Experimental study of electromagnetic pulse generation induced by laser interaction with solid targets on the Shenguang II upgrade facility
-
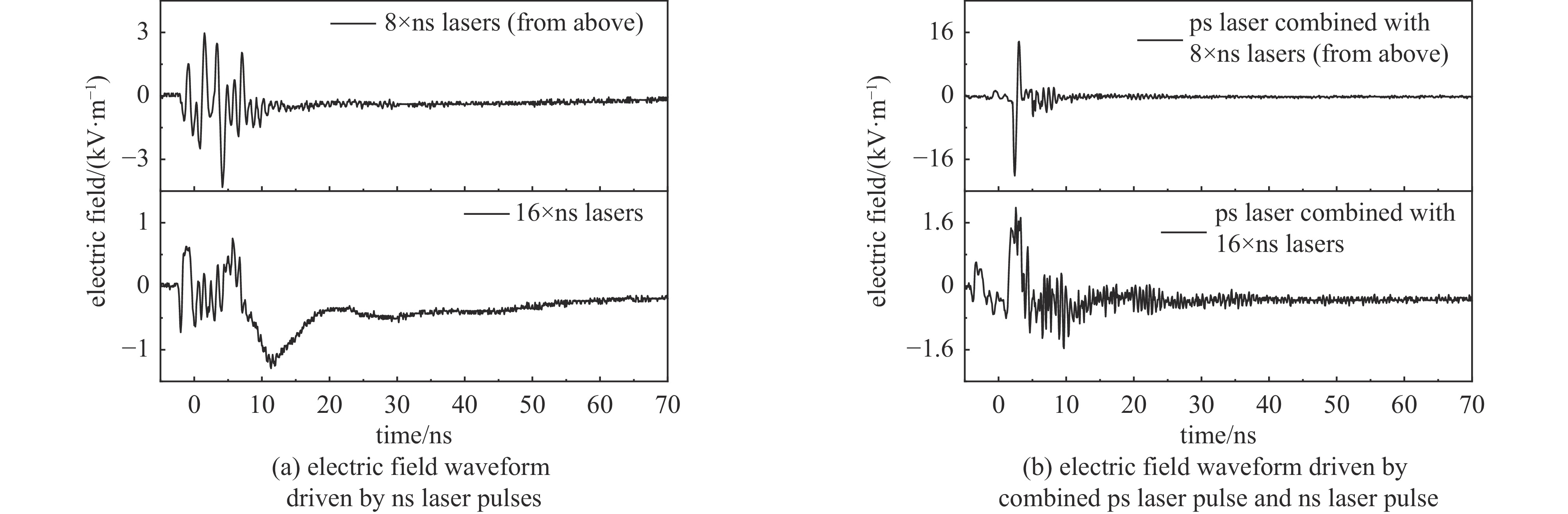
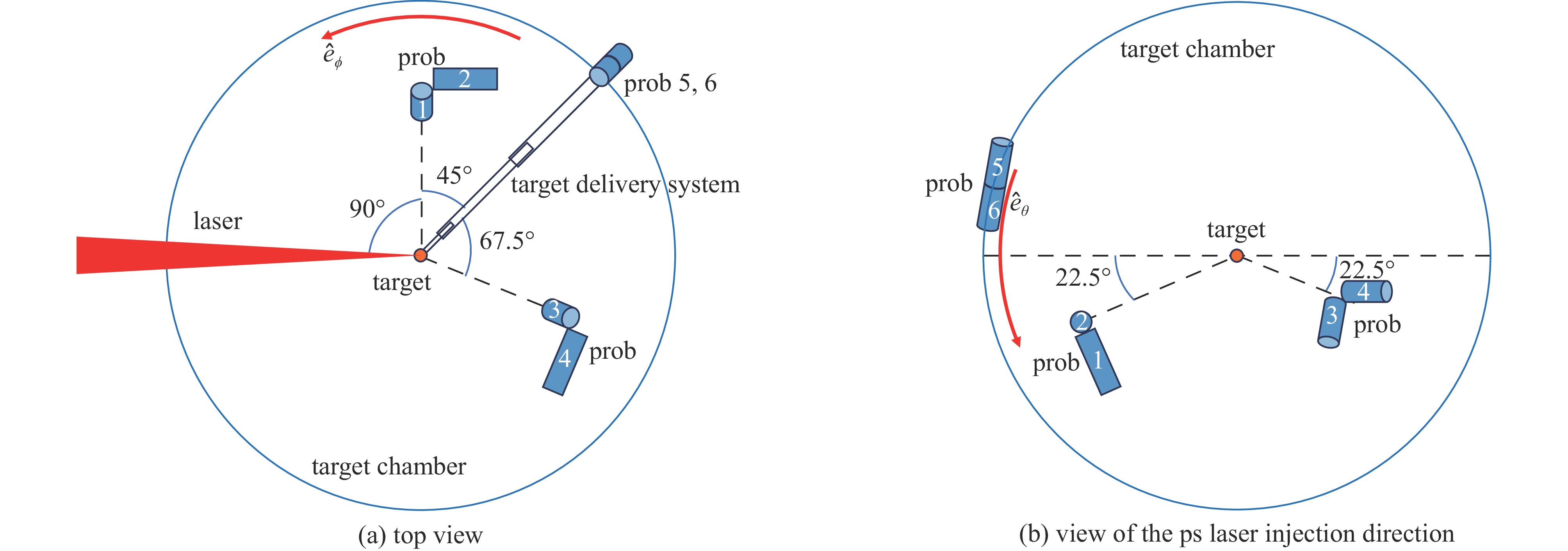
摘要: 研究了神光II升级装置上,高功率激光与固体靶相互作用产生的电磁脉冲特性及机制。实验中采用皮秒与纳秒脉冲激光,分析不同打靶方式下电磁脉冲的波形与频谱特征。结果表明,皮秒脉冲激光作用下的电磁脉冲主要由流经送靶装置的中和电流产生,其峰值电场强度随激光能量近似线性增加。纳秒脉冲激光作用下,电磁脉冲强度较低,振荡电场持续时间较短,并伴随较长的准直流分量。仅使用上方8路纳秒激光时,电磁脉冲强度显著高于16路同时作用,表明激光打靶构型对电磁脉冲产生具有调制作用。皮秒激光与纳秒激光组合实验中,皮秒激光产生的电磁脉冲峰值明显减弱,推测与纳秒激光形成的大尺度等离子体有关。研究结果为高功率激光—固体靶相互作用中的电磁干扰机理分析及实验装置防护提供了重要实验依据。Abstract:
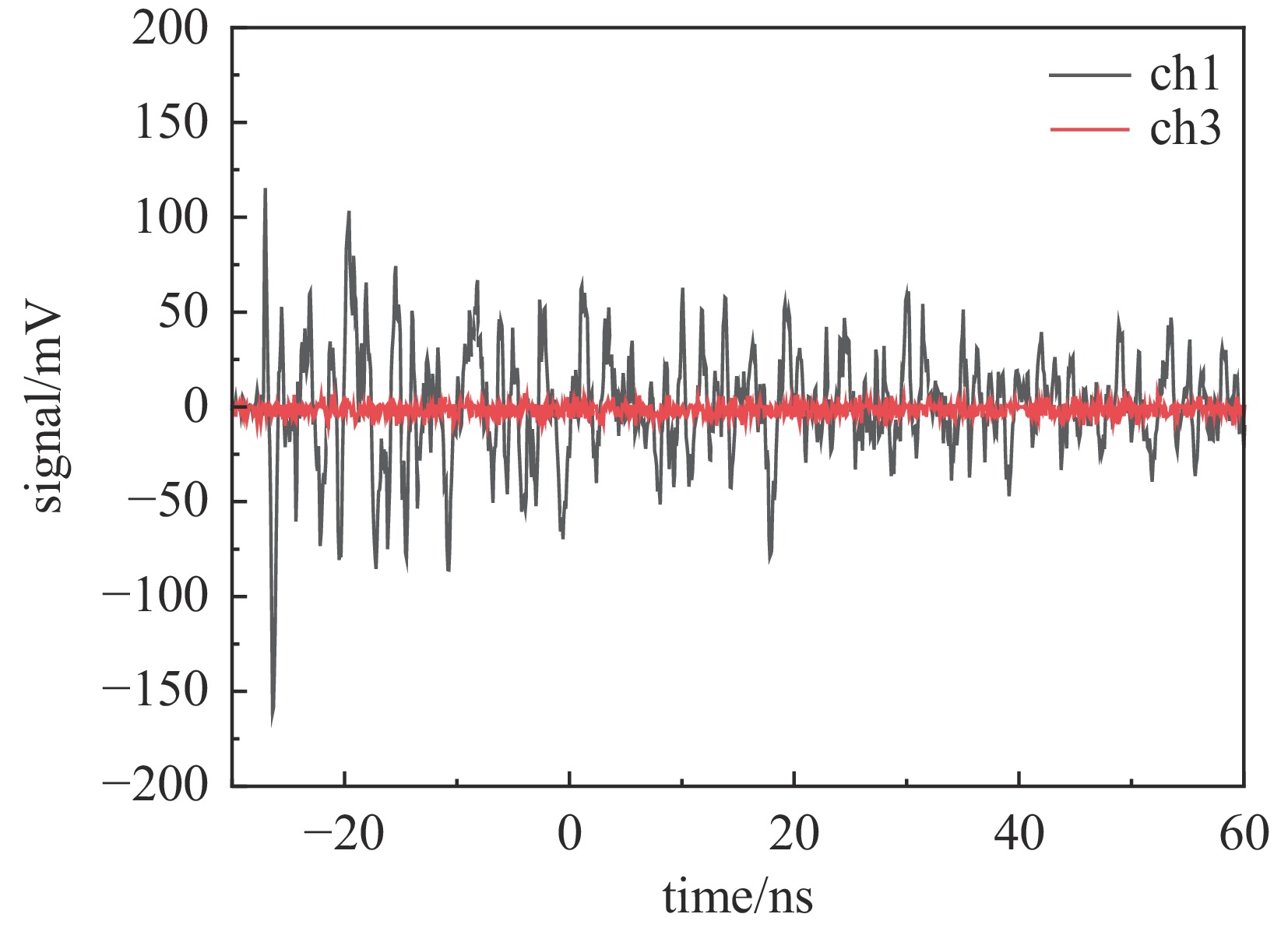
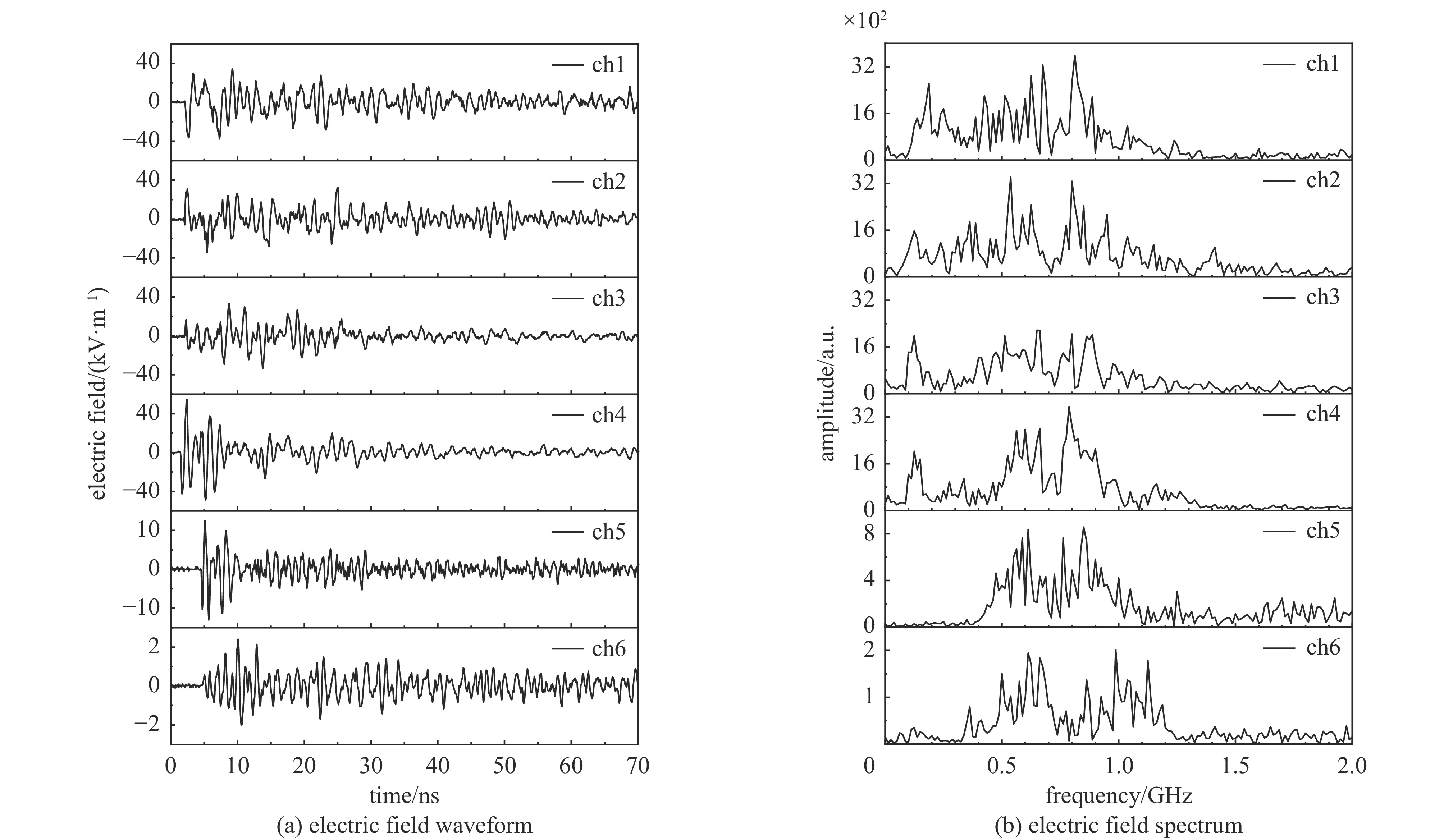
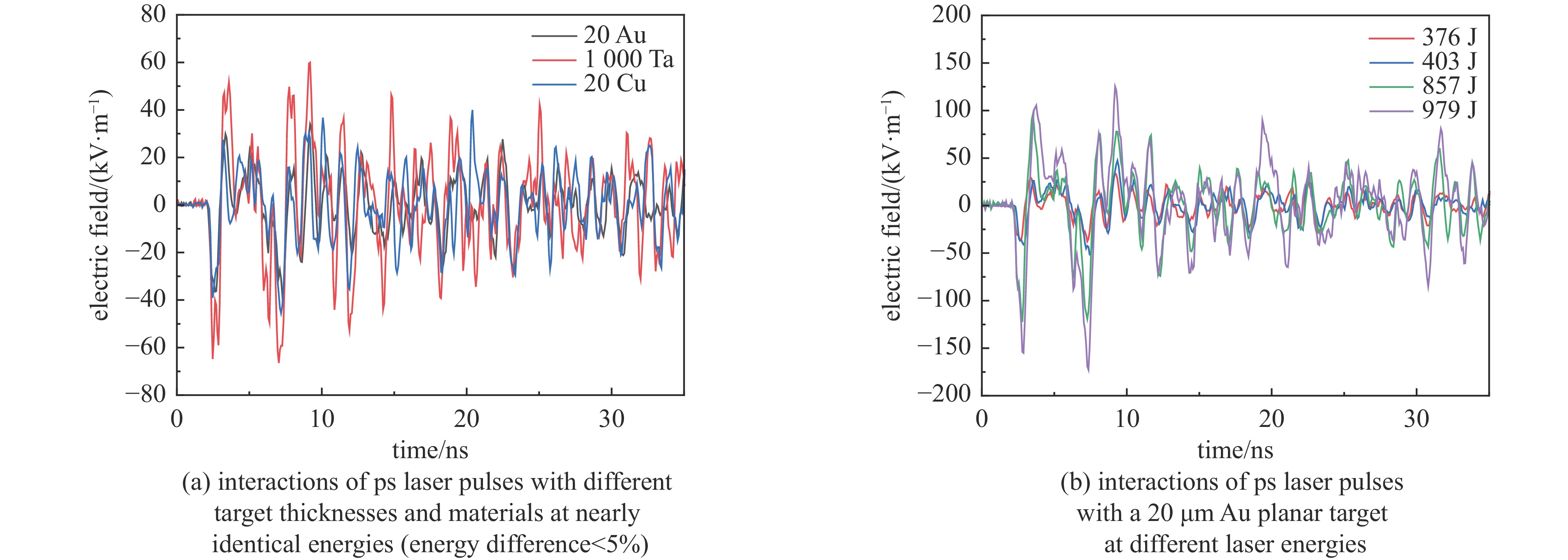
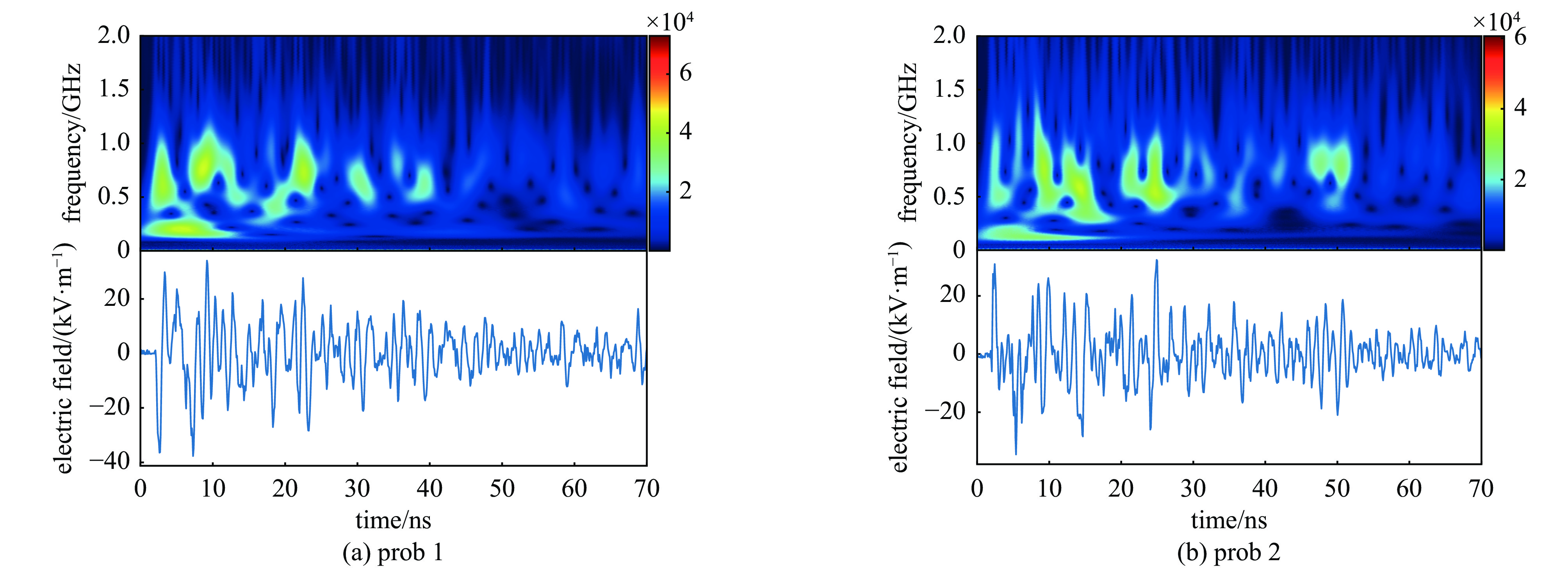
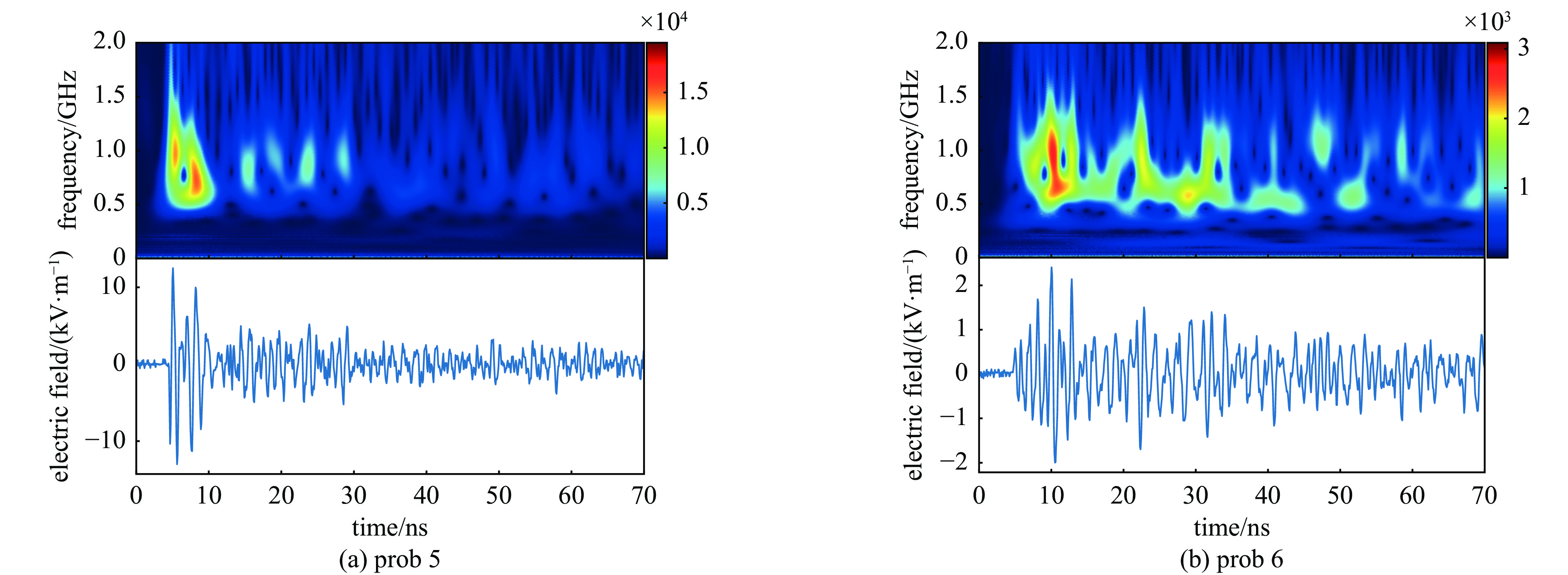
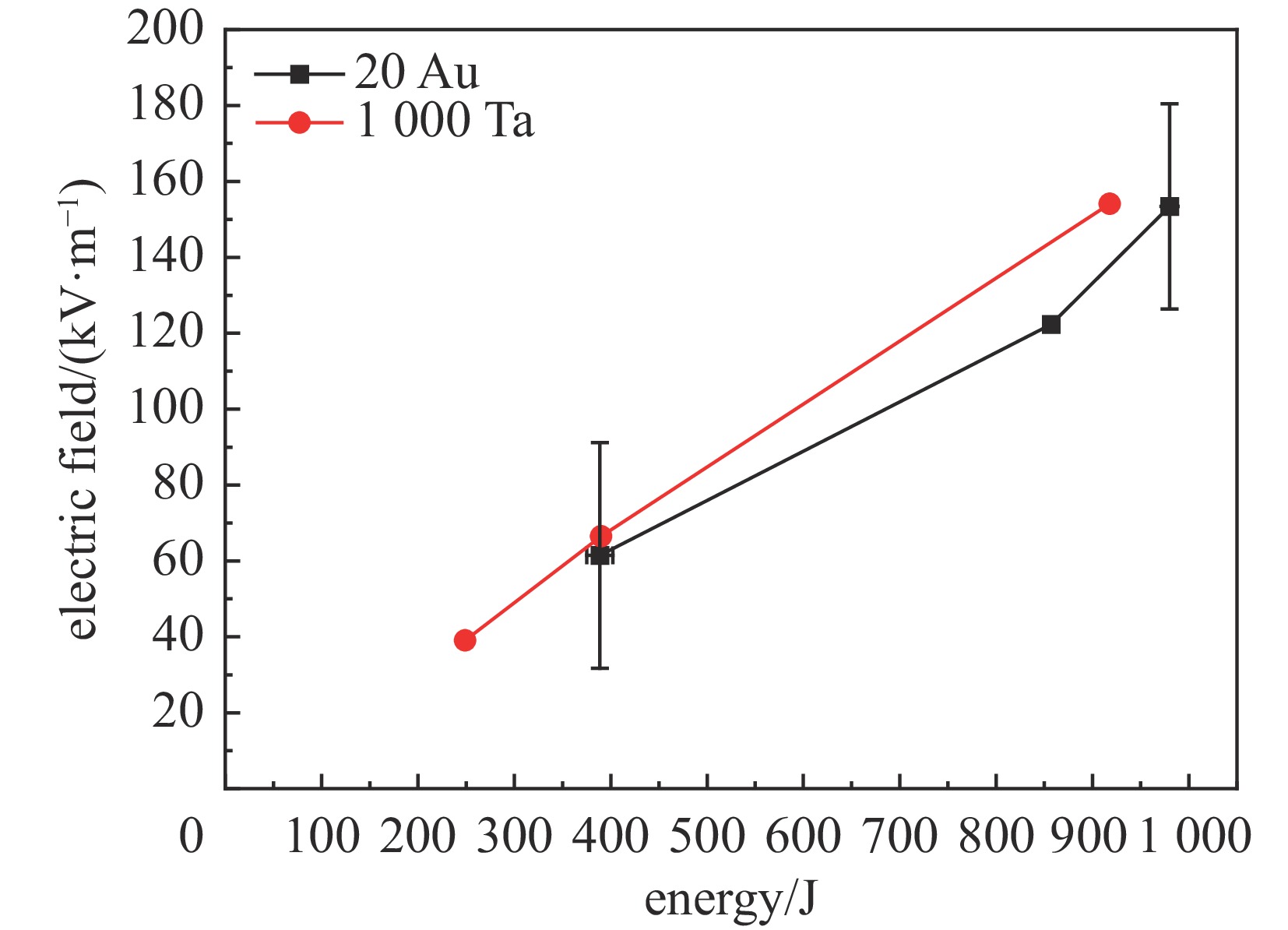
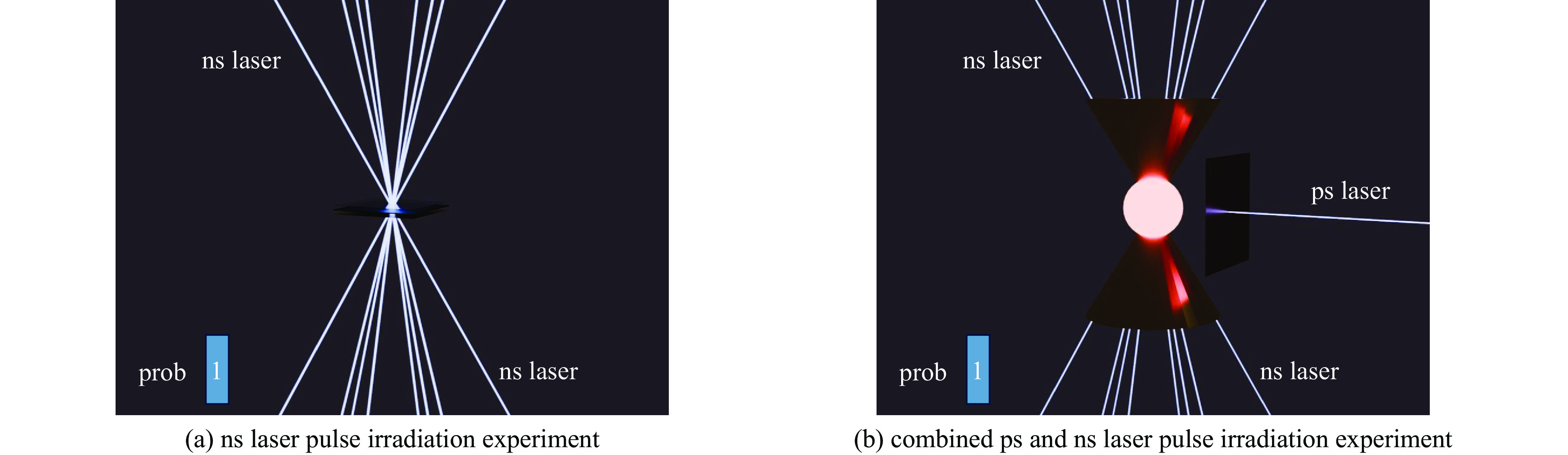
Background Electromagnetic pulses generated in high-power laser–solid interactions can cause serious electromagnetic interference and threaten diagnostic systems, making their mechanism study essential.Purpose This work aims to investigate the characteristics and generation mechanisms of electromagnetic pulses induced by picosecond and nanosecond laser irradiation on solid targets.Methods Experiments were carried out on the Shenguang II Upgrade laser facility. The temporal waveforms and frequency spectra of the emitted electromagnetic fields were measured under various pulse durations, laser energies, and irradiation geometries.Results For picosecond laser irradiation, the electromagnetic pulses mainly originated from the neutralization current flowing through the target mount, and the peak electric field increased nearly linearly with laser energy. In the nanosecond experiments, the electromagnetic pulse intensity was lower, with the electric field oscillation decaying rapidly and a quasi-DC component observed. Using only the upper eight nanosecond beams produced stronger pulses than sixteen-beam irradiation, showing a modulation. In the combined picosecond and nanosecond laser experiment, the electromagnetic pulse peak generated by the picosecond laser was significantly reduced, which is attributed to the large-scale plasma formed by the nanosecond laser.Conclusions These findings clarify the generation behavior of electromagnetic pulses and provide references for mitigating electromagnetic interference in high-power laser experiments. -
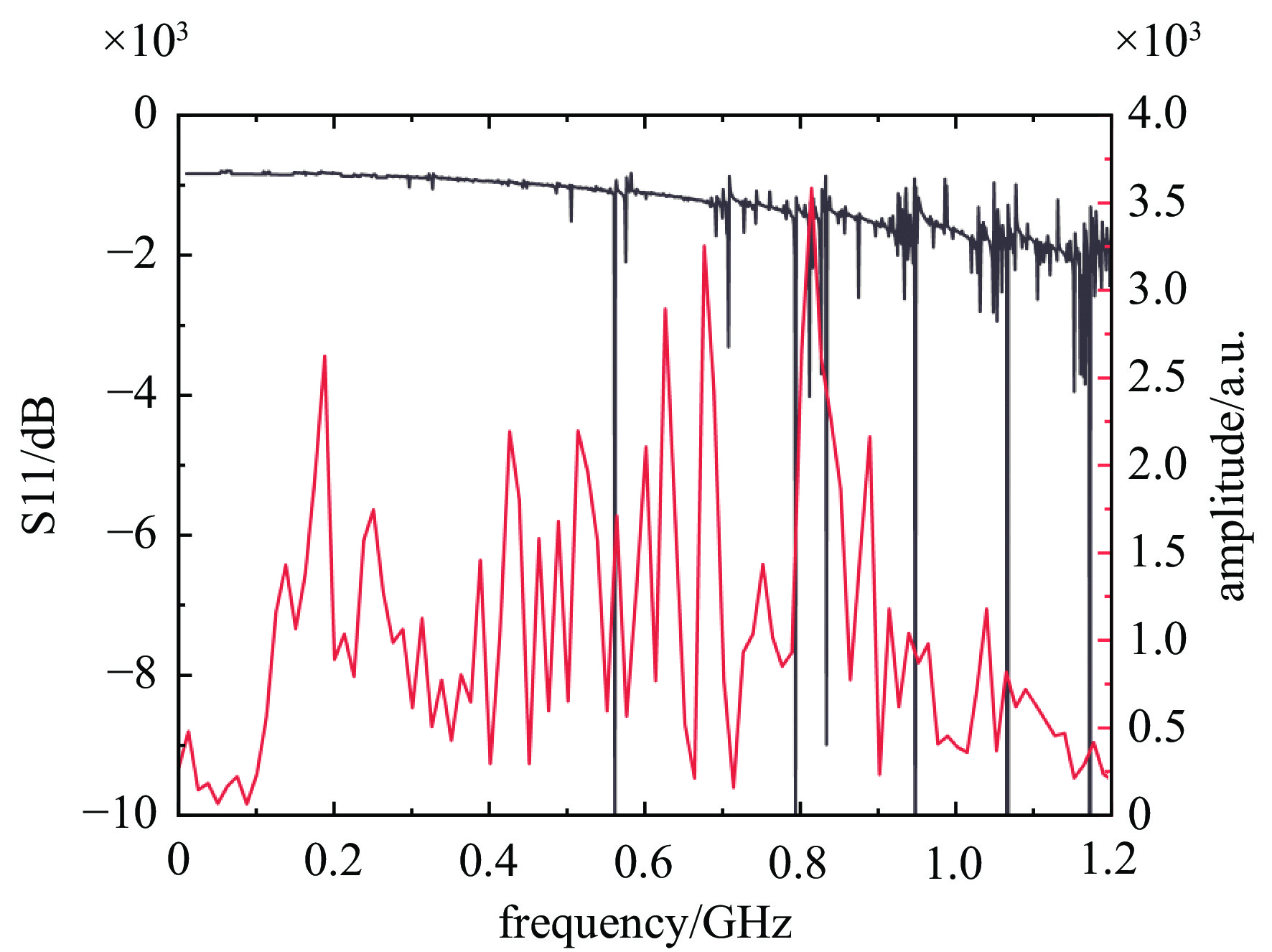
表 1 1.2 m球型靶室的本征频率
Table 1. Eigenfrequencies of the 1.2 m spherical target chamber
$ {p} $ $ {{f}}_{\text{TM}} $/GHz n=1 n=2 n=3 n=4 n=5 n=6 1 0.1092 0.1540 0.1979 0.2412 0.2841 0.3267 2 0.2434 0.2961 0.3470 0.3966 0.4452 0.4930 3 0.3707 0.4263 0.4800 0.5324 0.5837 0.6342 4 0.4968 0.5539 0.6093 0.6634 0.7166 0.7688 -
[1] Carillon A, Chen H Z, Dhez P, et al. Saturated and near-diffraction-limited operation of an XUV laser at 23.6 nm[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1992, 68(19): 2917-2920. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.68.2917 [2] Cipiccia S, Wiggins S M, Shanks R P, et al. A tuneable ultra-compact high-power, ultra-short pulsed, bright gamma-ray source based on bremsstrahlung radiation from laser-plasma accelerated electrons[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2012, 111: 063302. doi: 10.1063/1.3693537 [3] Esarey E, Shadwick B A, Catravas P, et al. Synchrotron radiation from electron beams in plasma-focusing channels[J]. Physical Review E, 2002, 65: 056505. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.65.056505 [4] Ledingham K W D, Spencer I, McCanny T, et al. Photonuclear physics when a multiterawatt laser pulse interacts with solid targets[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2000, 84(5): 899-902. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.84.899 [5] Lee K S H. EMP interaction: principles, techniques, and reference data[M]. Washington: Hemisphere Publishing Corporation, 1986. [6] Kojima S, Hata M, Iwata N, et al. Electromagnetic field growth triggering super-ponderomotive electron acceleration during multi-picosecond laser-plasma interaction[J]. Communications Physics, 2019, 2: 99. doi: 10.1038/s42005-019-0197-6 [7] Consoli F, Tikhonchuk V T, Bardon M, et al. Laser produced electromagnetic pulses: generation, detection and mitigation[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2020, 8: e22. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2020.13 [8] Consoli F, Andreoli P L, Cipriani M, et al. Sources and space–time distribution of the electromagnetic pulses in experiments on inertial confinement fusion and laser–plasma acceleration[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2021, 379: 20200022. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2020.0022 [9] Krása J, Krupka M, Agarwal S, et al. Advanced diagnostics of electrons escaping from laser-produced plasma[J]. Plasma, 2024, 7(2): 366-385. doi: 10.3390/plasma7020021 [10] Cikhardt J, Bradford P W, Ehret M, et al. Comprehensive characterization of electromagnetic pulses driven by a sub-nanosecond kilojoule laser[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2025, 13: e57. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2025.10035 [11] Lee J, Nam S. Effective area of a receiving antenna in a lossy medium[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2009, 57(6): 1843-1845. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2009.2019988 [12] Dubois J L, Lubrano-Lavaderci F, Raffestin D, et al. Target charging in short-pulse-laser–plasma experiments[J]. Physical Review E, 2014, 89: 013102. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.89.013102 [13] Poyé A, Dubois J L, Lubrano-Lavaderci F, et al. Dynamic model of target charging by short laser pulse interactions[J]. Physical Review E, 2015, 92: 043107. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.92.043107 [14] Poyé A, Hulin S, Bailly-Grandvaux M, et al. Physics of giant electromagnetic pulse generation in short-pulse laser experiments[J]. Physical Review E, 2015, 91: 043106. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.91.043106 [15] Bradford P, Woolsey N C, Scott G G, et al. EMP control and characterization on high-power laser systems[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2018, 6: e21. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2018.21 [16] Felber F S. Dipole radio-frequency power from laser plasmas with no dipole moment[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2005, 86: 231501. doi: 10.1063/1.1947911 [17] Pompili R, Anania M P, Bisesto F, et al. Ultrafast evolution of electric fields from high-intensity laser-matter interactions[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 3243. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21711-4 [18] Poyé A, Hulin S, Ribolzi J, et al. Thin target charging in short laser pulse interactions[J]. Physical Review E, 2018, 98: 033201. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.98.033201 [19] Mead M J, Neely D, Gauoin J, et al. Electromagnetic pulse generation within a petawatt laser target chamber[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2004, 75(10): 4225-4227. doi: 10.1063/1.1787606 [20] Robinson T S, Consoli F, Giltrap S, et al. Low-noise time-resolved optical sensing of electromagnetic pulses from petawatt laser-matter interactions[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 983. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01063-1 [21] Raven A, Rumsby P T, Stamper J A, et al. Dependence of spontaneous magnetic fields in laser produced plasmas on target size and structure[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1979, 35(7): 526-528. doi: 10.1063/1.91196 [22] Wilks S C, Kruer W L, Tabak M, et al. Absorption of ultra-intense laser pulses[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1992, 69(9): 1383-1386. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.69.1383 [23] Nakamura T, Kato S, Tamimoto M, et al. Stochastic acceleration by intense laser fields[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2002, 9(5): 1801-1805. doi: 10.1063/1.1468231 [24] Tanimoto M, Kato S, Miura E, et al. Direct electron acceleration by stochastic laser fields in the presence of self-generated magnetic fields[J]. Physical Review E, 2003, 68: 026401. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.68.026401 [25] Johzaki T, Nagatomo H, Sunahara A, et al. Pre-plasma effects on core heating and enhancing heating efficiency by extended double cone for FIREX[J]. Nuclear Fusion, 2011, 51: 073022. doi: 10.1088/0029-5515/51/7/073022 -




 下载:
下载: