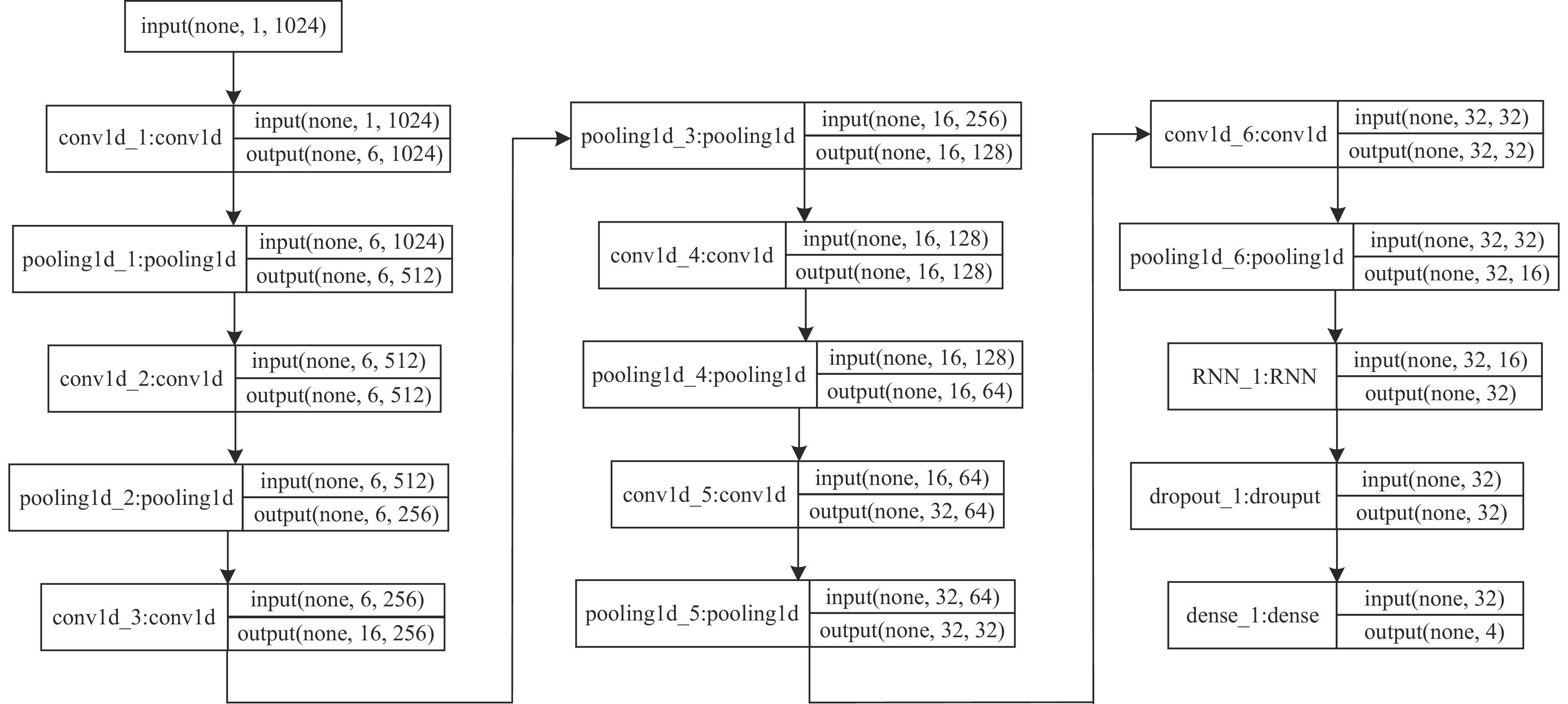
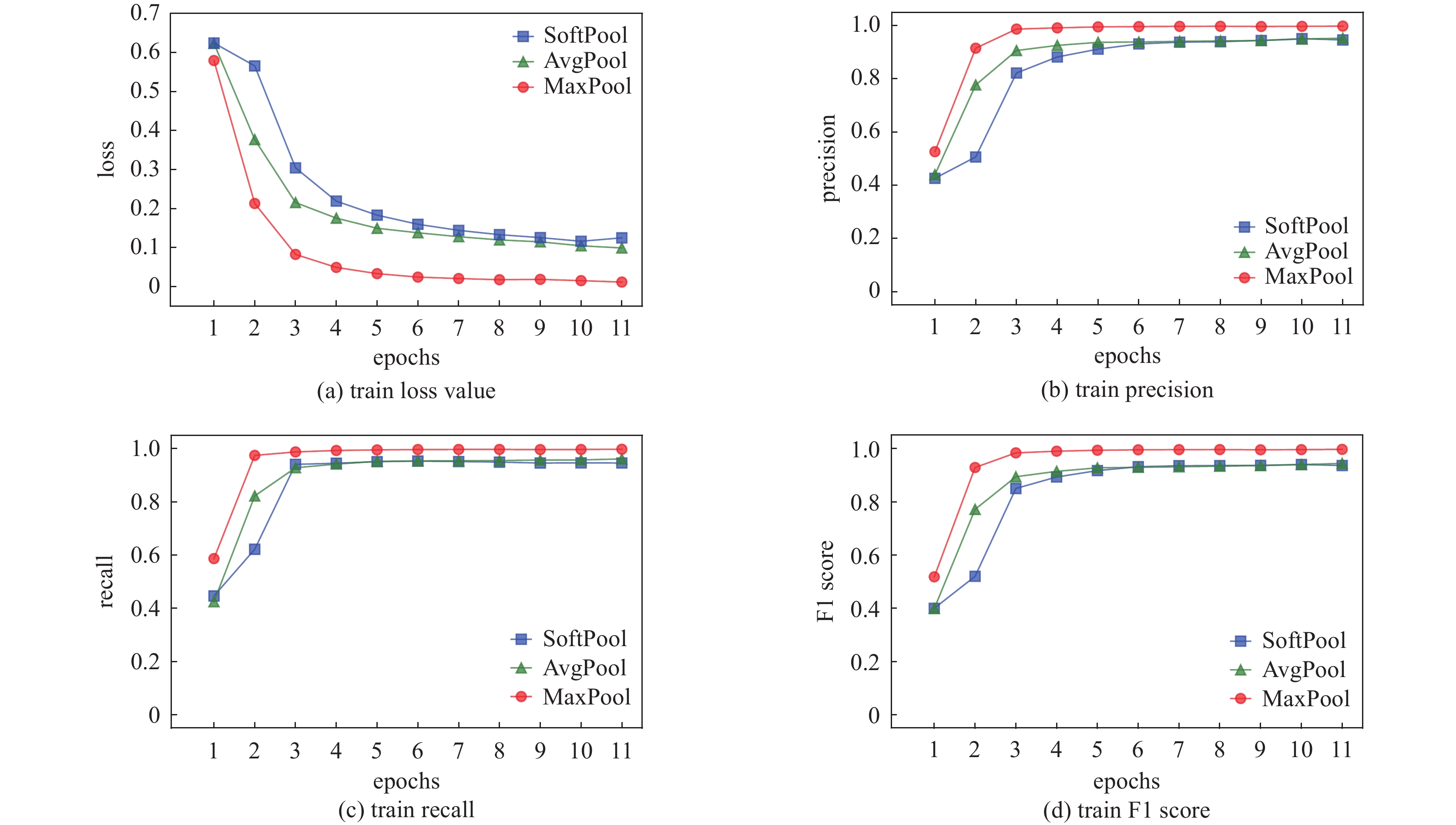
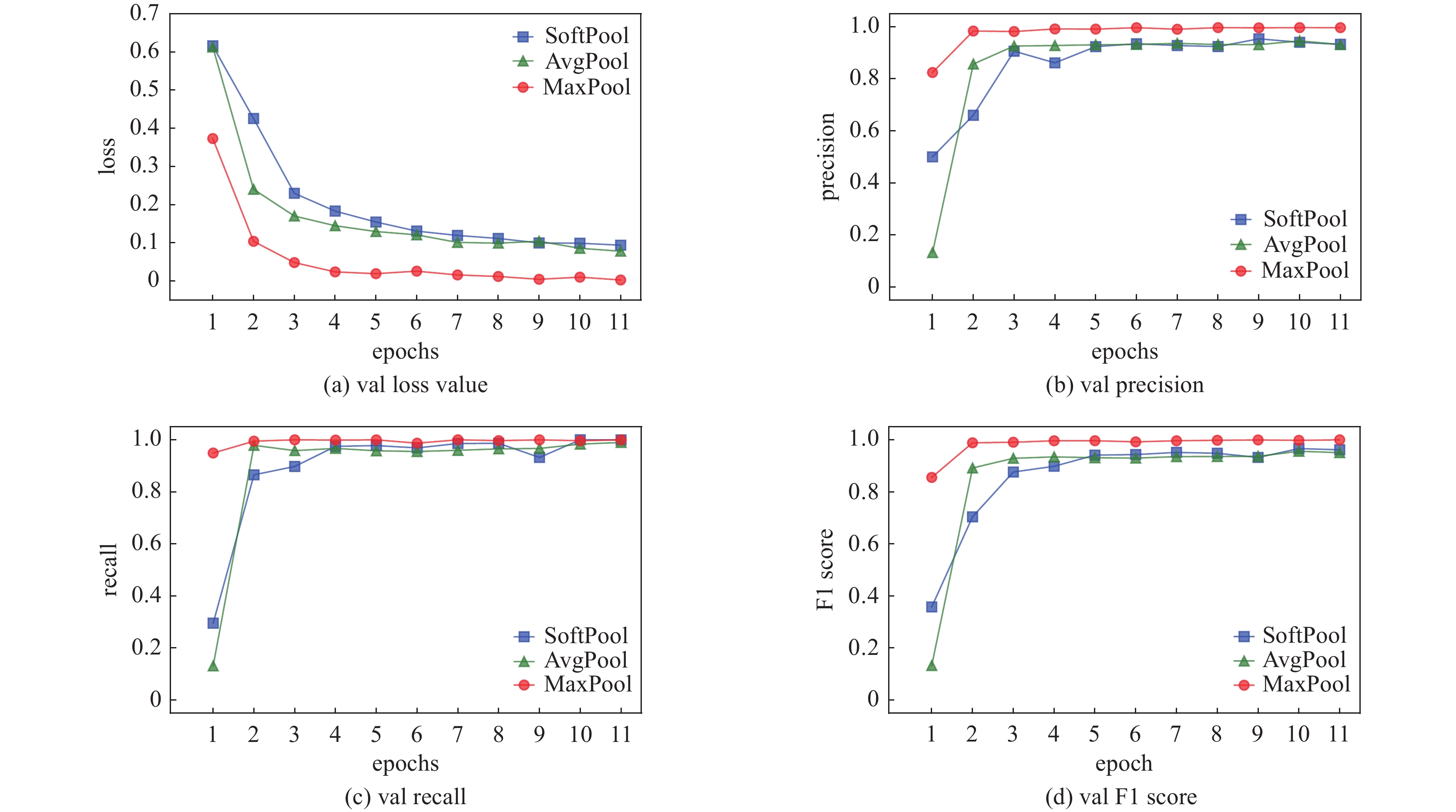
Research on nuclide identification method based on convolutional recurrent neural network
-
摘要: 核素的准确识别是提高放射性监测水平的关键。为进一步提升放射性核素识别性能,研究了基于卷积神经网络(CNN)和循环神经网络(RNN)结合的核素识别方法。使用碘化钠能谱仪采集8种单一和混合放射性核素γ能谱数据,通过计算γ光子在不同能量下的概率密度,采用随机抽样的方法生成大量γ能谱训练数据,并对数据进行归一化处理,然后利用CNN提取输入能谱数据的特征向量,并将提取到的特征向量输入RNN进行训练,最后由激活函数输出核素分类结果。为验证CNN-RNN识别核素的准确性,与基于卷积神经网络(CNN)和长短时记忆神经网络(LSTM)核素识别方法进行比较分析,得出在测试集上LSTM能谱模型对单核素的识别准确率优于97.5%,混合核素的识别率优于92.31%,CNN和CNN-RNN能谱模型对单核素的识别准确率为100%,混合核素的识别率分别优于92.95%和97.44%。结果表明,CNN-RNN能谱模型在γ能谱放射性核素识别中表现更优,通过与仅用实测数据训练的神经网络模型相比,加入增强数据可提升模型的训练效率和泛化能力。Abstract:
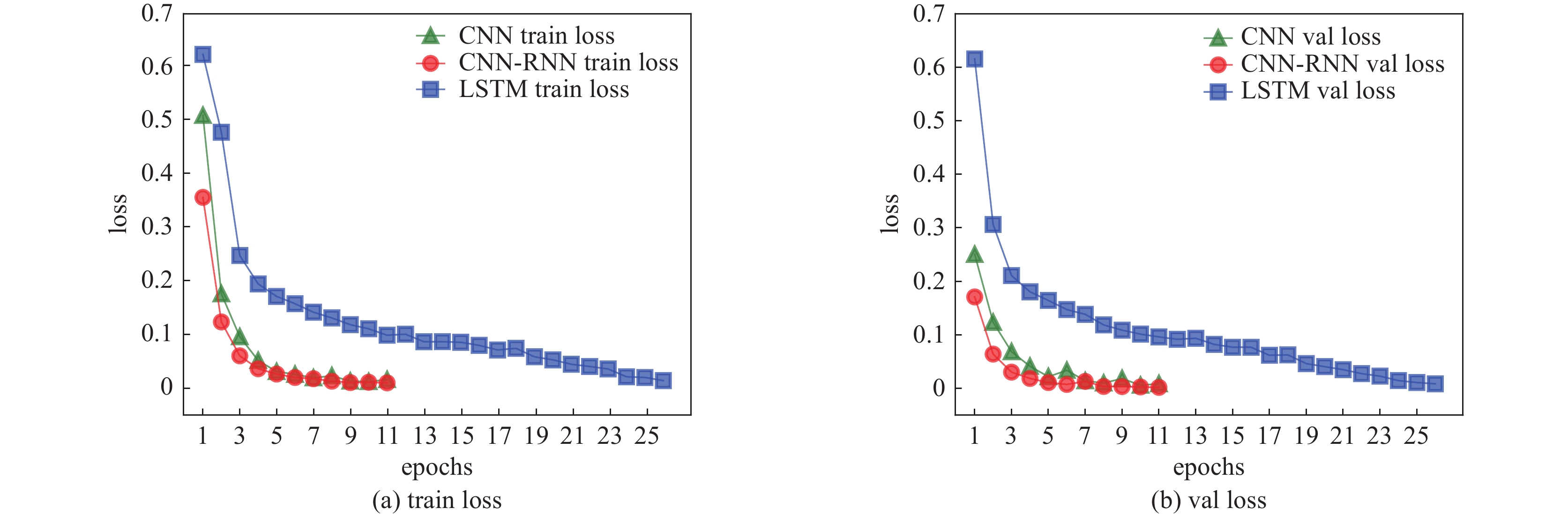
Background Accurate identification of radionuclides is the key to improving the level of radioactivity monitoring.Purpose To further enhance the performance of radionuclide identification, a method combining Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) for radionuclide identification has been studied.Methods Gamma-ray spectra data of eight single and mixed radioactive nuclides were collected using a sodium iodide spectrometer, and a large number of gamma-ray spectral training data were generated by calculating the probability density of gamma photons at different energy levels and using random sampling methods, followed by normalization of the data. The CNN was then used to extract feature vectors from the input spectral data, and these extracted feature vectors were fed into the RNN for training, with the final radionuclide classification results being output by the activation function.Results To verify the accuracy of the CNN-RNN method in identifying radionuclides, a comparative analysis was conducted with the radionuclide identification method based on Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network (LSTM), and the results showed that the LSTM spectral model achieved a recognition accuracy rate of over 97.5% for single nuclides and over 92.31% for mixed nuclides on the test set, while the CNN and CNN-RNN spectral models achieved a recognition accuracy rate of 100% for single nuclides and recognition rates of over 92.95% and 97.44% for mixed nuclides.Conclusions respectively, indicating that the CNN-RNN method performs better in gamma-ray spectral identification of radioactive nuclides, Compared with neural network models trained only on real - measured data, incorporating augmented data can improve the training efficiency and generalization ability of the models. -
表 1 评价指标与计算方法
Table 1. Evaluation metrics and calculation methods
name of evaluation
indicatorcalculation method of
evaluation indicatorthe name of macro-average
evaluation indicatorcalculation method of macro-average
evaluation indicatorprecision (P) $P = TP/(TP + FP)$ macro precision ($P_{Macro}$) $P_{Macro} = \dfrac{{\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^n {P_i} }}{n}$ recall (R) $R = TP/(TP + FN)$ macro recall ($R_{Macro}$) $R_{Macro} = \dfrac{{\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^n {R_i} }}{n}$ $F1{\text{ }}score$ $F1 = (2 \times P \times R)/(P + R)$ macro F1 ($F1_{Macro}$) $F1_{Macro} = \dfrac{{\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^n {F1_i} }}{n}$ 表 2 实验测量γ能谱测试数据统计表
Table 2. Experimental measurement of gamma spectra test data statistics table
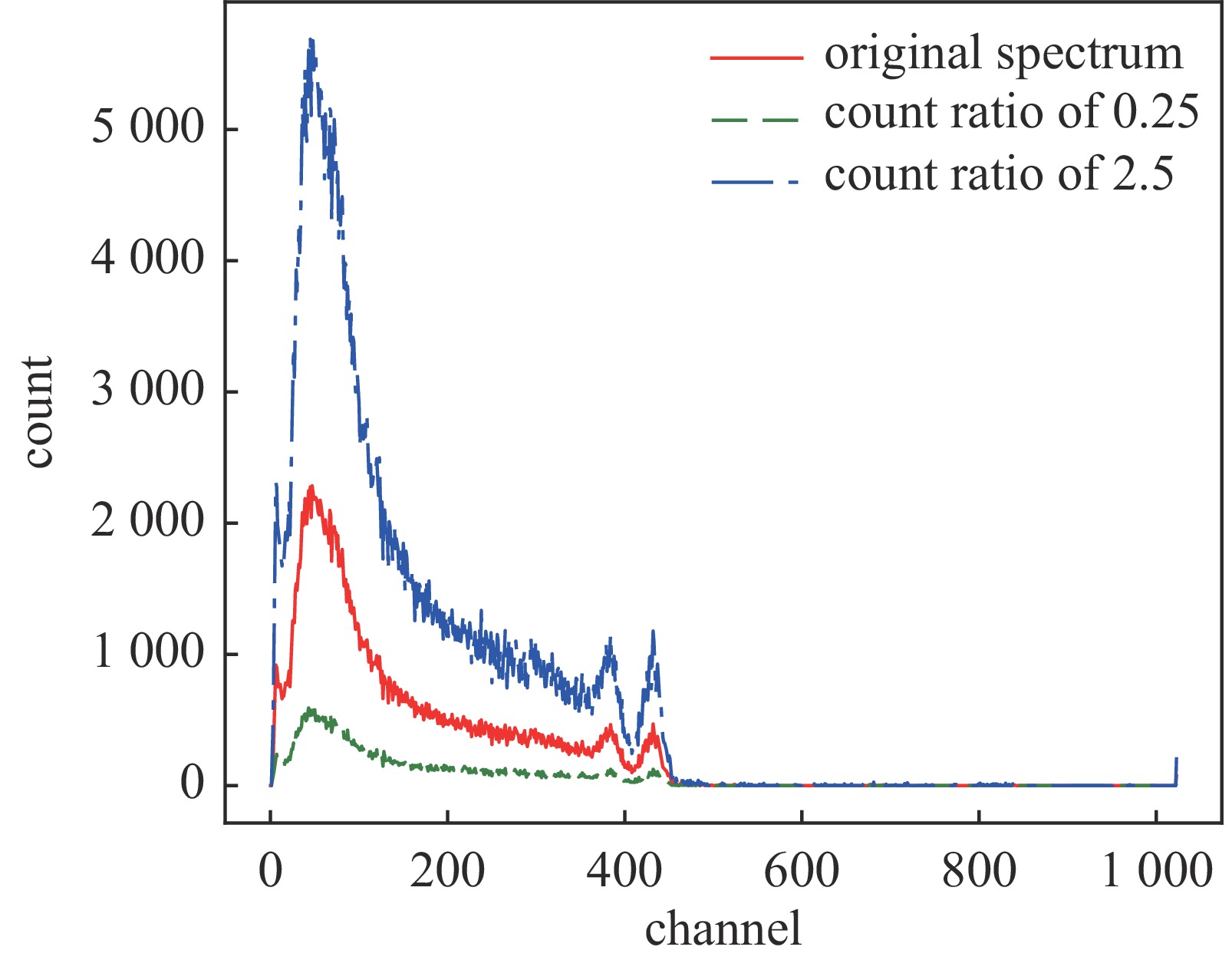
species quantity 137Cs 60 60Co 60 152Eu 40 40K 40 137Cs+60Co 60 137Cs+152Eu 39 60Co+152Eu 60 137Cs+60Co+152Eu 39 low-count spectra 12 表 3 核素识别结果准确率
Table 3. Nuclide identification accuracy
model name accuracy/% 137Cs 60Co 152Eu 40K 137Cs+60Co 137Cs+152Eu 60Co+152Eu 137Cs+60Co+152Eu LSTM 100 100 97.5 100 100 92.31 95.42 94.87 CNN 100 100 100 100 100 94.87 98.75 92.95 CNN-RNN 100 100 100 100 100 100 98.75 97.44 表 4 低计数能谱预测结果
Table 4. Prediction results of low-count spectra
model name predicted probability total counts 152Eu 60Co 137Cs 40K CNN-RNN 0.0001 0.0093 0.9999 0.0004 1743 0.0001 0.0042 0.9999 0.0005 1768 0.0001 0.0054 0.9999 0.0005 2916 CNN 0 0.9823 1.0000 0 1743 0 0.0104 1.0000 0 1768 0 1.0000 1.0000 0 2916 LSTM 0.0001 0.0023 0.9951 0.005 1743 0 0.002 0.6439 0.7839 1768 0.0004 0.0028 0.9989 0.0004 2916 表 5 各模型训练过程收敛所需训练步数和训练时长
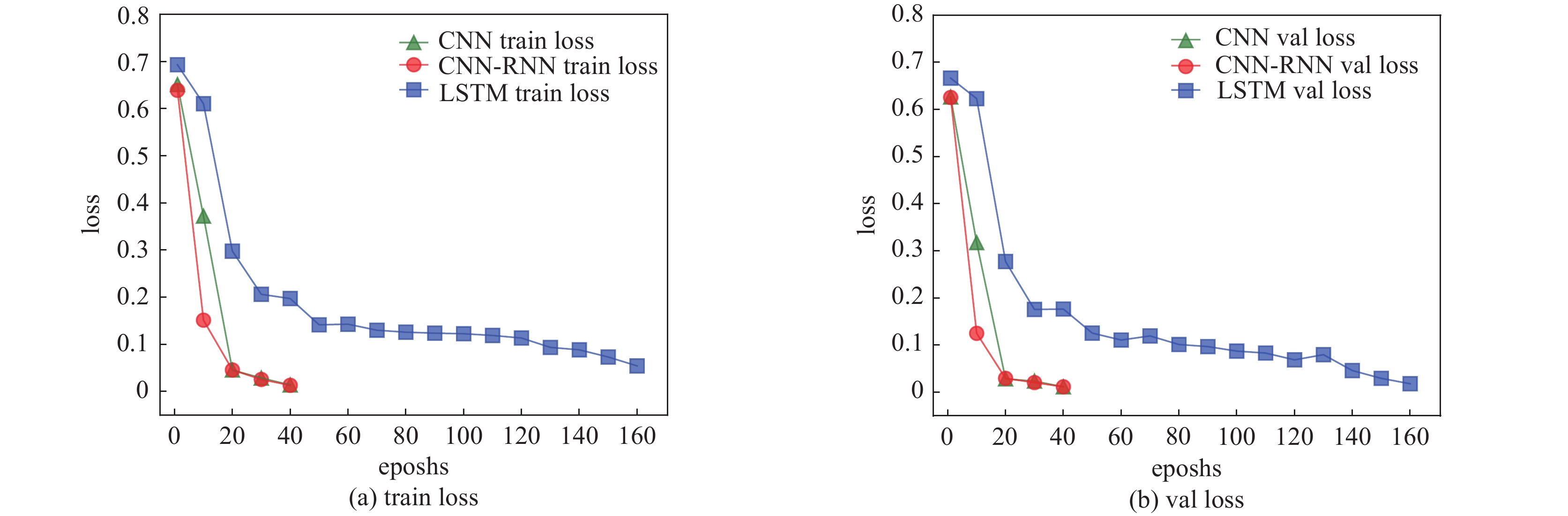
Table 5. The number of training steps and the duration required for convergence during the training process of each model
model training steps training time/s increase data no increase data increase data no increase data LSTM 26 160 94 567 CNN 11 40 50 127 CNN-RNN 11 40 52 124 表 6 实测数据训练模型核素识别结果准确率
Table 6. The accuracy of radionuclide identification results from the model trained with measured data
model name accuracy/% 137Cs 60Co 152Eu 40K 137Cs+60Co 137Cs+152Eu 60Co+152Eu 137Cs+60Co+152Eu LSTM 100 96.67 96.25 100 100 91.67 95 92.31 CNN 100 100 98.75 100 100 91.67 96.67 90.38 CNN-RNN 100 100 98.75 100 100 94.87 99.17 93.59 -
[1] 王晓涛, 周启甫, 陈栋梁. 我国核技术利用发展现状及存在的问题探讨[J]. 中国辐射卫生, 2012, 21(4): 468-469 doi: 10.13491/j.cnki.issn.1004-714x.2012.04.018Wang Xiaotao, Zhou Qifu, Chen Dongliang. A discussion on the current development status and existing problems of nuclear technology utilization in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Radiological Health, 2012, 21(4): 468-469 doi: 10.13491/j.cnki.issn.1004-714x.2012.04.018 [2] Li X, Dong C, Zhang Q, et al. Research and design of a rapid nuclide recognition system[J]. Journal of Instrumentation, 2022, 17: T06008. [3] Dess B W, Cardarelli J, Thomas M J, et al. Automated detection of radioisotopes from an aircraft platform by pattern recognition analysis of gamma-ray spectra[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2018, 192: 654-666. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2018.02.012 [4] 岳昌啓, 牛德青. 放射性核素能谱分析方法综述[J]. 兵工自动化, 2023, 42(6): 44-47Yue Changqi, Niu Deqing. Review of radionuclide energy spectrum analysis method[J]. Ordnance Industry Automation, 2023, 42(6): 44-47 [5] 卢大宇. 基于Resnet和DCGAN的少样本复杂核素识别研究[D]. 抚州: 东华理工大学, 2024: 13-15Lu Dayu. Research on complex nuclide identification with few samples based on Resnet and DCGAN[D]. Fuzhou: East China University of Technology, 2024: 13-15 [6] He Jianping, Tang Xiaobin, Gong Pin, et al. Rapid radionuclide identification algorithm based on the discrete cosine transform and BP neural network[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2018, 112: 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2017.09.032 [7] 贺楠, 吕会议, 王波, 等. 基于人工神经网络的核素识别方法[J]. 兵工自动化, 2022, 41(3): 91-96He Nan, Lyu Huiyi, Wang Bo, et al. Nuclide identification method based on artificial neural network[J]. Ordnance Industry Automation, 2022, 41(3): 91-96 [8] 王瑶, 刘志明, 万亚平, 等. 基于长短时记忆神经网络的能谱核素识别方法[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2020, 32: 106001Wang Yao, Liu Zhiming, Wan Yaping, et al. Energy spectrum nuclide recognition method based on long short-term memory neural network[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2020, 32: 106001 [9] 唐琪, 周伟, 李治和, 等. 卷积神经网络核素识别算法研究[J]. 核电子学与探测技术, 2021, 41(3): 437-442Tang Qi, Zhou Wei, Li Zhihe, et al. Research on nuclide identification algorithm of convolutional neural network[J]. Nuclear Electronics & Detection Technology, 2021, 41(3): 437-442 [10] 杜晓闯, 梁漫春, 黎岢, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的γ放射性核素识别方法[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 63(6): 980-986 doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2023.22.011Du Xiaochuang, Liang Manchun, Li Ke, et al. A gamma radionuclide identification method based on convolutional neural networks[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2023, 63(6): 980-986 doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2023.22.011 [11] Sun Jiaqian, Niu Deqing, Liang Jie, et al. Rapid nuclide identification algorithm based on self-attention mechanism neural network[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2024, 207: 110708. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2024.110708 [12] Daniel G, Ceraudo F, Limousin O, et al. Automatic and real-time identification of radionuclides in gamma-ray spectra: a new method based on convolutional neural network trained with synthetic data set[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2020, 67(4): 644-653. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2020.2969703 [13] Van Hiep C, Hung D T, Anh N N, et al. Nuclide identification algorithm for the large-size plastic detectors based on artificial neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2022, 69(6): 1203-1211. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2022.3173371 [14] Kim B J. Comparison of heart failure prediction performance using various machine learning techniques[J]. International Journal of Internet, Broadcasting and Communication, 2024, 16(4): 290-300. [15] Rasdi Rere L M, Fanany M I, Arymurthy A M. Metaheuristic algorithms for convolution neural network[J]. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2016, 2016: 1537325. [16] 赵红伟, 李朋, 程振飞. 基于Faster R-CNN图像处理的光伏并网变电站运行故障检测方法[J]. 电工技术, 2025(1): 27-29,32Zhao Hongwei, Li Peng, Cheng Zhenfei. Fault detection method for photovoltaic grid connected substations based on faster R-CNN image processing[J]. Electric Engineering, 2025(1): 27-29,32 [17] 杨进, 李阳, 曾辉, 等. 深度学习在水下目标检测与腐蚀评估中的应用进展[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2024, 45(9): 57-66Yang Jin, Li Yang, Zeng Hui, et al. Application advance of deep learning in underwater target detection and corrosion assessment[J]. Corrosion and Protection, 2024, 45(9): 57-66 [18] Abbaspour S, Fotouhi F, Sedaghatbaf A, et al. A comparative analysis of hybrid deep learning models for human activity recognition[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20: 5707. doi: 10.3390/s20195707 [19] 杨祎玥, 伏潜, 万定生. 基于深度循环神经网络的时间序列预测模型[J]. 计算机技术与发展, 2017, 27(3): 35-38,43Yang Yiyue, Fu Qian, Wan Dingsheng. A prediction model for time series based on deep recurrent neural network[J]. Computer Technology and Development, 2017, 27(3): 35-38,43 -




 下载:
下载: