Study on dual-polarization scattering characteristics of millimeter-wave nonspherical ice crystals
-
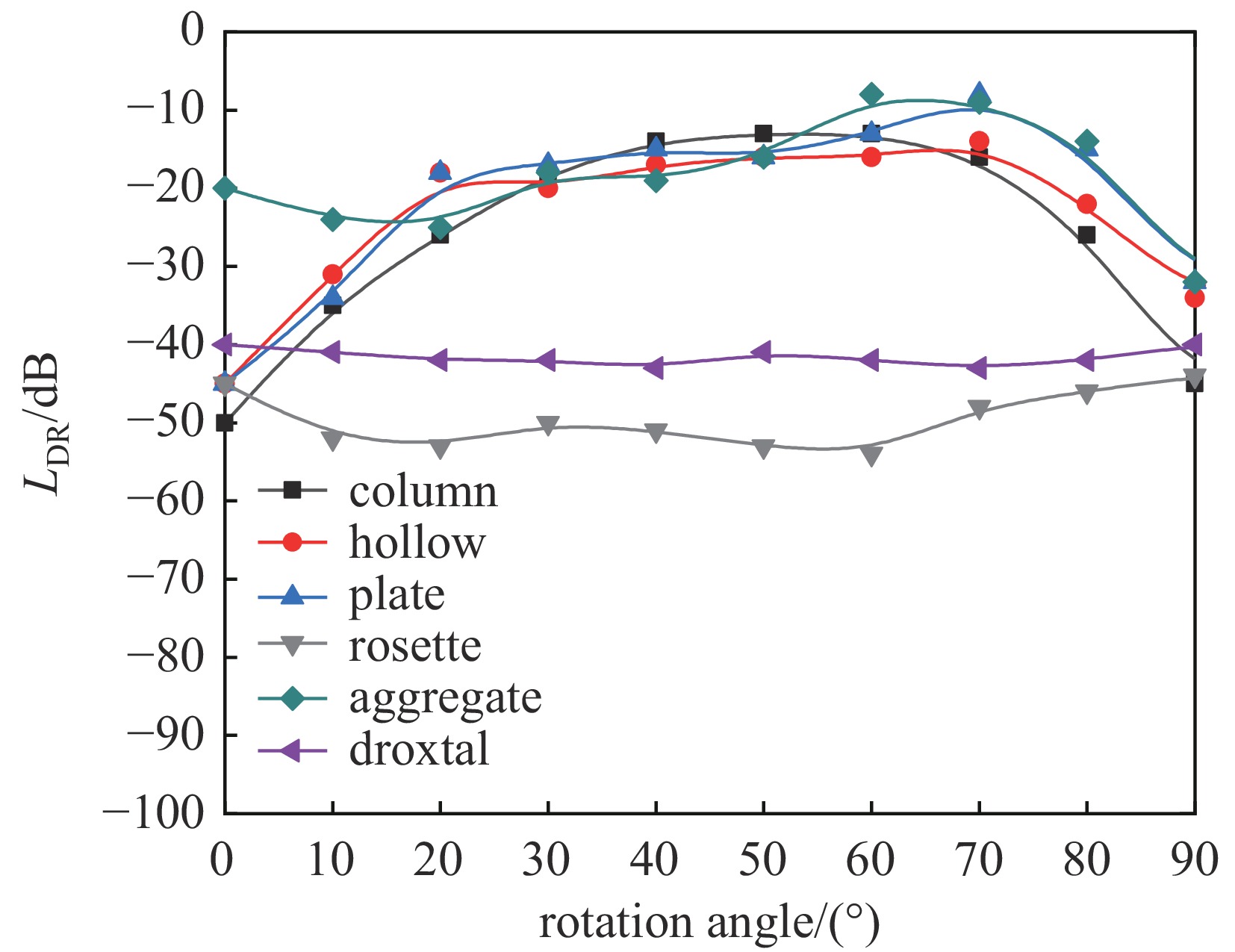
摘要: 传统Mie散射理论基于球形粒子假设,难以精准描述大气非球形冰晶的散射行为,现有研究多局限于94 GHz单频率,缺乏毫米波/亚毫米波宽频段双偏振参数量化,制约偏振雷达气象探测精度。探究六角棱柱、六角平板等六种典型非球形冰晶在35、94、140、220 GHz的双偏振散射特性,量化差分反射率因子(ZDR)、线性退极化比(LDR)对粒子形状与取向的响应。采用离散偶极子近似法(DDA)、时域有限差分法(FDTD),结合XFDTD、HFSS验证。结果显示:除聚合体外,DDA计算后向散射截面与商用软件误差≤1.5 dB;小粒子(等效半径<100 μm)反射率对波长不敏感,大粒子呈形状相关共振且共振位置随波长右移;六角平板ZDR变化最广(9 dB至–9 dB),轴对称粒子LDR集中于–40 dB至–50 dB。双偏振参数可降低对粒子尺寸的依赖,提升宽频段冰晶识别精度,为毫米波/亚毫米波偏振雷达云微物理探测提供理论支撑。Abstract:
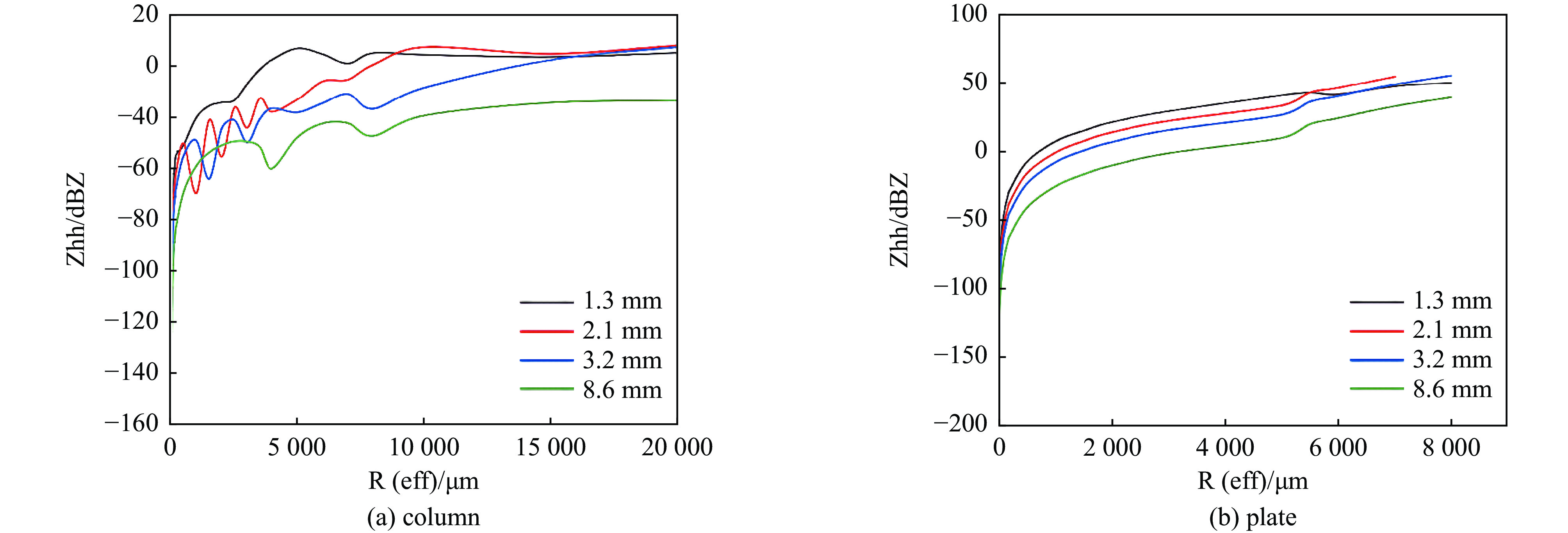
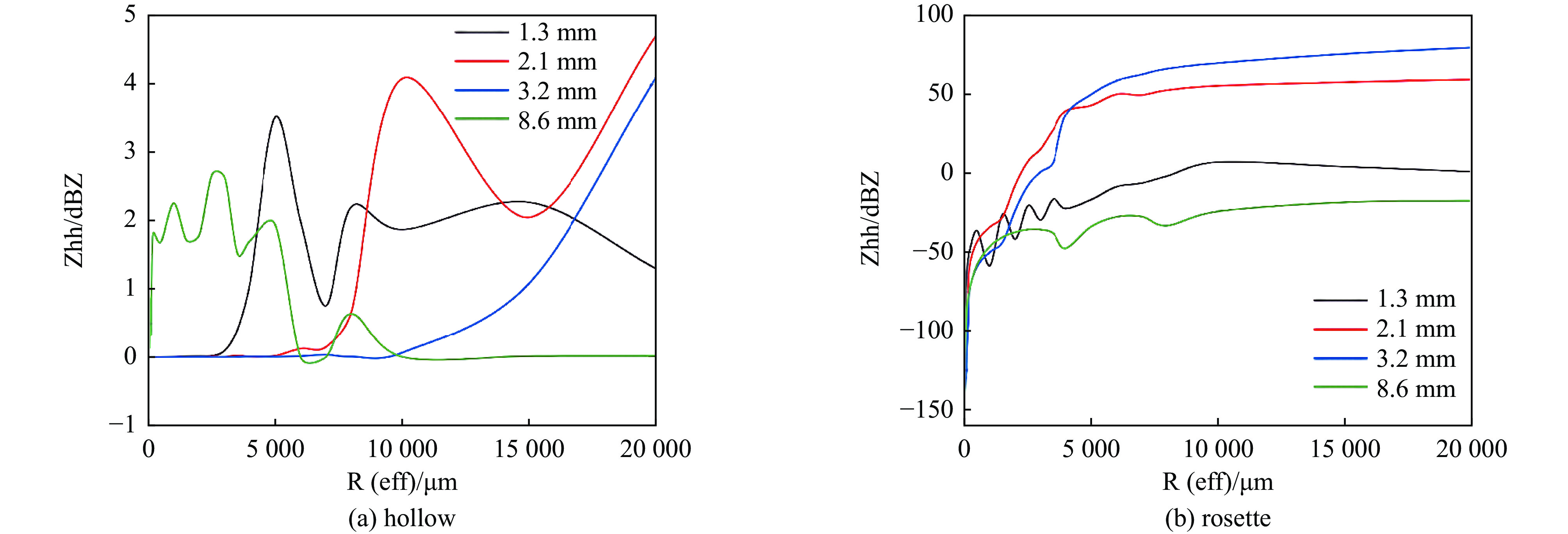
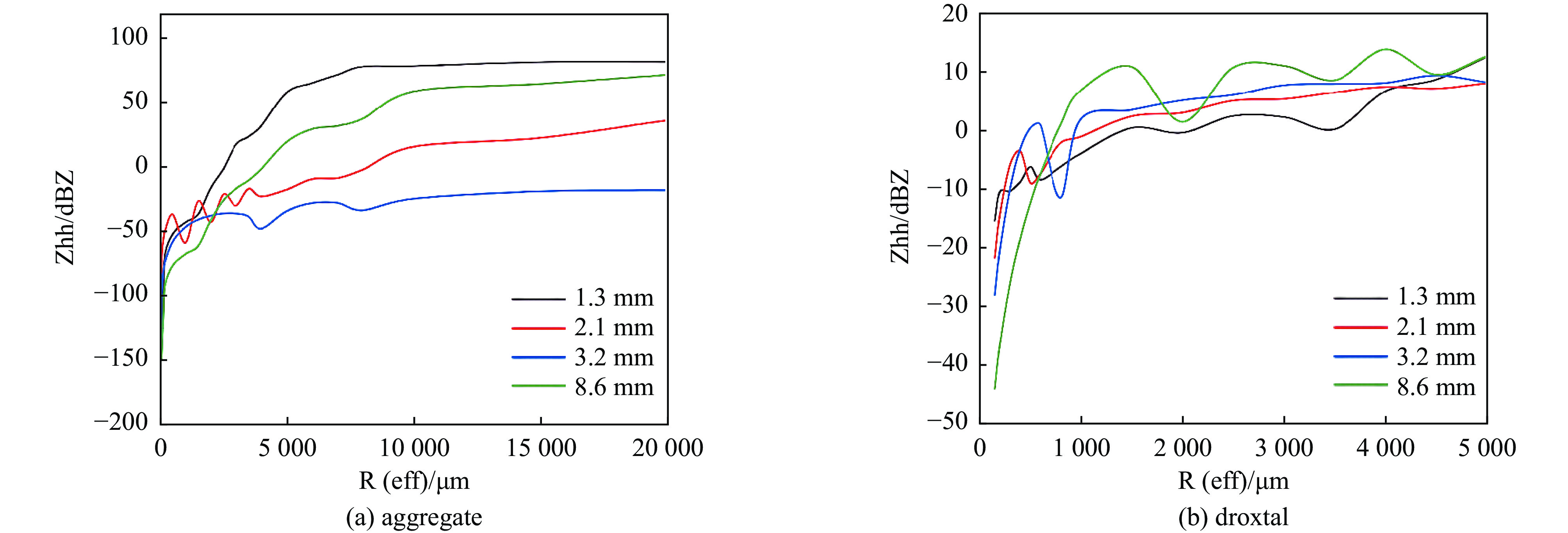
Background Traditional Mie theory, assuming spherical particles, is inadequate for characterizing the scattering of atmospheric non-spherical ice crystals. Existing studies are largely limited to single frequency (e.g., 94 GHz), lacking systematic quantification of key dual-polarization parameters across the millimeter/submillimeter wave spectrum, which constrains the accuracy of polarimetric radar for meteorological target detection and classification.Purpose This study aims to systematically investigate the dual-polarization scattering properties of six typical non-spherical ice crystals—hexagonal columns, plates, hollow columns, bullet rosettes, aggregates, and supercooled water droplets—across 35, 94, 140, and 220 GHz bands. It quantifies the responses of differential reflectivity (ZDR) and linear depolarization ratio (LDR) to particle shape and orientation, providing crucial theoretical support for wideband polarimetric radar meteorology.Methods Scattering models were developed using the Discrete Dipole Approximation (DDA) and Finite-Difference Time-Domain (FDTD) methods, cross-validated with commercial software (XFDTD, HFSS). Backscattering cross-sections, ZDR, and LDR were computed for different ice crystals across the frequency bands, analyzing the influence of particle size, geometry, and frequency.Results 1)The reliability of DDA was systematically validated across the 35–220 GHz range. Calculation errors for backscattering cross-sections were ≤1.5 dB for all particles except highly random aggregates. 2) Radar reflectivity factor showed a coupled wavelength dependence: small particles (equivalent radius <100 μm) were wavelength-insensitive (<1 dB difference), while large particles (>100 μm) exhibited significant shape-dependent resonance. The equivalent radius corresponding to resonance extrema increased with wavelength. 3) Characteristic ranges of ZDR and LDR for the six ice crystal types were quantified. Hexagonal plates showed the widest ZDR range (9 dB to –9 dB), while axisymmetric particles exhibited stable LDR values (–40 dB to –50 dB).Conclusions This wideband, multi-particle study addresses prior limitations in frequency coverage and parameter quantification. It demonstrates that the shape-sensitive ZDR and LDR parameters can reduce dependence on particle size distribution and significantly improve ice crystal identification accuracy, providing a key theoretical basis for millimeter/submillimeter wave polarimetric radar applications in cloud microphysics and meteorological target classification. -
表 1 六种典型冰晶粒子的形状及其参数[17]
Table 1. Tab.1 Six common shapes of ice crystal particles and their parameters
geometric names geometric shapes axle ratio column 
$\begin{cases}a=0.35 L & (L<100 \mu m) \\ a=3.48 L^{0.5} & (L \geqslant 100 \mu m)\end{cases}$ (1) plate 
$\begin{cases}L=2 a & (a \leqslant 2 \mu m) \\ L=2.4883 a^{0.474} & (a \geqslant 5 \mu m) \\ L=2+\left(\left(2.4883 a^{0.474}-2\right) / 4\right) \cdot(a-1) & (2 \mu m<a<5 \mu m)\end{cases}$ (2) hollow 
$\begin{cases}a=0.35 L & (L<100 \mu m) \\ a=3.48 L^{0.5} & (L \geqslant 100 \mu m) \\ h=0.25 L & \end{cases}$ (3) rosette 
$\left\{\begin{array}{l}a=1.552 L^{0.63} \\ t=\dfrac{\sqrt{3} a}{2 \tan \alpha} \quad \alpha=28^{\circ}\end{array}\right.$ (4) aggregate 
$\begin{array}{ll}a_1=0.291 L_1 & a_2=0.323 L_2 \\ a_3=0.359 L_3 & a_4=0.381 L_4 \\ a_5=0.368 L_5 & a_6=0.352 L_6 \\ a_7=0.333 L_7 & a_8=0.312 L_8 \\ D=7.297 L_{\min } & \end{array}$ (5) droxtal 
$\begin{array}{ll}D=2 R & \\ a_1=R \sin \theta_1 & a_2=R \sin \theta_2 \\ L_1=R \cos \theta_1 & L_2=\cos \theta_2 \\ \theta_1=32.35^{\circ} & \theta_2=71.81^{\circ}\end{array}$ (6) 表 2 各毫米波频率下复折射率的拟合值
Table 2. The fitted values of the complex refractive index under each millimeter wave frequency
frequency/GHz complex refractive index/m 35 (8.6 mm) 1.7861 +0.0011i94 (3.2 mm) 1.7864 +0.0032i140 (2.1 mm) 1.7866 +0.0043i220 (1.3 mm) 1.7868 +0.0052i表 3 对比XFDTD、HFSS和DDA计算六种非球形冰晶粒子在94 GHz下的后向散射截面
Table 3. Comparison of XFDTD, HFSS, and DDA calculations for six types of non-spherical ice crystal particles at 94 GHz for backscattering cross section
particle shapes XFDTD/dBm2 HFSS/dBm2 DDA/ dBm2 column −86.82 −84.85 −86.75 plate −86.01 −85.63 −85.79 hollow −87.93 −85.83 −86.01 rosette −74.19 −75.77 −74.77 aggregate −66.26 −60.58 −62.85 droxtal −72.29 −69.86 −70.23 -
[1] 魏邦海. 气溶胶和冰水两相粒子的散射特性[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2015: 25-31Wei Banghai. Scattering properties of aerosols and ice water two-phase particle[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, 2015: 25-31 [2] 董振贤, 李妙英. 双偏振多普勒天气雷达的偏振参量及其应用[J]. 解放军理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 5(3): 98-102 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3443.2004.03.025Dong Zhenxian, Li Miaoying. Polarimetric measurements of dual-polarization radar and application[J]. Journal of PLA University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2004, 5(3): 98-102 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3443.2004.03.025 [3] Seliga T A, Bringi V N. Potential use of radar differential reflectivity measurements at orthogonal polarizations for measuring precipitation[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 1976, 15(1): 69-76. doi: 10.1175/1520-0450(1976)015<0069:PUORDR>2.0.CO;2 [4] Ryzhkov A V, Zrnić D S. Comparison of dual-polarization radar estimators of rain[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 1995, 12(12): 249-256. [5] 刘黎平, 钱永甫, 王致君. 用双线偏振雷达研究云内粒子相态及尺度的空间分布[J]. 气象学报, 1996, 54(5): 590-599Liu Liping, Qian Yongfu, Wang Zhijun. The study of spacial distribution of phase and size of hydrometeorsin cloud by dual linear polarization radar[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 1996, 54(5): 590-599 [6] 曹俊武, 刘黎平, 葛润生. 模糊逻辑法在双线偏振雷达识别降水粒子相态中的研究[J]. 大气科学, 2005, 29(5): 827-836Cao Junwu, Liu Liping, Ge Runsheng. A study of fuzzy logic method in classification of hydrometeors based on polarimetric radar measurement[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2005, 29(5): 827-836 [7] 王金虎, 蔡嘉晗, 谢槟泽, 等. 基于Mie散射的带电粒子散射特性的研究[J]. 光散射学报, 2021, 33(1): 65-71 doi: 10.13883/j.issn1004-5929.202101009Wang Jinhu, Cai Jiahan, Xie Binze, et al. Study on the scattering characteristics of charged particles based on Mie scattering[J]. The Journal of Light Scattering, 2021, 33(1): 65-71 doi: 10.13883/j.issn1004-5929.202101009 [8] Purcell E M, Pennypacker C R. Scattering and absorption of light by nonspherical dielectric grains[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 1973, 186: 705-714. doi: 10.1086/152538 [9] Draine B T, Flatau P J. Discrete-dipole approximation for scattering calculations[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1994, 11(4): 1491-1499. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.11.001491 [10] 任神河, 高明, 王明军, 等. 不同空间取向冰晶粒子的光散射[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2024, 53: 20240336 doi: 10.3788/IRLA20240336Ren Shenhe, Gao Ming, Wang Mingjun, et al. Light scattering of ice crystal particles with different spatial orientations[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2024, 53: 20240336 doi: 10.3788/IRLA20240336 [11] 贺锦涛, 王明军, 张佳琳. 团聚核壳蓝藻粒子的蓝绿激光散射和吸收特性研究[J]. 光学学报, 2021, 41: 1729001 doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.1729001He Jintao, Wang Mingjun, Zhang Jialin. Blue-green laser scattering and absorption properties of agglomerated core-shell cyanobacteria particles[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2021, 41: 1729001 doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.1729001 [12] 许小永. 非球形雨滴和冰雹微波散射特征研究[D]. 南京: 南京气象学院, 2002: 8-17Xu Xiaoyong. Scattering of microwaves by non-spherical raindrops and hails[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, 2002: 8-17 [13] 冯晋勤, 张深寿, 吴陈锋, 等. 双偏振雷达产品在福建强对流天气过程中的应用分析[J]. 气象, 2018, 44(12): 1565-1574 doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2018.12.006Feng Jinqin, Zhang Shenshou, Wu Chenfeng, et al. Application of dual polarization weather radar products to severe convective weather in Fujian[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2018, 44(12): 1565-1574 doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2018.12.006 [14] 罗晓翩, 冯力天, 尹微, 等. 基于相干激光雷达的双偏振探测技术[J]. 激光技术, 2025, 49(1): 8-13Luo Xiaopian, Feng Litian, Yin Wei, et al. Dual polarization detection technology based on coherent LiDAR[J]. Laser Technology, 2025, 49(1): 8-13 [15] Gallagher M W, Connolly P J, Whiteway J, et al. An overview of the microphysical structure of cirrus clouds observed during EMERALD-1[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2005, 131(607): 1143-1169. doi: 10.1256/qj.03.138 [16] Baran A J. A review of the light scattering properties of cirrus[J]. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 2009, 110(14/16): 1239-1260. [17] Hong G. Radar backscattering properties of nonspherical ice crystals at 94 GHz[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2007, 112: D22203. [18] Polyanskiy M N. Refractiveindex. info database of optical constants[J]. Scientific Data, 2024, 11: 94. doi: 10.1038/s41597-023-02898-2 [19] 王金虎, 葛俊祥, 杨泽鑫, 等. 毫米波频率下冰晶粒子散射特性的研究[C]//第31届中国气象学会年会S1气象雷达探测技术研究与应用. 2014: 346-351Wang Jinhu, Ge Junxiang, Yang Zexin, et al. Study on the scattering characteristics of ice crystal particles at millimeter-wave frequencies[C]//The 31st Annual Conference of the Chinese Meteorological Society S1: Research and Application of Meteorological Radar Detection Technology. 2014: 346-351 -





 下载:
下载: