Laser self-mixing interference micro displacement reconstruction based on convolutional neural network
-
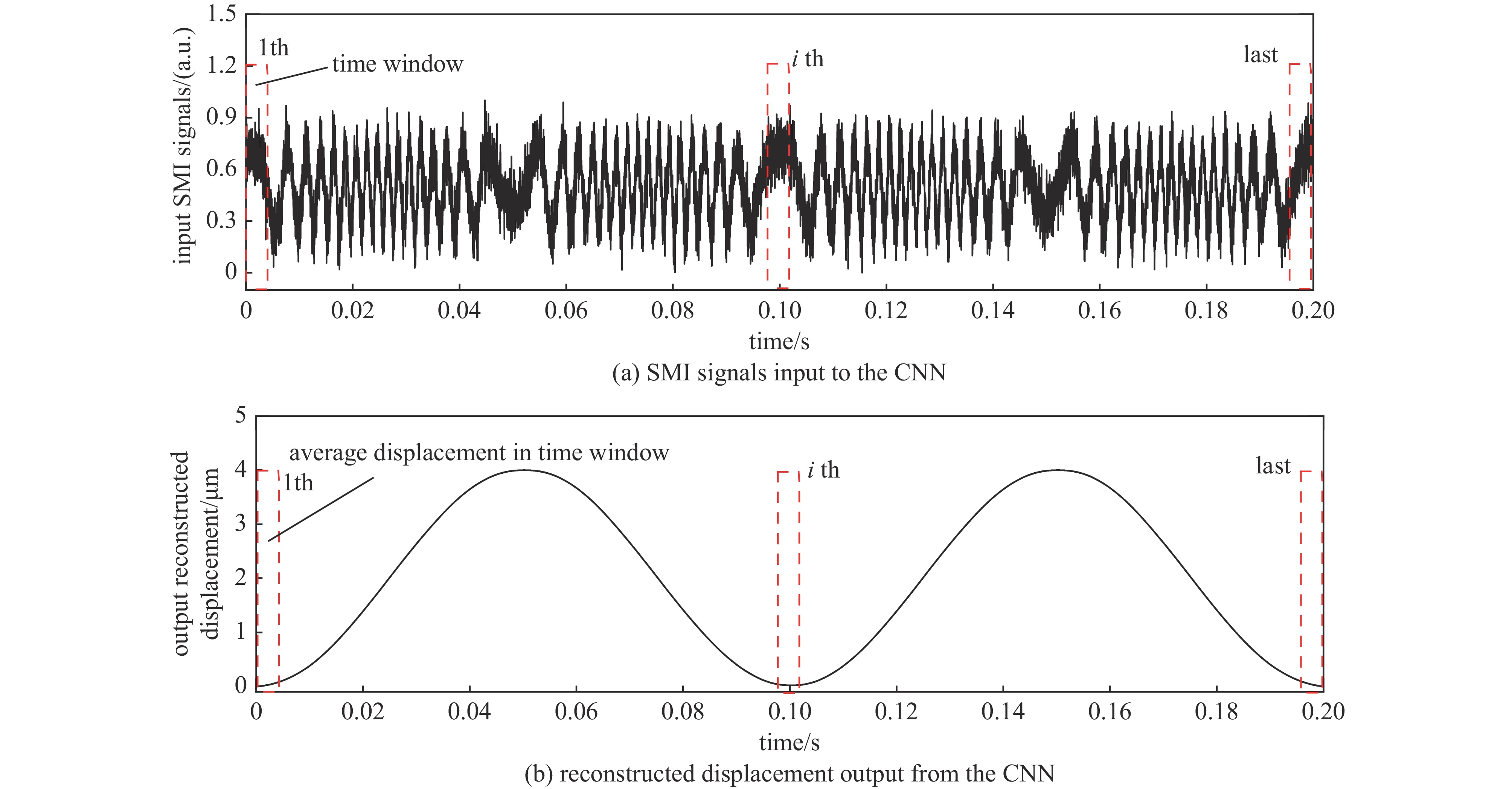
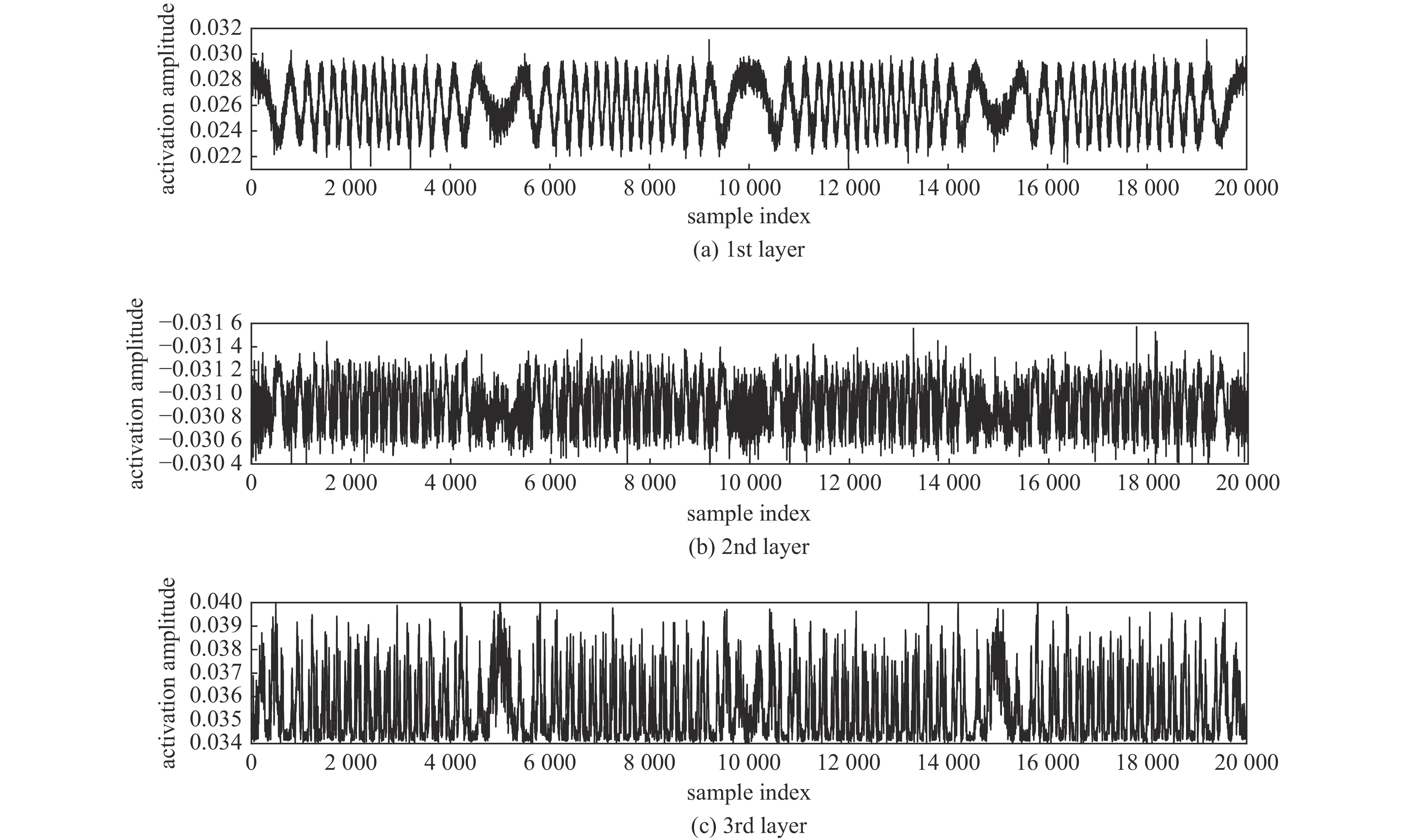
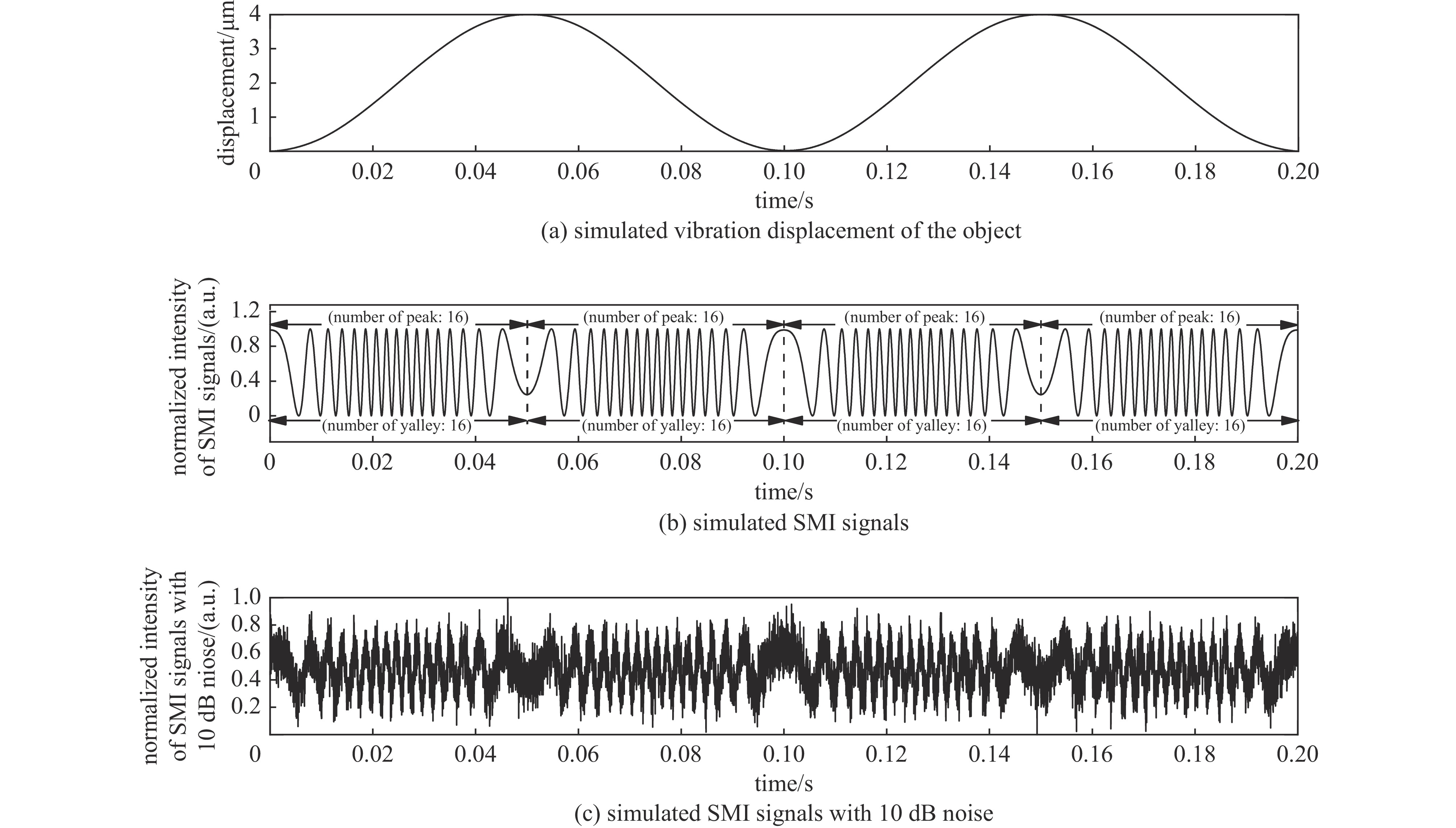
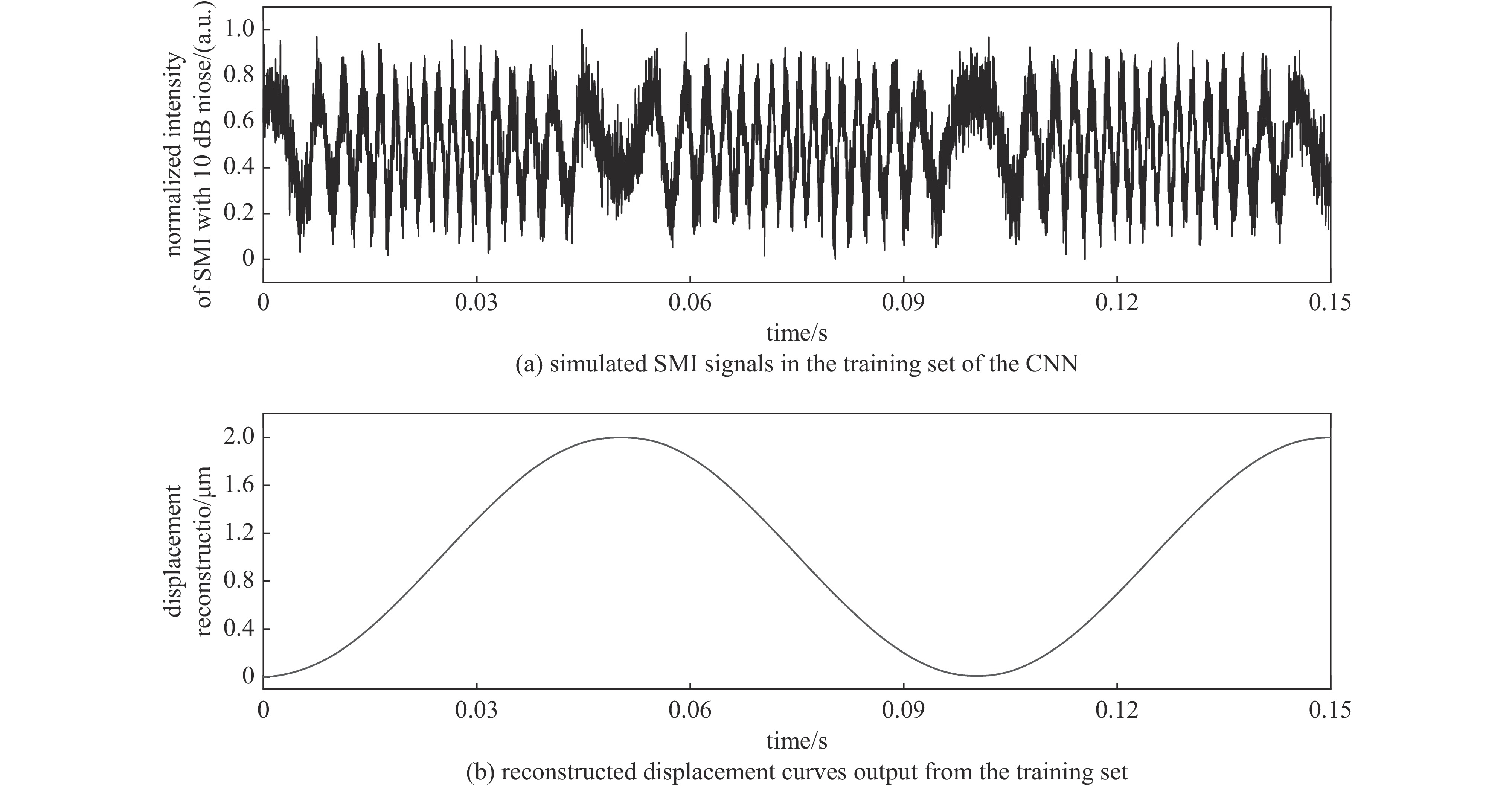
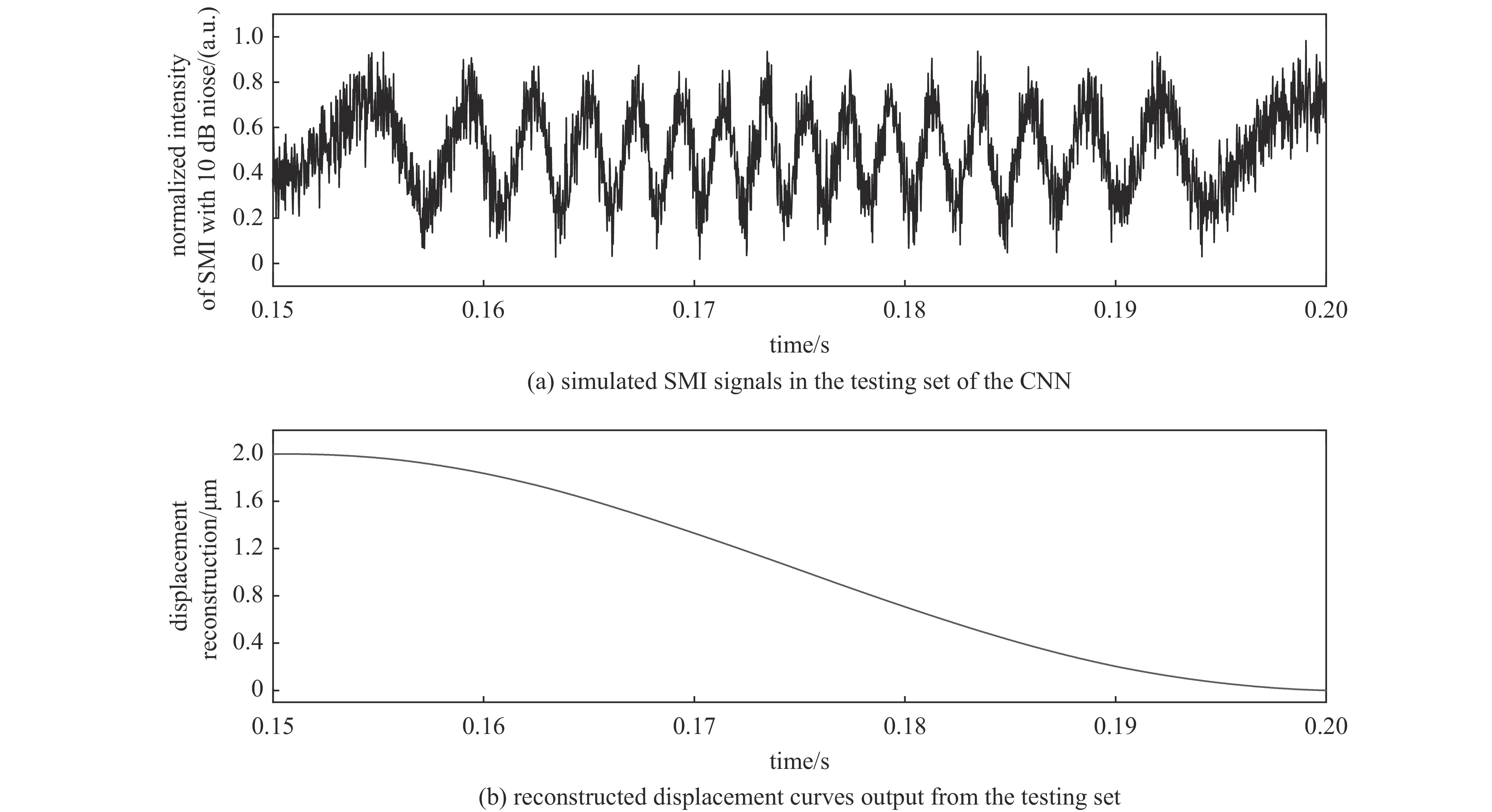
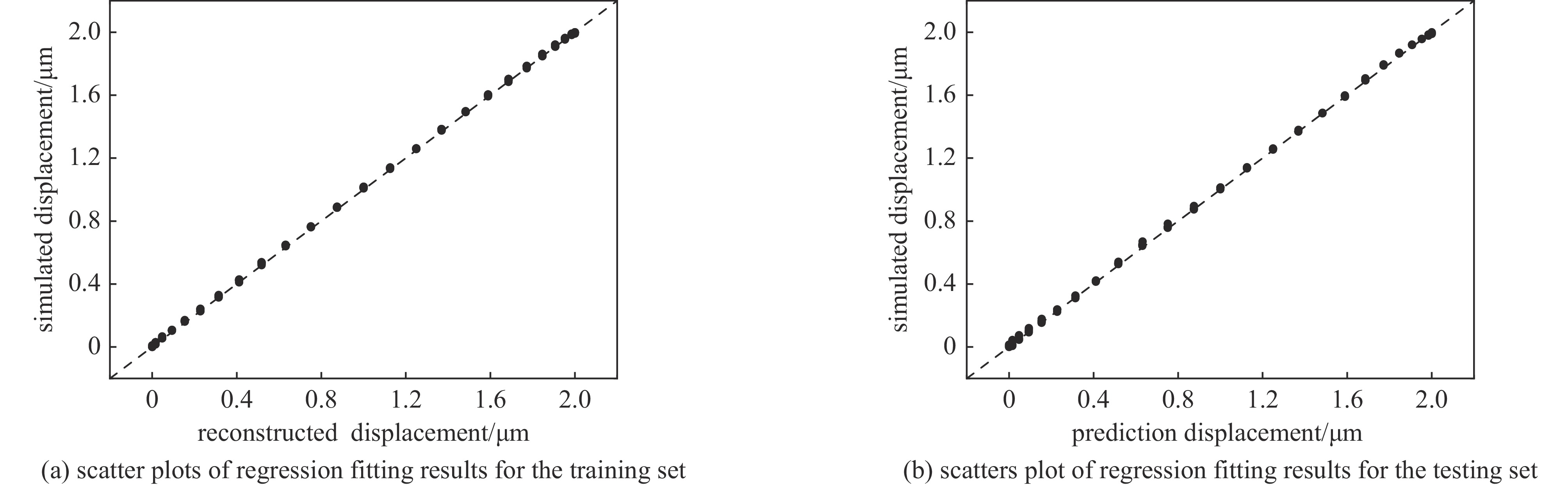
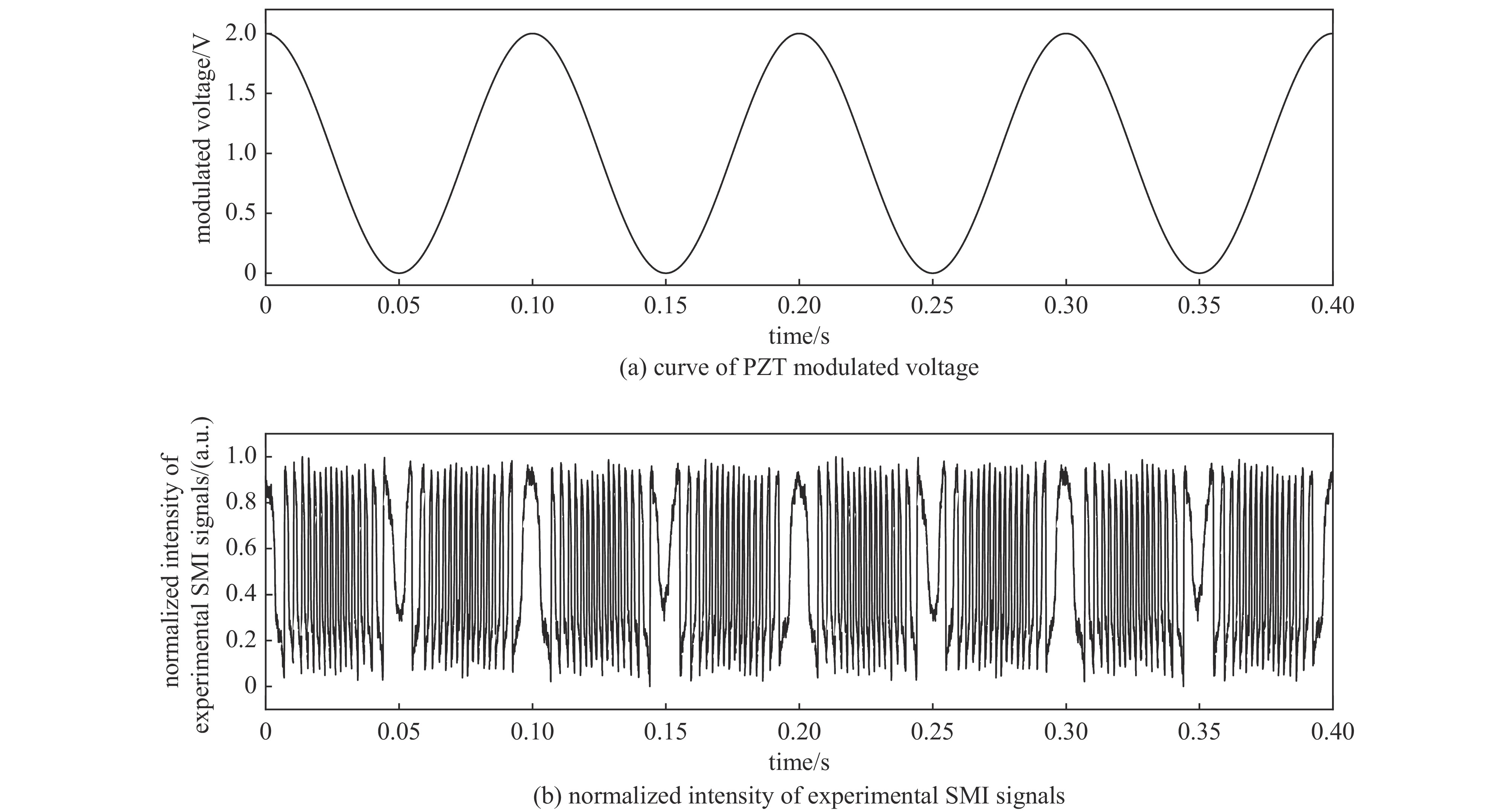
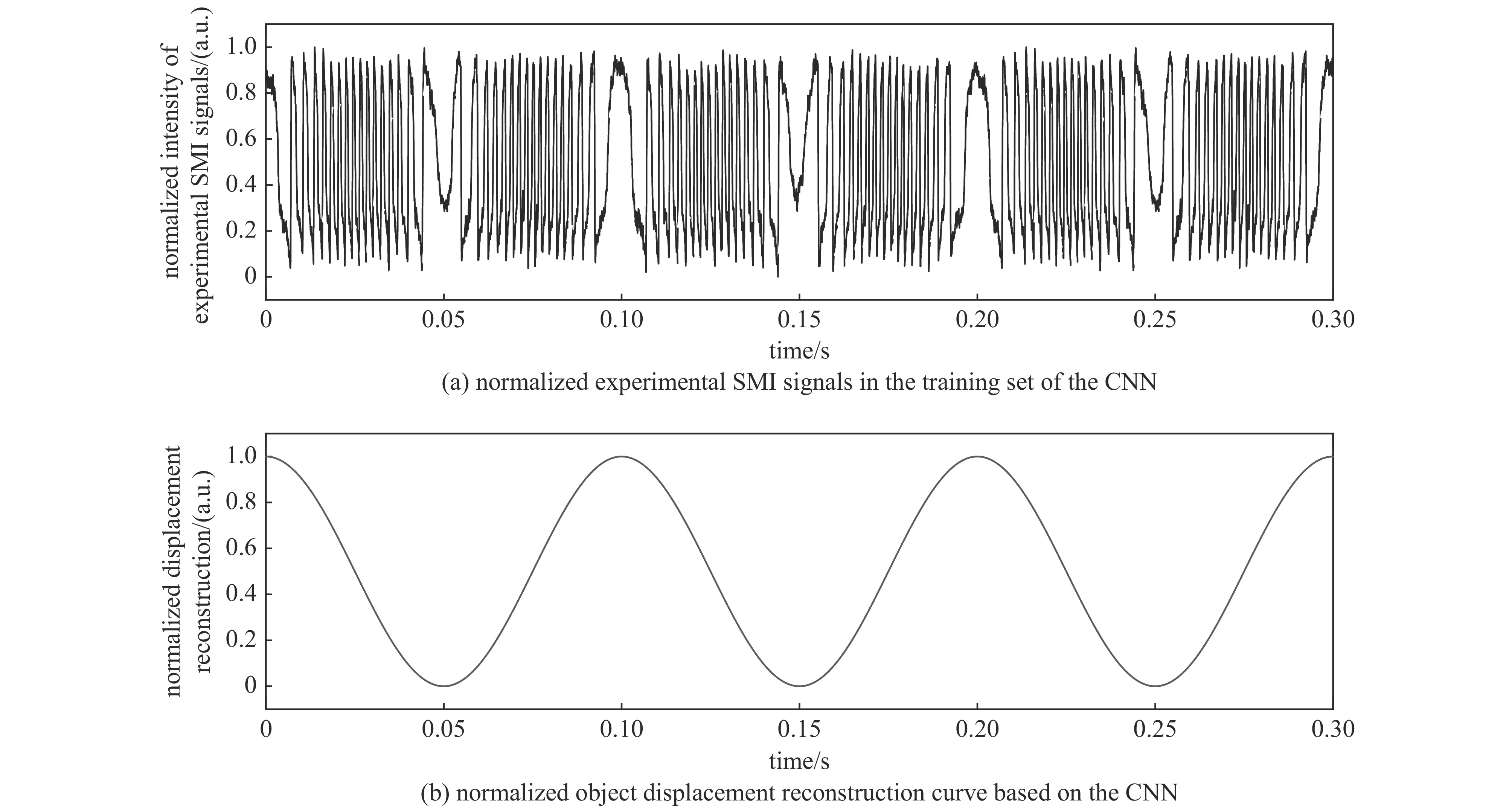
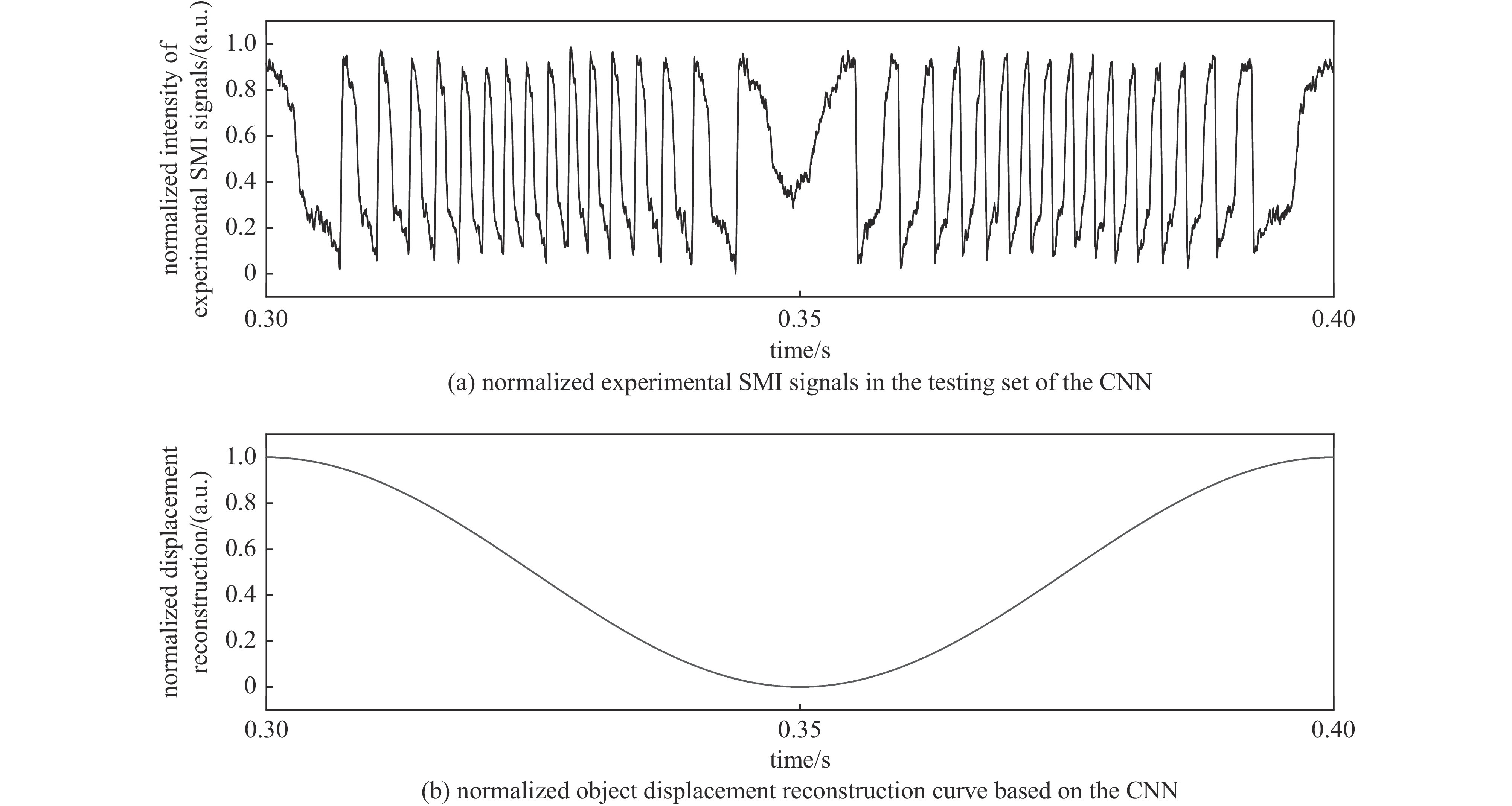
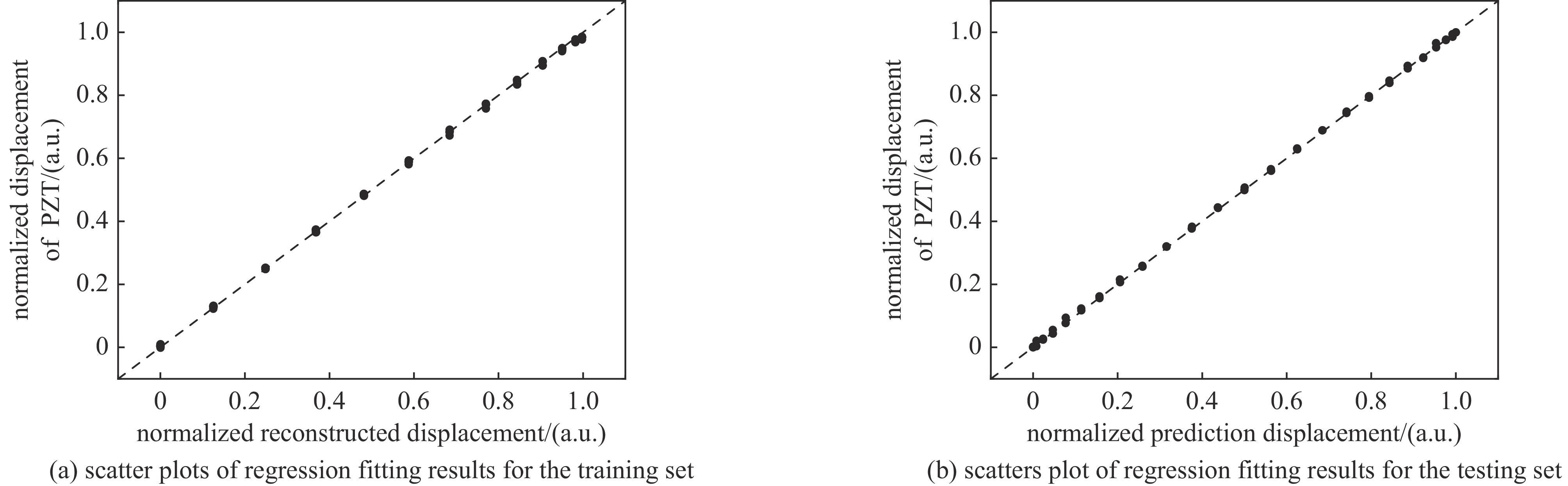
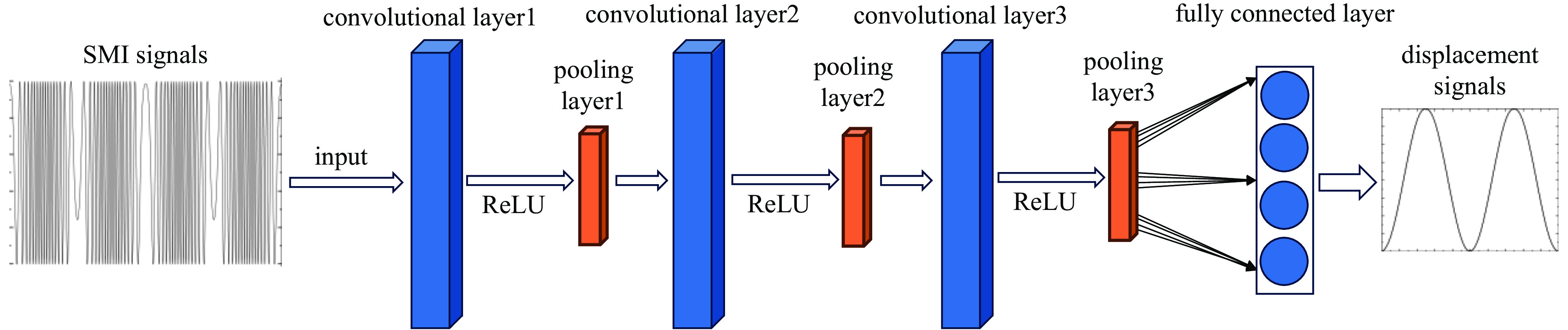
摘要: 提出了一种基于卷积神经网络CNN)的半导体激光自混合干涉(SMI)微位移重构方法,将SMI信号分段并以窗口平均位移作为标签输入卷积神经网络,实现了物体微米量级位移的直接重构,避免了位移重构过程中复杂的SMI信号相位解包裹计算过程。所使用的卷积神经网络由三组卷积层、池化层和线性整流函数组成,其中卷积层用于提取SMI信号中的局部位移特征,池化层用于压缩SMI信号中的特征信息并增强抗干扰能力,线性整流函数有助于突出SMI信号中的关键位移特征。在理论仿真中,将具有10 dB噪声的SMI信号输入至已训练完成的卷积神经网络中,直接输出物体重构微位移的均方根误差为
$ 5.3\times {10}^{-8} $ ;在实验中,将包含系统噪声的SMI信号输入已训练完成的卷积神经网络中,直接输出物体重构微位移的均方根误差为$ 2.1\times {10}^{-7} $ 。理论仿真与实际实验结果均表明,卷积神经网络通过分析SMI信号的时序片段,能够实现半导体激光自混合干涉信号的微米量级位移重构。Abstract:Background Laser self-mixing interferometry (SMI) is a highly sensitive and non-contact technique widely used for micro-displacement measurement. However, traditional displacement reconstruction methods typically involve complex phase unwrapping calculations, which increases computational difficulty and limits the efficiency of signal processing in practical applications.Purpose This study aims to propose a novel micro-displacement reconstruction method for semiconductor laser SMI based on convolutional neural networks (CNN). The objective is to achieve direct and accurate reconstruction of micron-scale displacement while bypassing the tedious phase unwrapping process.Methods The proposed method involves segmenting the SMI signal and using the window-averaged displacement as the label for training the CNN. The architecture of the network consists of three sets of convolutional layers, pooling layers, and Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) functions. Specifically, the convolutional layers are utilized to extract local displacement features from the SMI signal, the pooling layers are designed to compress feature information and enhance noise immunity, and the ReLU functions help highlight critical displacement features within the signal.Results In theoretical simulations, SMI signals with 10 dB noise were input into the trained CNN, resulting in a displacement reconstruction RMSE of 5.3 × 10−8. In experimental tests, SMI signals containing system noise were processed by the network, yielding a reconstructed displacement RMSE of 2.1 × 10−7. The simulation and experimental results demonstrate consistent performance.Conclusions Both theoretical and experimental results indicate that the convolutional neural network can effectively achieve micron-level displacement reconstruction by analyzing the temporal segments of SMI signals. This method provides an efficient alternative for semiconductor laser self-mixing interference systems by eliminating the need for complex phase-based algorithms. -
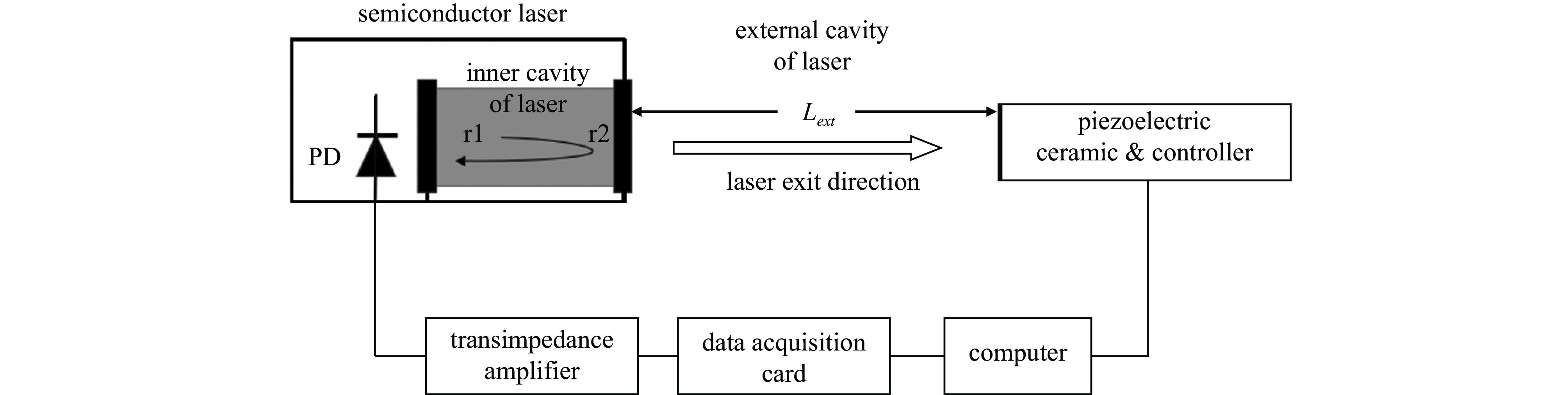
表 1 数值模拟中使用的参数
Table 1. Parameters used in numerical simulation
$ {\boldsymbol{L}}_{\boldsymbol{e}\boldsymbol{x}\boldsymbol{t}} $ (distance from the laser
to the object)/mm$ \boldsymbol{L} $ (cavity length of diode
laser)/mmt (simulation
time)/sA (vibration amplitude of
external object)/$ \mu \mathrm{m} $49.43 0.5 0.2 2 f (external object vibration
frequency)/$ \mathrm{Hz} $$ \boldsymbol{\alpha } $ (linewidth enhancement
factor)/C (feedback
parameter)/$ \lambda $ (wavelength of the laser
diode)/nm10 4.15 0.8 635 -
[1] Guo Changying, Wang Qi. Laser self-mixing interference displacement signal filtering method based on empirical mode decomposition and wavelet threshold[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2024, 35: 045201. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/ad166c [2] Li Qinyu, Li Quan, Wei Xia, et al. Laser self-mixing interferometry for direct displacement reconstruction using deep learning[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2025, 192: 113423. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2025.113423 [3] Liu Hui, Li Xintao, You Yaqiang, et al. Wiener filtering in wavelet domain on laser self-mixing interference for micro-displacement reconstruction[J]. Photonics, 2025, 12: 40. doi: 10.3390/photonics12010040 [4] Skripal A V, Dobdin S Y, Inkin M G, et al. Measurement of distance by the maximum frequency of the interference signal with harmonic deviation of the wavelength of the self-mixing laser[J]. Technical Physics, 2024, 69(5): 1400-1406. doi: 10.1134/S1063784224040406 [5] 曹雪, 冯立娜, 王秀芳, 等. 基于差分的激光自混合光栅干涉位移测量[J]. 吉林大学学报(信息科学版), 2023, 41(4): 583-589 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5896.2023.04.002Cao Xue, Feng Lina, Wang Xiufang, et al. Displacement measurement of self-mixing grating interferometer based on difference[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Information Science Edition), 2023, 41(4): 583-589 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5896.2023.04.002 [6] 张玉杰, 徐雷, 管钰晴, 等. 基于平面反射式全息光栅的激光自混合纳米位移测量研究[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2023, 52: 20220676 doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220676Zhang Yujie, Xu Lei, Guan Yuqing, et al. Research on laser self-mixing Nano-displacement measurement based on plane reflective holographic grating[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2023, 52: 20220676 doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220676 [7] 彭婉妮, 牛海莎, 潘雨婷, 等. 基于全光纤激光自混合干涉技术的石英玻璃热光系数测量[J]. 光电子·激光, 2022, 33(6): 578-584 doi: 10.16136/j.joel.2022.06.0684Peng Wanni, Niu Haisha, Pan Yuting, et al. Measurement of thermo-optical coefficient of quartz glass based on all-fiber laser self-mixing interference technology[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics·Laser, 2022, 33(6): 578-584 doi: 10.16136/j.joel.2022.06.0684 [8] 张晨, 陈涛, 赵宇. 基于激光自混合干涉技术的单个微纳颗粒探测[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57: 192803 doi: 10.3788/LOP57.192803Zhang Chen, Chen Tao, Zhao Yu. Single micro-Nano particle detection based on laser self-mixing interference technology[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57: 192803 doi: 10.3788/LOP57.192803 [9] 蔡家轩, 楚卫东. 基于THz-QCL自混合干涉的运动传感[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2022, 20(10): 985-990 doi: 10.11805/TKYDA2021303Cai Jiaxuan, Chu Weidong. Motion sensing based on Self-Mixing interferometry with THz-QCL[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2022, 20(10): 985-990 doi: 10.11805/TKYDA2021303 [10] Yu Lian, Yang Yu, Liu Bin, et al. Laser self-mixing interference: optical fiber coil sensors for acoustic emission detection[J]. Photonics, 2023, 10: 958. doi: 10.3390/photonics10090958 [11] Xie Yan, Wang Yingxin, Li Lianhe, et al. Realization of high depth resolution using two-beam self-mixing interferometry with a terahertz quantum cascade laser[J]. Optics Communications, 2023, 545: 129737. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2023.129737 [12] Jha A, Cenkeramaddi L R, Royo S. Generalized multi-cavity laser self-mixing interferometry based on scattering theory[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(10): 16508-16522. doi: 10.1364/OE.484086 [13] Liu Hui, You Yaqiang, Li Sijia, et al. Denoising of laser self-mixing interference by improved wavelet threshold for high performance of displacement reconstruction[J]. Photonics, 2023, 10: 943. doi: 10.3390/photonics10080943 [14] 尤亚强, 李鑫涛, 刘晖, 等. 基于小波阈值滤波和S-G滤波相结合的激光自混合干涉微位移重构[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2024, 36: 081002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.240125You Yaqiang, Li Xintao, Liu Hui, et al. Micro displacement reconstruction of laser self mixing interference based on wavelet threshold filtering and S-G filtering[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2024, 36: 081002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.240125 [15] 吴军, 陈杨, 赵君伟, 等. 基于激光自混合原理的涡轮叶片转速与叶尖间隙动态同步测量方法[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2023, 44(11): 13-21 doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J2311652Wu Jun, Chen Yang, Zhao Junwei, et al. Dynamic synchronous measurement method of turbine blade speed and blade tip clearance based on laser self-mixing principle[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2023, 44(11): 13-21 doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J2311652 [16] 韩玉祥, 丛至诚, 高丙坤, 等. 基于激光自混合干涉调频信号的位移测量实验[J]. 激光与红外, 2022, 52(5): 695-699Han Yuxiang, Cong Zhicheng, Gao Bingkun, et al. Displacement measurement experiment based on laser self mixing interference frequency modulation signal[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2022, 52(5): 695-699 [17] Zhao Yan, Zhang Baofeng, Han Lianfu. Laser self-mixing interference displacement measurement based on VMD and phase unwrapping[J]. Optics Communications, 2020, 456: 124588. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2019.124588 [18] 樊毓臻, 寇科, 王晛, 等. 线性调频激光自混合干涉双通道微位移测量方法研究[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2023, 44(10): 22-29Fan Yuzhen, Kou Ke, Wang Xian, et al. Study on the dual-channel displacement measurement method using linearly tuned laser self-mixing interference[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2023, 44(10): 22-29 [19] Huang Yidan, Lai Wenzong, Chen Enguo. Displacement sensing for laser self-mixing interferometry by amplitude modulation and integral reconstruction[J]. Sensors, 2024, 24: 3785. doi: 10.3390/s24123785 [20] Awad A, Eldosoky M A A, Soliman A M, et al. Automatic diagnosis of hyperkinetic dysphonia from speech recordings based on deep learning approaches[J]. Engineering Research Express, 2025, 7: 035263. doi: 10.1088/2631-8695/adf9c3 [21] Liu Ying, Xue Jiahao, Li Daxiang, et al. Image recognition based on lightweight convolutional neural network: recent advances[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2024, 146: 105037. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2024.105037 [22] Farajollahi A, Fakhrabadi M M S. Convolutional neural networks to predict dispersion surfaces-based properties of acoustic metamaterials with arbitrary-shaped unit cells[J]. Results in Engineering, 2025, 26: 104905. doi: 10.1016/j.rineng.2025.104905 [23] Novac P E, Rodriguez L, Barland S. Integrating embedded neural networks and self-mixing interferometry for smart sensors design[C]//2024 IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium (SAS). 2024: 1-6. [24] An Lei, Liu Bin. Measuring parameters of laser self-mixing interferometry sensor based on back propagation neural network[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(11): 19134-19144. doi: 10.1364/OE.460625 [25] Siddiqui A A, Zabit U, Bernal O D. Fringe detection and displacement sensing for variable optical feedback-based self-mixing interferometry by using deep neural networks[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22: 9831. doi: 10.3390/s22249831 [26] Sawada A, Miyagawa T, Ebihara A, et al. Convolutional neural networks for time-dependent classification of variable-length time series[C]//Proceedings of the 2022 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). 2022: 1-8. [27] Chagnon J, Hagenbuchner M, Tsoi A C, et al. On the effects of recursive convolutional layers in convolutional neural networks[J]. Neurocomputing, 2024, 591: 127767. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2024.127767 [28] Walter B. Analysis of convolutional neural network image classifiers in a hierarchical max-pooling model with additional local pooling[J]. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 2023, 224: 109-126. doi: 10.1016/j.jspi.2022.11.001 [29] Liu Bin, Ruan Yuxi, Yu Yanguang. Determining system parameters and target movement directions in a laser self-mixing interferometry sensor[J]. Photonics, 2022, 9: 612. doi: 10.3390/photonics9090612 -






 下载:
下载: