| [1] |
Snitzer E. Optical maser action of Nd+3 in a barium crown glass[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1961, 7(12): 444-446. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.7.444
|
| [2] |
周朴. 我国高功率光纤激光技术学科方向的历程、现状、挑战与建议[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2023, 52: 20230071 doi: 10.3788/IRLA20230071Zhou Pu. Review on the discipline of high power fiber laser in China[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2023, 52: 20230071 doi: 10.3788/IRLA20230071
|
| [3] |
Zhou Jiaqi, Pan Weiwei, Qi Weiao, et al. Ultrafast Raman fiber laser: a review and prospect[J]. PhotoniX, 2022, 3: 18. doi: 10.1186/s43074-022-00064-2
|
| [4] |
Richardson D J, Fini J M, Nelson L E. Space-division multiplexing in optical fibres[J]. Nature Photonics, 2013, 7(5): 354-362. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2013.94
|
| [5] |
Gao Le, Zhang Qiming, Gu Min. Femtosecond laser micro/nano processing: from fundamental to applications[J]. International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing, 2025, 7: 022010. doi: 10.1088/2631-7990/ad943e
|
| [6] |
Wang Jianwei, Sciarrino F, Laing A, et al. Integrated photonic quantum technologies[J]. Nature Photonics, 2020, 14(5): 273-284. doi: 10.1038/s41566-019-0532-1
|
| [7] |
Wu Jiafeng, Xu Xizhen, Liao Changrui, et al. Optimized femtosecond laser direct-written fiber Bragg gratings with high reflectivity and low loss[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(3): 3831-3838. doi: 10.1364/OE.482198
|
| [8] |
金东臣, 段云锋, 孙青, 等. 150 kW超高功率光纤激光器[J]. 中国激光, 2024, 51: 1416001 doi: 10.3788/CJL240738Jin Dongchen, Duan Yunfeng, Sun Qing, et al. 150 kW ultra-high power fiber laser[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2024, 51: 1416001 doi: 10.3788/CJL240738
|
| [9] |
Radier C, Chalus O, Charbonneau M, et al. 10 PW peak power femtosecond laser pulses at ELI-NP[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2022, 10: e21. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2022.11
|
| [10] |
Piccoli R, Brown J M, Jeong Y G, et al. Intense few-cycle visible pulses directly generated via nonlinear fibre mode mixing[J]. Nature Photonics, 2021, 15(12): 884-889. doi: 10.1038/s41566-021-00888-7
|
| [11] |
Carstens H, Högner M, Saule T, et al. High-harmonic generation at 250 MHz with photon energies exceeding 100 eV[J]. Optica, 2016, 3(4): 366-369.
|
| [12] |
Koltashev V V, Denker B I, Galagan B I, et al. 150 mW Tb3+ doped chalcogenide glass fiber laser emitting at λ > 5 μm[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2023, 161: 109233. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2023.109233
|
| [13] |
Li Wei, Ma Pengfei, Chen Yisha, et al. Confined-doped fiber enabled kilowatt-level all-fiber laser with 1.28 GHz linewidth[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(5): 8855-8863. doi: 10.1364/OE.484330
|
| [14] |
常琦, 高志强, 邓宇, 等. 强噪声下光纤激光相干合成突破千路[J]. 中国激光, 2023, 50: 0616001Chang Qi, Gao Zhiqiang, Deng Yu, et al. [J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2023, 50: 0616001
|
| [15] |
Guo Xinqian, Zhang Linbo, Liu Jun, et al. An automatic frequency stabilized laser with hertz-level linewidth[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2022, 145: 107498. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2021.107498
|
| [16] |
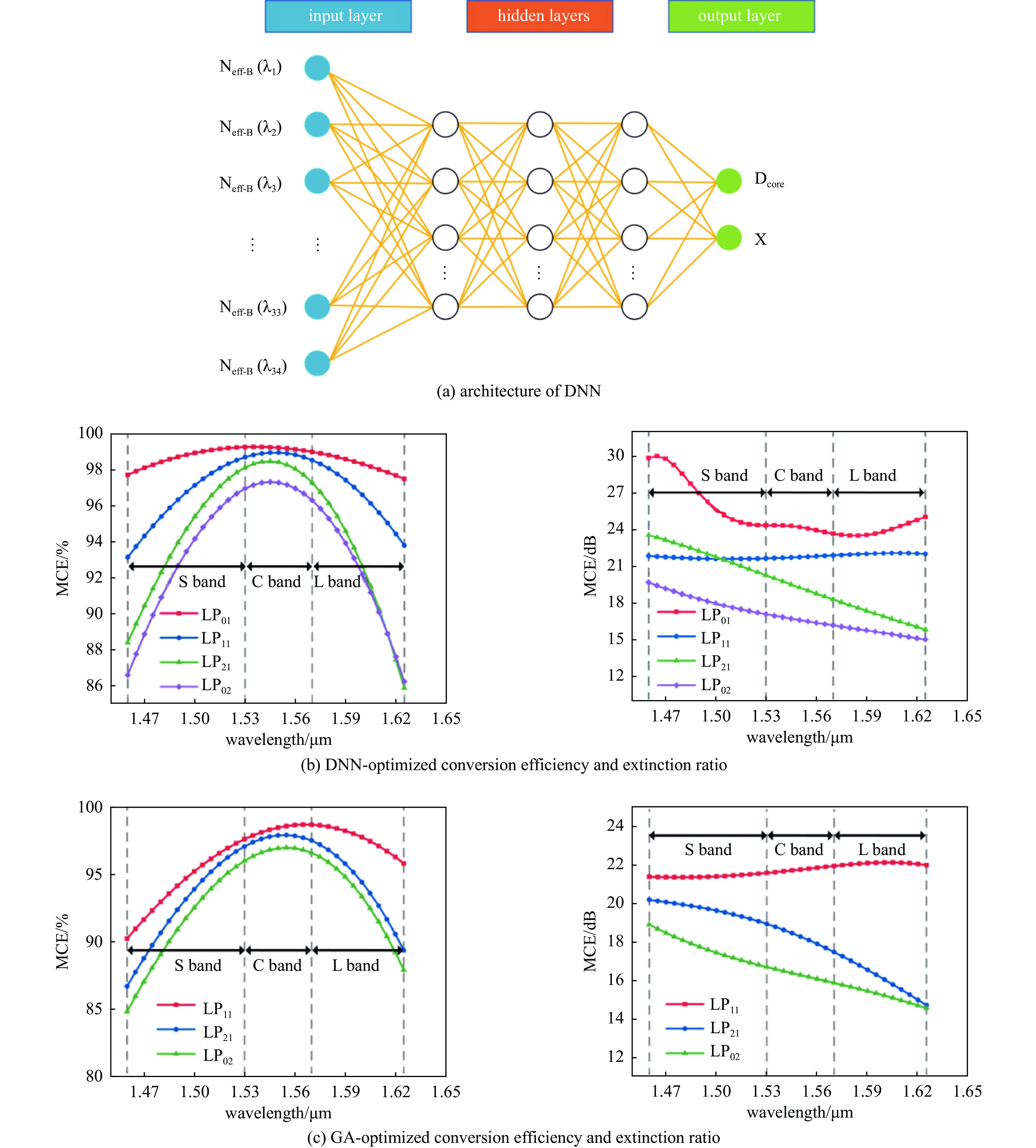
王文笙, 宁提纲, 裴丽, 等. 基于遗传算法的少模光纤放大器增益均衡[J]. 光学学报, 2021, 41: 0906001 doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.0906001Wang Wensheng, Ning Tigang, Pei Li, et al. Gain equalization of few-mode fiber amplifier based on genetic algorithm[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2021, 41: 0906001 doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.0906001
|
| [17] |
安毅, 蒋敏, 陈潇, 等. 机器学习预测多折射率层有源光纤的模场特性[J]. 中国激光, 2023, 50: 1101013 doi: 10.3788/CJL230476An Yi, Jiang Min, Chen Xiao, et al. Machine learning predicting mode properties for multi-layer active fibers[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2023, 50: 1101013 doi: 10.3788/CJL230476
|
| [18] |
侯文强, 裴丽, 王建帅, 等. 基于神经网络和多目标优化算法的掺铋光纤放大器设计[J]. 光学学报, 2024, 44: 0206001 doi: 10.3788/AOS231173Hou Wenqiang, Pei Li, Wang Jianshuai, et al. Design of bismuth-doped fiber amplifier based on neural network and multi-objective optimization algorithm[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2024, 44: 0206001 doi: 10.3788/AOS231173
|
| [19] |
朱福喜, 裴丽, 王建帅, 等. 多芯超模光纤放大器增益均衡设计(内封底文章)[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2024, 53: 20230504 doi: 10.3788/IRLA20230504Zhu Fuxi, Pei Li, Wang Jianshuai, et al. Design of gain equalization for multi-core supermode fiber amplifier (inside back cover paper)[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2024, 53: 20230504 doi: 10.3788/IRLA20230504
|
| [20] |
Jiang Xiaotian, Dong Jiawei, Song Yuchen, et al. Physics-informed machine learning for EDFA: parameter identification and gain estimation[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2025, 43(11): 5040-5054. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2025.3548285
|
| [21] |
Johnson S G, Joannopoulos J D. Block-iterative frequency-domain methods for Maxwell’s equations in a planewave basis[J]. Optics Express, 2001, 8(3): 173-190. doi: 10.1364/oe.8.000173
|
| [22] |
Koshiba M, Saitoh K. Applicability of classical optical fiber theories to holey fibers[J]. Optics Letters, 2004, 29(15): 1739-1741. doi: 10.1364/OL.29.001739
|
| [23] |
Shokooh-Saremi M, Mirsalehi M M. Analysis of femtosecond optical pulse propagation in one-dimensional nonlinear photonic crystals using finite-difference time-domain method[J]. Optik, 2005, 116(10): 486-492. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2005.02.014
|
| [24] |
Rodríguez-Esquerre V F, Isídio-Lima J J, Dourado-Sisnando A, et al. Artificial neural networks for the chromatic dispersion prediction of photonic crystal fibers[J]. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 2013, 55(9): 2179-2181. doi: 10.1002/mop.27753
|
| [25] |
Chugh S, Gulistan A, Ghosh S, et al. Machine learning approach for computing optical properties of a photonic crystal fiber[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(25): 36414-36425. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.036414
|
| [26] |
Yao Tianhang, Huang Tianye, Yan Bin, et al. Inverse design of dispersion for photonic devices based on LSTM and gradient-free optimization algorithms hybridization[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 2023, 40(6): 1525-1532. doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.491490
|
| [27] |
Xu Qibo, Yang Hua, Yuan Xiaofang, et al. Enhanced grey wolf algorithm for automatic tuning of an ensemble neural network in predicting PCF optical properties[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(26): 43790-43803. doi: 10.1364/OE.503978
|
| [28] |
Yuan Shuyu, Chen Shengchao, Yang Jianli, et al. Efficient calculation of optical properties of suspended-core fiber via a machine learning algorithm[J]. Applied Optics, 2022, 61(19): 5714-5721. doi: 10.1364/AO.458048
|
| [29] |
Ma Fuxiao, Ma Yunjie, Li Peili, et al. Inverse design of broadband dispersion compensation fiber based on deep learning and differential evolution algorithm[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2023, 15: 7201307. doi: 10.1109/jphot.2023.3277129
|
| [30] |
Qin Haibo, Huang Wei, Song Binbin, et al. Hybrid method for inverse design of orbital angular momentum transmission fiber based on neural network and optimization algorithms[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2022, 40(17): 5974-5985. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2022.3185059
|
| [31] |
Deng Ang, He Linzhen, Wang Yuxi, et al. Megawatt peak-power, single-mode, mid-infrared femtosecond pulse delivery at 5–6 μm via a silica-based anti-resonant hollow core fiber[J]. Optics Letters, 2025, 50(7): 2149-2152. doi: 10.1364/OL.555306
|
| [32] |
姚静远, 张鑫, 顾帅, 等. 基于空芯反谐振光纤的高功率激光传输技术研究进展(特邀)[J]. 中国激光, 2024, 51: 1901002 doi: 10.3788/CJL240969Yao Jingyuan, Zhang Xin, Gu Shuai, et al. Research progress of high-power laser transmission technology based on hollow-core anti-resonant fibers (invited)[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2024, 51: 1901002 doi: 10.3788/CJL240969
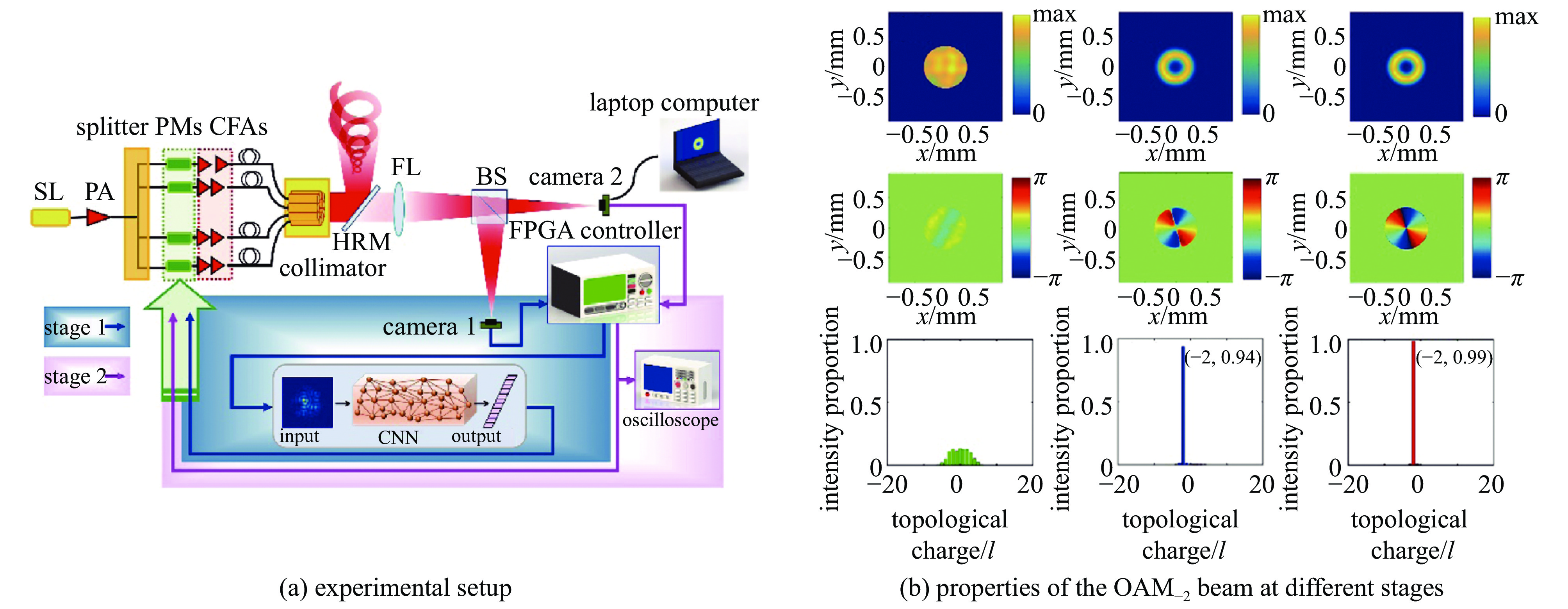
|
| [33] |
Meng Fanchao, Zhao Xiaoting, Ding Jinmin, et al. Use of machine learning to efficiently predict the confinement loss in anti-resonant hollow-core fiber[J]. Optics Letters, 2021, 46(6): 1454-1457. doi: 10.1364/OL.422511
|
| [34] |
Meng Fanchao, Ding Jinmin, Zhao Xiaoting, et al. Artificial intelligence designer for optical Fibers: inverse design of a Hollow-Core Anti-Resonant fiber based on a tandem neural network[J]. Results in Physics, 2023, 46: 106310. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2023.106310
|
| [35] |
Gu Zhenyu, Ning Tigang, Pei Li, et al. Confinement loss prediction in diverse anti-resonant fibers through neural networks[J]. Optics Express, 2024, 32(6): 8903-8918. doi: 10.1364/OE.517026
|
| [36] |
Teng Fei, Jin Zhen, Chen Shuo, et al. Neural network for the inverse design of polarization-maintaining few-mode panda-type ring-core fiber[C]//2020 Asia Communications and Photonics Conference (ACP) and International Conference on Information Photonics and Optical Communications (IPOC). 2020: 1-3.
|
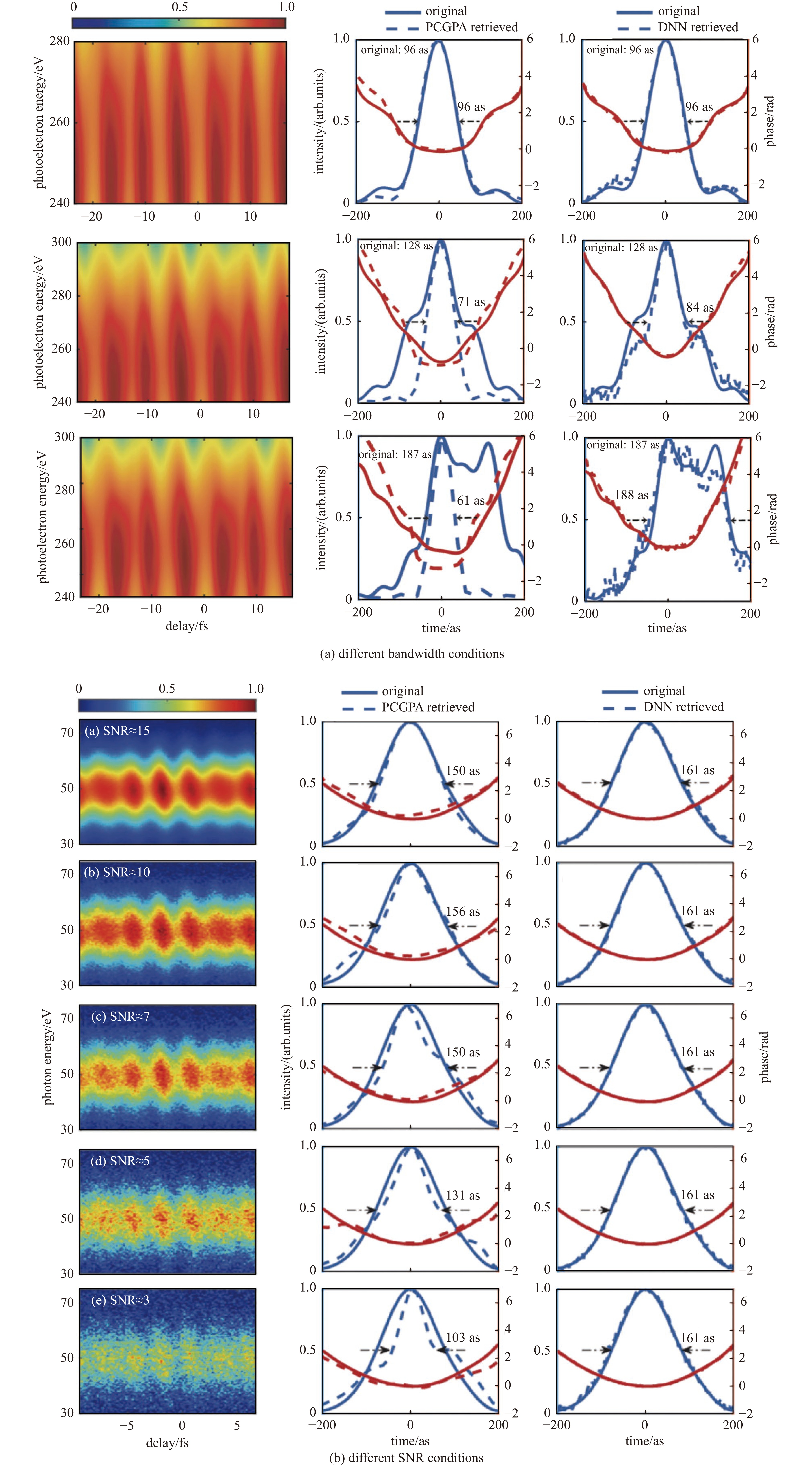
| [37] |
Hu Junling, Li Hongwei, Chen Hailiang, et al. Forward design method for the design of panda polarization-maintaining few-mode optical fiber based on artificial neural network[J]. Optics Express, 2024, 32(21): 36848-36864. doi: 10.1364/OE.536591
|
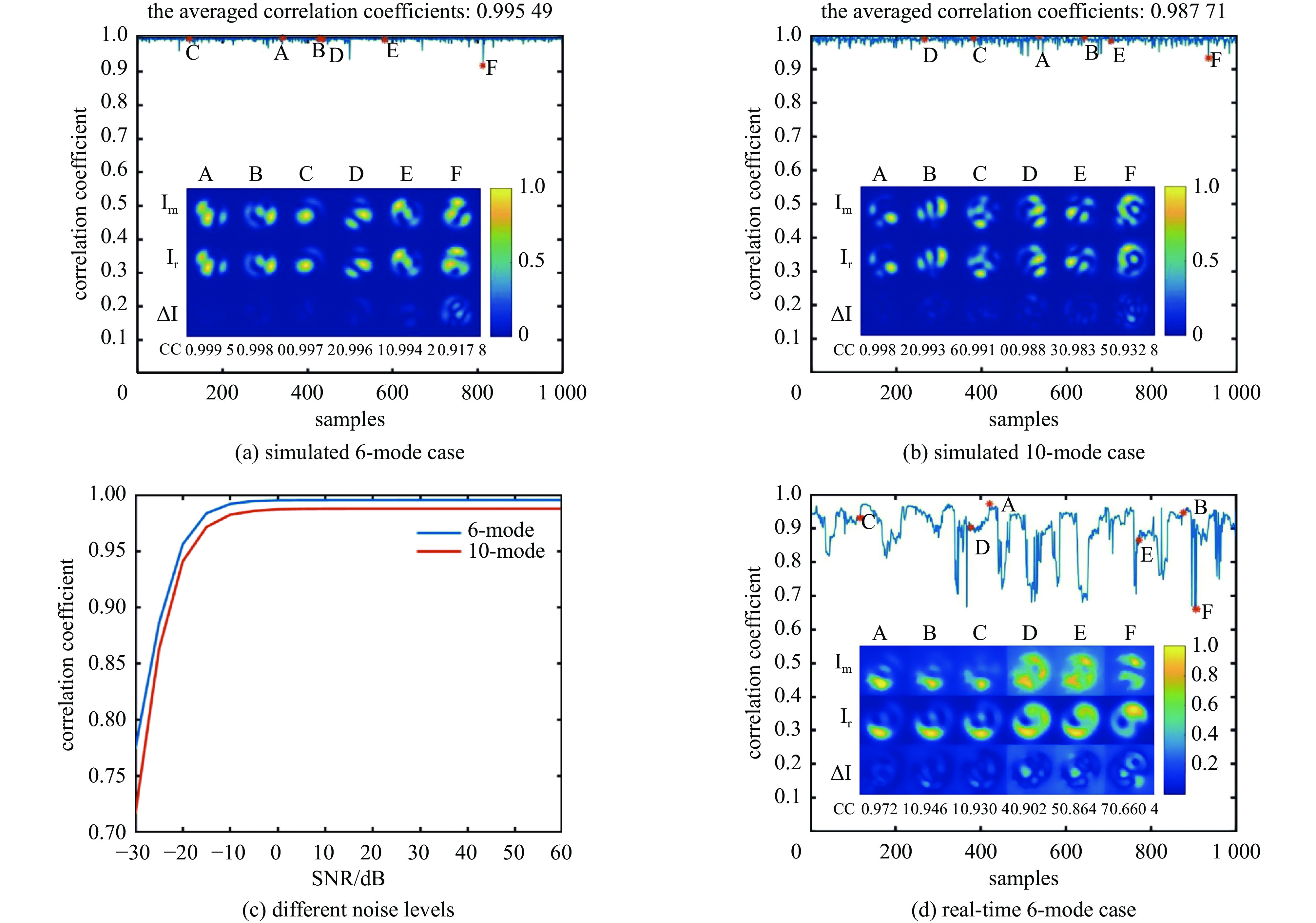
| [38] |
Yu Qingshan, Norris B R M, Edvell G, et al. Inverse design and optimization of an aperiodic multi-notch fiber Bragg grating using neural networks[J]. Applied Optics, 2024, 63(14): D50-D58. doi: 10.1364/AO.514987
|
| [39] |
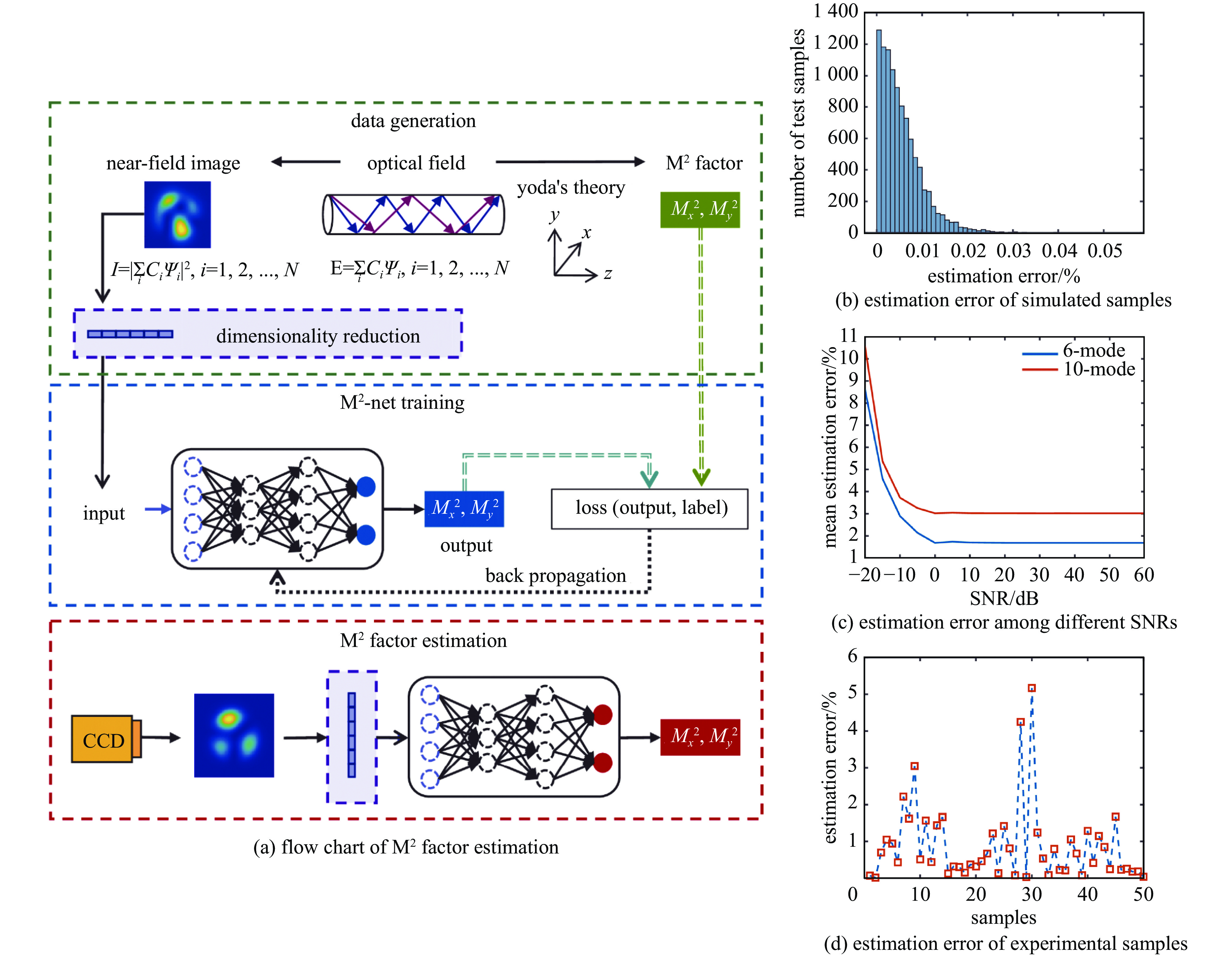
Adibnia E, Ghadrdan M, Mansouri-Birjandi M A. Chirped apodized fiber Bragg gratings inverse design via deep learning[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2025, 181: 111766. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2024.111766
|
| [40] |
Adibnia E, Ghadrdan M, Mansouri-Birjandi M A. Inverse design of FBG-based optical filters using deep learning: a hybrid CNN-MLP approach[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2025, 43(9): 4452-4461. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2025.3534275
|
| [41] |
Zhang Senyu, Zhang Cong, Zeng Yan, et al. Machine learning assisted ultra-wideband fiber-optics mode selective coupler design[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2022, 28: 4500110. doi: 10.1109/jstqe.2022.3171596
|
| [42] |
Fan Junjie, Huang Wei, Zhang Ran, et al. Resonance prediction and inverse design of multi-core selective couplers based on neural networks[J]. Applied Optics, 2022, 61(32): 9350-9359. doi: 10.1364/AO.474905
|
| [43] |
李力, 郑家容, 马修泉. 基于非等温流模型与神经网络的光纤拉锥尺寸预测[J]. 中国激光, 2023, 50: 1101015 doi: 10.3788/CJL230502Li Li, Zheng Jiarong, Ma Xiuquan. Prediction of optical fiber tapering diameter based on nonisothermal flow model and neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2023, 50: 1101015 doi: 10.3788/CJL230502
|
| [44] |
梁宏涛, 徐建良. 机器学习算法在光功率预测中的应用[J]. 激光杂志, 2015, 36(7): 131-134 doi: 10.14016/j.cnki.jgzz.2015.07.131Liang Hongtao, Xu Jianliang. Application of machines learning algorithm in optical power forecasting[J]. Laser Journal, 2015, 36(7): 131-134 doi: 10.14016/j.cnki.jgzz.2015.07.131
|
| [45] |
Huang Yishen, Samoud W, Gutterman C L, et al. A machine learning approach for dynamic optical channel add/drop strategies that minimize EDFA power excursions[C]//Proceedings of the 42nd European Conference on Optical Communication. 2016: 1-3.
|
| [46] |
Gutterman C L, Mo Weiyang, Zhu Shengxiang, et al. Neural network based wavelength assignment in optical switching[C]//Proceedings of the Workshop on Big Data Analytics and Machine Learning for Data Communication Networks. 2017: 37-42.
|
| [47] |
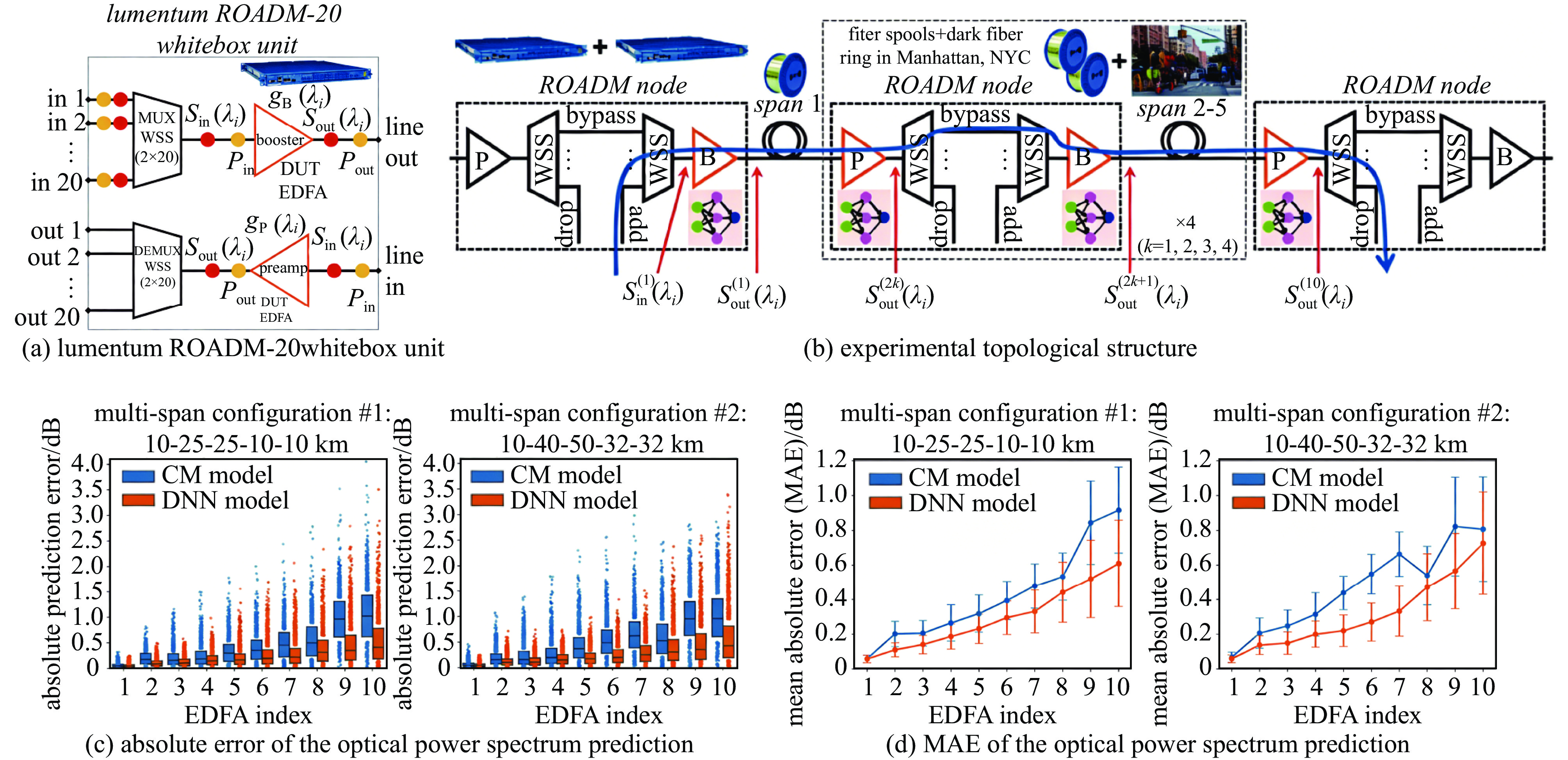
Wang Zehao, Akinrintoyo E, Kilper D, et al. Optical signal spectrum prediction using machine learning and in-line channel monitors in a multi-span ROADM system[C]//2022 European Conference on Optical Communication (ECOC). 2022: 1-4.
|
| [48] |
Salmela L, Tsipinakis N, Foi A, et al. Predicting ultrafast nonlinear dynamics in fibre optics with a recurrent neural network[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2021, 3(4): 344-354. doi: 10.1038/s42256-021-00297-z
|
| [49] |
Sui Hao, Zhu Hongna, Jia Huanyu, et al. Predicting nonlinear multi-pulse propagation in optical fibers via a lightweight convolutional neural network[J]. Optics Letters, 2023, 48(18): 4889-4892. doi: 10.1364/OL.496973
|
| [50] |
Sun Jingxuan, Shu Yiqing, Ge Yanqi, et al. Reversely exploring higher-order effects in a fiber laser through physics-informed recursive neural network[J]. ACS Photonics, 2024, 11(10): 4306-4315. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.4c01235.s001
|
| [51] |
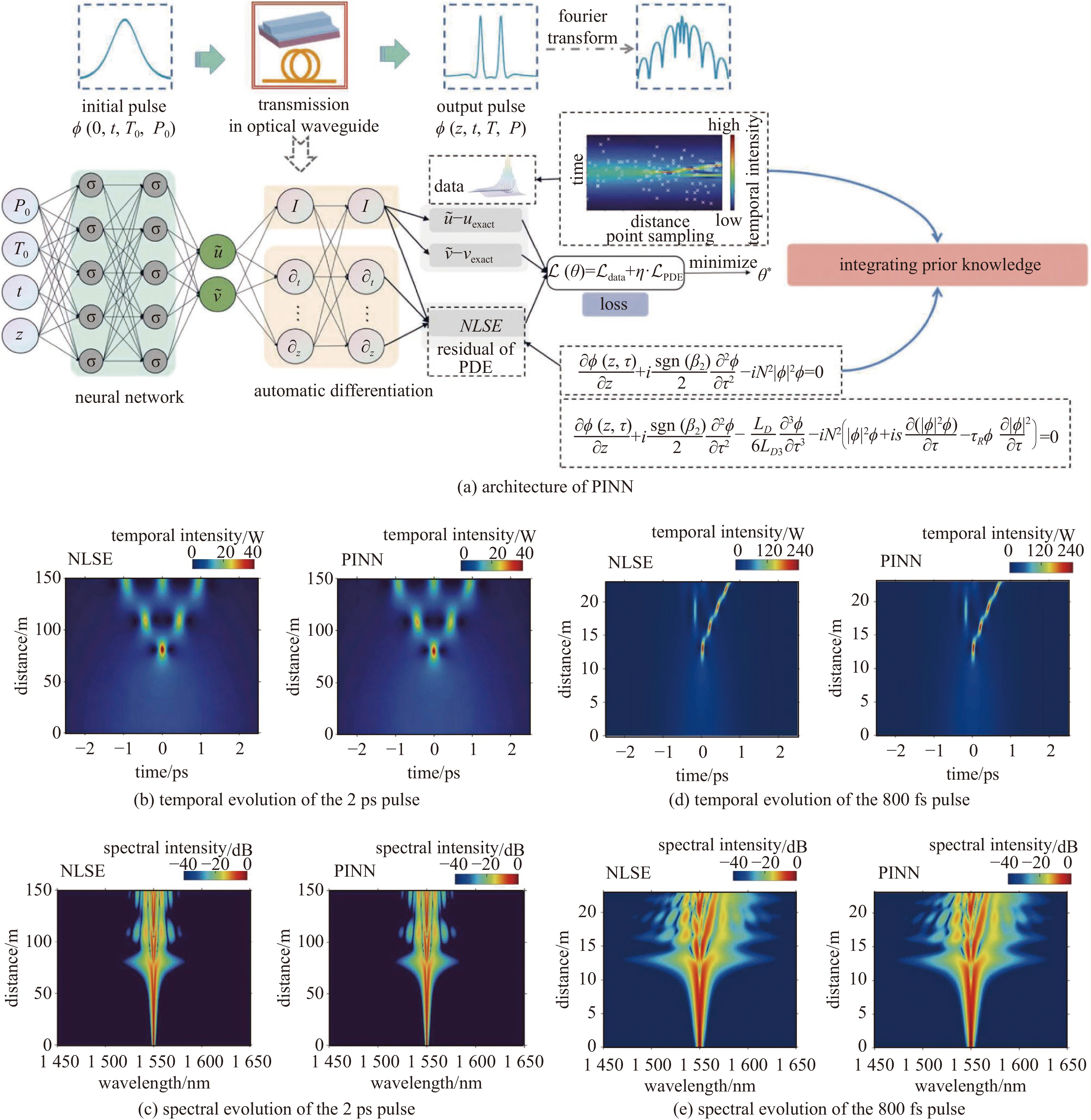
Wu Jinhong, Wang Zimiao, Chen Ruifeng, et al. Efficient physics-informed neural network for ultrashort pulse dynamics in optical fibers[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2025, 43(3): 1372-1380. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2024.3477409
|
| [52] |
Salmela L, Hary M, Dudley J M, et al. Predicting supercontinuum generation dynamics using a neural network[C]//2021 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Europe & European Quantum Electronics Conference. 2021.
|
| [53] |
Liu Shuo, Han Xu, Wang Yueyu, et al. Analysis of rogue wave in the mid-infrared supercontinuum under femtosecond weak seed pulse conditions based on deep learning[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2024, 188: 115575.
|
| [54] |
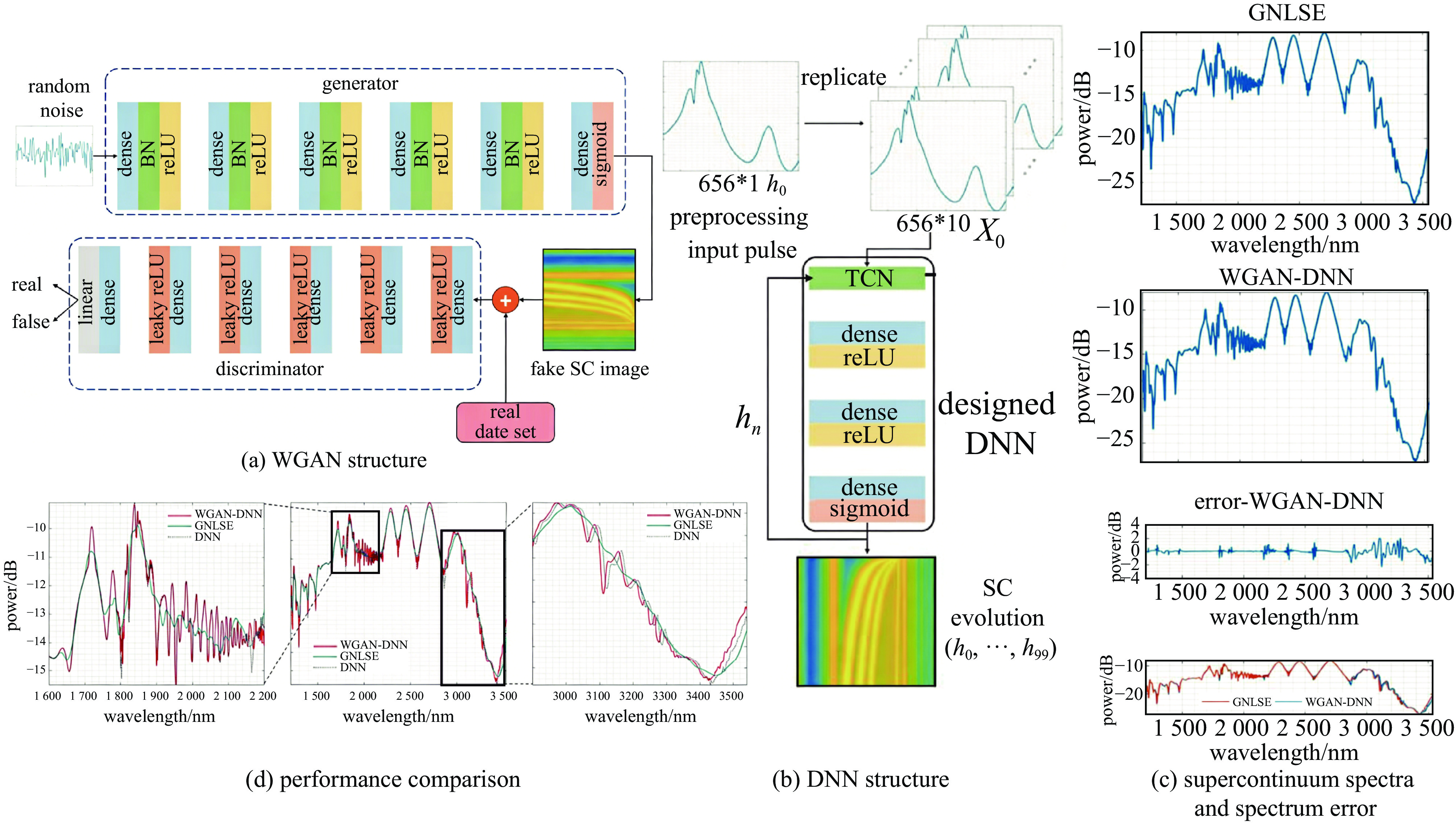
Yang Dan, Liu Hong, Xu Bin, et al. A hybrid network with DNN and WGAN for supercontinum prediction[J]. Optical Fiber Technology, 2024, 85: 103816. doi: 10.1016/j.yofte.2024.103816
|
| [55] |
Li Sha, Xu Jun, Chen Guoliang, et al. An automatic mode-locked system for passively mode-locked fiber laser[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 9043, 2013 International Conference on Optical Instruments and Technology: Optoelectronic Devices and Optical Signal Processing. 2013: 904313.
|
| [56] |
Shen Xuling, Li Wenxue, Yan Ming, et al. Electronic control of nonlinear-polarization-rotation mode locking in Yb-doped fiber lasers[J]. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(16): 3426-3428. doi: 10.1364/OL.37.003426
|
| [57] |
Wu H, Huang Pinhan, Teng Yuanhe, et al. Automatic generation of noise-like or mode-locked pulses in an ytterbium-doped fiber laser by using two-photon-induced current for feedback[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2018, 10: 7105608. doi: 10.1109/jphot.2018.2880772
|
| [58] |
Andral U, Si Fodil R, Amrani F, et al. Fiber laser mode locked through an evolutionary algorithm[J]. Optica, 2015, 2(4): 275-278. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.2.000275
|
| [59] |
Pu Guoqing, Yi Lilin, Zhang Li, et al. Intelligent control of mode-locked femtosecond pulses by time-stretch-assisted real-time spectral analysis[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2020, 9: 13.
|
| [60] |
Pu Guoqing, Yi Lilin, Zhang Li, et al. Genetic algorithm-based fast real-time automatic mode-locked fiber laser[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2020, 32(1): 7-10. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2019.2954806
|
| [61] |
Winters D G, Kirchner M S, Backus S J, et al. Electronic initiation and optimization of nonlinear polarization evolution mode-locking in a fiber laser[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(26): 33216-33225. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.033216
|
| [62] |
Luo Chao, Pu Guoqing, Hu Weisheng, et al. High-repetition-rate real-time automatic mode-locked fibre laser enabled by a pre-stretch technique[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2022, 34(15): 791-794. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2022.3185989
|
| [63] |
Wei Xiaoming, Jing J C, Shen Yuecheng, et al. Harnessing a multi-dimensional fibre laser using genetic wavefront shaping[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2020, 9: 149.
|
| [64] |
Wu Xiuqi, Peng Junsong, Boscolo S, et al. Intelligent breathing soliton generation in ultrafast fiber lasers[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2022, 16: 2100191. doi: 10.1002/lpor.202100191
|
| [65] |
Fu Xing, Brunton S L, Nathan Kutz J. Classification of birefringence in mode-locked fiber lasers using machine learning and sparse representation[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(7): 8585-8597. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.008585
|
| [66] |
Baumeister T, Brunton S L, Nathan Kutz J. Deep learning and model predictive control for self-tuning mode-locked lasers[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 2018, 35(3): 617-626. doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.35.000617
|
| [67] |
Sun Jingxuan, Liu Zhen, Shu Yiqing, et al. Reproduction of mode-locked pulses by spectrotemporal domain-informed deep learning[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(21): 34100-34111. doi: 10.1364/OE.501721
|
| [68] |
Sun Chang, Kaiser E, Brunton S L, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for optical systems: a case study of mode-locked lasers[J]. Machine Learning: Science and Technology, 2020, 1: 045013. doi: 10.1088/2632-2153/abb6d6
|
| [69] |
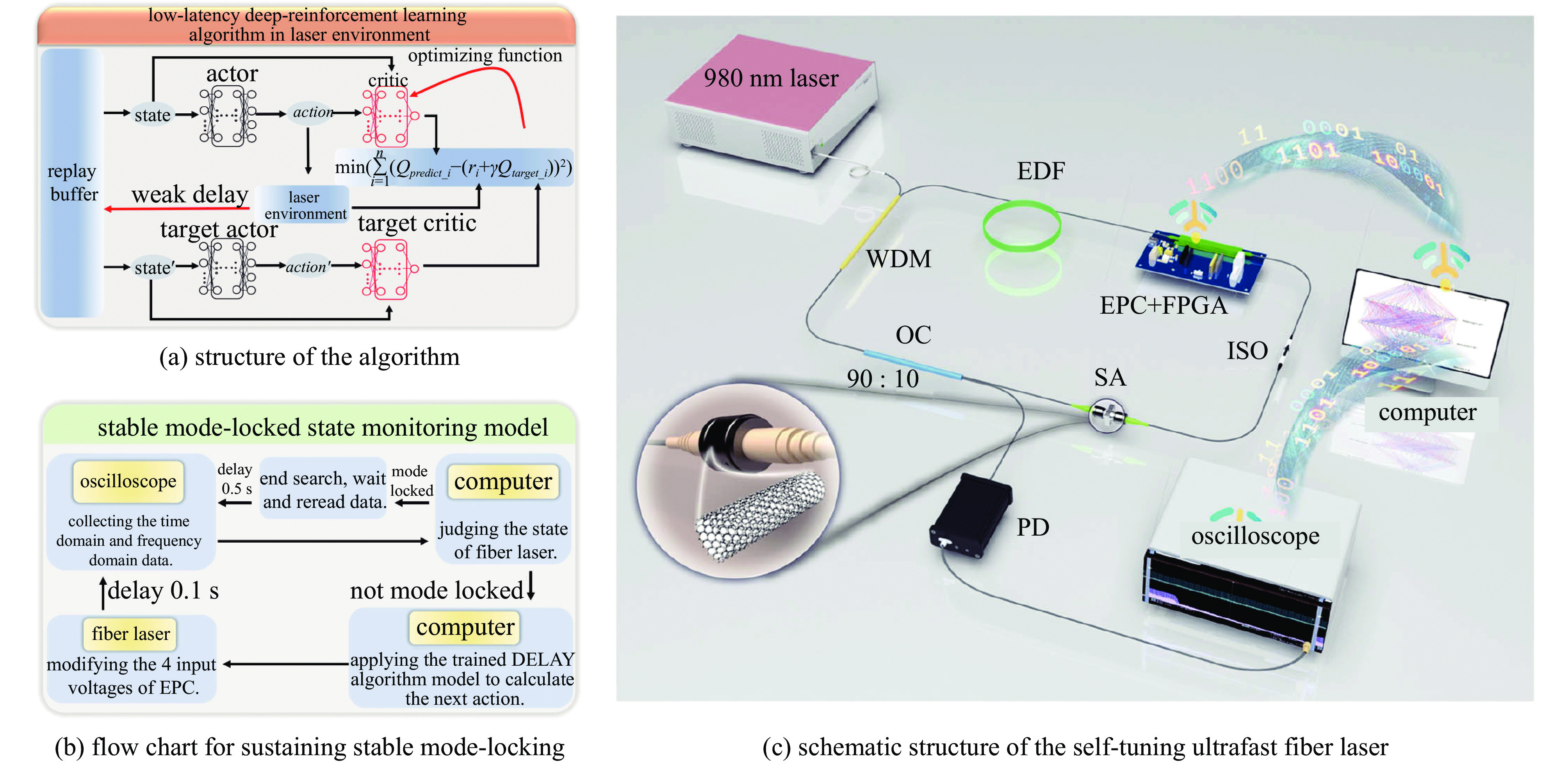
Yan Qiuquan, Deng Qinghui, Zhang Jun, et al. Low-latency deep-reinforcement learning algorithm for ultrafast fiber lasers[J]. Photonics Research, 2021, 9(8): 1493-1501. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.428117
|
| [70] |
Zhan Li, Yang Shuaishuai, Xiao Qi, et al. Deep reinforcement with spectrum series learning control for a mode-locked fiber laser[J]. Photonics Research, 2022, 10(6): 1491-1500. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.455493
|
| [71] |
Kokhanovskiy A, Ivanenko A, Kobtsev S, et al. Machine learning methods for control of fibre lasers with double gain nonlinear loop mirror[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 2916. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39759-1
|
| [72] |
Xiao Rui, Hou J, liu M, et al. Coherent combining technology of master oscillator power amplifier fiber arrays[J]. Optics Express, 2008, 16(3): 2015-2022. doi: 10.1364/oe.16.002015
|
| [73] |
Seise E, Klenke A, Limpert J, et al. Coherent addition of fiber-amplified ultrashort laser pulses[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(26): 27827-27835. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.027827
|
| [74] |
Kabeya D, Kermene V, Fabert M, et al. Active coherent combining of laser beam arrays by means of phase-intensity mapping in an optimization loop[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(24): 31059-31068. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.031059
|
| [75] |
Vorontsov M A, Carhart G W, Ricklin J C. Adaptive phase-distortion correction based on parallel gradient-descent optimization[J]. Optics Letters, 1997, 22(12): 907-909. doi: 10.1364/OL.22.000907
|
| [76] |
Vorontsov M A, Sivokon V P. Stochastic parallel-gradient-descent technique for high-resolution wave-front phase-distortion correction[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1998, 15(10): 2745-2758. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.15.002745
|
| [77] |
Che Dongbo, Li Yuanyang, Wu Yunhan, et al. Theory of AdmSPGD algorithm in fiber laser coherent synthesis[J]. Optics Communications, 2021, 492: 126953. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2021.126953
|
| [78] |
Ma Yanxing, Zhou Pu, Wang Xiaolin, et al. Coherent beam combination with single frequency dithering technique[J]. Optics Letters, 2010, 35(9): 1308-1310. doi: 10.1364/OL.35.001308
|
| [79] |
Tünnermann H, Shirakawa A. Deep reinforcement learning for coherent beam combining applications[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(17): 24223-24230. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.024223
|
| [80] |
Zhang Xi, Li Pingxue, Zhu Yunchen, et al. Coherent beam combination based on Q-learning algorithm[J]. Optics Communications, 2021, 490: 126930. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2021.126930
|
| [81] |
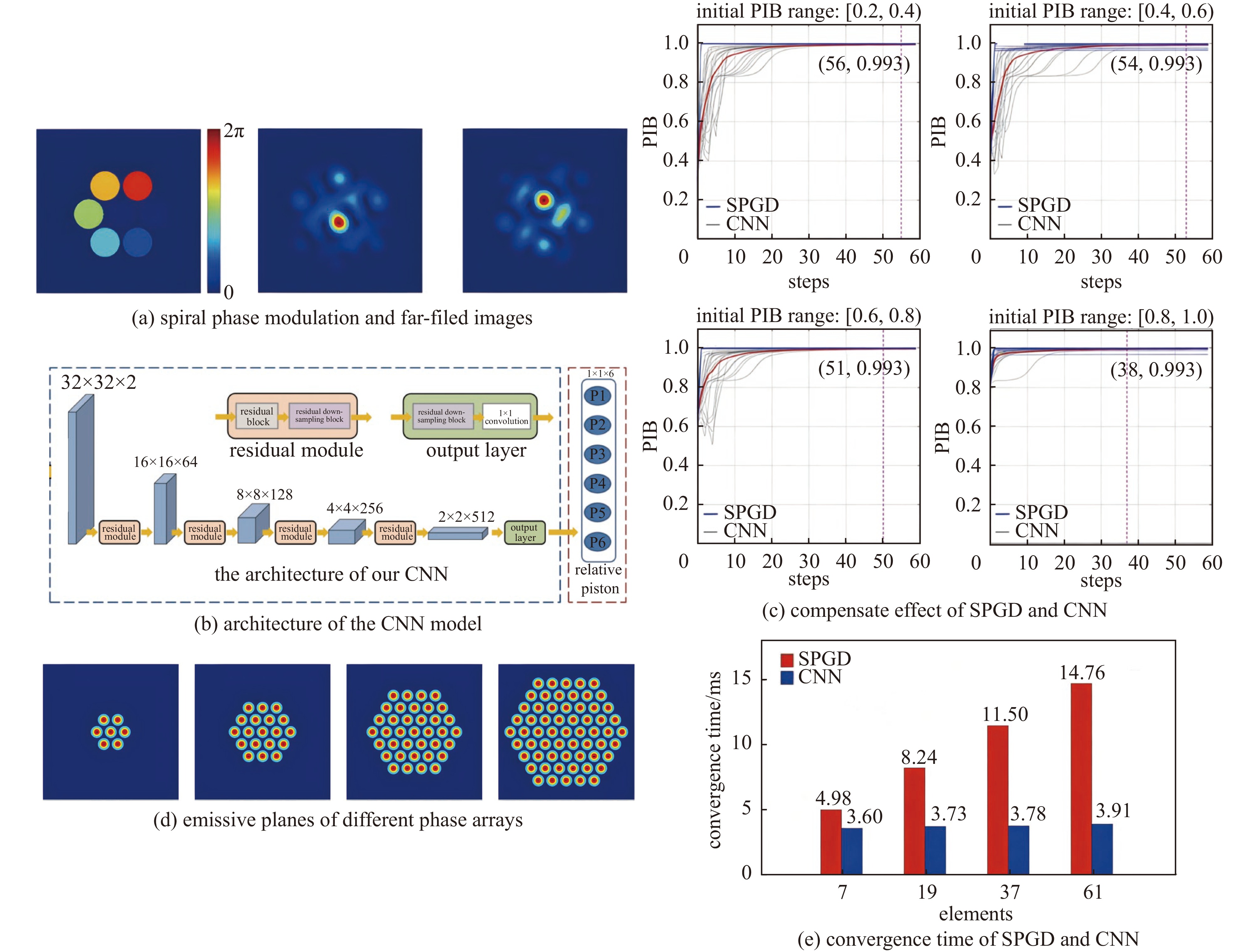
Zuo Jing, Jia Haolong, Geng Chao, et al. Deep learning piston aberration control of fiber laser phased array by spiral phase modulation[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2022, 40(12): 3980-3991. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2022.3151628
|
| [82] |
Abuduweili A, Wang Jie, Yang Bowei, et al. Reinforcement learning based robust control algorithms for coherent pulse stacking[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(16): 26068-26081. doi: 10.1364/OE.426906
|
| [83] |
Wang Dan, Du Qiang, Zhou Tong, et al. Machine learning pattern recognition algorithm with applications to coherent laser combination[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2022, 58: 6100309. doi: 10.36227/techrxiv.19750192
|
| [84] |
Schimpf D N, Ruchert C, Nodop D, et al. Compensation of pulse-distortion in saturated laser amplifiers[J]. Optics Express, 2008, 16(22): 17637-17646. doi: 10.1364/OE.16.017637
|
| [85] |
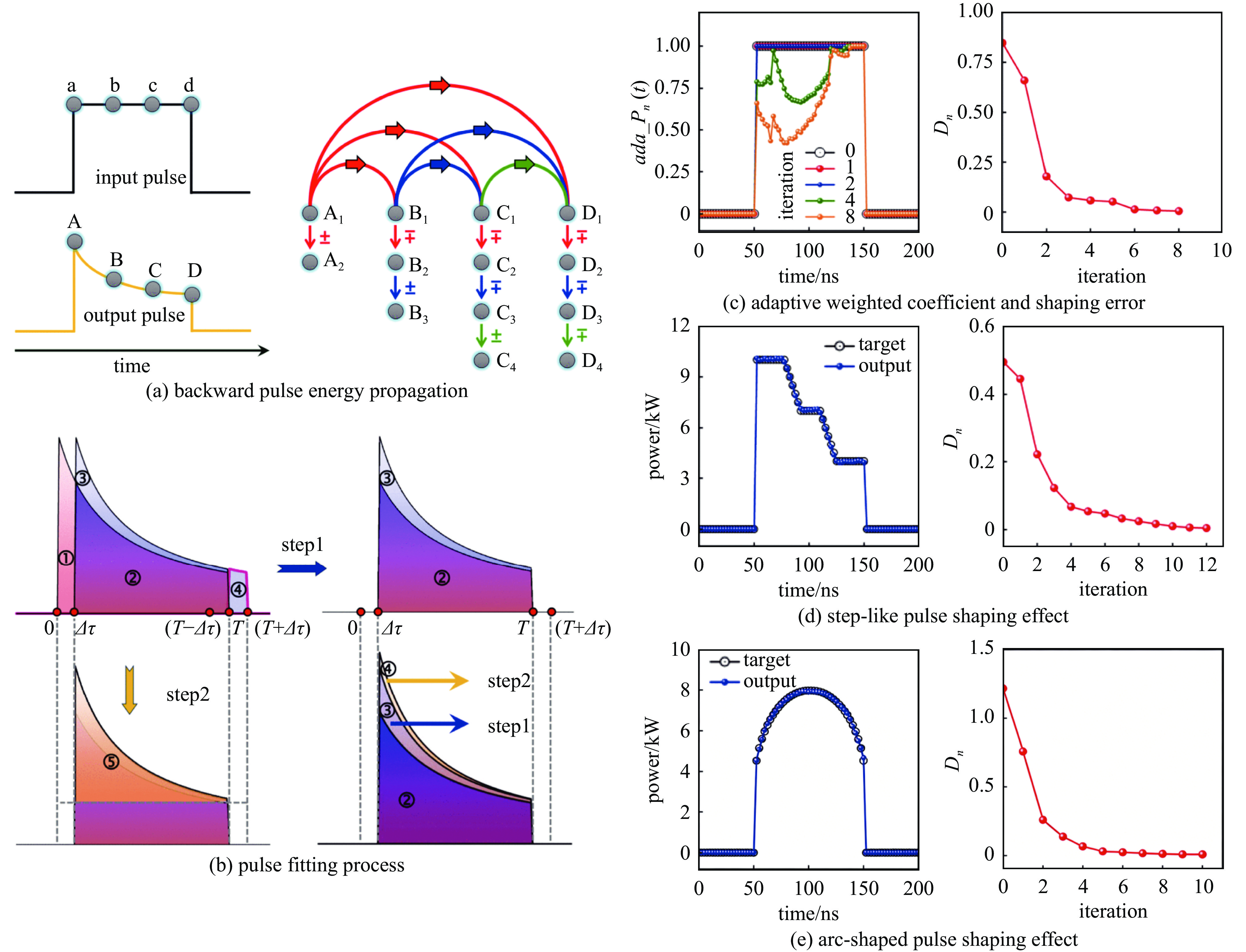
Jiang Min, Su Rongtao, Zhang Pengfei, et al. Arbitrary temporal shape pulsed fiber laser based on SPGD algorithm[J]. Laser Physics Letters, 2018, 15: 065101. doi: 10.1088/1612-202X/aab250
|
| [86] |
Bu Yuanzhuang, Zhang Bin, Liu Shuailin, et al. Ultra-efficient temporal shaping scheme in nanosecond pulsed fiber MOPA system[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2025, 43(5): 2284-2290. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2024.3492043
|
| [87] |
Zibar D, Brusin A M R, de Moura U C, et al. Inverse system design using machine learning: the Raman amplifier case[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2020, 38(4): 736-753. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2019.2952179
|
| [88] |
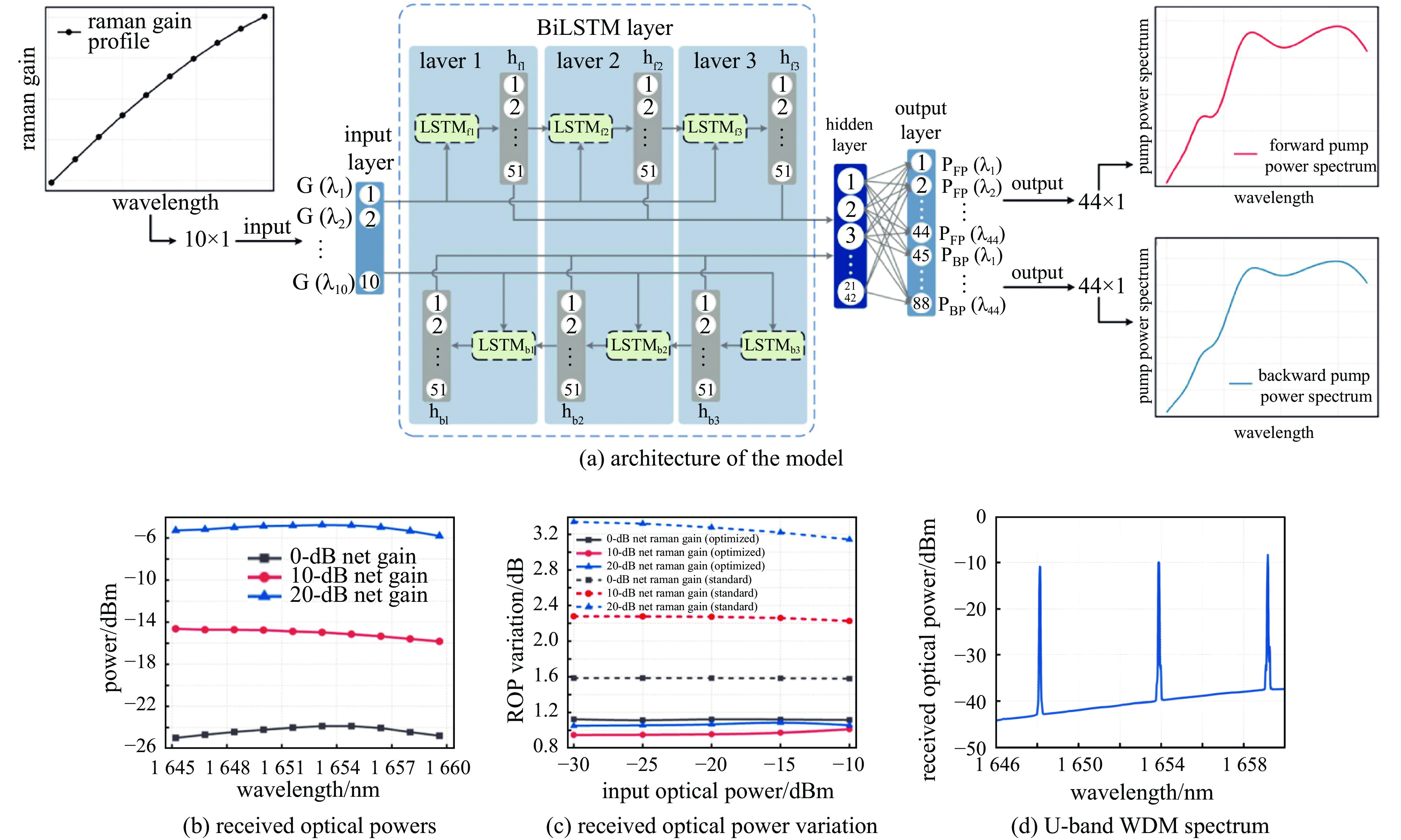
Lan Tangyanjun, Xiang Junjiang, Zhou Gai, et al. Inverse design of incoherent Raman pump sources for U-band WDM transmission over 125 km G. 652. D fiber[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2024, 16: 7202106. doi: 10.1109/jphot.2024.3453870
|
| [89] |
Liu Xiaomin, Zhang Yihao, Cai Meng, et al. SMOF: simultaneous modeling and optimization framework for Raman amplifiers in C+L-band optical networks[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2024, 42(9): 3174-3183. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2024.3359255
|
| [90] |
Teğin U, Rahmani B, Kakkava E, et al. Learning spatiotemporal nonlinearities in graded-index multimode fibers with deep neural networks[C]//2019 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Europe & European Quantum Electronics Conference. 2019.
|
| [91] |
Hary M, Salmela L, Dudley J M, et al. Machine learning control of nonlinear fiber supercontinuum generation for application in molecular spectroscopy[C]//Optica Advanced Photonics Congress 2022. 2022: NpTu1G. 2.
|
| [92] |
Hoang V T, Boussafa Y, Sader L, et al. Smart control of supercontinuum generation by machine learning towards multiphoton microscopy applications[C]//2023 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Europe & European Quantum Electronics Conference. 2023.
|
| [93] |
Di Leonardo R, Ianni F, Ruocco G. Computer generation of optimal holograms for optical trap arrays[J]. Optics Express, 2007, 15(4): 1913-1922. doi: 10.1364/OE.15.001913
|
| [94] |
Dufresne E R, Spalding G C, Dearing M T, et al. Computer-generated holographic optical tweezer arrays[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2001, 72(3): 1810-1816. doi: 10.1063/1.1344176
|
| [95] |
Hou Tianyue, An Yi, Chang Qi, et al. Deep-learning-assisted, two-stage phase control method for high-power mode-programmable orbital angular momentum beam generation[J]. Photonics Research, 2020, 8(5): 715-722. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.388551
|
| [96] |
Hou Tianyue, An Yi, Chang Qi, et al. Deep learning of coherent laser arrays in angular domain for orbital angular momentum beams customization[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2022, 28: 0900110. doi: 10.1109/jstqe.2022.3153965
|
| [97] |
Oguz I, Hsieh J L, Dinc N U, et al. Programming nonlinear propagation for efficient optical learning machines[J]. Advanced Photonics, 2024, 6: 016002. doi: 10.1117/1.ap.6.1.016002
|
| [98] |
Gobé B, Saucourt J, Shpakovych M, et al. Machine learning method to measure the transmission matrix of a multimode optical fiber without reference beam for 3D beam tailoring[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 12871, Laser Resonators, Microresonators, and Beam Control XXVI. 2024: 128710F.
|
| [99] |
Saucourt J, Gobé B, Helbert D, et al. Machine learning-driven complex models for wavefront shaping through multimode fibers[J]. Optical Fiber Technology, 2024, 88: 104017. doi: 10.1016/j.yofte.2024.104017
|
| [100] |
韦芊屹, 倪洁蕾, 李灵, 等. 超高时空分辨显微成像技术研究进展[J]. 物理学报, 2023, 72(17): 178701Wei Qianyi, Ni Jielei, Li Ling, et al. Research progress of ultra-high spatiotemporally resolved microscopy[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2023, 72: 178701
|
| [101] |
孟黎辉, 兰鹏飞, 陆培祥. 高平均功率高次谐波光源的研究进展(特邀)[J]. 光子学报, 2024, 53: 0653202 doi: 10.3788/gzxb20245306.0653202Meng Lihui, Lan Pengfei, Lu Peixiang. Research progress of high average power high harmonic source (Invited)[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2024, 53: 0653202 doi: 10.3788/gzxb20245306.0653202
|
| [102] |
吴琴菲, 文锦辉. 基于智能搜寻者优化的频率分辨光学开关重构算法[J]. 物理学报, 2021, 70(9): 090601Wu Qinfei, Wen Jinhui. Reconstructing algorithm for frequency-resolved optical gating based on intelligent seeker optimization[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2021, 70: 090601
|
| [103] |
毛安君, 刘呈普. 多FROG构型下非方形迹的超短脉冲重建[J]. 中国激光, 2021, 48: 0704004 doi: 10.3788/CJL202148.0704004Mao Anjun, Liu Chengpu. Ultrashort pulse reconstruction from non-square FROG traces in different geometric schemes[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2021, 48: 0704004 doi: 10.3788/CJL202148.0704004
|
| [104] |
Jensen S, Anderson M E. Measuring ultrashort optical pulses in the presence of noise: an empirical study of the performance of spectral phase interferometry for direct electric field reconstruction[J]. Applied Optics, 2004, 43(4): 883-893. doi: 10.1364/AO.43.000883
|
| [105] |
Zahavy T, Dikopoltsev A, Moss D, et al. Deep learning reconstruction of ultrashort pulses[J]. Optica, 2018, 5(5): 666-673. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.5.000666
|
| [106] |
Zhu Zheyuan, White J, Chang Zenghu, et al. Attosecond pulse retrieval from noisy streaking traces with conditional variational generative network[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 5782. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62291-6
|
| [107] |
Stanfield M, Ott J, Gardner C, et al. Real-time reconstruction of high energy, ultrafast laser pulses using deep learning[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12: 5299. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09041-y
|
| [108] |
Meng Lihui, Liang Shiqi, He Lixin, et al. Deep learning for isolated attosecond pulse reconstruction with the all-optical method[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 2023, 40(10): 2536-2545. doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.489019
|
| [109] |
Mendlovic D, Ozaktas H M. Fractional Fourier transforms and their optical implementation: I[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1993, 10(9): 1875-1881. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.10.001875
|
| [110] |
Bianco V, Memmolo P, Paturzo M, et al. Quasi noise-free digital holography[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2016, 5: e16142.
|
| [111] |
An Yi, Huang Liangjin, Li Jun, et al. Learning to decompose the modes in few-mode fibers with deep convolutional neural network[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(7): 10127-10137. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.010127
|
| [112] |
Jiang Min, An Yi, Su Rongtao, et al. Deep mode decomposition: real-time mode decomposition of multimode fibers based on unsupervised learning[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2022, 28: 0900207. doi: 10.1109/jstqe.2022.3195203
|
| [113] |
Kim B, Na J, Jeong Y. Convolutional neural network combined with stochastic parallel gradient descent to decompose fiber modes based on far-field measurements[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2023, 41(18): 5973-5982. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2023.3276366
|
| [114] |
Dong Xiaowei, Yu Zhihui. Modal decomposition in multimode optical fibres by solving the challenges posed by phase ambiguity and large datasets[J]. Journal of Modern Optics, 2024, 71(19/21): 753-761. doi: 10.1080/09500340.2025.2452875
|
| [115] |
An Yi, Li Jun, Huang Liangjin, et al. Deep learning enabled superfast and accurate M2 evaluation for fiber beams[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(13): 18683-18694. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.018683
|
| [116] |
Jiang Min, An Yi, Huang Liangjin, et al. M2 factor estimation in few-mode fibers based on a shallow neural network[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(15): 27304-27313. doi: 10.1364/OE.462170
|
| [117] |
Wei Mengda, Liao Meisong, Chen Liang, et al. Practical and accurate evaluation of numerical aperture and beam quality factor in photonic crystal fibers by mechanical learning[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2025, 17: 5800108. doi: 10.1109/jphot.2024.3506622
|




 下载:
下载: