Characterization and mitigation of oscilloscope baseline distortion caused by transient electromagnetic pulse in diamond detector TOF measurement
-
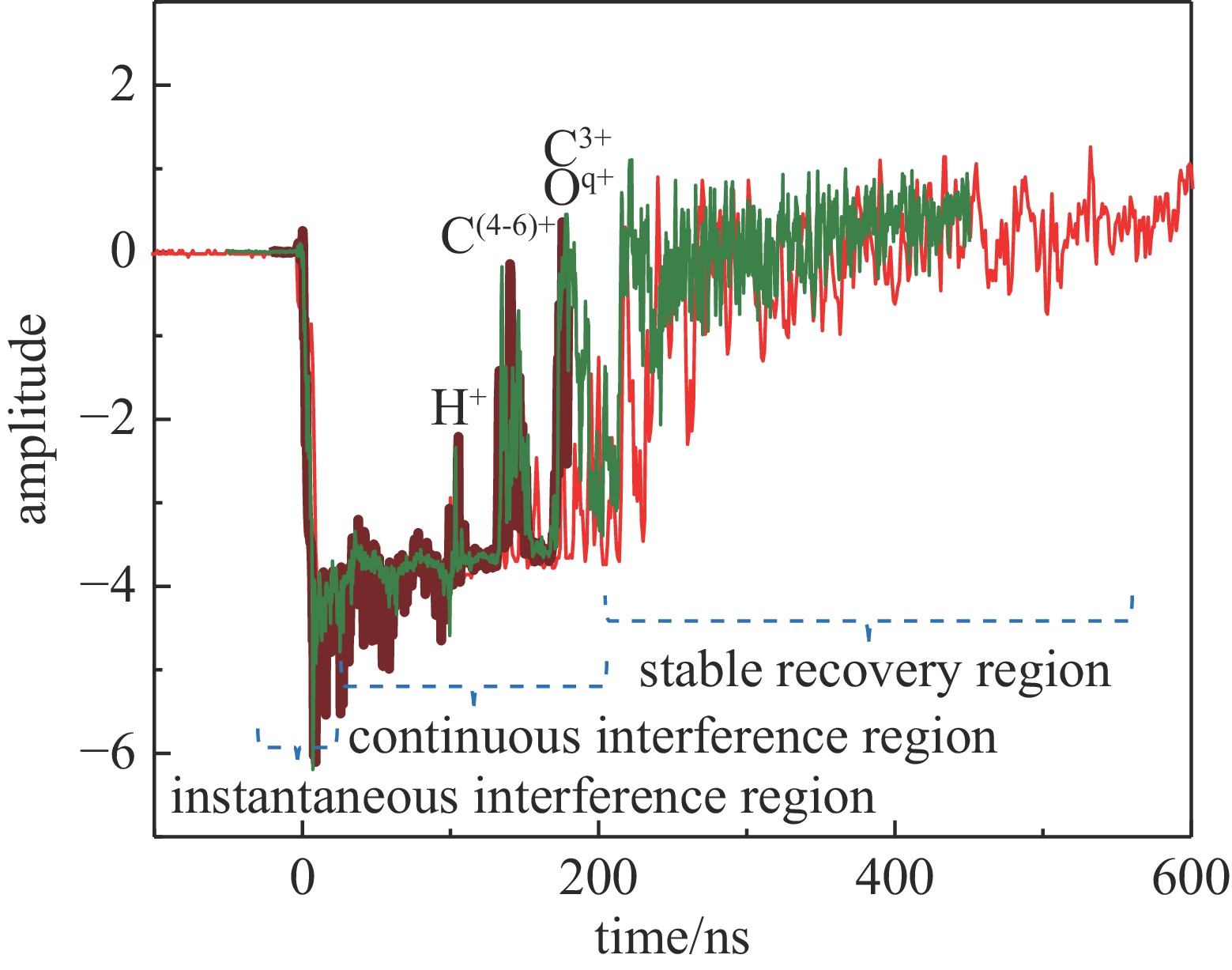
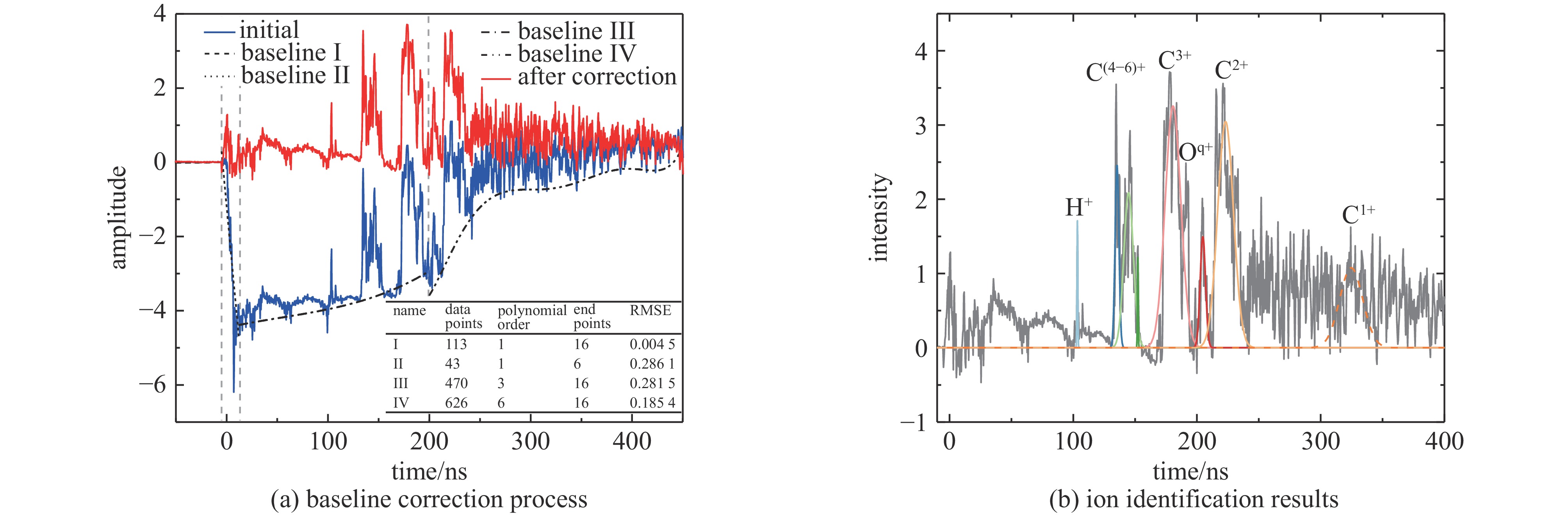
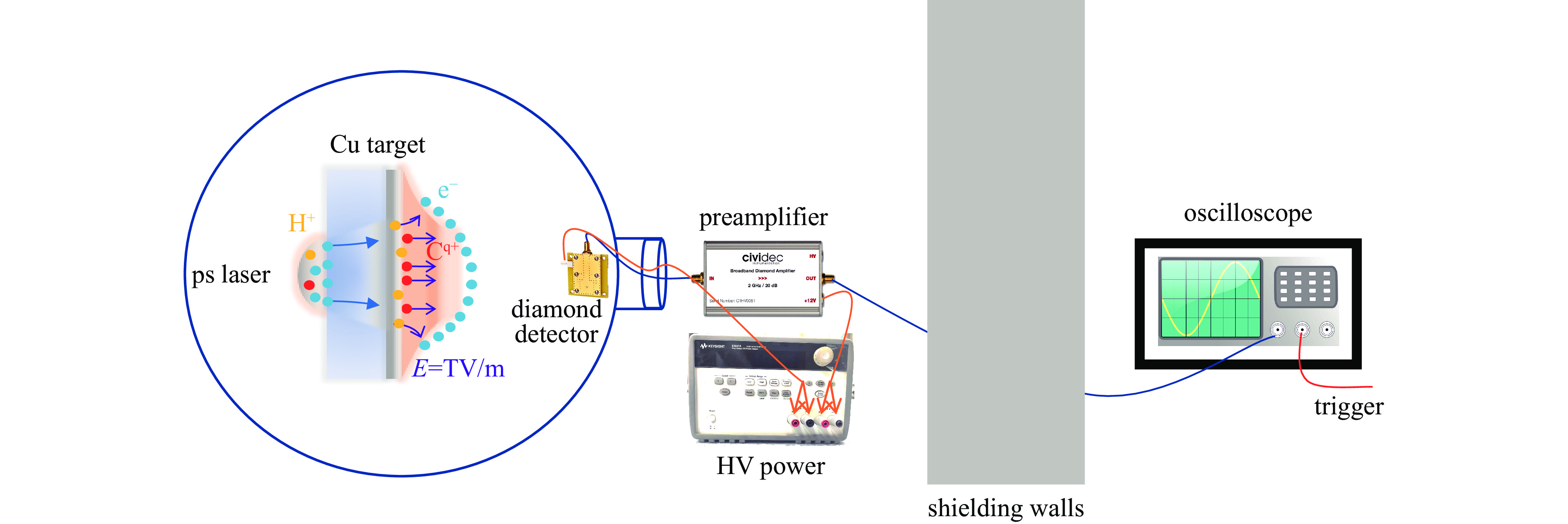
摘要: 在激光加速离子实验中,基于金刚石探测器的飞行时间法是获取加速离子能谱分布的关键诊断手段之一。然而,强激光与靶相互作用产生的瞬态电磁脉冲会严重干扰数据获取系统,导致示波器基线电位发生显著畸变,污染甚至淹没关键的离子信号,从而给离子能谱的精确测量带来了严峻挑战。基于XG-III激光装置上开展的多次皮秒激光加速离子实验,研究了金刚石探测器记录信号中出现的示波器基线偏置现象。结果发现激光打靶瞬间产生的强电磁脉冲会通过电缆耦合进入测量系统,引发幅度高达-5 V的基线下拉干扰,持续时间约200 ns后逐步恢复至正常水平。针对该时变特征与多发次实验数据特性,结合机器学习算法建立了一种自适应的时变基线恢复模型。该模型能够对基线的时变特性进行合理刻画,为后续实现单发次离子TOF谱的在线干扰校正提供了可行的技术思路。Abstract:
Background In laser-driven ion acceleration experiments, the time-of-flight (TOF) technique based on diamond detector serves as a key diagnostic approach for measuring the energy spectrum of accelerated ions. However, transient electromagnetic pulse (EMP) generated during the interaction between intense laser pulse and solid target can strongly interfere with the data acquisition system, leading to significant baseline distortion in the oscilloscope signals. Such distortions may contaminate or even obscure the ion signals, posing serious challenges to accurate spectrum measurement.Purpose This study aims to characterize EMP induced baseline distortion in diamond detector TOF measurements and develop an adaptive correction algorithm to recover baseline to accurate ion energy spectra from contaminated single-shot data.Methods We developed a machine learning assisted time varying polynomial baseline correction method. The algorithm employs a segmented fitting strategy. Additionally, an adaptive moving window selection for dynamic optimization of reference point identification is introduced, with the window width adjustable from 20 ns to 10 ns.Results The results show that intense EMP generated at the moment of laser-target interaction couple into the diagnostic system through the transmission cables, inducing baseline drops up to −5 V, which gradually recover to the normal level after approximately 200 ns. Polynomial orders are assigned region-specifically: first-order for Instantaneous interference I and II region, third-order for continuous interference region, and sixth-order for stable recovery region. Model accuracy is validated through root mean square error (RMSE). After correction, previously obscured TOF peaks for protons and carbon ions (C1+ to C6+) became clearly identifiable, enhancing the detection of low-energy ions.Conclusions This study presents an adaptive baseline correction method, which effectively reduces the EMP interference on baseline in laser-driven ion acceleration diagnostics. The proposed model reasonably characterizes the temporal evolution of the baseline and provides a feasible approach for future online interference correction of single-shot ion TOF spectra. -
表 1 各特征区域所需的拟合函数和涉及的相关物理参数
Table 1. The fitting functions required for each feature region and the related physical parameters
region time range/ns fitting function dominant physical feature key influencing parameter instantaneous interference I <−5 $A_1(t)=a_0+a_1 t$ background, stable baseline − instantaneous interference II −5-12$ \text{±} $3 $A_2(t)=b_0+b_1 t$ sharp baseline drop laser energy, target thickness, conducitivity continuous interference 12$ \text{±} $3-200$ \text{±} $20 $A_3(t)=\displaystyle\sum c_i t^i, i=0-3$ effects of EMP and ion signals detector response time stable recovery $ \text{>} $200$ \text{±} $20 $A_4(t)=\displaystyle\sum d_i t^i, i=0-6$ gradual return of baseline system recovery time -
[1] 马文君, 刘志鹏, 王鹏杰, 等. 激光加速高能质子实验研究进展及新加速方案[J]. 物理学报, 2021, 70: 084102 doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20202115Ma Wenjun, Liu Zhipeng, Wang Pengjie, et al. Experimental progress of laser-driven high-energy proton acceleration and new acceleration schemes[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2021, 70: 084102 doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20202115 [2] 杨月, 孙斌, 邓志刚, 等. 拍瓦激光驱动纳米刷靶高品质质子束的产生[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2024, 36: 101004Yang Yue, Sun Bin, Deng Zhigang, et al. Generation of high-quality proton beam in nanobrush targets driven by PW laser pulse[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2024, 36: 101004 [3] Poole P L, Obst L, Cochran G E, et al. Laser-driven ion acceleration via target normal sheath acceleration in the relativistic transparency regime[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2018, 20: 013019. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/aa9d47 [4] Labaune C, Baccou C, Depierreux S, et al. Fusion reactions initiated by laser-accelerated particle beams in a laser-produced plasma[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 2506. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3506 [5] Huang Chengkun, Alvarez M A, Batha S H, et al. Characterization of laser-accelerated proton beams from a 0.5 kJ sub-picosecond laser for radiography applications[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2025, 32: 033107. doi: 10.1063/5.0251284 [6] Guo Zhiyuan, Liu Shuang, Zhou Bing, et al. Preclinical tumor control with a laser-accelerated high-energy electron radiotherapy prototype[J]. Nature Communications, 2025, 16: 1895. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57122-z [7] Bolton P R, Borghesi M, Brenner C, et al. Instrumentation for diagnostics and control of laser-accelerated proton (ion) beams[J]. Physica Medica, 2014, 30(3): 255-270. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2013.09.002 [8] Torrisi L, Costa G. Ion acceleration by fs laser in target-normal-sheath-acceleration regime and comparison of time-of-flight spectra with particle-in-cell simulations[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2020, 23: 011304. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.23.011304 [9] Zhou Zexian, Guo Bin, Cheng Rui, et al. In situ ions energy spectrum measurement using a diamond detector in laser-accelerated ions–plasma interaction[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2022, 1026: 166191. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2021.166191 [10] Scuderi V, Milluzzo G, Doria D, et al. TOF diagnosis of laser accelerated, high-energy protons[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2020, 978: 164364. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2020.164364 [11] Ren Jieru, Deng Zhigang, Qi Wei, et al. Observation of a high degree of stopping for laser-accelerated intense proton beams in dense ionized matter[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 5157. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18986-5 [12] Torrisi L, Foti G, Giuffrida L, et al. Single crystal silicon carbide detector of emitted ions and soft x rays from power laser-generated plasmas[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2009, 105: 123304. doi: 10.1063/1.3153160 [13] 伍波, 董克攻, 吴玉迟, 等. 利用CR39上的径迹鉴别激光加速离子产物[J]. 强激光与离子束, 2013, 25(2): 381-384 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132502.0381Wu Bo, Dong Kegong, Wu Yuchi, et al. Identification of ion products produced from laser acceleration experiments using tracks on CR39[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(2): 381-384 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132502.0381 [14] Jahn D, Träger M, Kis M, et al. Chemical-vapor deposited ultra-fast diamond detectors for temporal measurements of ion bunches[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2018, 89: 093304. doi: 10.1063/1.5048667 [15] Tapper R J. Diamond detectors in particle physics[J]. Reports on Progress in Physics, 2000, 63(8): 1273-1316. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/63/8/203 [16] He Qiangyou, Wang Zitao, Deng Zhigang, et al. Generation and regulation of electromagnetic pulses induced by multi-petawatt laser coupling with gas jets[J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2025, 36: 100. doi: 10.1007/s41365-025-01692-6 [17] Poyé A, Hulin S, Bailly-Grandvaux M, et al. Physics of giant electromagnetic pulse generation in short-pulse laser experiments[J]. Physical Review E, 2015, 91: 043106. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.91.043106 [18] Xia Yadong, Zhang Feng, Cai Hongbo, et al. Analysis of electromagnetic pulses generation from laser coupling with polymer targets: effect of metal content in target[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2020, 5: 017401. doi: 10.1063/1.5114663 [19] He Q Y, Yan W, Liu Z P, et al. Measurement of electromagnetic pulse in laser acceleration enhanced by near-critical density targets[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2024, 31: 103303. doi: 10.1063/5.0231143 [20] Wu Yuchi, Zhu Bin, Dong Kegong, et al. XingGuang III laser facility and its experimental ability to drive high-energy particle beams[J]. Laser Physics, 2020, 30: 096001. doi: 10.1088/1555-6611/aba3ca [21] 张强强, 于明海, 魏来, 等. 皮秒脉冲激光产生的X射线源能谱精密诊断[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2022, 34: 122004Zhang Qiangqiang, Yu Minghai, Wei Lai, et al. Spectrum measurements for picosecond laser produced X-ray sources[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2022, 34: 122004 [22] Zhang Zhao, Li Yaju, Yang Guanghui, et al. Estimating the grain size of microgranular material using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with machine learning algorithms[J]. Plasma Science and Technology, 2024, 26: 055506. doi: 10.1088/2058-6272/ad1792 -




 下载:
下载: