| [1] |
Dong Kegong, Zhang Tiankui, Yu Minghai, et al. Micro-spot gamma-ray generation based on laser Wakefield acceleration[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2018, 123: 243301. doi: 10.1063/1.4997142
|
| [2] |
Wu Y C, Zhu B, Li G, et al. Towards high-energy, high-resolution computed tomography via a laser driven micro-spot gamma-ray source[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 15888. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33844-7
|
| [3] |
Emma C, Van Tilborg J, Assmann R, et al. Free electron lasers driven by plasma accelerators: status and near-term prospects[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2021, 9: e57. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2021.39
|
| [4] |
张高维, 矫金龙, 齐伟, 等. 拍瓦激光与铜靶作用产生光核中子的数值模拟研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2016, 28: 102002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201628.160102Zhang Gaowei, Jiao Jinlong, Qi Wei, et al. Numerical simulation study of photonuclear neutron generation by PW laser[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2016, 28: 102002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201628.160102
|
| [5] |
仲佳勇, 安维明, 平永利, 等. 强激光实验室天体物理介绍[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2020, 32: 092003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202032.200123Zhong Jiayong, An Weiming, Ping Yongli, et al. Introduction of laboratory astrophysics with intense lasers[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2020, 32: 092003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202032.200123
|
| [6] |
Danson N C, Haefner C, Bromage J, et al. Petawatt and exawatt class lasers worldwide[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2019, 7: 03000e54. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2014.52
|
| [7] |
Zhu Qihua, Zhou Kainan, Su Jingqin, et al. The Xingguang-III laser facility: precise synchronization with femtosecond, picosecond and nanosecond beams[J]. Laser Physics Letters, 2018, 15: 015301. doi: 10.1088/1612-202X/aa94e9
|
| [8] |
Yoon J W, Kim Y G, Choi I W, et al. Realization of laser intensity over 1023 W/cm2[J]. Optica, 2021, 8(5): 630-635.
|
| [9] |
Lindl J. Development of the indirect-drive approach to inertial confinement fusion and the target physics basis for ignition and gain[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 1995, 2(11): 3933-4024. doi: 10.1063/1.871025
|
| [10] |
An H H, Wang W, Xiong J, et al. Accelerated protons with energies up to 70 MeV based on the optimized SG-II Peta-watt laser facility[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2023, 11: e63. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2023.54
|
| [11] |
Sueoka K, Kataoka J, Takabe M, et al. Development of a new pinhole camera for imaging in high dose-rate environments[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2018, 912: 115-118. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2017.10.082
|
| [12] |
Finocchiaro G, Naselli E, Mishra B, et al. Space-resolved electron density and temperature evaluation by x-ray pinhole camera method in an ECR plasma[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2024, 31: 062506. doi: 10.1063/5.0207185
|
| [13] |
Stoeckl C, Cao D, Ceurvorst L, et al. Beam-pointing verification using x-ray pinhole cameras on the 60-beam OMEGA laser[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2022, 93: 103524. doi: 10.1063/5.0098941
|
| [14] |
侯立飞, 韦敏习, 袁永腾, 等. 神光Ⅱ升级装置X光针孔相机研制[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2013, 25(9): 2313-2316 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132509.2313Hou Lifei, Wei Minxi, Yuan Yongteng, et al. Development of X-ray pinhole camera on Shengguang II-up equipment[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(9): 2313-2316 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132509.2313
|
| [15] |
董建军, 刘慎业, 杨国洪, 等. 实时测量的X射线针孔相机信号强度估算[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2009, 21(9): 1347-1350Dong Jianjun, Liu Shenye, Yang Guohong, et al. Estimation of signal intensity for online measurement X-ray pinhole camera[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2009, 21(9): 1347-1350
|
| [16] |
Wang C, An H H, Xiong J, et al. A pinhole camera for ultrahigh-intensity laser plasma experiments[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2017, 88: 113501. doi: 10.1063/1.5009189
|
| [17] |
江少恩, 于燕宁. 用于神光II激光装置的X光针孔相机[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2005, 5(22): 1713-1716Jiang Shaoen, Yu Yanning. X-ray pinhole camera used on Shenguang II facility[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2005, 5(22): 1713-1716
|




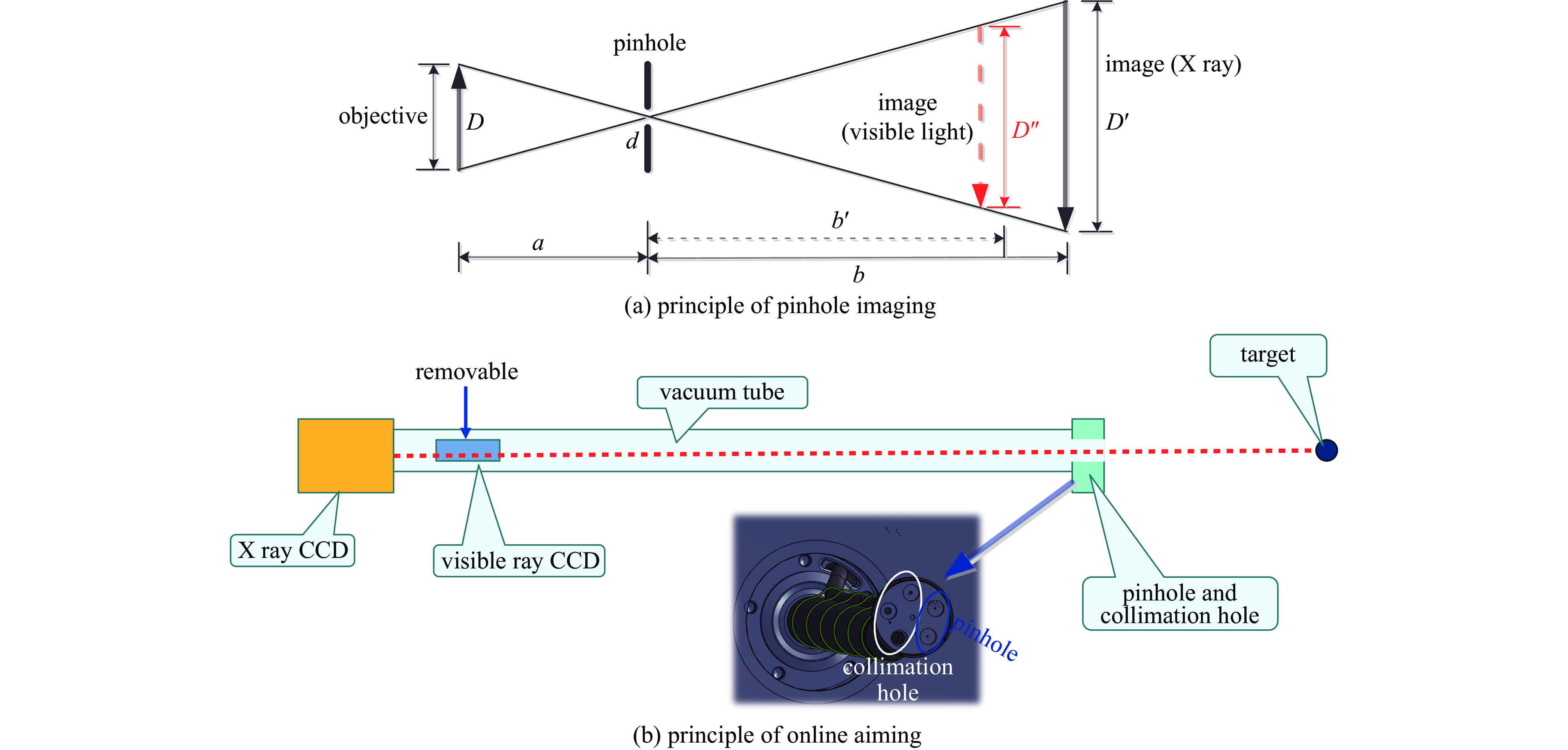
 下载:
下载: