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 2001 [17] Anderson I S, Andreani C, Carpenter J M, et al. Research opportunities with compact accelerator-driven neutron sources[J]. Physics Reports, 2016, 654: 1-58. doi: 10.1016/j.physrep.2016.07.007 [18] Baxter D V, Cameron J M, Derenchuk V P, et al. Status of the low energy neutron source at Indiana university[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2005, 241(1/4): 209-212. [19] Tasaki S, Nagae T, Hirose M, et al. Properties and possible applications of Kyoto University accelerator based neutron source (KUANS)[J]. Physics Procedia, 2014, 60: 181-185. doi: 10.1016/j.phpro.2014.11.026 [20] Otake Y. RIKEN accelerator-driven compact neutron systems[C]//8th International Meeting of Union for Compact Accelerator-Driven Neutron Sources. 2020: 01009. [21] Xiao Yongshun, Chen Zhiqiang, Yang Yigang, et al. Development progress of the neutron imaging station in CPHS[J]. Physics Procedia, 2015, 69: 96-103. doi: 10.1016/j.phpro.2015.07.014 [22] 陈伯显, 张智. 核辐射物理及探测学[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学出版社, 2011Chen Boxian, Zhang Zhi. Nuclear physics and detection[M]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University Press, 2011 -




 下载:
下载: