Research on Magnetron Injection Gun with Curved Cathode for Megawatt-class Gyrotron Traveling Wave Tube
-
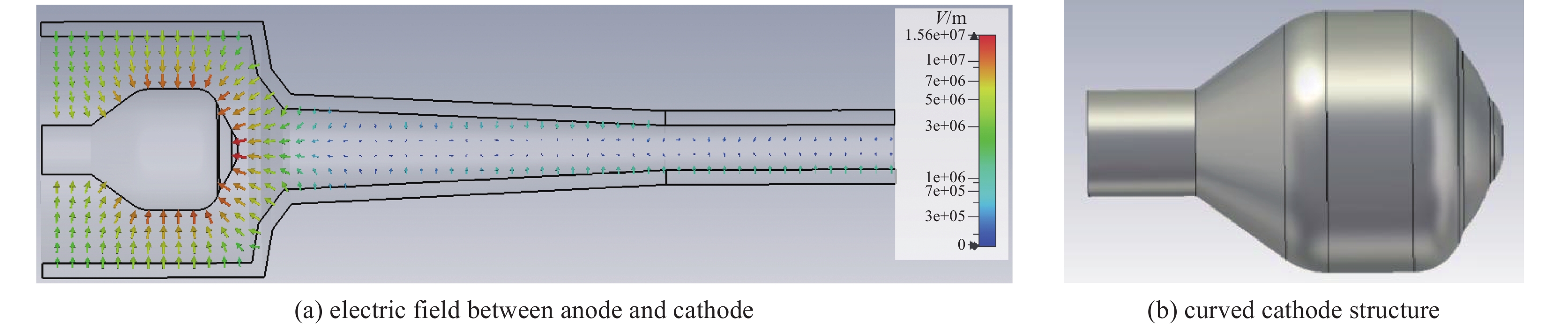
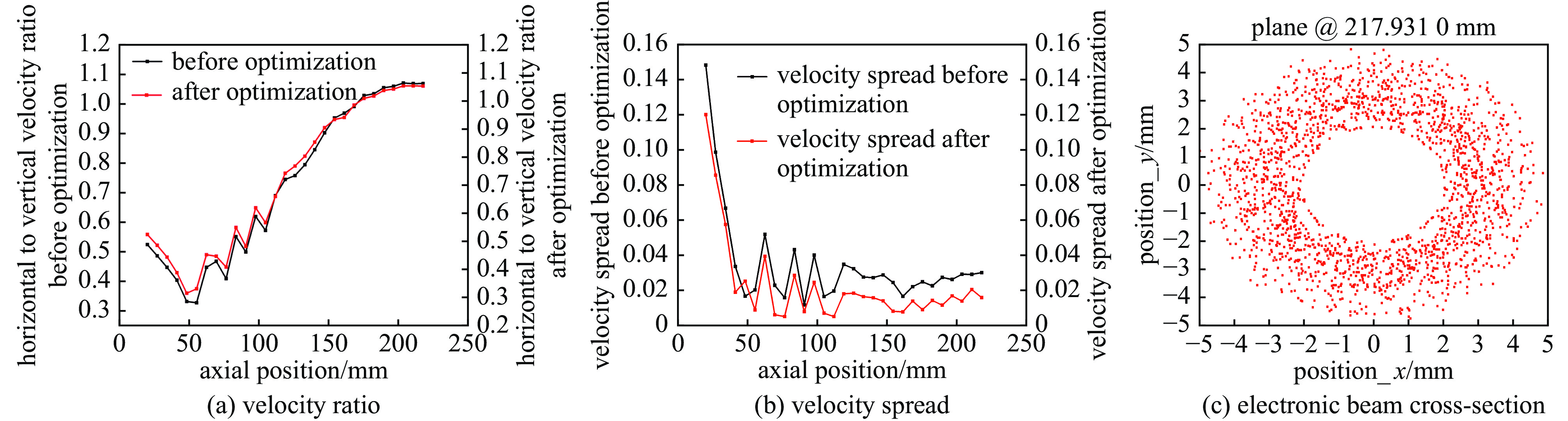
摘要: 为了满足研制兆瓦级大功率回旋行波管对高压、大电流、低电子注速度零散磁控注入电子枪的迫切需求,本文针对性地给出了一支新型磁控注入单阳极电子枪的设计方案。该新型电子枪方案引入曲面阴极结构,以降低电子枪的速度零散,同时有效增大阴极发射带面积,降低阴极发射密度,从根本上提高电子枪的工作稳定性与寿命。PIC仿真的结果表明:在115 kV、43 A的工作条件下,该电子枪的横纵速度比为1.05,速度零散为1.63%,引导中心半径为3.41 mm,满足应用需求。Abstract:
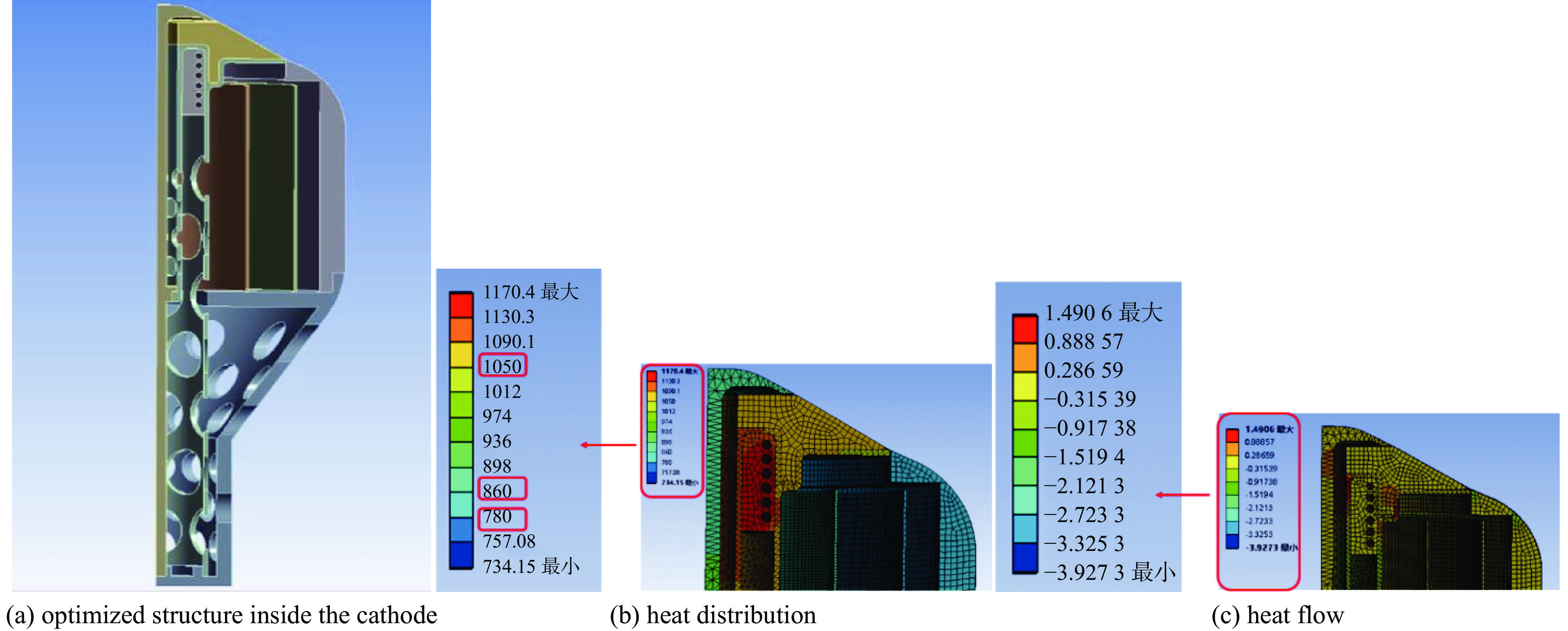
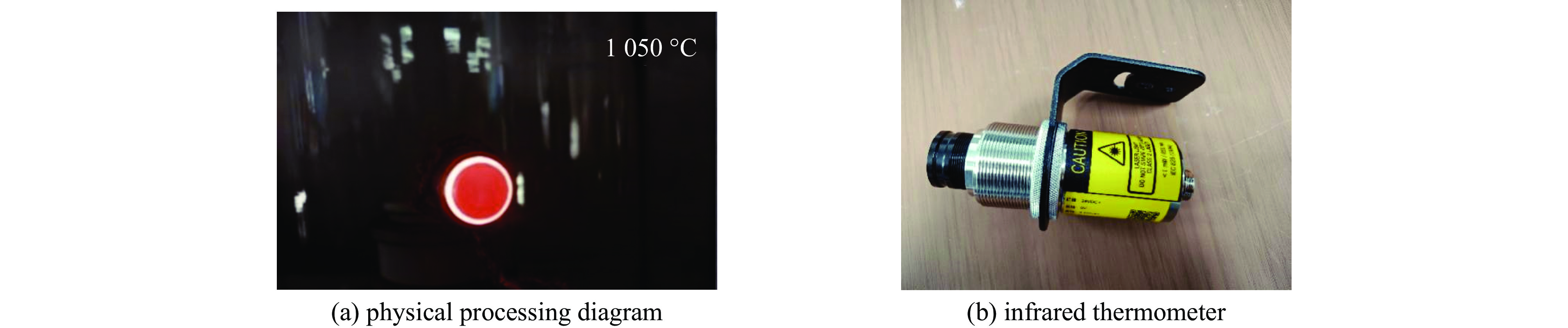
Background Gyrotron traveling wave tube (Gyro-TWT) is a vacuum electronic device with broad application prospects. Magnetron injection gun (MIG) is one of the core components of gyro-TWT, and its performance directly determines the success or failure of gyro-TWT. From the current research results on MIGs at home and abroad, it can be seen that the working voltage and current of existing MIGs are mostly low, and the velocity spread is generally high, which cannot meet the requirements of future megawatt-class gyro-TWT for MIG.Purpose In order to meet the requirement for MIG with high voltage, high current, and low electron beam velocity spread in the development of megawatt-class high-power gyro-TWT, this paper presents a novel design scheme for a single anode electron gun.Methods The novel electron gun scheme introduces a curved cathode structure to reduce the velocity spread of the electron beam, while effectively increasing the cathode emission band area and reducing the cathode emission density.Results The results of PIC simulation show that under the working conditions of 115 kV and 43 A, the designed electron gun has a transverse to longitudinal velocity ratio of 1.05, a velocity spread of 1.63%, and a guiding center radius of 3.41 mm. The thermal analysis results indicate that the MIG can heat the cathode to1050 ℃ at a power of 76 W.Conclusions The simulation and thermal analysis results indicate that the designed MIG meets the design expectations and satisfies the requirements of high voltage, high current, and low electron beam velocity spread for megawatt level gyro-TWT.-
Key words:
- gyro-TWT /
- MIG /
- high power millimeter wave /
- curved cathode /
- velocity spread
-
表 1 高压大电流低速度零散电子枪设计输入参数
Table 1. Design input parameters of high voltage, high current, low velocity spread electron gun
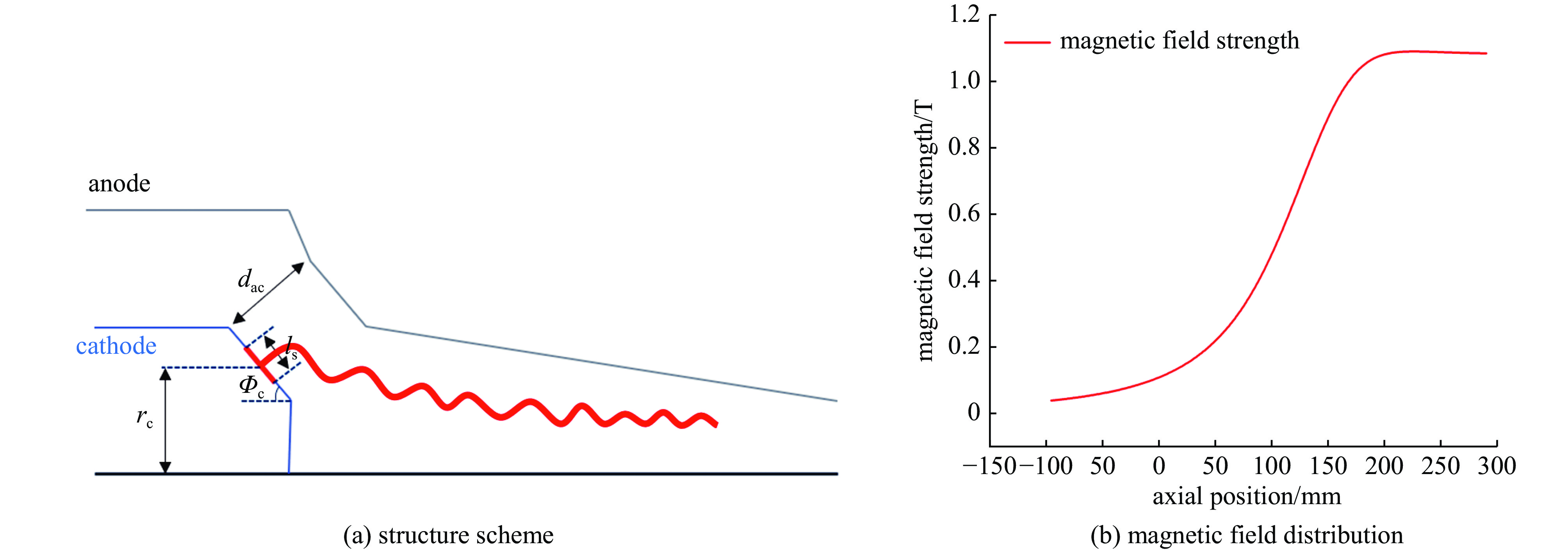
Va/kV I0/A B0/T α Δβ rg0/mm P/W Ec/V/m Jc/(A·cm−2) 115 43 1.09 1.05 <2% 3.4±1.5 <100 <1.6×107 <10 表 2 高压大电流低速度零散电子枪初始设计输出参数
Table 2. Initial design output parameters of high voltage, high current, low velocity spread electron gun
rc/mm ls/mm ϕc fm dac/mm 9.3 7.7 55° 7 12.5 表 3 回旋行波管电子枪阴极各组件材料
Table 3. Materials of each component of the cathode of the gyro-TWT electron gun
cathode structure material thermal conductivity/
(W·m−1·K−1)thermal expansion
coefficient/(μm·K−1)Young’s modulus/
GPaPoisson’s
ratioemission belt Ba-W alloy 200 4 300 0.28 pre and post formed poles, support and heat shield Mo 138 5.35 330 0.38 filament filling material alumina powder 7 5.5 350 0.22 base steel stainless 50 11 200 0.26 表 4 阴极各组件形变量
Table 4. Variable deformation of cathode components
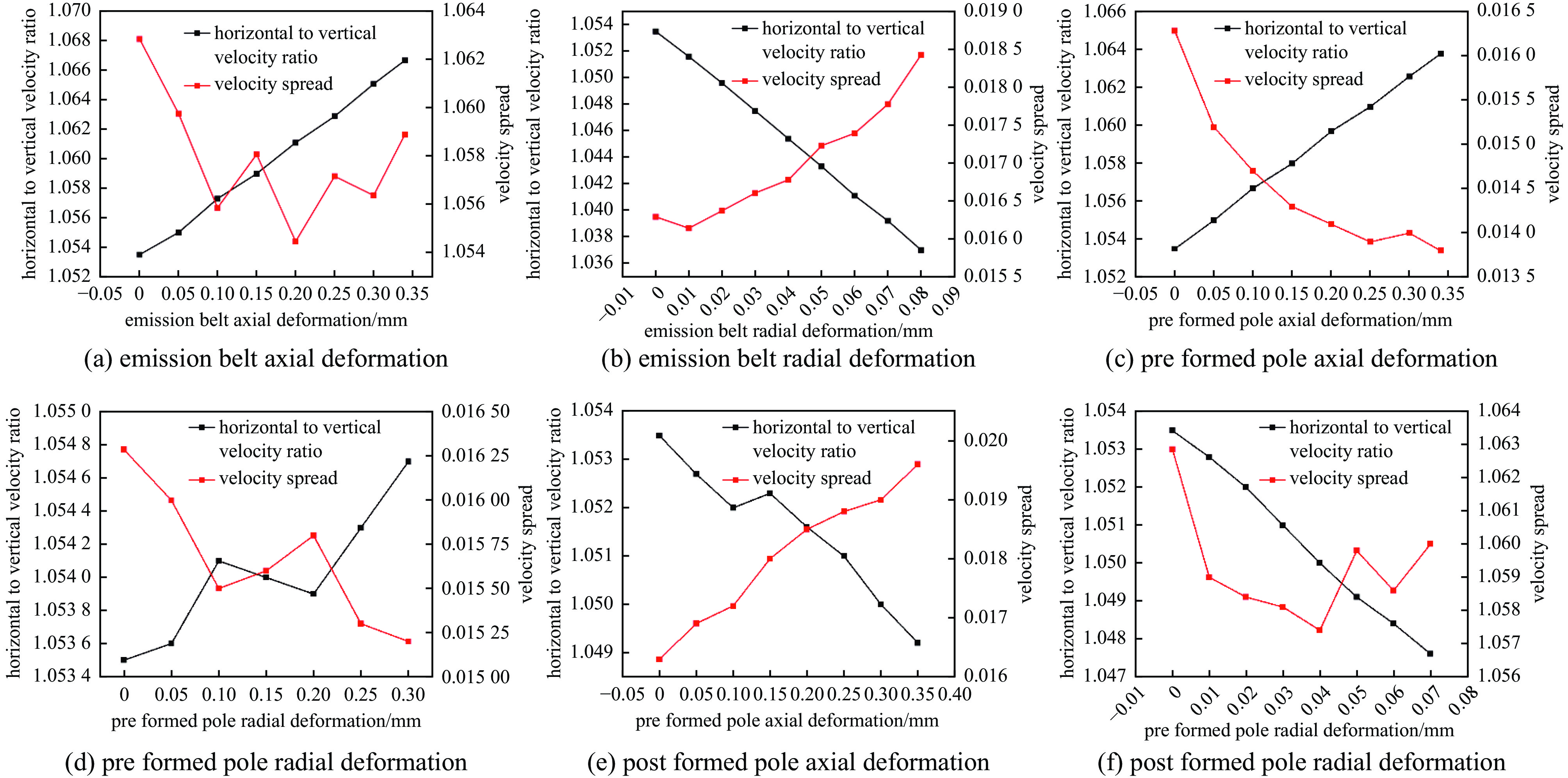
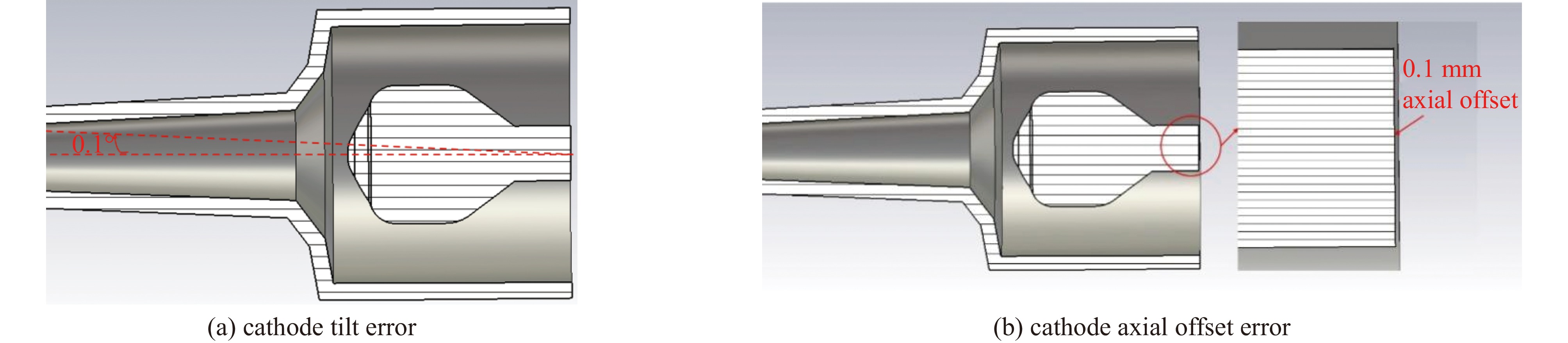
cathode component maximum axial deformation/mm maximum radial deformation/mm emission belt 0.343 0.062 pre formed pole 0.335 0.028 post formed pole 0.34 0.06 -
[1] Xu Yong, Mao Ya, Wang Weijie, et al. Proof-of-principle experiment of a 20-kW-average-power Ka-band gyro-traveling wave tube with a cut-off waveguide section[J]. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2020, 41(5): 769-772. doi: 10.1109/LED.2020.2979629 [2] 薛智浩, 刘濮鲲, 杜朝海. Ka波段螺旋波纹波导回旋行波管[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2012, 24(5): 1013-1014 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122405.1013Xue Zhihao, Liu Pukun, Du Chaohai. Linear calculation of Ka-band gyro-TWT with helical waveguide[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2012, 24(5): 1013-1014 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122405.1013 [3] Zhang Minghao, Wei Yanyu, Yue Lingna, et al. A research of 140-GHz folded rectangular groove waveguide traveling-wave tube[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2015, 24(4): 873-876. doi: 10.1049/cje.2015.10.035 [4] 安晨翔, 周宁, 陈坤, 等. 220 GHz共焦波导回旋行波管放大器衍射损耗率分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2025, 37: 093003An Chenxiang, Zhou Ning, Chen Kun, et al. Analysis of reasonable diffraction loss rate in 220 GHz confocal waveguide gyro-TWT amplifier[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2025, 37: 093003 [5] Cao Yingjian, Wang Yu, Liu Guo, et al. High-power multifrequency radiation source based on gyro-TWT with external coupling feedback[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2024, 52(5): 1654-1660. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2024.3400219 [6] Hu Peng, Guo Jun, Sun Dimin, et al. Design and experiment of an X-band high-efficiency gyro-TWT demonstrating 100-kW 1-second long-pulse radiations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2023, 70(6): 2712-2718. doi: 10.1109/TED.2022.3217114 [7] Wang Jianxun, Luo Yong, Luhmann N C. The simulation of a high-power low-velocity-spread space-charge-limited (SCL) cusp gun[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2010, 38(12): 3356-3362. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2010.2085090 [8] Samsonov S V, Leshcheva K A, Manuilov V N. Multitube helical-waveguide gyrotron traveling-wave amplifier: device concept and electron-optical system modeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2020, 67(8): 3385-3390. doi: 10.1109/TED.2020.3001491 [9] Jiang Wei, Lu Chaoxuan, Liu Yunpeng, et al. Investigation of a multibeam magnetron injection gun for a w-band sectorial-tunnel gyro-TWT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2021, 68(10): 5211-5214. doi: 10.1109/TED.2021.3102889 [10] Dong Kun, Luo Yong, Li Hao, et al. Design of a novel MIG for a 140-GHz 2-kW confocal gyrotron traveling-wave tube[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2015, 62(11): 3832-3836. doi: 10.1109/TED.2015.2477356 [11] Akash, Thottappan M. Design and efficiency enhancement studies of periodically dielectric loaded W-band gyro-TWT amplifier[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2020, 67(7): 2925-2932. doi: 10.1109/TED.2020.2996191 [12] Dai Boxin, Jiang Wei, Han Binyang, et al. Investigation of a magnetron injection gun with an external anode for Ka-band gyro-TWT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2025, 72(3): 1448-1454. doi: 10.1109/TED.2025.3534181 [13] Jiang Wei, Liu Yunpeng, Lu Chaoxuan, et al. Design and analysis of a diode magnetron injection gun for a G-band gyro-TWT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2022, 69(3): 1429-1434. doi: 10.1109/TED.2022.3144649 [14] 王威. K波段双模回旋行波管电子枪研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2024: 12-15Wang Wei. Research on dual mode electron gun for K band Gyro-TWT[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2024: 12-15 [15] 安晨翔, 周宁, 陈坤, 等. 相对论强流电子束驱动的X波段同轴回旋管腔体设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2025, 37: 073001An Chenxiang, Zhou Ning, Chen Kun, et al. Design of X-band coaxial gyrotron cavity driven by intense relativistic electron beam[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2025, 37: 073001 [16] Xue Cun, Wang Qingyu, Ren Hanxi, et al. Case studies on time-dependent Ginzburg-Landau simulations for superconducting applications[J]. Electromagnetic Science, 2024, 2(2): 1-20. [17] 董坤, 罗勇, 蒋伟, 等. W波段回旋行波管新型曲线阴极磁控注入电子枪优化设计[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2016, 35(4): 483-487,495Dong Kun, Luo Yong, Jiang Wei, et al. Optimal design of a novel magnetron injection gun with curved emitter for a W-band gyrotron traveling wave tube[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2016, 35(4): 483-487,495 -




 下载:
下载: