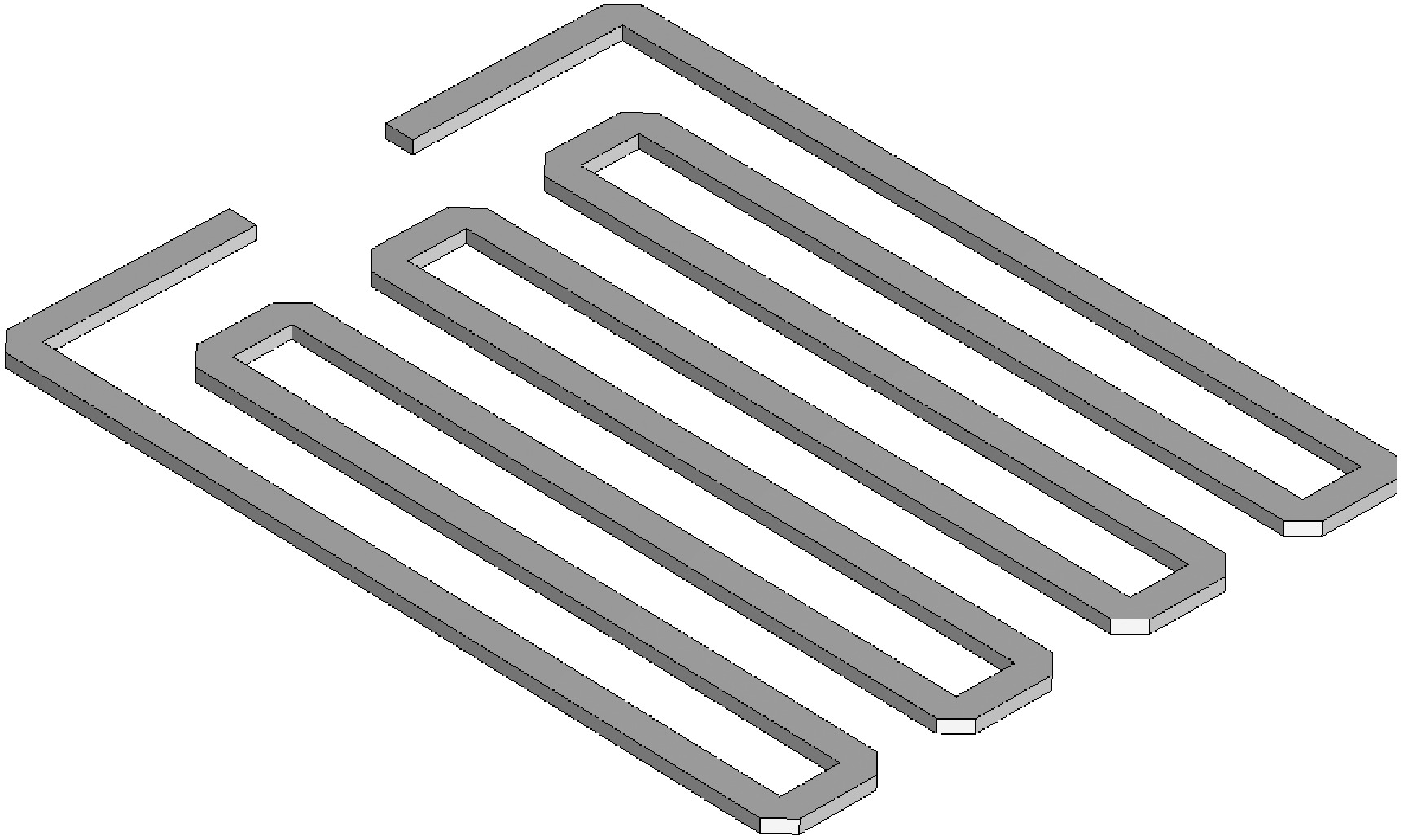
Design of a ring-shaped high-power microwave pulse compressor
-
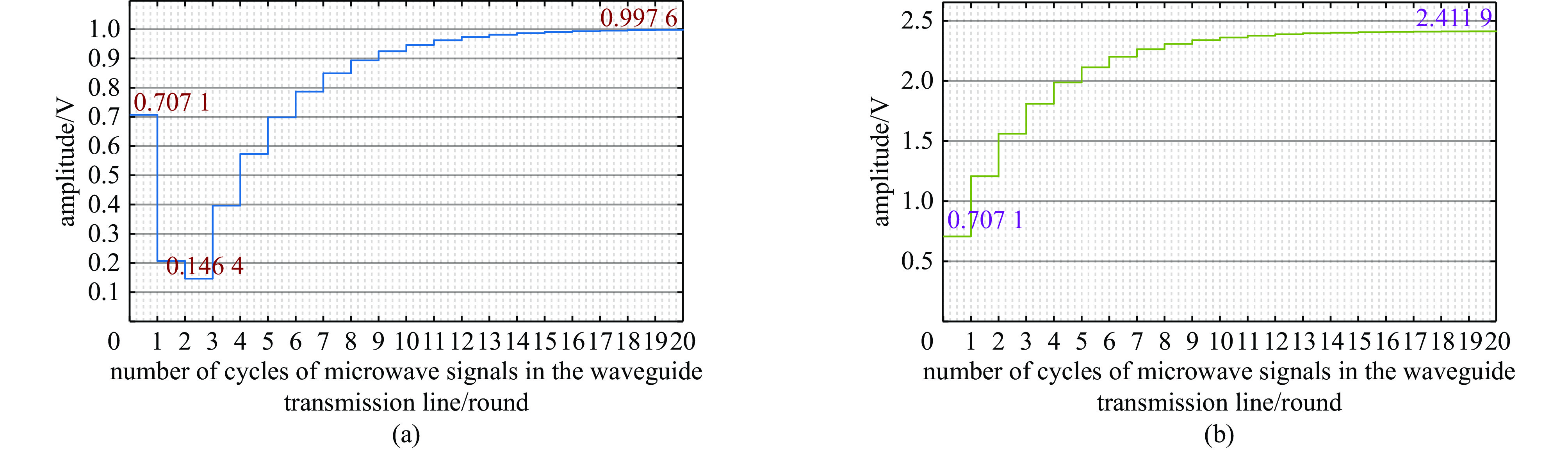
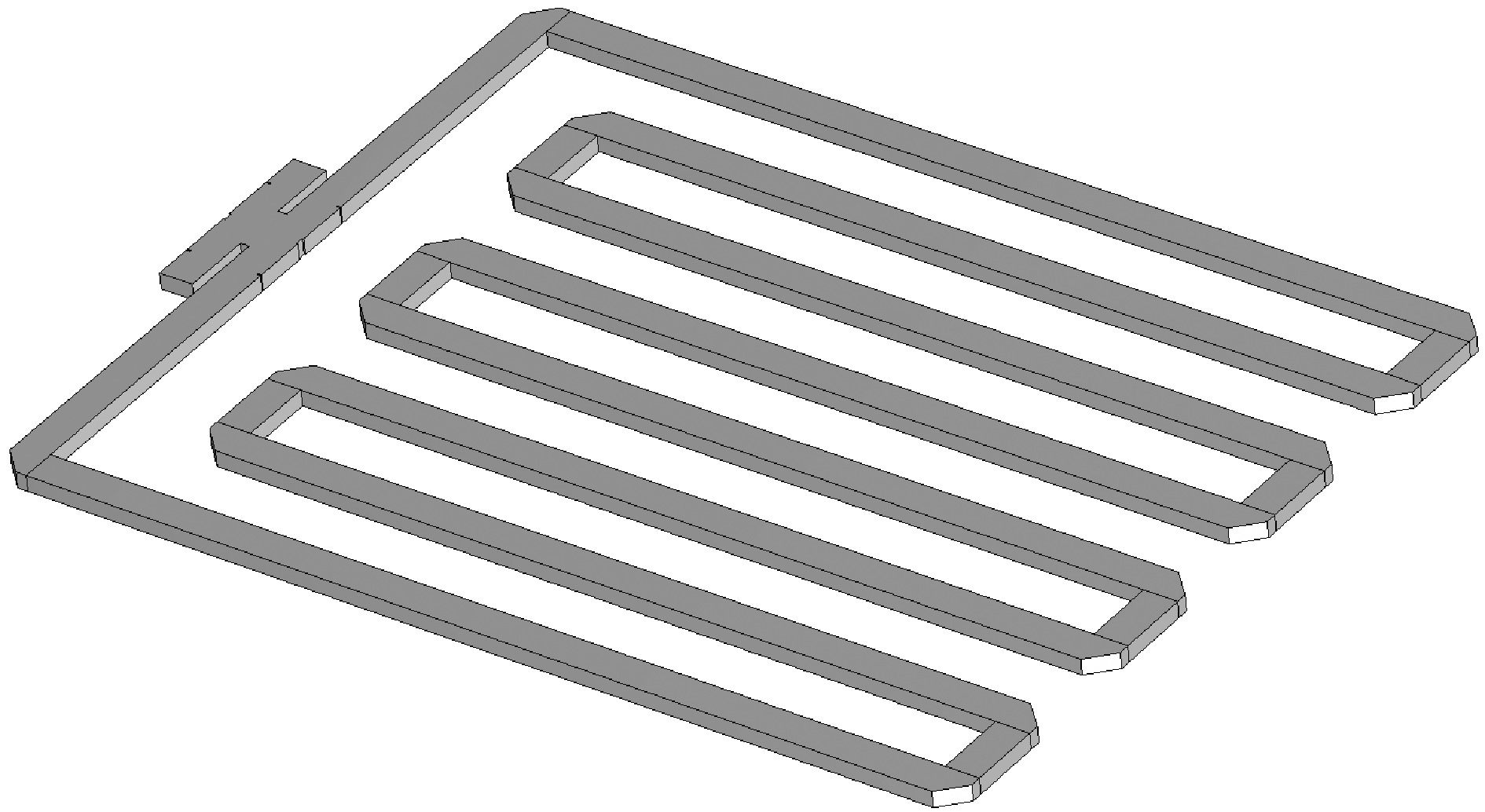
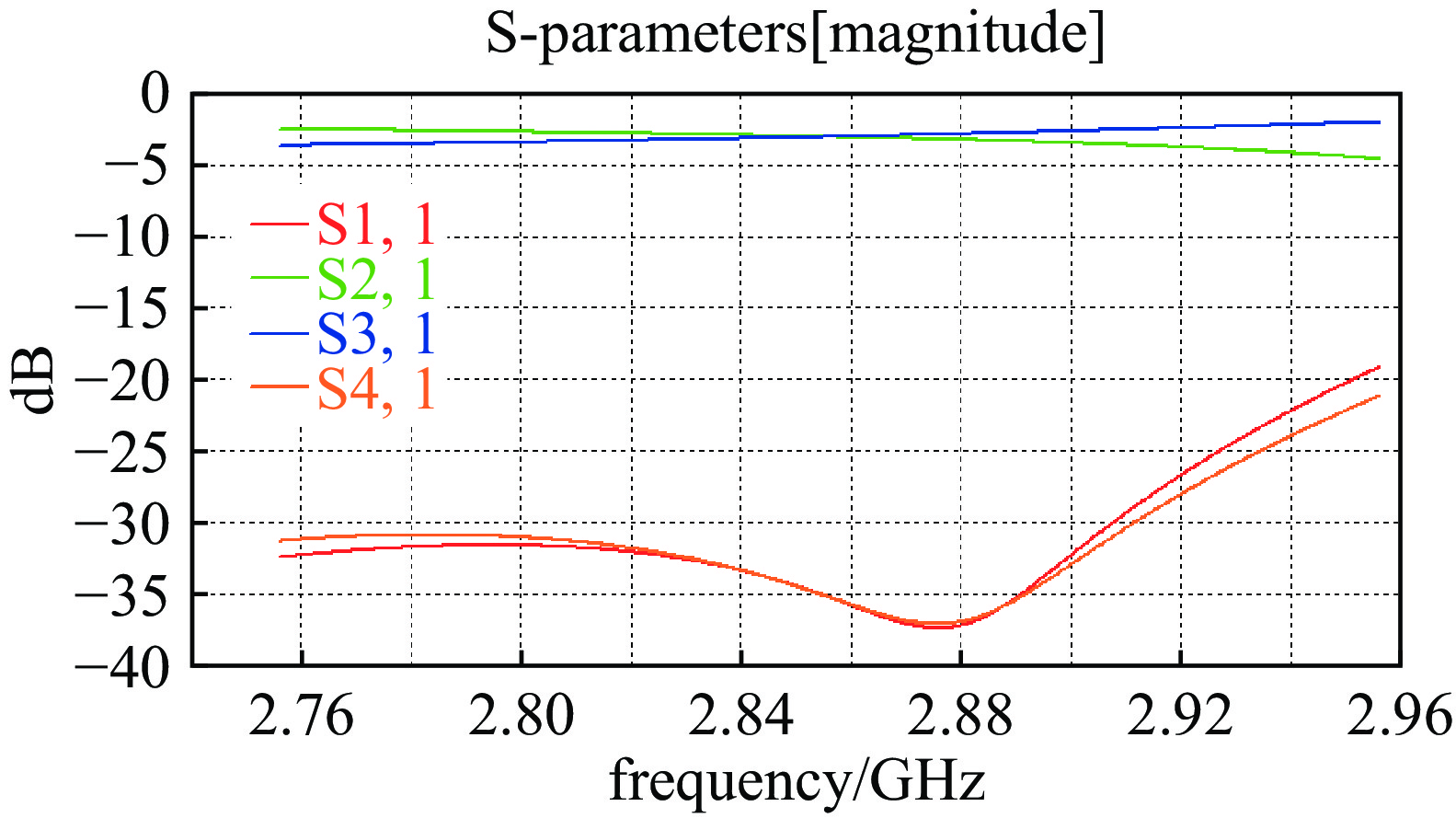
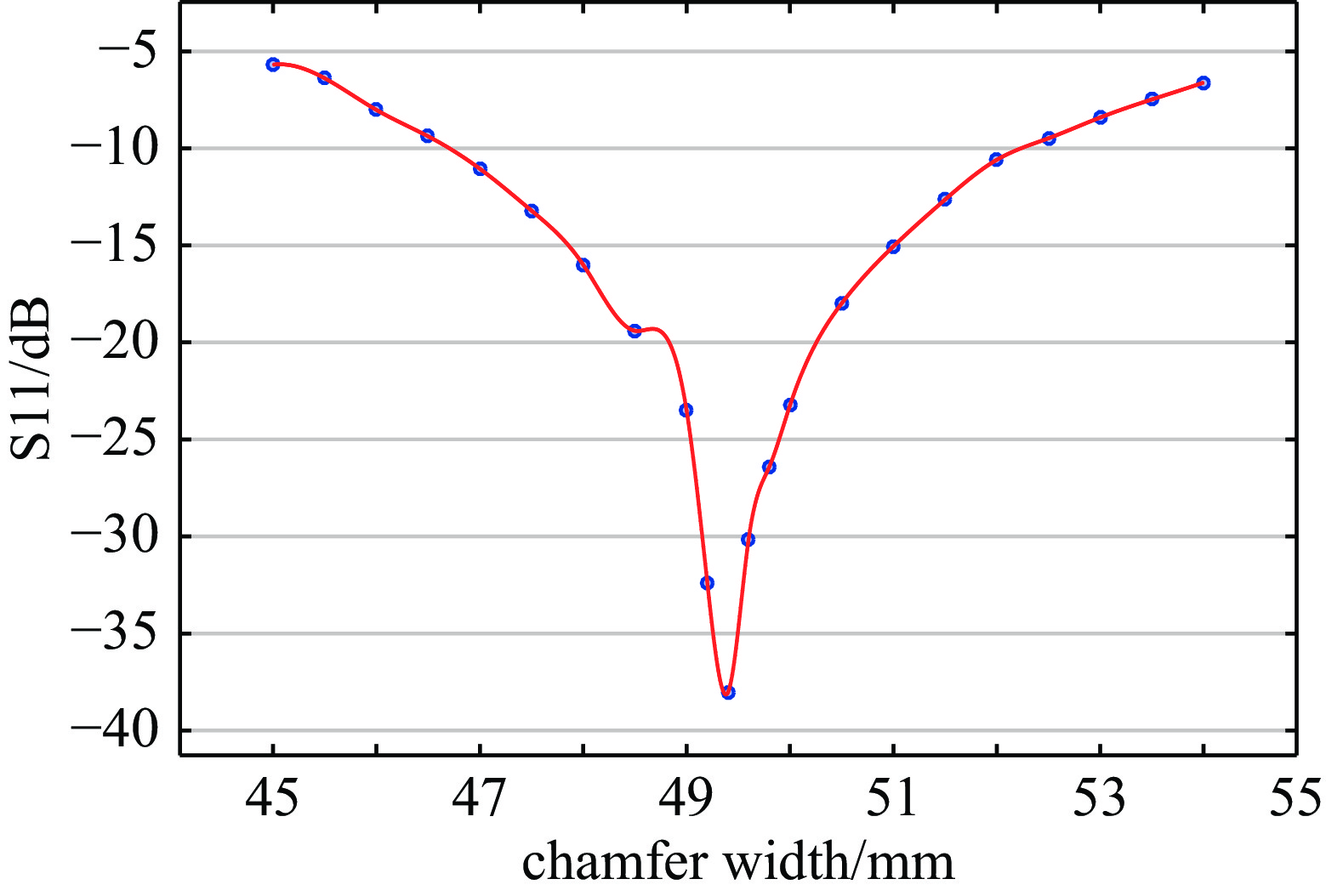
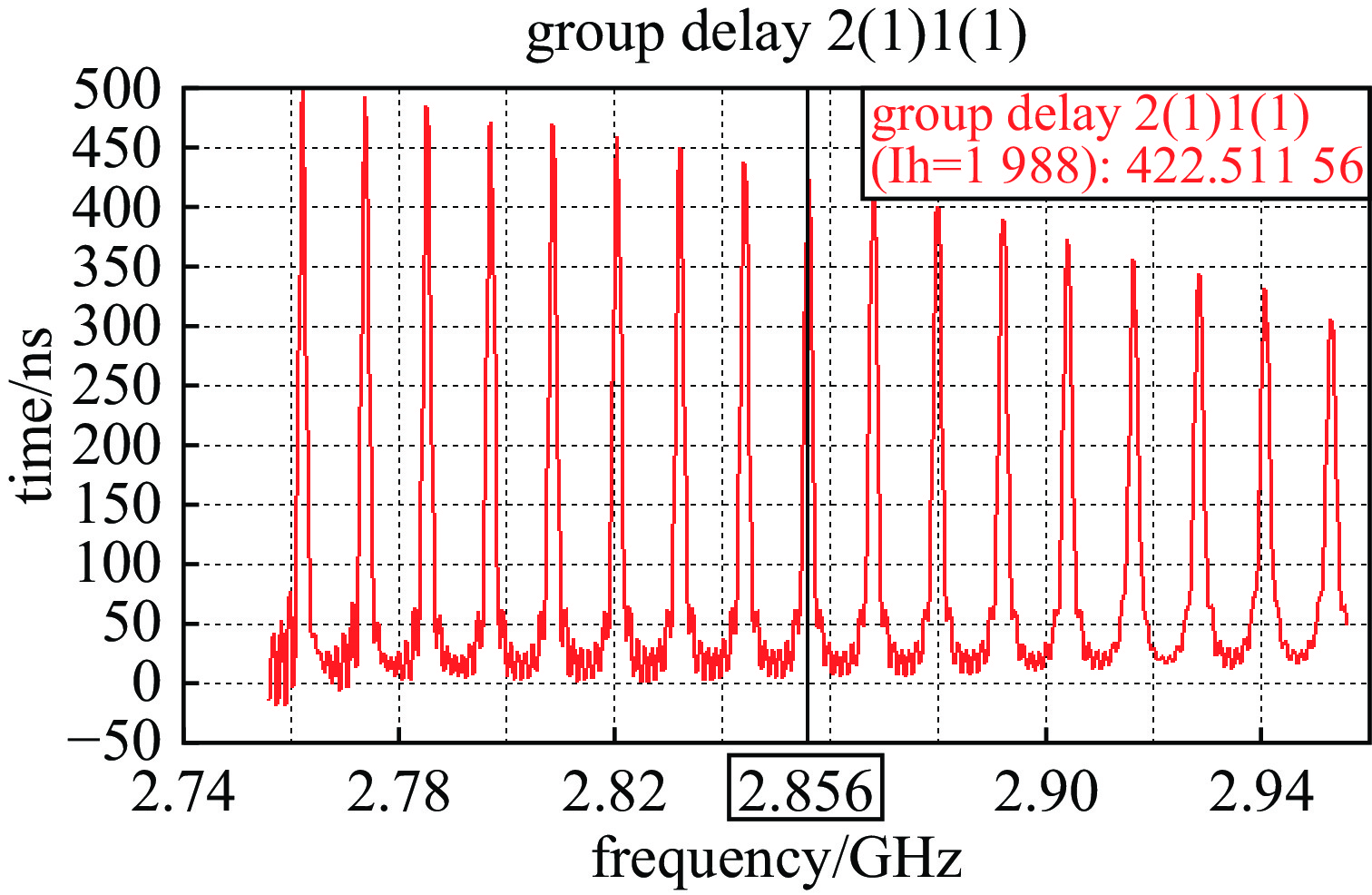
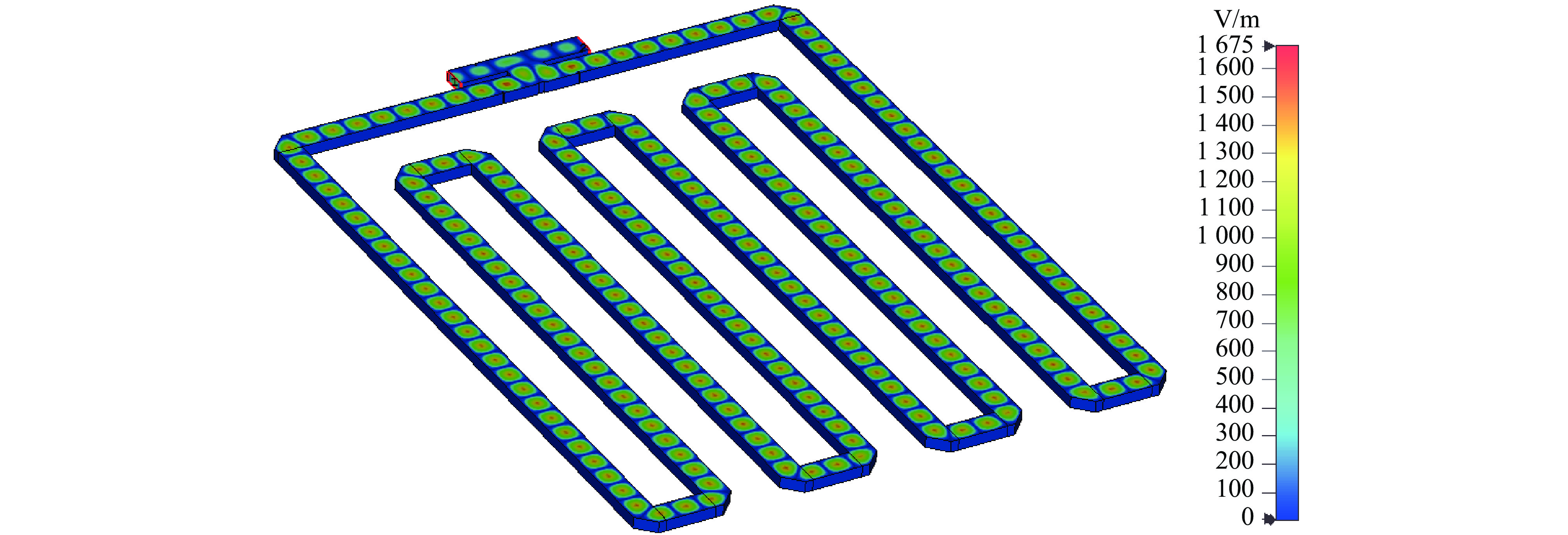
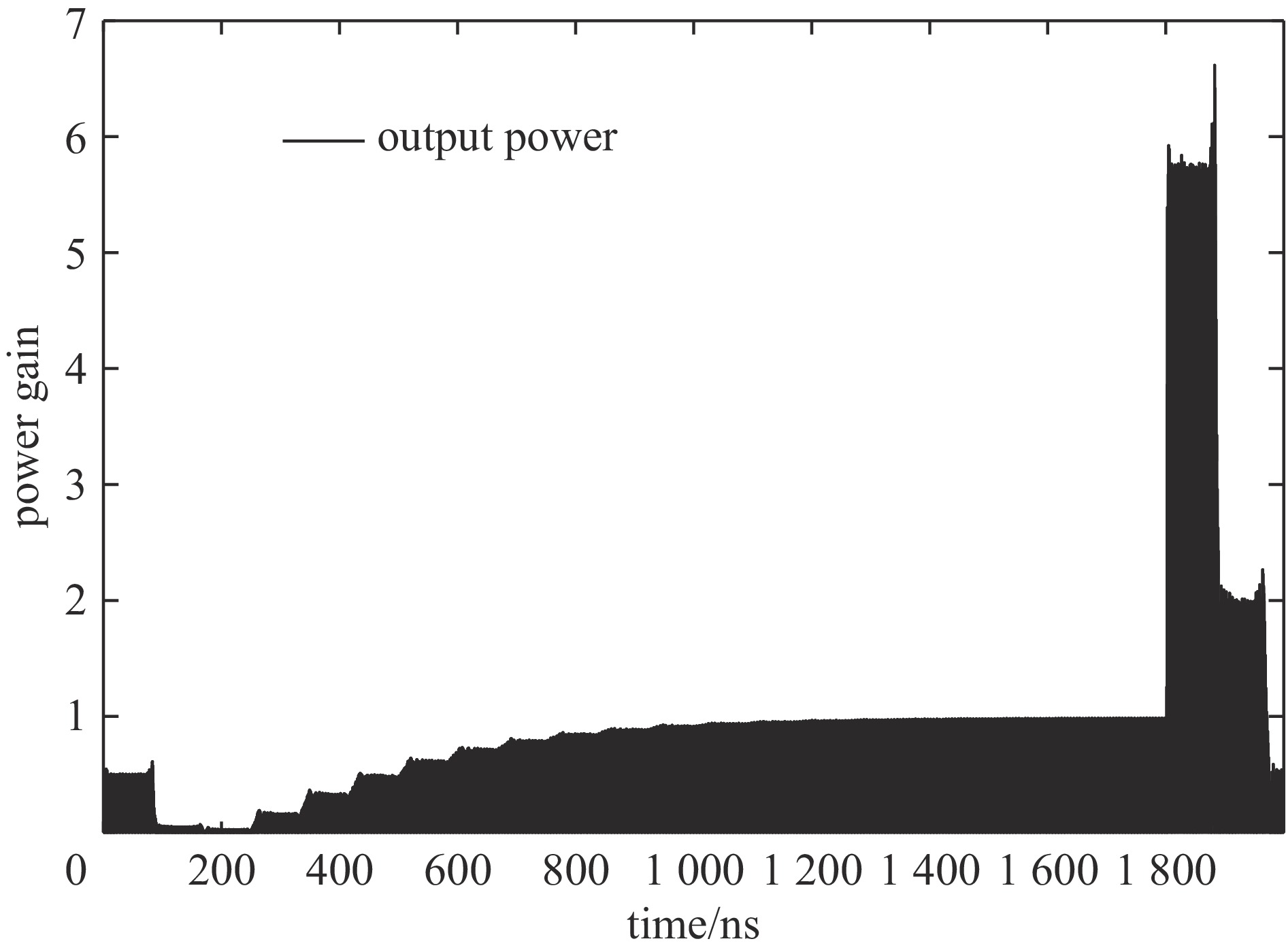
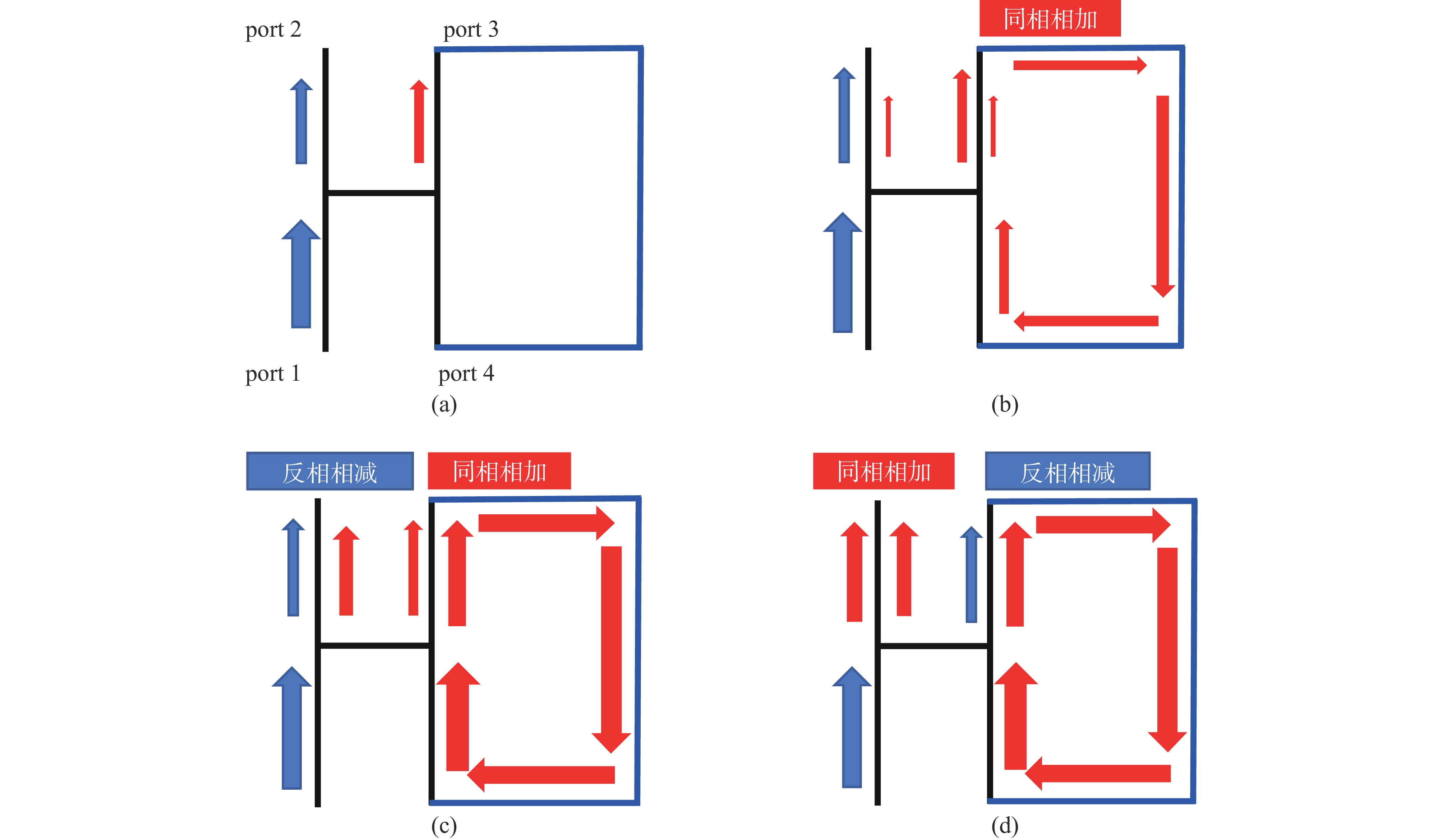
摘要: 在高功率微波和脉冲压缩领域,相对于指数衰减的微波脉冲,平顶输出具有降低结构表面最大瞬态场以及增强系统稳定性等核心优势,因此具有重要的技术意义和应用价值。提出一种S波段基于行波储能的环形高功率微波脉冲压缩器,通过控制环形波导传输线的长度使输入微波通过定向耦合器完成线性叠加储能,通过输入信号倒相完成功率的倍增和微波信号的平稳输出。基于散射矩阵理论分析其储能过程及输入倒相之后的功率增益和平顶输出宽度,并用CST进行仿真验证。仿真结果显示,其功率增益达5.7倍以上,平顶宽度80 ns,且波形平缓,若采用金属壁表面击穿阈值300 kV/cm来估计功率容量,则脉冲压缩器的功率容量可以达到160 MW。与现有技术相比,该设计结构简单、体积紧凑、加工维护便捷,为高功率微波能量平稳输出以及两级脉冲压缩系统的研究提供新方案。Abstract:
Background In the fields of high-power microwaves and pulse compression, compared with exponentially decaying microwave pulses, flat-top output has core advantages such as reducing the maximum transient surface field of the structure and enhancing system stability. Therefore, it has significant technical significance and application value.Purpose The purpose of this study is to develop a new method for power doubling that generates a flat-topped output and to observe its benefits through simulation experiments.Methods The research analyzes the energy storage process and the power gain and flat-top output width after input inversion based on the scattering matrix theory, and conducts simulation experiments using CST.Results The simulation experiment results show that its power gain is more than 5.7 times, the flat top width is 80 ns, the waveform is gentle, and the power capacity can reach 160 MW.Conclusions Compared with the existing technology, this design has a simple structure, compact volume and convenient processing and maintenance, providing a new solution for the stable output of high-power microwave energy and the research of two-stage pulse compression systems. -
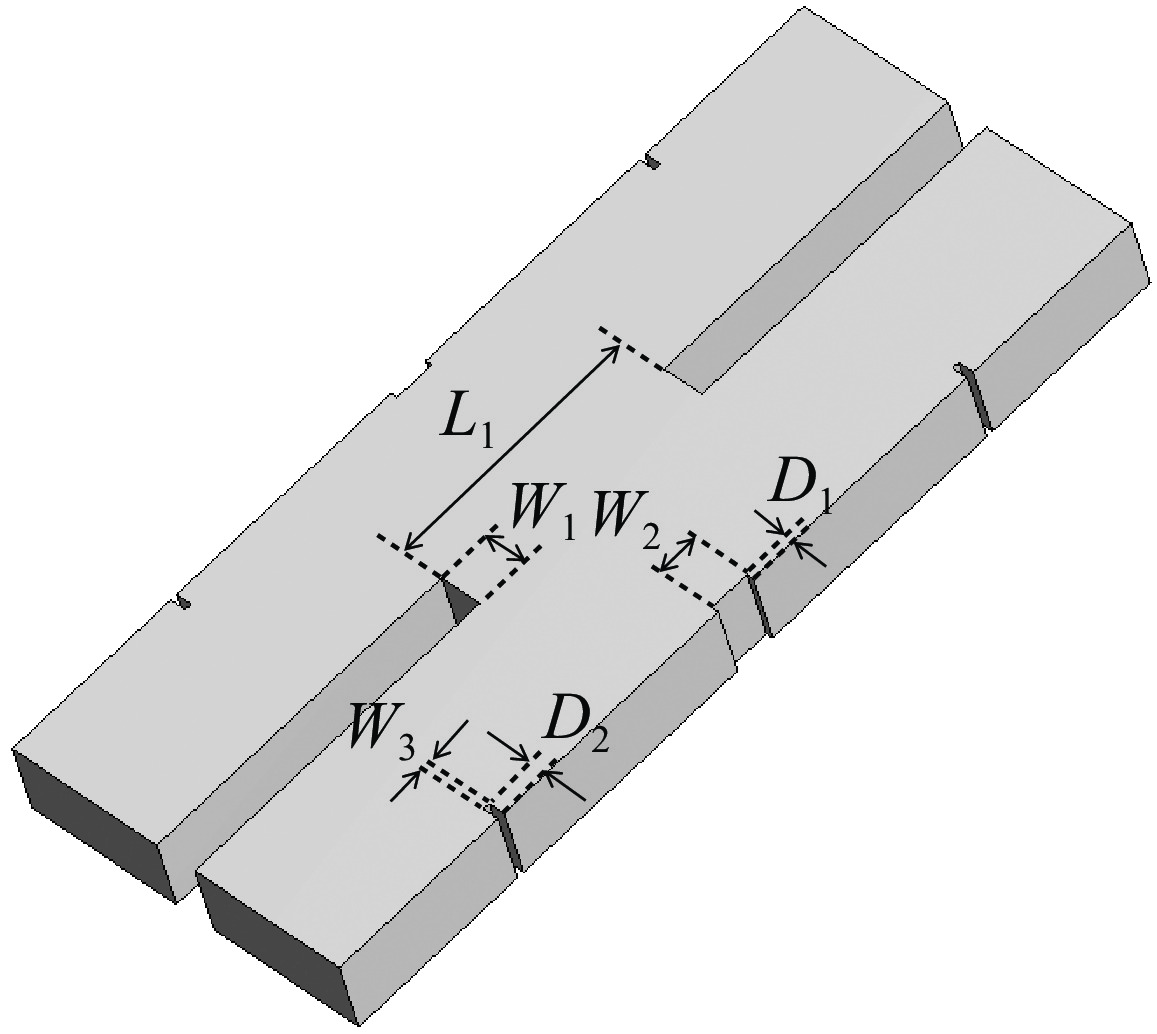
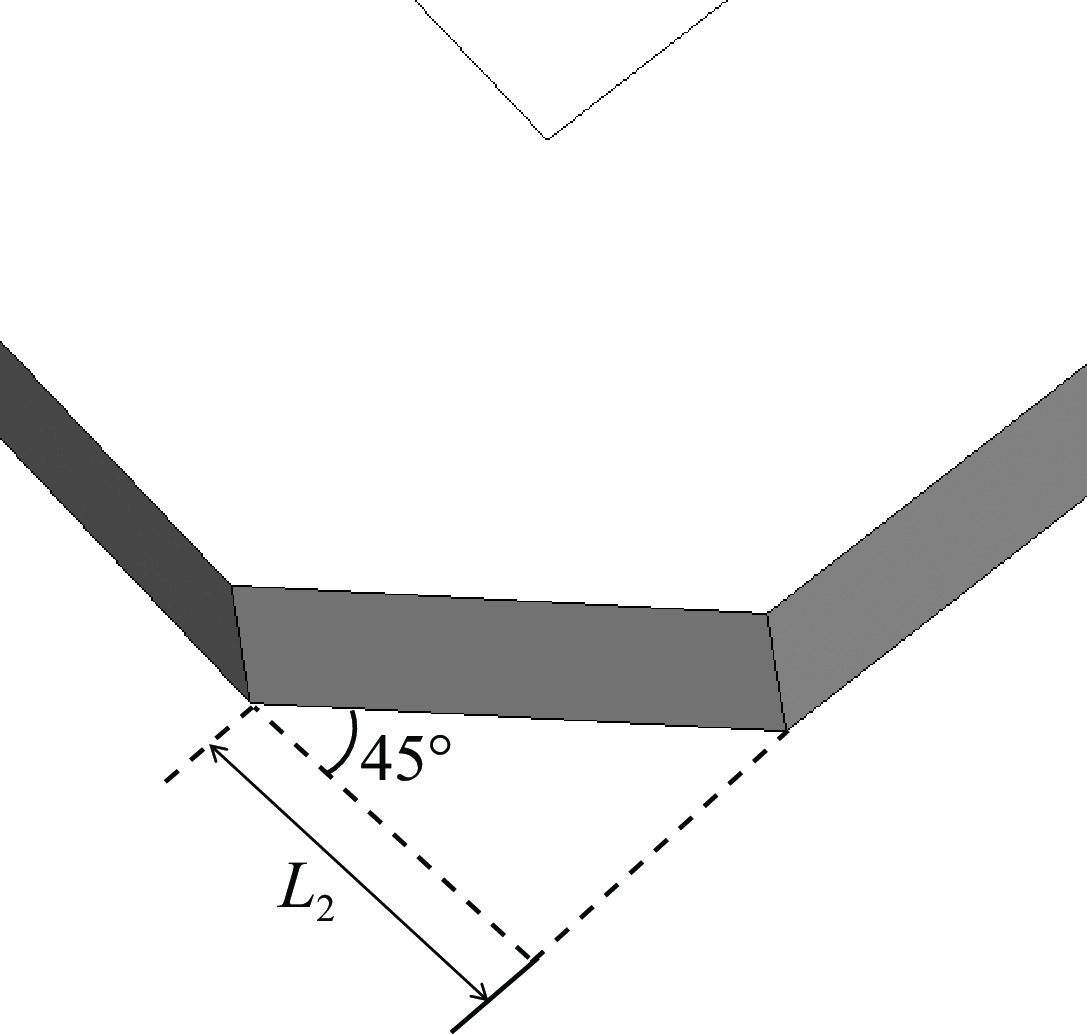
表 1 定向耦合器参数优化结果
Table 1. Results of directional coupler parameter optimization (mm)
L1 W1 D1 W2 D2 W3 112.37 19 3.1 17.66 7.23 3 -
[1] Farkas Z D, Hogg H A, Loew G A, et al. SLED: a method of doubling SLAC's energy[C]//Proceedings 9th International Conference on the High-Energy Accelerators. 1974: 576-583. [2] Balakin V E, Syrachev I V. Status VLEPP RF power multiplier (VPM)[C]//3rd European Particle Accelerator Conference. 1992: 1173-1175. [3] Shu Guan, Zhao Fengli, He Xiang. RF study of a C-band barrel open cavity pulse compressor[J]. Chinese Physics C, 2015, 39: 057005. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/39/5/057005 [4] Jiang Yuliang, Shi Jiaru, Wang Ping, et al. Compact two-stage pulse compression system for producing gigawatt microwave pulses[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2021, 69(10): 4533-4540. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2021.3093554 [5] Lin Xiancai, Zha Hao, Shi Jiaru, et al. X-band two-stage rf pulse compression system with correction cavity chain[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2022, 25: 120401. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.25.120401 [6] Kashiwagi S, Hayano H, Kubo K, et al. Beam loading compensation using phase to amplitude modulation method in ATF[C]//Proceedings of the 19th International Linear Accelerator Conference. 1998: 91-93. [7] Shu Guan, Zhao Fengli, Pei Shilun, et al. RF modulation studies on an S band pulse compressor[J]. Chinese Physics C, 2016, 40: 037002. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/40/3/037002 [8] Wilson P B, Farkas Z D, Ruth R D. SLED II: a new method of RF pulse compression[R]. Menlo Park: Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, 1990. [9] Hantista C, Farkas Z D, Kroll N M, et al. High-power RF pulse compression with SLED-II at SLAC[C]//Proceedings of International Conference on Particle Accelerators. 1993: 1196-1198. [10] Tantawi S G, Nantista C D, Dolgashev V A, et al. High-power multimode X-band rf pulse compression system for future linear colliders[J]. Physical Review Special Topics—Accelerators and Beams, 2005, 8: 042002. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.8.042002 [11] Tantawi S G, Nantista C D, Dolgashev V A, et al. Status of high-power tests of dual mode SLED-II system for an X-band linear collider[C]//Proceedings of LINAC 2004. 2004: 852-856. [12] Xiong Zhengfeng, Chen Huaibi, Ning Hui, et al. High power microwave system based on power combination and pulse compression of conventional klystrons[C]//2018 12th International Symposium on Antennas, Propagation and EM Theory (ISAPE). 2018: 1-4. [13] Kazakov S Y. Pulse shape correction for RF pulse compression system[J]. Spectrum, 1992, 5: 9. [14] Wang Ping, Zha Hao, Syratchev I, et al. RF design of a pulse compressor with correction cavity chain for klystron-based compact linear collider[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2017, 20: 112001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.20.112001 [15] Jiang Yuliang, Zha Hao, Wang Ping, et al. Demonstration of a cavity-based pulse compression system for pulse shape correction[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2019, 22: 082001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.22.082001 [16] Wang Ping, Grudiev A. Single cylinder-based RF-cavity-system types for correction cavities in a klystron-based Compact Linear Collider[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2025, 28: 032002. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.28.032002 [17] Hassanein A, Insepov Z, Norem J, et al. Effects of surface damage on rf cavity operation[J]. Physical Review Special Topics—Accelerators and Beams, 2006, 9: 062001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.9.062001 [18] Jiang Tao, Jiang Zili, Bai Weida, et al. An X-band compact rectangular waveguide TE10-circular waveguide TE01 mode converter[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2023, 94: 044704. doi: 10.1063/5.0146263 -




 下载:
下载: