Research on prediction method of flashover voltage in SF6 gas under nanosecond pulse
-
摘要: 纳秒脉冲下SF6中的沿面闪络涉及物理过程复杂,如何准确预测该环境下的绝缘介质沿面闪络电压是高压脉冲功率设备设计与绝缘可靠性评估的关键挑战。与传统工频或直流电压相比,纳秒脉冲极短的上升时间和高幅值导致空间电荷效应显著、放电发展机制迥异,使得基于经典理论的预测模型面临严峻挑战。近年来,随着计算机算力的飞速提升和人工智能算法的突破性进展,基于数据驱动的机器学习方法在解决复杂非线性绝缘问题中展现出了巨大潜力。针对纳秒脉冲下这一特定难题,选取了支持向量机、多层感知机、随机森林和极端梯度提升树等四种算法对15~500 mm多尺度距离范围内不同实验条件下的闪络电压数据进行了训练和预测,其预测结果的ROC 曲线下面积(AUC)值均在0.9以上,表现最优的是支持向量机算法。同时,为了验证预测模型的准确性,选取表现较为优异的支持向量机模型对另选取的100 mm距离数据进行了预测,AUC值达到0.99,这表明预测准确率高,可以认为模型具备较强的泛化性,从而验证了不同实验条件下基于数据驱动的SF6中闪络电压预测方法的可行性。Abstract:
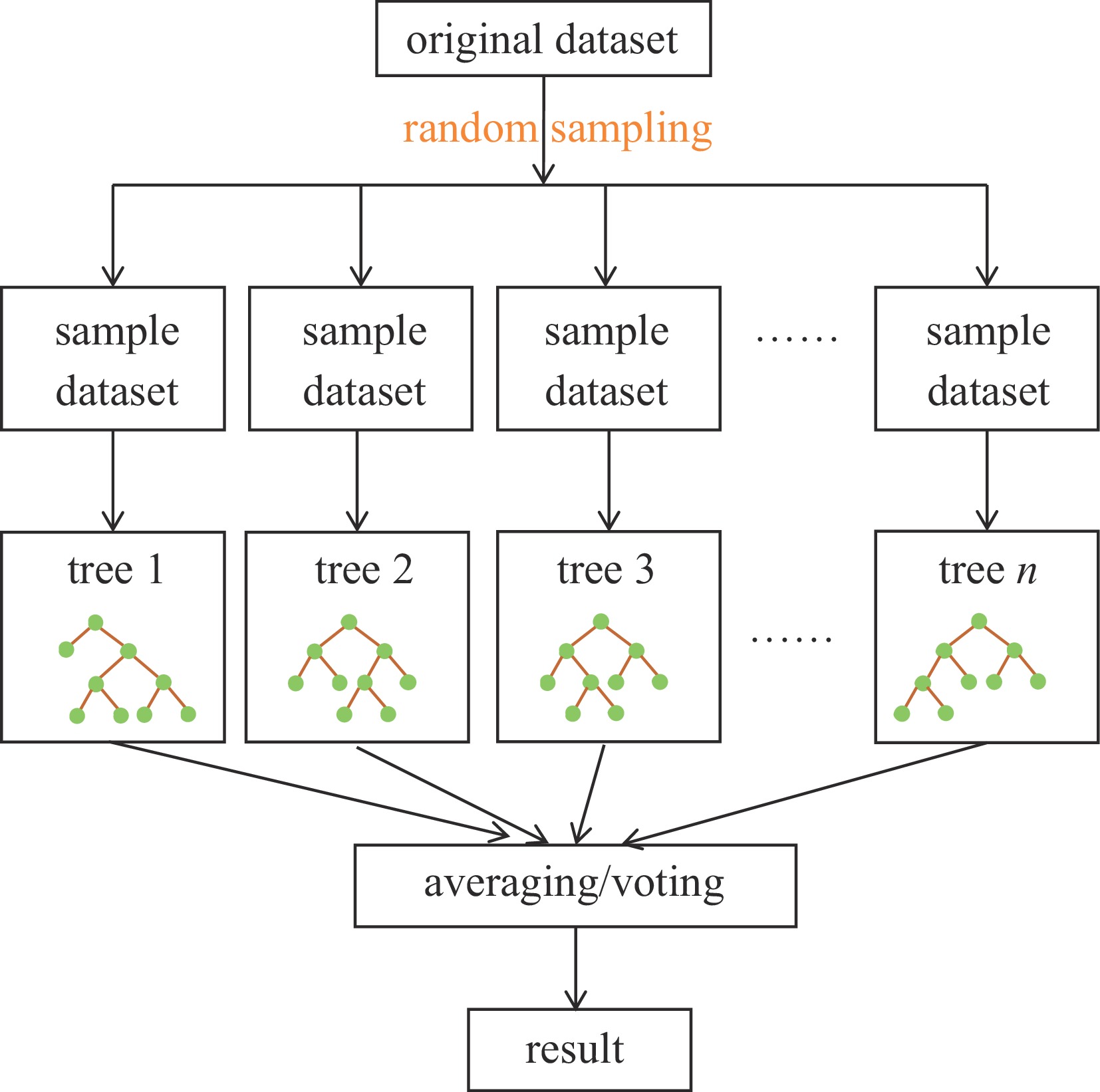
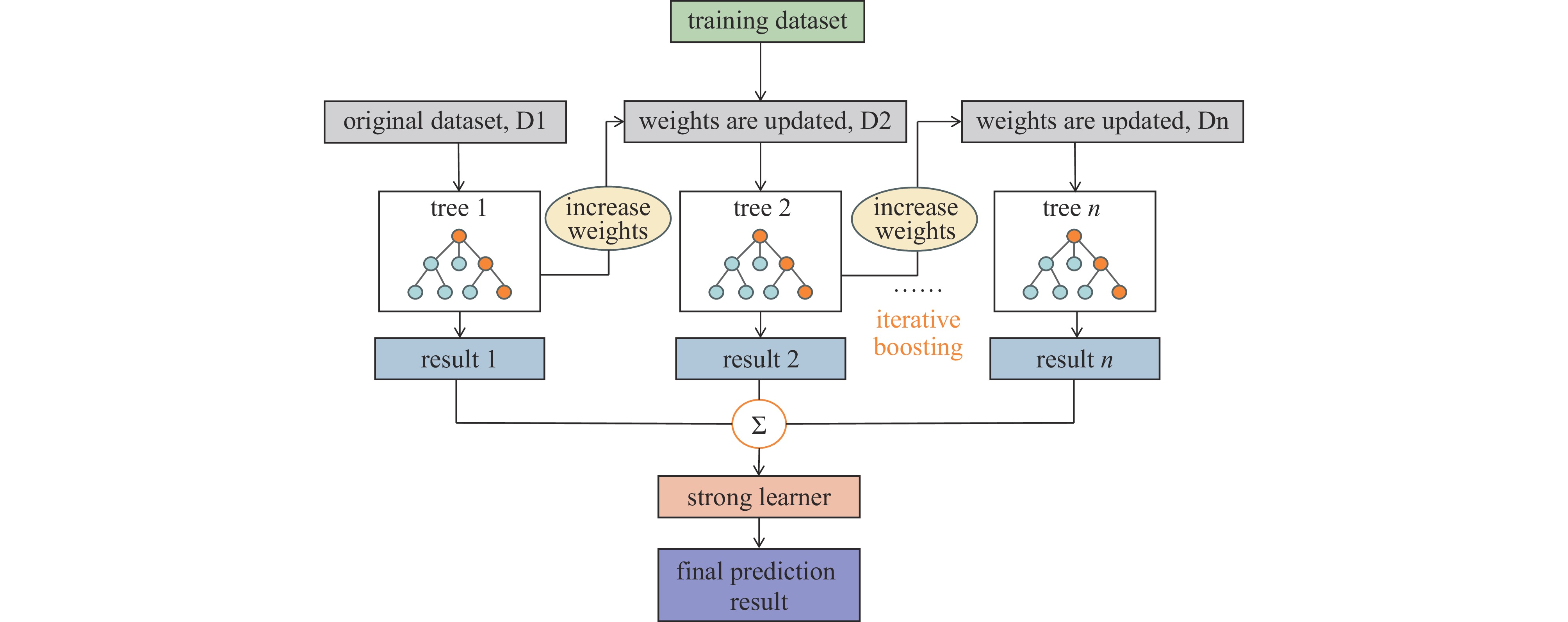
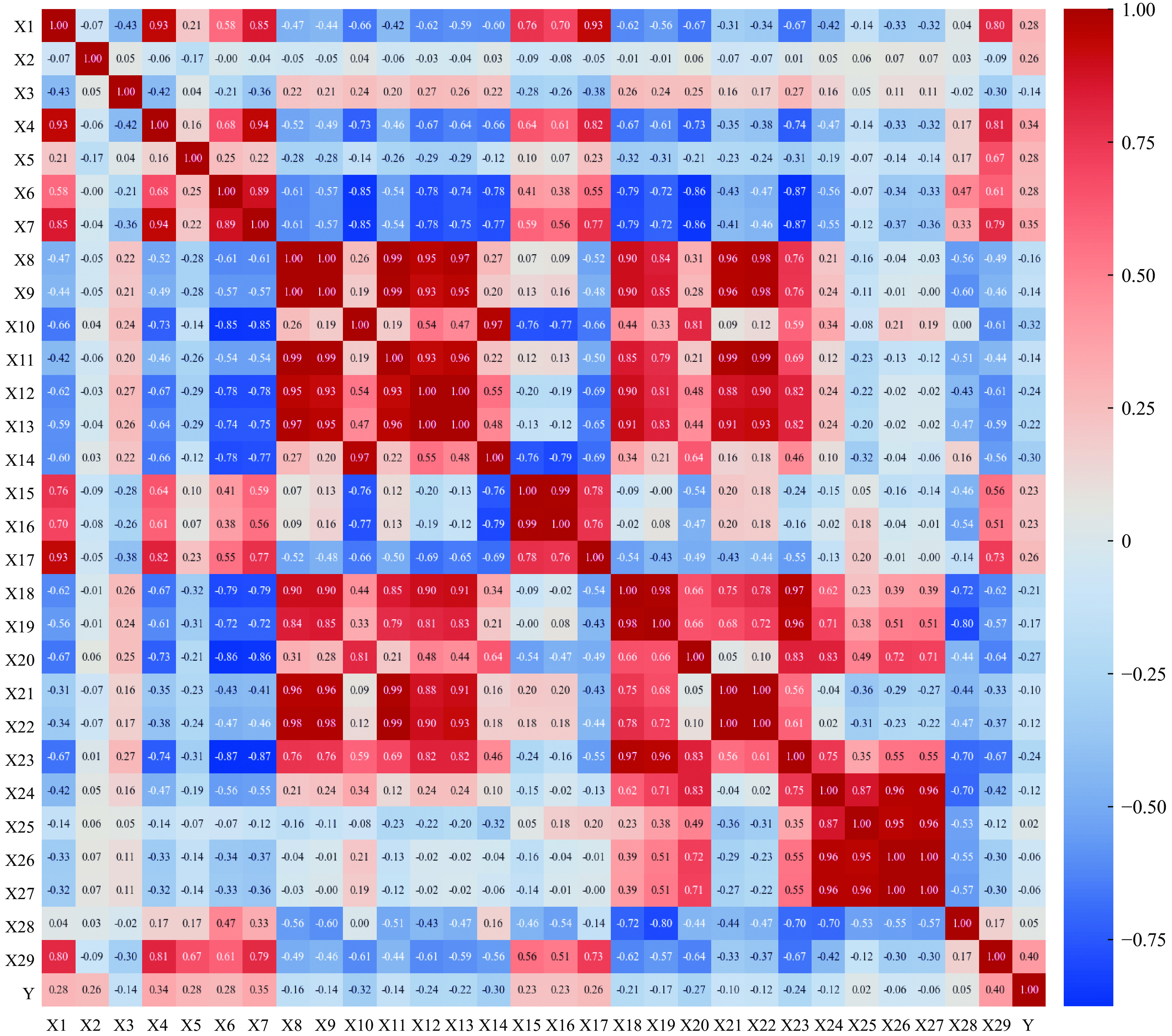
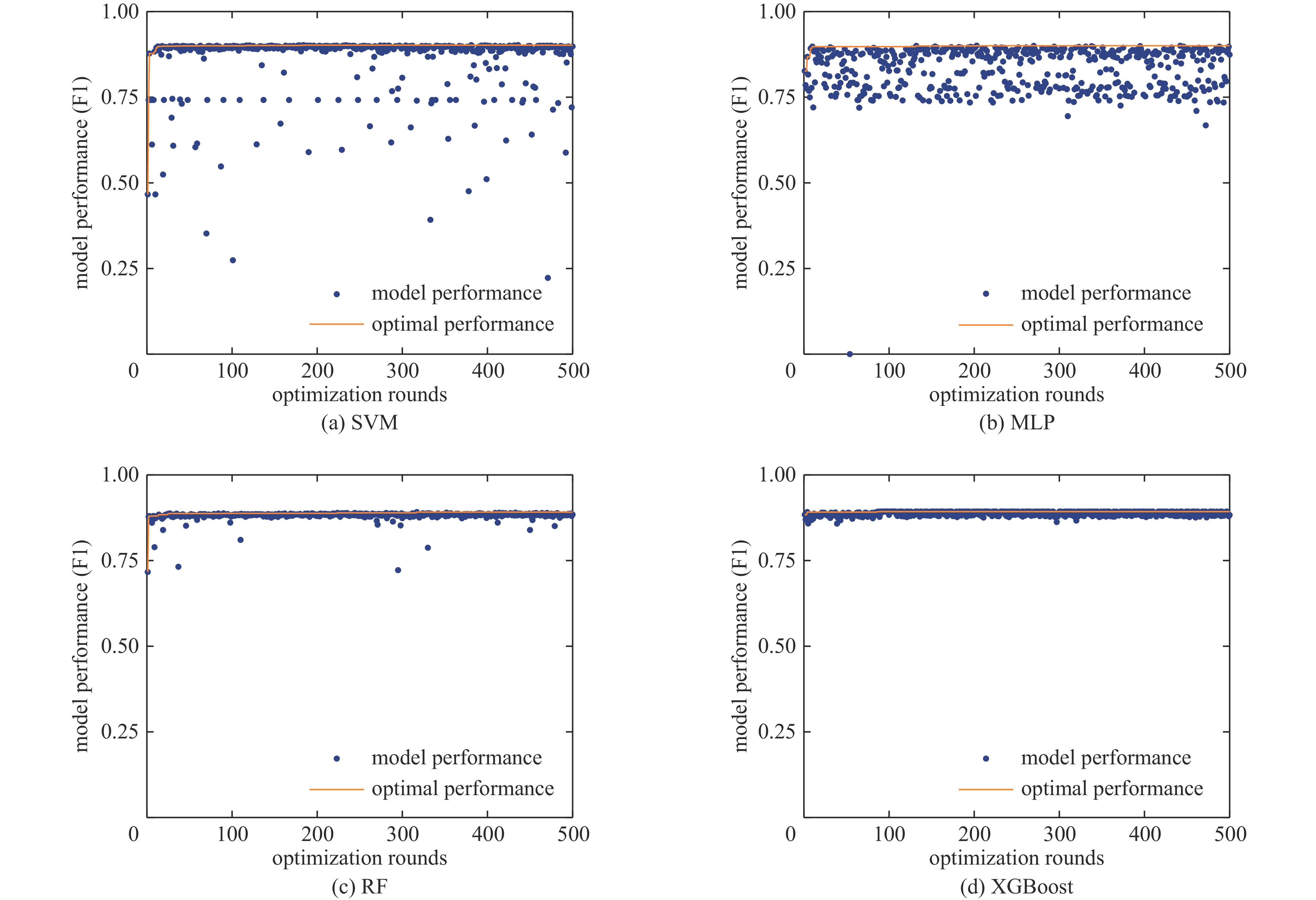
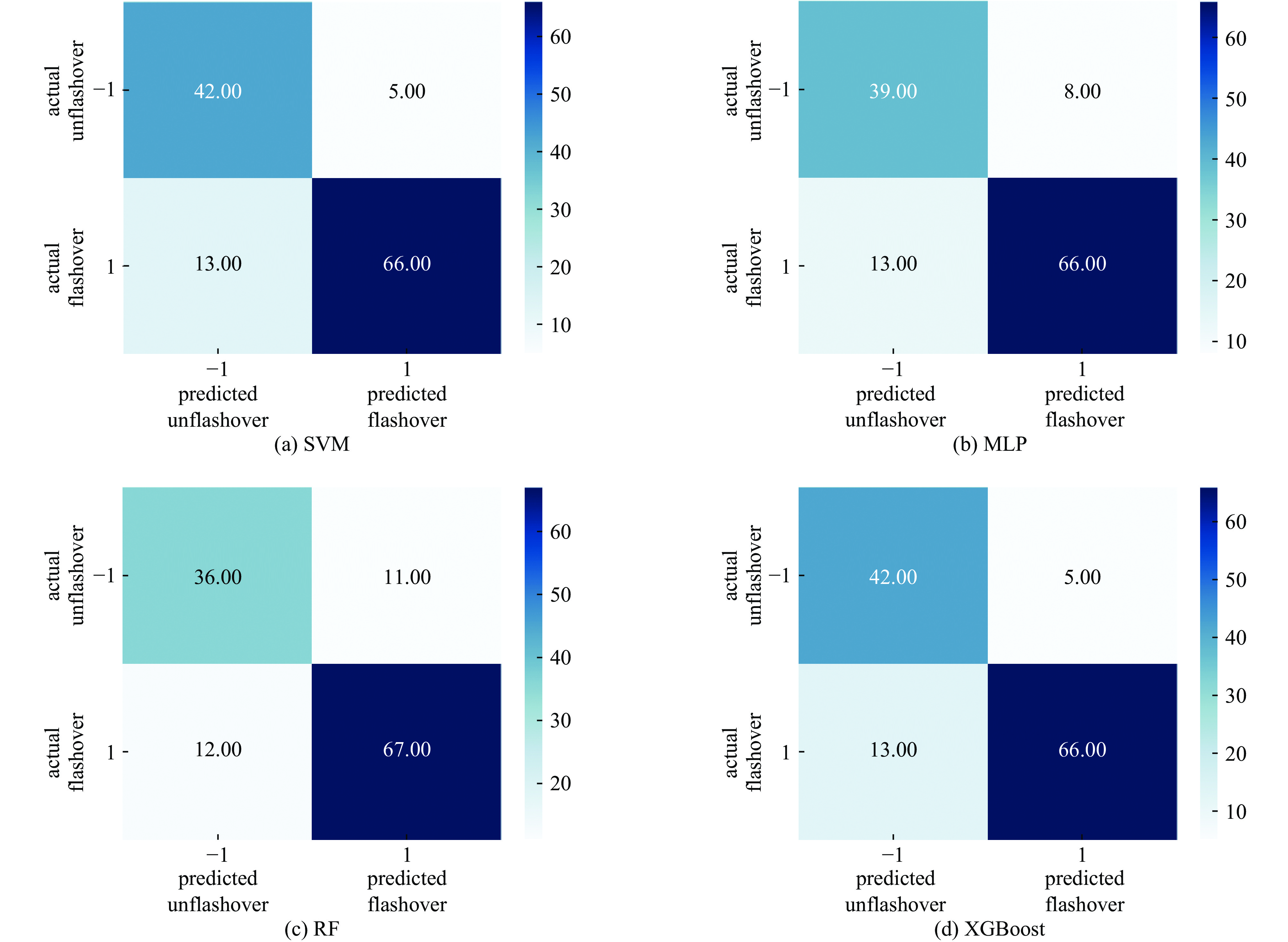
Background The surface flashover in SF6 under nanosecond pulses involves complex physical processes, and accurately predicting the surface flashover voltage of insulating media in such environments constitutes a critical challenge for the design of high-voltage pulsed power equipment and the evaluation of insulation reliability. Compared with traditional AC or DC voltages, the extremely short rise time and high amplitude of nanosecond pulses lead to significant space charge effects and distinct discharge development mechanisms, thereby posing severe challenges to prediction models based on classical theories. In recent years, with the rapid improvement of computer computing power and breakthroughs in artificial intelligence algorithms, data-driven machine learning methods have demonstrated great potential in solving complex nonlinear insulation problems.Purpose Targeting this specific challenge under nanosecond pulses, this paper selects four algorithms, including support vector machine (SVM), multi-layer perceptron (MLP), random forest (RF), and extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost), to train and predict flashover voltage data under different experimental conditions within the multi-scale distance range of 15 mm to 500 mm.Methods First, external operating conditions such as electric field distribution, voltage waveform, and gas pressure were parametrically extracted and characterized. The Pearson correlation coefficient was employed to conduct a correlation analysis on the aforementioned characteristic parameters, and ultimately 22 feature quantities were screened out as the model inputs. Subsequently, the Bayes hyperparameter optimization algorithm was utilized to perform hyperparameter optimization for four types of algorithms, and the 10-fold cross-validation method was adopted to select the optimal hyperparameter combination for each algorithm. After that, the sample training set was input into the four algorithms for training, and each algorithm was validated on the test set.Results The four algorithms demonstrated overall good performance. Among them, Random Forest (RF) and XGBoost exhibited excellent performance on the training set but poor performance on the validation set, which is likely a manifestation of overfitting in ensemble learning and indicates weak generalization ability. Support Vector Machine (SVM) achieved relatively outstanding performance on both the training set and the validation set. Furthermore, the generalization performance of the SVM and XGBoost algorithms was validated using data outside the sample dataset. The results showed that SVM yielded better prediction outcomes on the data outside the sample dataset.Conclusions SVM achieved high prediction accuracy on the training set, test set, and data outside the sample dataset, making it more suitable for the insulation design of electromagnetic pulse simulation devices.-
Key words:
- surface flashover /
- support vector machine /
- voltage prediction /
- artificial intelligence /
- data-driven
-
表 1 特征量列表
Table 1. The list of features
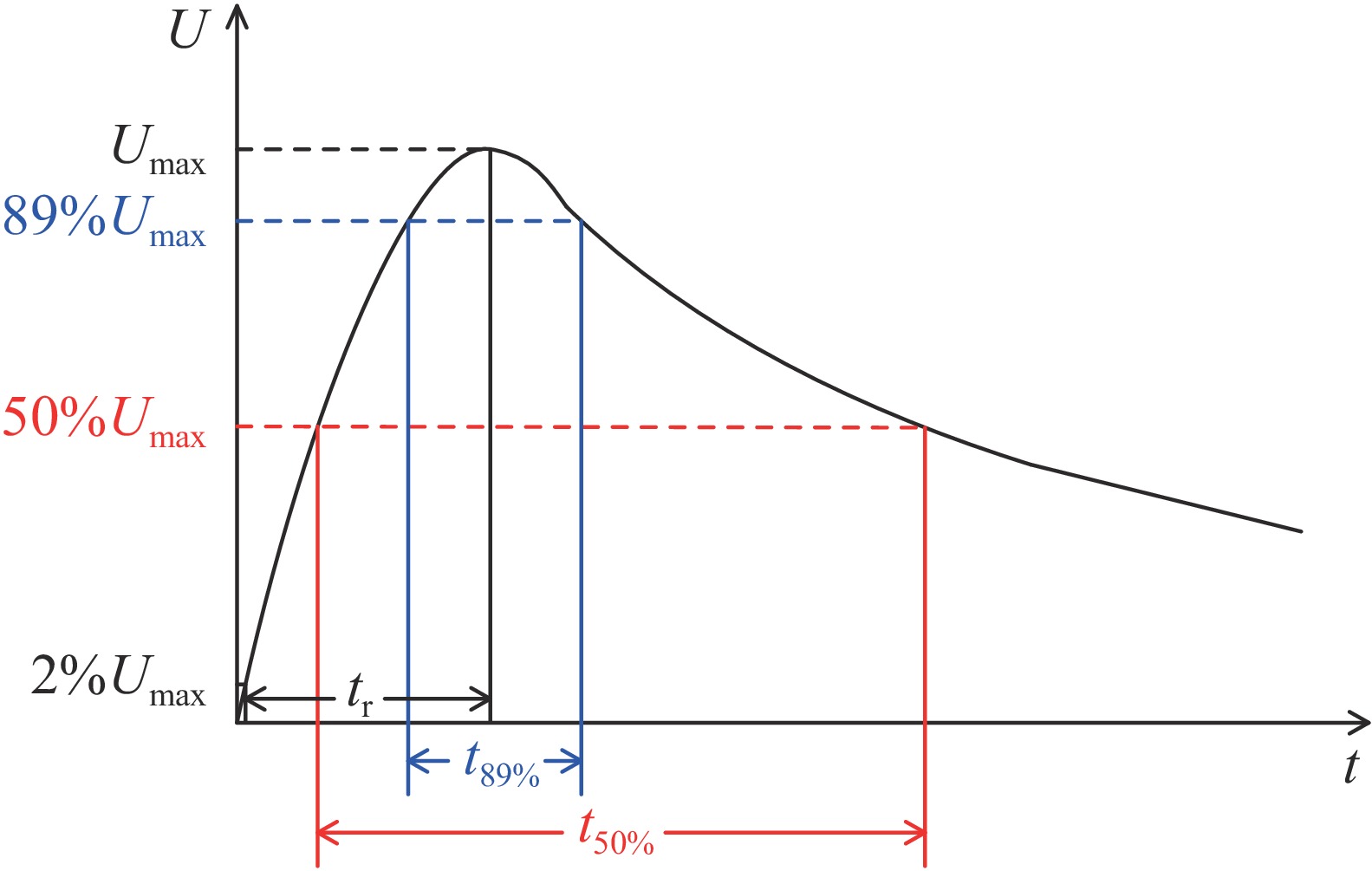
Feature No. class features X1 surface distance L X2 voltage polarity Up X3 gas pressure p X4 voltage rise time tr X5 voltage rise velocity du/dt X6, X7 voltage time features t50,t89 X8~X10 maximum of electric field Emax、Emax_x、Emax_y X11 mean squared error of electric field Estd X12~X14 average value of electric field Eave、Eave_x、Eave_y X15~X17 nonuniformity of electric field Ef、Ef_x、Ef_y X18~X20 gradient of electric field Ega、Ega_x、Ega_y X21, X22 sum of squares of electric field W、Wa X23~X25 electric field integral of the sum of squares We、Wex、Wp X26~X28 integral of electric field V90、V90_x、V90_y X29 voltage amplitude U Y whether flashover occurs −1(unflashover) or 1(flashover) 表 2 输入特征量列表
Table 2. The list of input features
feature No. class features X1 surface distance L X2 voltage polarity Up X3 gas pressure p X4 voltage rise time tr X5 voltage rise velocity du/dt X6, X7 voltage time features t50,t89 X8, X9 maximum of electric field Emax、Emax_y X10 mean squared error of electric field Estd X11, X12 average value of electric field Eave、Eave_y X13, X14 nonuniformity of electric field Ef、Ef_y X15~X17 gradient of electric field Ega、Ega_x、Ega_y X18 sum of squares of electric field Wa X19, X20 electric field integral of the sum of squares We、Wex X21 integral of electric field V90 X22 voltage amplitude U Y whether flashover occurs −1(unflashover) or 1(flashover) 表 3 样本数据表
Table 3. The sample data table
surface distance/mm tr and t50/ns electrodes gas pressure/MPa voltage polarity sample count 15 70/271 needle-plane 0.1 positive 22 negative 27 0.2 positive 19 negative 44 0.3 positive 27 negative 46 rod-ring 0.1 positive 54 negative 33 0.2 positive 46 negative 56 0.3 positive 45 negative 65 plane-plane 0.1 positive 36 negative 43 0.2 positive 39 negative 52 0.3 positive 45 negative 52 50 110/ 1960 plane-plane 0.1 positive 27 negative 29 0.2 positive 23 negative 19 0.3 positive 28 negative 19 200 110/ 1960 plane-plane 0.1 positive 42 negative 72 0.2 positive 23 negative 41 0.3 positive 36 negative 19 300~500 230/ 1470 plane-plane 0.1 positive 44 negative 92 表 4 四种算法的最优超参数组合
Table 4. The optimal hyperparameter combinations of the four algorithms
algorithms hyperparameters optimization range optimal results SVM kernel function polynomial function, radial bases function and sigmoid function radial bases function regularization coefficient 10−2~ 10000 679.17 kernel function bias term −10~10 5.32 kernel coefficient 10−8~100 6.06 polynomial kernel function degree 2~10 none MLP the number of neurons in the 1st hidden layer 100~ 1000 636 the number of neurons in the 2nd hidden layer 100~ 1000 973 learning rate 10−3~1 6.52×10−3 regularization coefficient 10−4~10−2 2.49×10−4 RF the number of base models 0~ 1000 119 maximum tree depth 1~25 16 minimum number of samples to split 2~30 6 minimum leaf node weight 1~20 4 XGBoost the number of base models 0~ 1000 761 learning rate 0.001~0.95 0.9 maximum tree depth 1~25 12 minimum leaf node weight 0~5 2 regularization coefficient 0~5 2 表 5 四种算法的F1值与AUC值
Table 5. The F1 scores and AUC values of the four algorithms
algorithms dataset F1 AUC SVM training set 0.9169 0.9659 validation set 0.8800 0.9496 MLP training set 0.9014 0.9435 validation set 0.8627 0.9200 RF training set 0.9332 0.9818 validation set 0.8535 0.9324 XGBoost training set 0.9197 0.9712 validation set 0.8800 0.9386 表 6 SVM和XGBoost算法对100mm实验的预测结果
Table 6. The prediction results of SVM and XGBoost for 100 mm experiments
algorithms F1 AUC SVM 0.8683 0.8961 XGBoost 0.8216 0.8520 -
[1] 邱孟通, 呼义翔, 吴伟, 等. 西北核技术研究所强脉冲辐射模拟装置近年发展综述[J]. 现代应用物理, 2024, 15: 030101Qiu Mengtong, Hu Yixiang, Wu Wei, et al. Review of the development of intense pulsed radiation simulator and its technology in northwest institute of nuclear technology in the past decade[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2024, 15: 030101 [2] 朱湘琴, 吴伟, 王海洋. 大型水平极化电磁脉冲有界波模拟器的辐射场分布特性分析[J]. 现代应用物理, 2020, 11: 040502Zhu Xiangqin, Wu Wei, Wang Haiyang. Characteristics of radiation electric field distribution in large EMP bounded wave simulator with horizontal polarization[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2020, 11: 040502 [3] Peek F W. The law of corona and the dielectric strength of Air-IV the mechanism of corona formation and loss[J]. Transactions of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers, 1927, XLVI: 1009-1024. [4] Zaengl W S, Petcharaks K. Application of streamer breakdown criterion for inhomogeneous fields in dry air and SF6[M]//Christophorou L G, James D R. Gaseous Dielectrics VII. New York: Springer, 1994: 153-159. [5] Niemeyer L, Ullrich L, Wiegart N. The mechanism of leader breakdown in electronegative gases[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electrical Insulation, 1989, 24(2): 309-324. doi: 10.1109/14.90289 [6] Seeger M, Niemeyer L, Bujotzek M. Partial discharges and breakdown at protrusions in uniform background fields in SF6[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2008, 41: 185204. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/41/18/185204 [7] MartinT H, Guenther A H, Kristiansen M. J. C. Martin on pulsed power[M]. New York: Springer, 1996. [8] 刘锡三. 高功率脉冲技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2005Liu Xisan. High pulsed power technology[M]. Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, 2005 [9] Ghosh P S, Chlakravorti S, Chatterjee N. Estimation of time-to-flashover characteristics of contaminated electrolytic surfaces using a neural netlwork[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 1995, 2(6): 1064-1074. [10] 杨庆, 司马文霞, 蒋兴良, 等. 复杂环境条件下绝缘子闪络电压预测神经网络模型的建立及应用[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2005, 25(13): 155-159Yang Qing, Sima Wenxia, Jiang Xingliang, et al. The building and application of a neural network model for forecasting the flashover voltage of the insulator in complex ambient conditions[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2005, 25(13): 155-159 [11] 石岩, 蒋兴良, 苑吉河. 基于RBF网络的覆冰绝缘子闪络电压预测模型[J]. 高电压技术, 2009, 35(3): 591-596Shi Yan, Jiang Xingliang, Yuan Jihe. Flashover voltage forecasting mode of iced insulator based on RBF network[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2009, 35(3): 591-596 [12] 王永强, 王巨伟, 张斌, 等. 基于FLN的覆雪绝缘子闪络电压预测方法[J]. 电瓷避雷器, 2017(6): 241-245Wang Yongqiang, Wang Juwei, Zhang Bin, et al. Study on prediction method of flashover voltage of snow-covered insulators based on FLN[J]. Insulators and Surge Arresters, 2017(6): 241-245 [13] 舒立春, 白困利, 胡琴, 等. 基于支持向量机的复杂环境条件下绝缘子闪络电压的预测[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2006, 26(17): 127-131Shu Lichun, Bai Kunli, Hu Qin, et al. Insulator flashover voltage forecasting under complex circumstance based on support vector machine[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2006, 26(17): 127-131 [14] 阮江军, 徐闻婕, 邱志斌, 等. 基于支持向量机的雾中棒–板间隙击穿电压预测[J]. 高电压技术, 2018, 44(3): 711-718Ruan Jiangjun, Xu Wenjie, Qiu Zhibin, et al. Breakdown voltage prediction of rod-plane gap in fog based on support vector machine[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2018, 44(3): 711-718 [15] Vapnik V N. The nature of statistical learning theory[M]. New York: Springer, 1995: 138-146. [16] 邓乃扬, 田英杰. 支持向量机: 理论、算法和拓展[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 43-62Deng Naiyang, Tian Yingjie. The theory, algorithm and application of support vector machine[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009: 43-62 [17] 高同虎. 基于SVM的附着藻类绝缘子电场畸变与闪络电压预测研究[D]. 淄博: 山东理工大学, 2020Gao Tonghu. Prediction of electric field distortion and flashover voltage of algae-covered insulators based on SVM[D]. Zibo: Shandong University of Technology, 2020 [18] 李云淏, 咸日常, 张海强, 等. 基于改进灰狼算法与最小二乘支持向量机耦合的电力变压器故障诊断方法[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47(4): 1470-1477Li Yunhao, Xian Richang, Zhang Haiqiang, et al. Fault diagnosis for power transformers based on improved grey wolf algorithm coupled with least squares support vector machine[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47(4): 1470-1477 [19] 郝蛟, 林宏, 李雨森, 等. 基于改进多层感知机的电网运行风险评估方法[J]. 现代电力, 2023, 40(4): 474-483Hao Jiao, Lin Hong, Li Yusen, et al. A method to assess power grid operation risk based on improved multi-layer perceptron[J]. Modern Electric Power, 2023, 40(4): 474-483 [20] Hayati M, Rezaei A, Seifi M. CNT-MOSFET modeling based on artificial neural network: application to simulation of nanoscale circuits[J]. Solid-State Electronics, 2010, 54(1): 52-57. doi: 10.1016/j.sse.2009.09.027 [21] 罗艳, 肖辅盛, 王庭刚, 等. 基于随机森林的电网实时运行风险评估方法[J]. 信息技术, 2020, 44(4): 23-26,31Luo Yan, Xiao Fusheng, Wang Tinggang, et al. Real-time risk assessment method for power grid operation based on random forest[J]. Information Technology, 2020, 44(4): 23-26,31 [22] 周云浩, 杨宝杰, 刘丹, 等. 基于随机森林算法的电力工程数据预测分析建模与仿真[J]. 电子设计工程, 2024, 32(4): 103-106,111Zhou Yunhao, Yang Baojie, Liu Dan, et al. Modeling and simulation of power engineering data prediction and analysis based on Random Forest algorithm[J]. Electronic Design Engineering, 2024, 32(4): 103-106,111 [23] Mantas C J, Castellano J G, Moral-García S, et al. A comparison of random forest based algorithms: random credal random forest versus oblique random forest[J]. Soft Computing, 2019, 23(21): 10739-10754. doi: 10.1007/s00500-018-3628-5 [24] Chen Jinxiang, Zhao Feng, Sun Yanguang, et al. Improved XGBoost model based on genetic algorithm[J]. International Journal of Computer Applications in Technology, 2020, 62(3): 240-245. doi: 10.1504/IJCAT.2020.106571 [25] Su Wei, Jiang Fan, Shi Chunyan, et al. An XGBoost-based knowledge tracing model[J]. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, 2023, 16(1): 13. doi: 10.1007/s44196-023-00192-y [26] 刘琳, 李晓昂, 张锐, 等. 影响GIS支柱绝缘子闪络电压的沿面电场特征参数[J]. 高电压技术, 2019, 45(9): 2740-2747Liu Lin, Li Xiaoang, Zhang Rui, et al. Characteristic parameters of electric field along the surface affecting the flashover voltage of GIS pillar insulators[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2019, 45(9): 2740-2747 [27] Qiu Zhibin, Ruan Jiangjun, Lu Wei, et al. Feature extraction of electric field distribution and its application in discharge voltage prediction of large sphere-plane air gaps[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2018, 25(3): 1030-1038. doi: 10.1109/TDEI.2018.006851 [28] 樊嵘, 孟大志, 徐大舜. 统计相关性分析方法研究进展[J]. 数学建模及其应用, 2014, 3(1): 1-12Fan Rong, Meng Dazhi, Xu Dashun. Survey of research process on statistical correlation analysis[J]. Mathematical Modeling and its Applications, 2014, 3(1): 1-12 [29] 崔佳旭, 杨博. 贝叶斯优化方法和应用综述[J]. 软件学报, 2018, 29(10): 3068-3090Cui Jiaxu, Yang Bo. Survey on bayesian optimization methodology and applications[J]. Journal of Software, 2018, 29(10): 3068-3090 -




 下载:
下载: