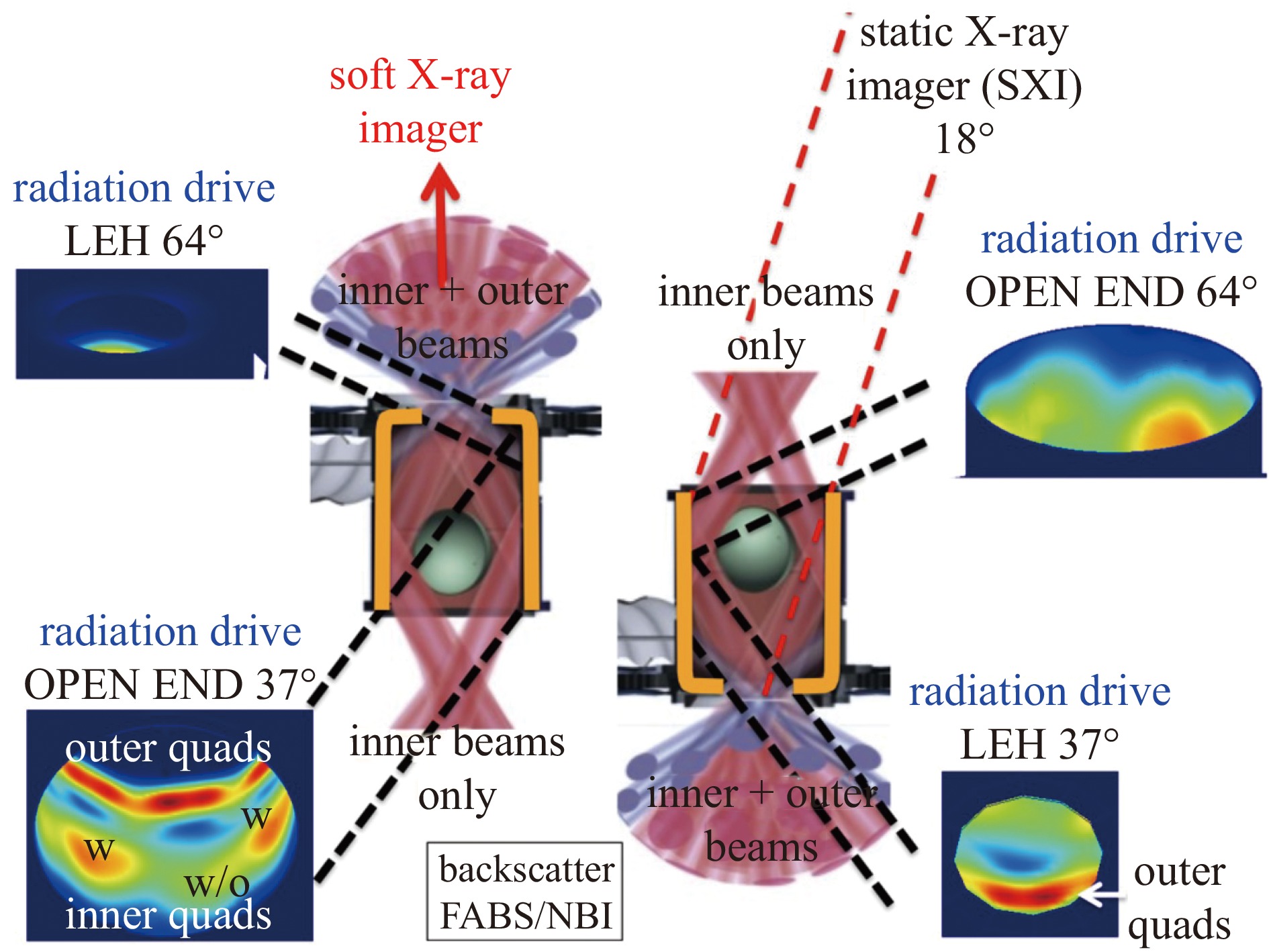
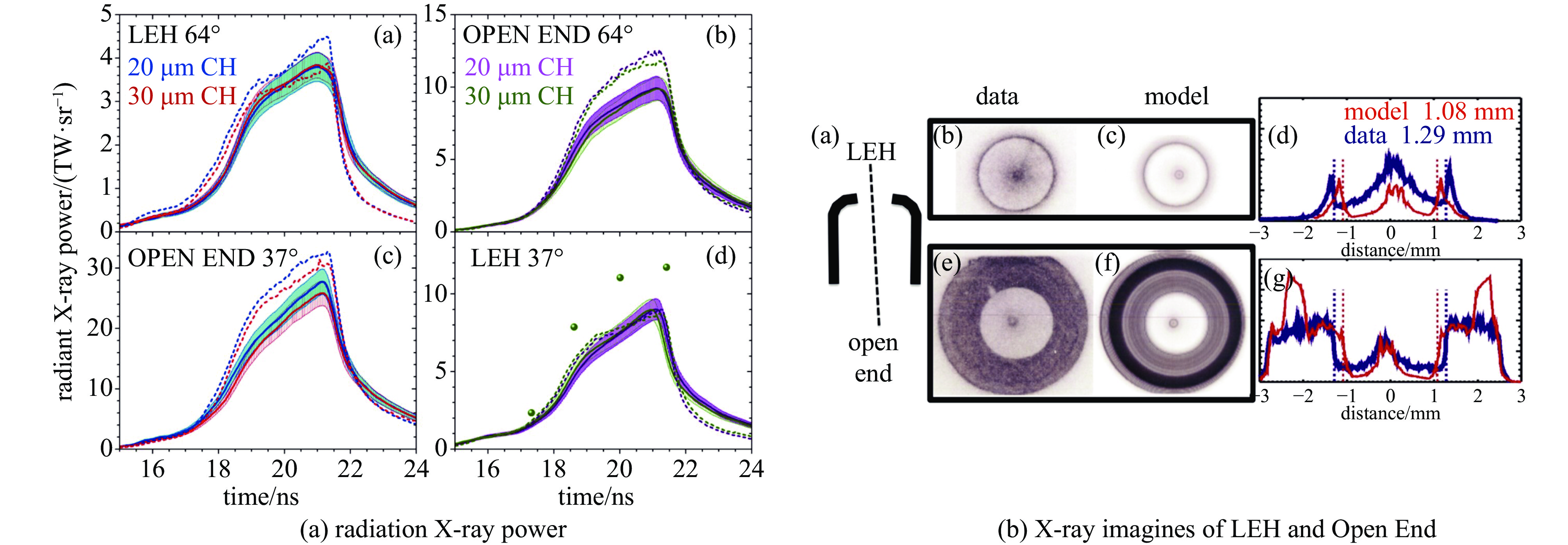
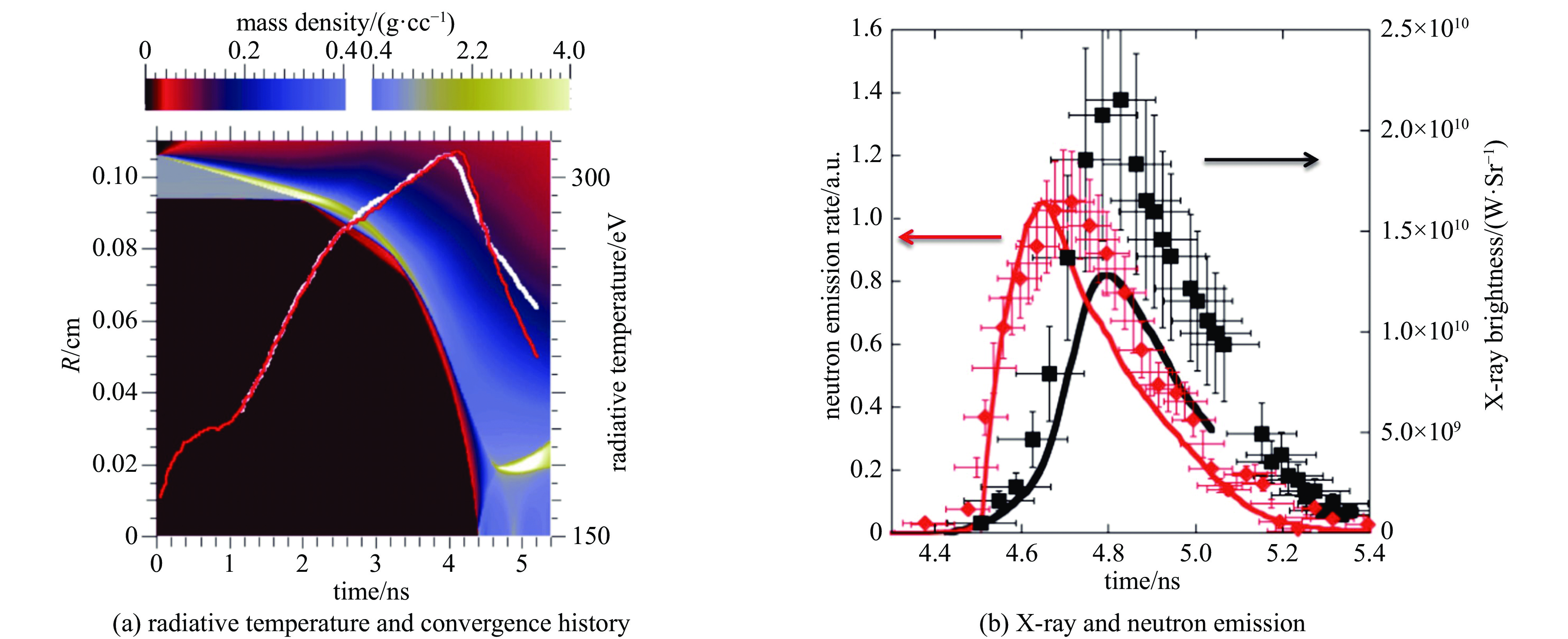
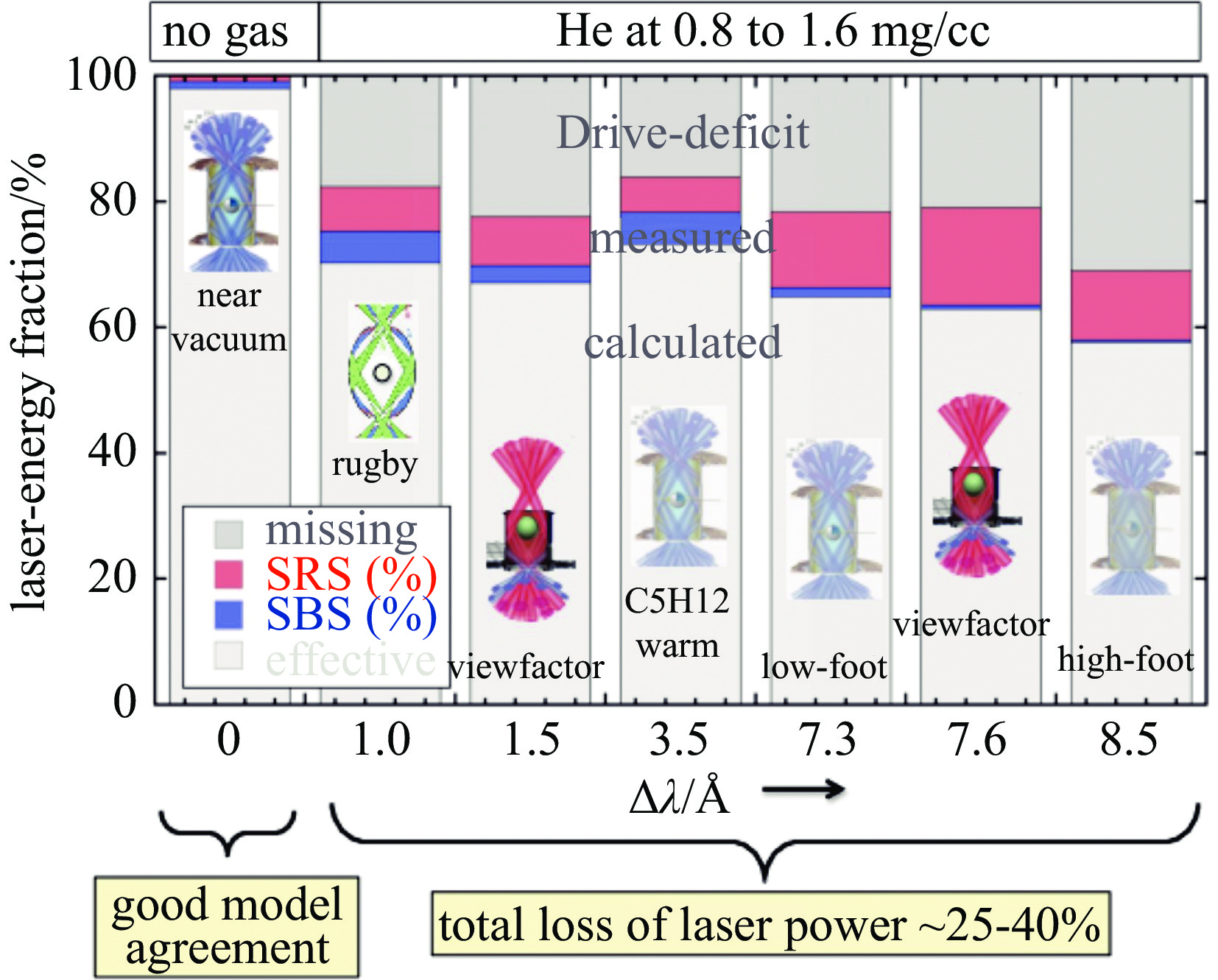
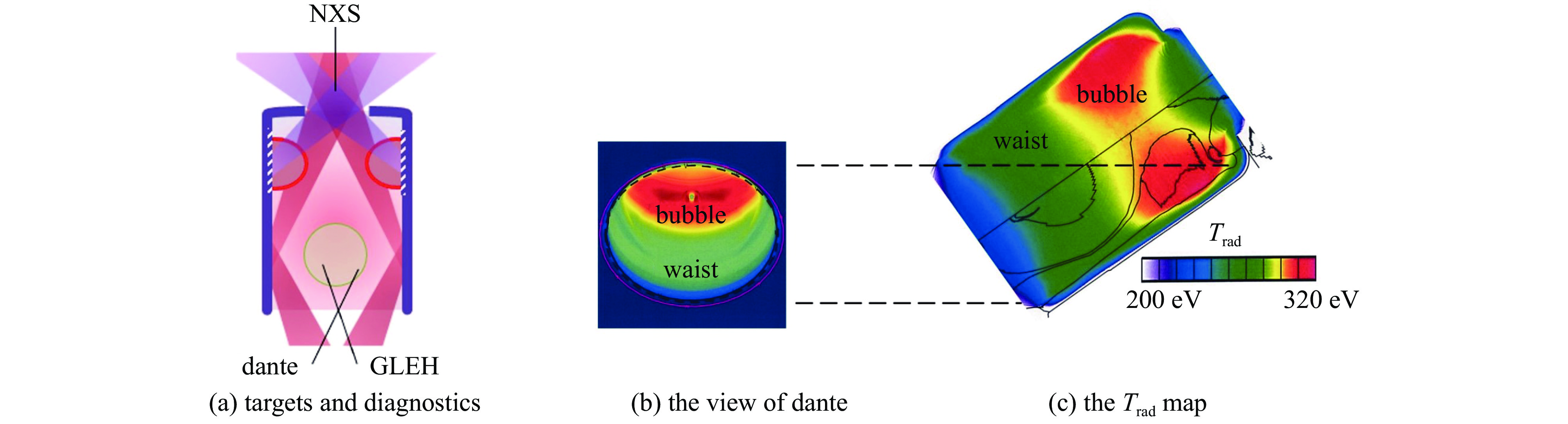
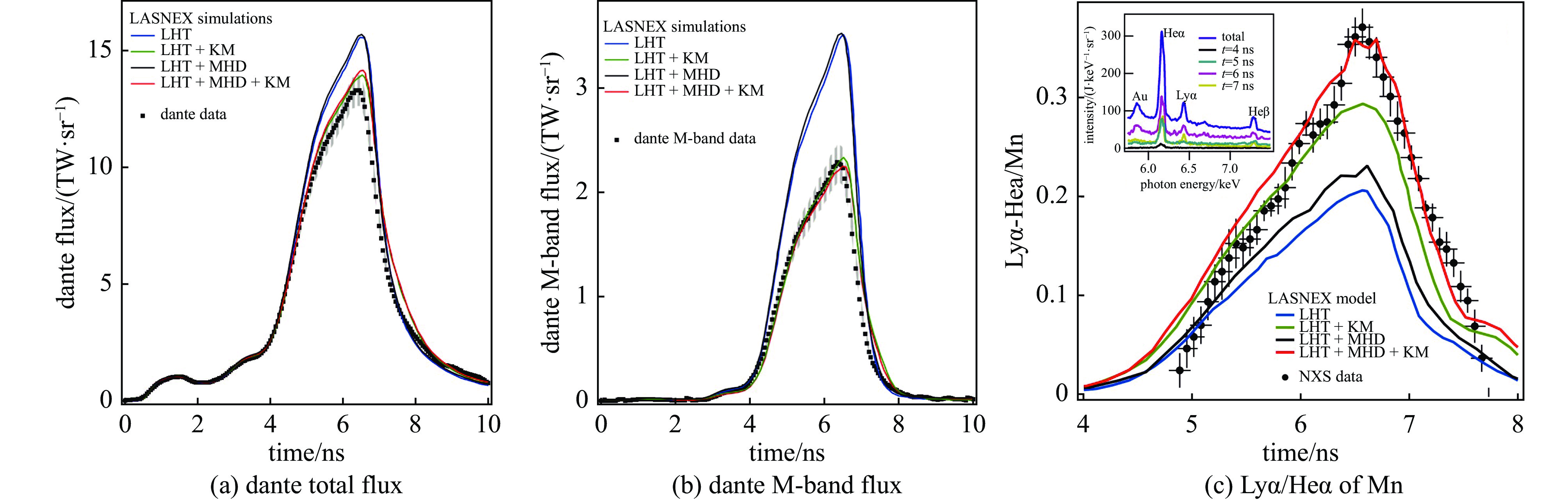
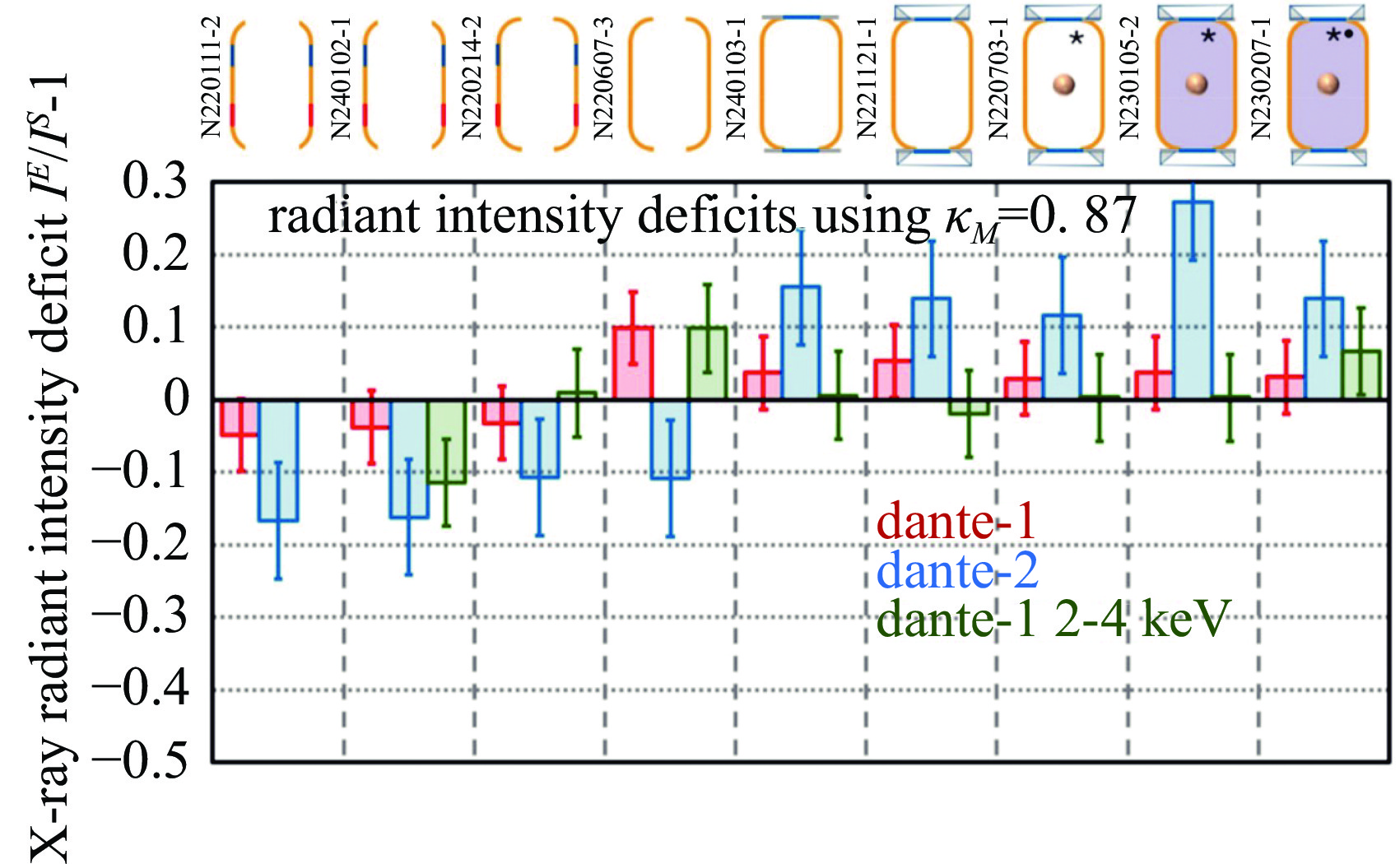
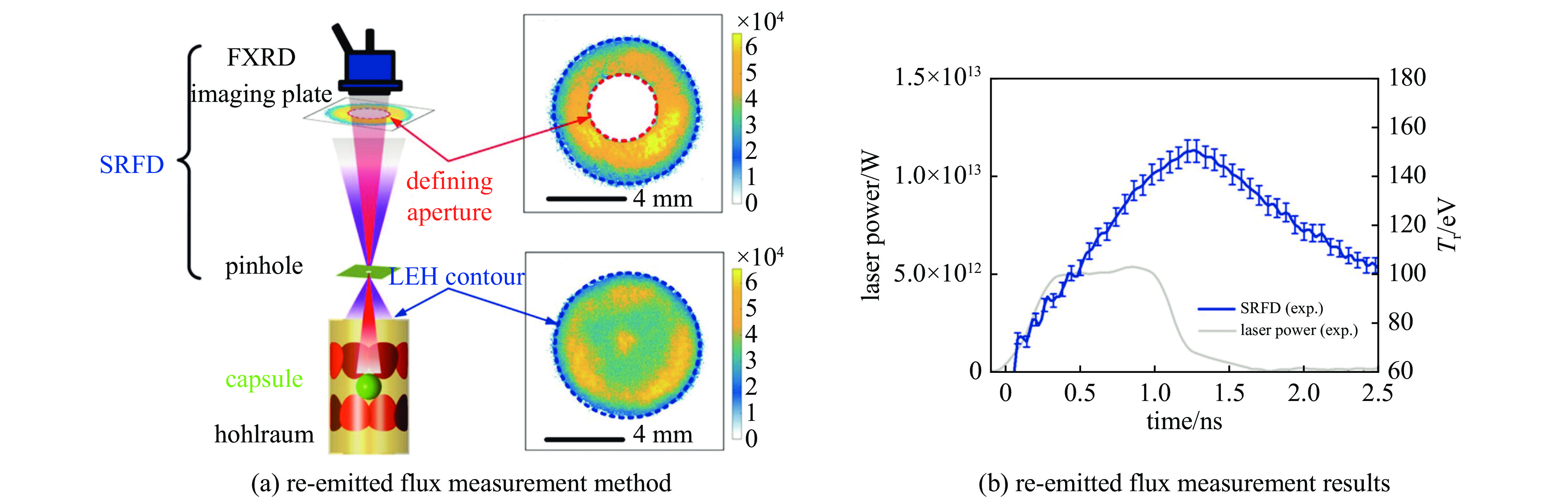
| [1] |
Amendt P, Glendinning S G, Hammel B A, et al. Direct measurement of X-ray drive from surrogate targets in Nova hohlraums[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 77(18): 3815-3818. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.3815
|
| [2] |
Glenzer S H, Suter L J, Turner R E, et al. Energetics of inertial confinement fusion hohlraum plasmas[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1998, 80(13): 2845-2848. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.80.2845
|
| [3] |
Kline J L, Glenzer S H, Olson R E, et al. Observation of high soft X-ray drive in large-scale hohlraums at the national ignition facility[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2011, 106: 085003. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.085003
|
| [4] |
Clark D S, Hinkel D E, Eder D C, et al. Detailed implosion modeling of deuterium-tritium layered experiments on the National Ignition Facility[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2013, 20: 056318. doi: 10.1063/1.4802194
|
| [5] |
Kritcher A L, Clark D, Haan S, et al. Comparison of plastic, high density carbon, and beryllium as indirect drive NIF ablators[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2018, 25: 056309. doi: 10.1063/1.5018000
|
| [6] |
Xie Xufei, Hou Lifei, Cai Hongbo, et al. Measurement of time-dependent drive flux on the capsule for indirectly driven inertial confinement fusion experiments[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2022, 128: 075001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.128.075001
|
| [7] |
Meezan N B, Atherton L J, Callahan D A, et al. National ignition campaign Hohlraum energetics[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2010, 17: 056304. doi: 10.1063/1.3354110
|
| [8] |
Glenzer S H, Macgowan B J, Meezan N B, et al. Demonstration of ignition radiation temperatures in indirect-drive inertial confinement fusion hohlraums[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2011, 106: 085004. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.085004
|
| [9] |
Farmer W A, Bruulsema C, Swadling G F, et al. Validation of heat transport modeling using directly driven beryllium spheres[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2020, 27: 082701. doi: 10.1063/5.0005776
|
| [10] |
Kline J L, Widmann K, Warrick A, et al. The first measurements of soft x-ray flux from ignition scale Hohlraums at the National Ignition Facility using DANTE (invited)[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2010, 81: 10E321. doi: 10.1063/1.3491032
|
| [11] |
Rosen M D, Scott H A, Hinkel D E, et al. The role of a detailed configuration accounting (DCA) atomic physics package in explaining the energy balance in ignition-scale hohlraums[J]. High Energy Density Physics, 2011, 7(3): 180-190. doi: 10.1016/j.hedp.2011.03.008
|
| [12] |
Kirkwood R K, Moody J D, Kline J, et al. A review of laser–plasma interaction physics of indirect-drive fusion[J]. Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 2013, 55: 103001. doi: 10.1088/0741-3335/55/10/103001
|
| [13] |
Town R P J, Rosen M D, Michel P A, et al. Analysis of the National Ignition Facility ignition hohlraum energetics experiments[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2011, 18: 056302. doi: 10.1063/1.3562552
|
| [14] |
Hicks D G, Meezan N B, Dewald E L, et al. Implosion dynamics measurements at the National Ignition Facility[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2012, 19: 122702. doi: 10.1063/1.4769268
|
| [15] |
Jones O S, Cerjan C J, Marinak M M, et al. A high-resolution integrated model of the National Ignition Campaign cryogenic layered experiments[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2012, 19: 056315. doi: 10.1063/1.4718595
|
| [16] |
Moody J D, Callahan D A, Hinkel D E, et al. Progress in hohlraum physics for the National Ignition Facility[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2014, 21: 056317. doi: 10.1063/1.4876966
|
| [17] |
MacLaren S A, Schneider M B, Widmann K, et al. Novel characterization of capsule X-ray drive at the national ignition facility[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2014, 112: 105003. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.105003
|
| [18] |
Meezan N B, MacKinnon A J, Hicks D G, et al. X-ray driven implosions at ignition relevant velocities on the National Ignition Facility[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2013, 20: 056311. doi: 10.1063/1.4803915
|
| [19] |
Le Pape S, Divol L, Berzak Hopkins L, et al. Observation of a reflected shock in an indirectly driven spherical implosion at the National Ignition Facility[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2014, 112: 225002. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.225002
|
| [20] |
Robey H F, Boehly T R, Celliers P M, et al. Shock timing experiments on the National Ignition Facility: initial results and comparison with simulation[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2012, 19: 042706. doi: 10.1063/1.3694122
|
| [21] |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL). Laser Indirect Drive input to NNSA 2020 Report[R]. 2020.
|
| [22] |
Kritcher A L, Young C V, Robey H F, et al. Design of inertial fusion implosions reaching the burning plasma regime[J]. Nature Physics, 2022, 18(3): 251-258. doi: 10.1038/s41567-021-01485-9
|
| [23] |
Kritcher A L, Zylstra A B, Callahan D A, et al. Achieving record hot spot energies with large HDC implosions on NIF in Hybrid-E[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2021, 28: 072706. doi: 10.1063/5.0047841
|
| [24] |
Jones O S, Suter L J, Scott H A, et al. Progress towards a more predictive model for hohlraum radiation drive and symmetry[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2017, 24: 056312. doi: 10.1063/1.4982693
|
| [25] |
Hansen S B, Bauche J, Bauche-Arnoult C, et al. Hybrid atomic models for spectroscopic plasma diagnostics[J]. High Energy Density Physics, 2007, 3(1/2): 109-114. doi: 10.1016/j.hedp.2007.02.032
|
| [26] |
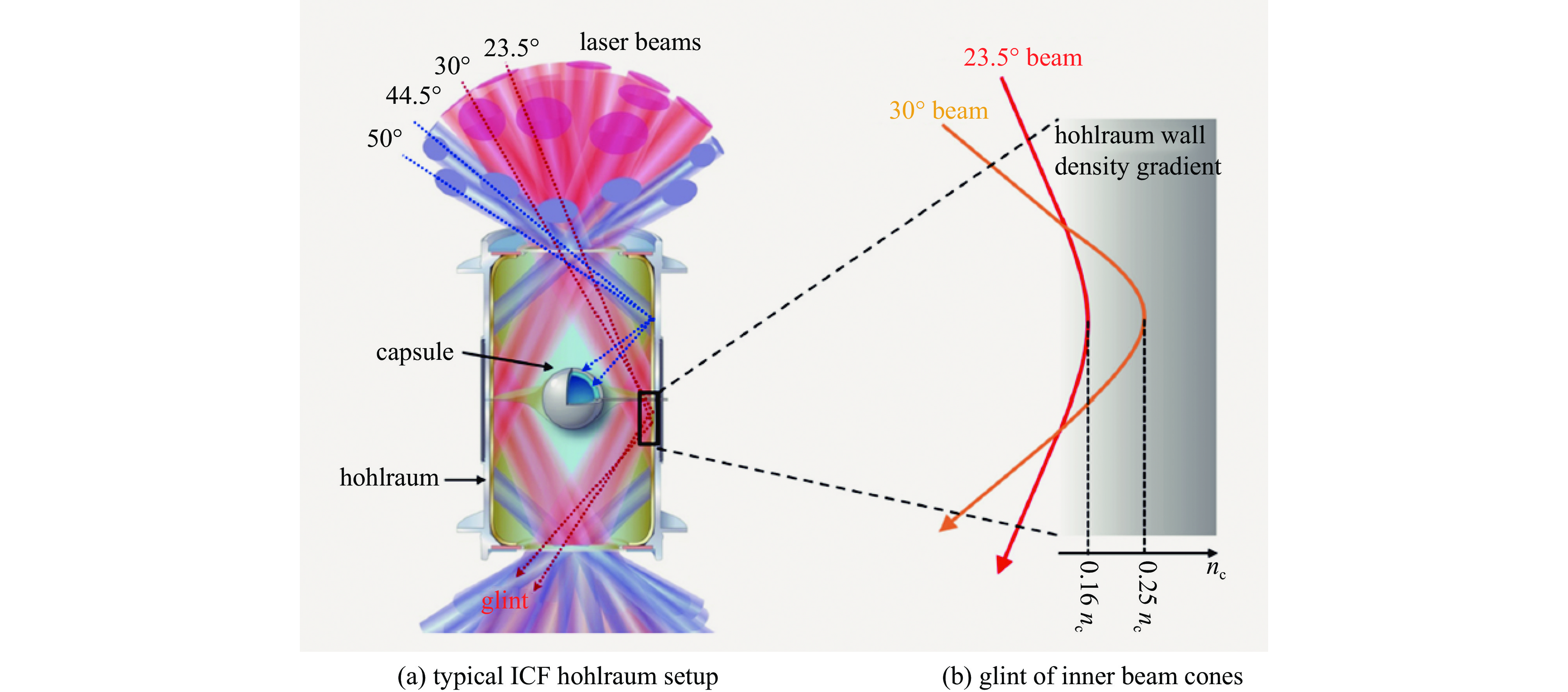
Lemos N, Farmer W A, Izumi N, et al. Specular reflections (“glint”) of the inner beams in a gas-filled cylindrical hohlraum[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2022, 29: 092704. doi: 10.1063/5.0099937
|
| [27] |
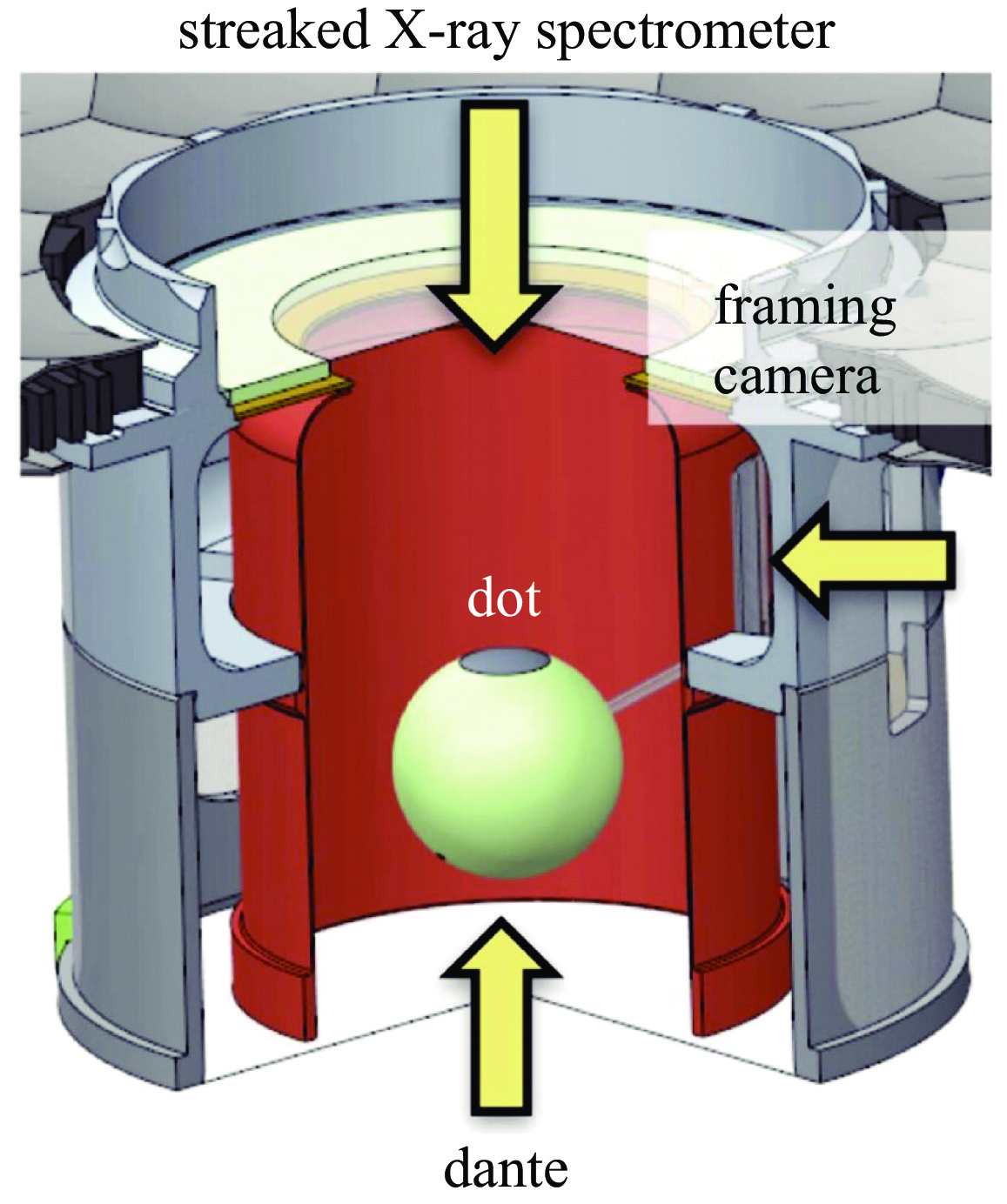
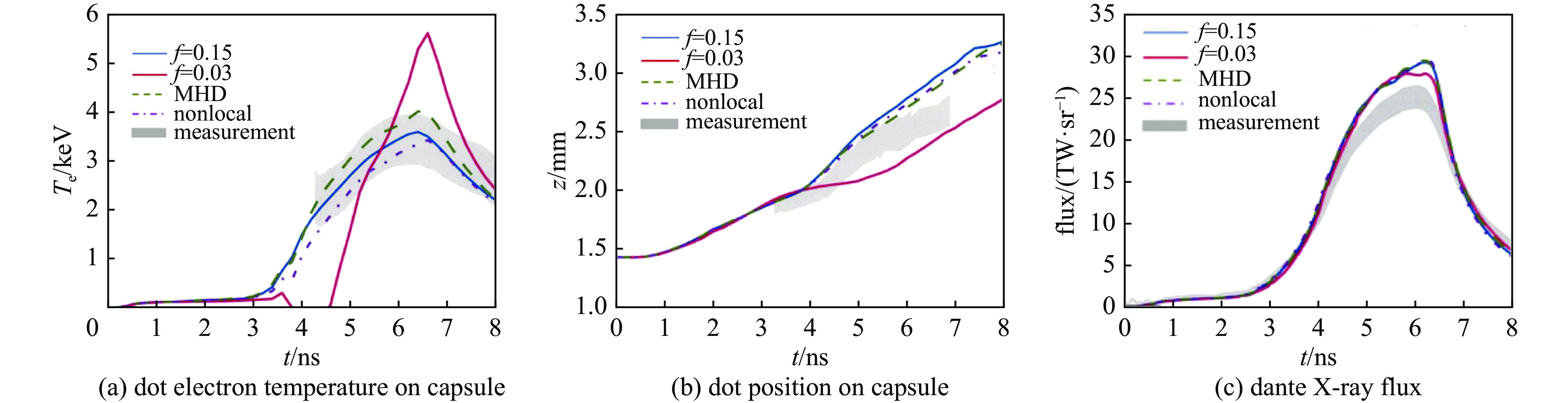
Farmer W A, Jones O S, Barrios M A, et al. Heat transport modeling of the dot spectroscopy platform on NIF[J]. Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 2018, 60: 044009. doi: 10.1088/1361-6587/aaaefd
|
| [28] |
Farmer W A, Koning J M, Strozzi D J, et al. Simulation of self-generated magnetic fields in an inertial fusion hohlraum environment[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2017, 24: 052703. doi: 10.1063/1.4983140
|
| [29] |
Schurtz G P, Nicolaï P D, Busquet M. A nonlocal electron conduction model for multidimensional radiation hydrodynamics codes[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2000, 7(10): 4238-4249. doi: 10.1063/1.1289512
|
| [30] |
Amendt P, Ross J S, Milovich J L, et al. Low-adiabat rugby hohlraum experiments on the National Ignition Facility: comparison with high-flux modeling and the potential for gas-wall interpenetration[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2014, 21: 112703. doi: 10.1063/1.4901195
|
| [31] |
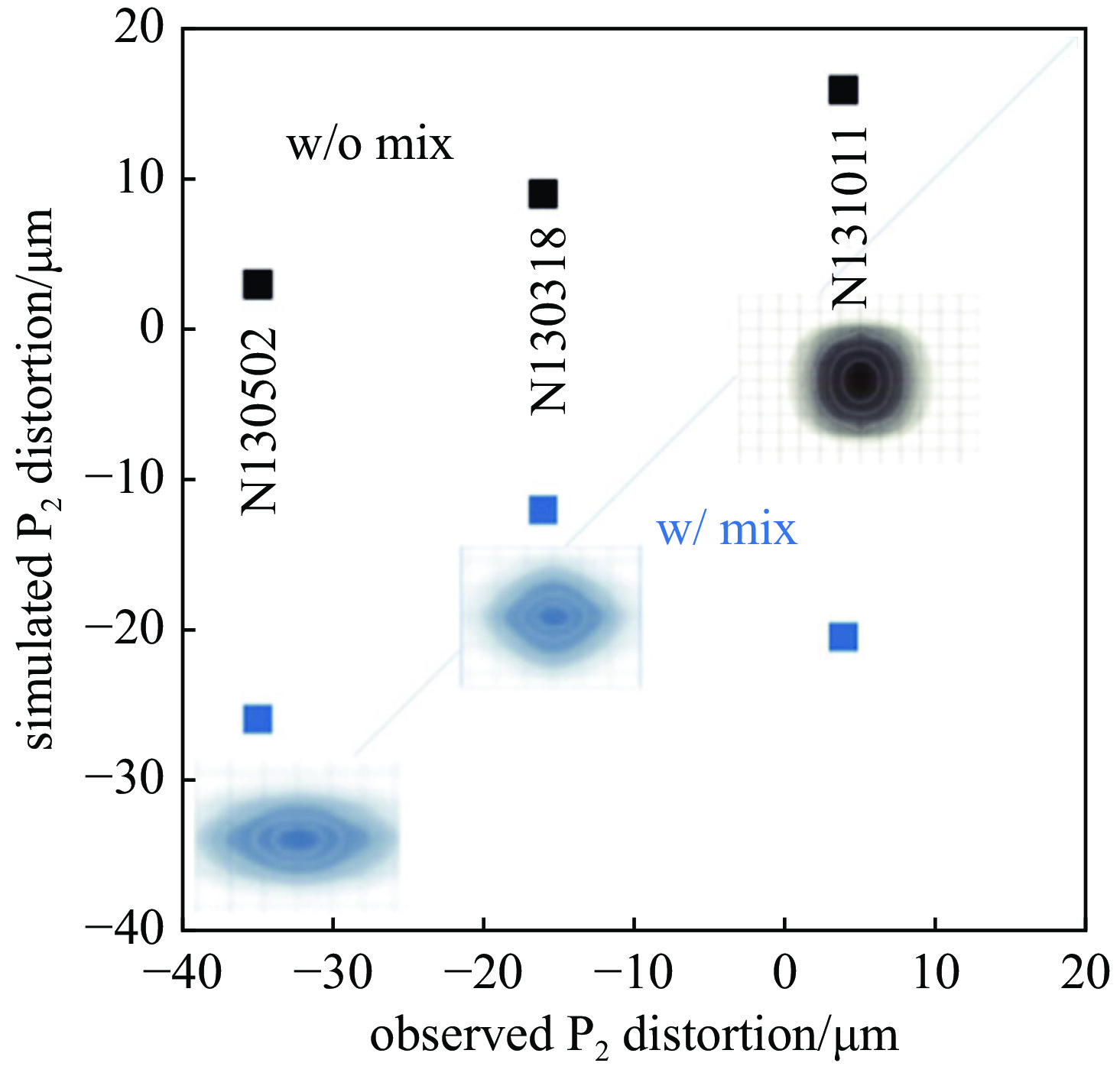
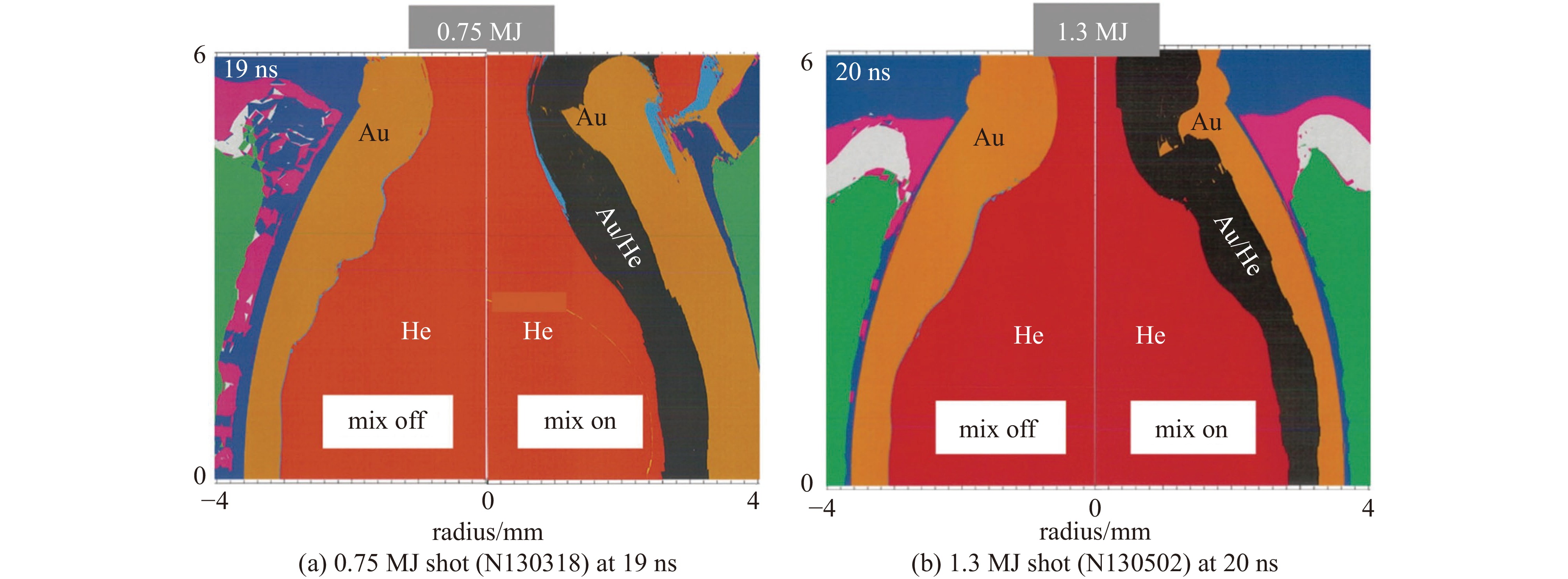
Amendt P. Entropy generation from hydrodynamic mixing in inertial confinement fusion indirect-drive targets[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2021, 28: 072701. doi: 10.1063/5.0049114
|
| [32] |
Vandenboomgaerde M, Bonnefille M, Gauthier P. The Kelvin-Helmholtz instability in National Ignition Facility hohlraums as a source of gold-gas mixing[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2016, 23: 052704. doi: 10.1063/1.4948468
|
| [33] |
Chen Hui, Woods D T, Farmer W A, et al. Understanding the deficiency in inertial confinement fusion hohlraum x-ray flux predictions using experiments at the National Ignition Facility[J]. Physical Review E, 2024, 110: L013201. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.110.L013201
|
| [34] |
Swadling G F, Farmer W A, Chen H, et al. Resolving discrepancies in bang-time predictions for indirect-drive ICF experiments on the NIF: insights from the Build-A-Hohlraum campaign[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2025, 32: 052707. doi: 10.1063/5.0259922
|
| [35] |
Ren Kuan, Liu Shenye, Du Huabing, et al. New two-dimensional space-resolving flux detection technique for measurement of hohlraum inner radiation in Shenguang-III prototype[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2015, 86: 103112. doi: 10.1063/1.4934250
|
| [36] |
Ren Kuan, Liu Shenye, Xie Xufei, et al. First exploration of radiation temperatures of the laser spot, re-emitting wall and entire hohlraum drive source[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 5050. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41424-6
|
| [37] |
Xie Xufei, Wu Changshu, Chen Jinwen, et al. Characterization of radiation drive by measuring the localized re-emitted flux from the capsule in inertial confinement fusion experiments[J]. Nuclear Fusion, 2022, 62: 126008. doi: 10.1088/1741-4326/ac8fa2
|
| [38] |
Kuang Longyu, Li Hang, Jing Longfei, et al. A novel three-axis cylindrical hohlraum designed for inertial confinement fusion ignition[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 34636. doi: 10.1038/srep34636
|
| [39] |
Li Xin, Dong Yunsong, Kang Dongguo, et al. First indirect drive experiment using a six-cylinder-port hohlraum[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2022, 128: 195001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.128.195001
|
| [40] |
Farmer W A, Tabak M, Hammer J H, et al. High-temperature hohlraum designs with multiple laser-entrance holes[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2019, 26: 032701. doi: 10.1063/1.5087140
|




 下载:
下载: