Recent Advances in Betatron Radiation Sources Driven by Laser–Plasma Interactions
-
摘要: 随着超短超强激光技术的飞速发展,激光等离子体加速已成为产生GeV量级高能电子束与高品质辐射源的重要途径。其中,Betatron辐射作为一种机制紧凑、脉冲持续时间达飞秒量级的新型射线源,具有源尺寸小,高亮度等特点。在高能量密度物理、材料科学、成像及超快动态探测与高空间分辨成像等领域展现出巨大应用潜力。系统梳理了激光尾波场加速与直接激光加速两种核心机制产生Betatron辐射的物理原理、研究进展与发展趋势。详细对比了LWFA与DLA两种方案所产生Betatron辐射在关键参数(如光子能量、通量、亮度、能谱与稳定性)上的特性差异,总结了其各自的品质因子与适用场景。最后,展望了该领域未来面临的挑战,如提升光子的中心能量、产额、亮度及转换效率,并为基于下一代强激光大科学装置开展相关实验研究提供了方向性参考。
-
关键词:
- 激光尾场加速 /
- 激光直接加速 /
- 等离子体 /
- Betatron辐射
Abstract: The rapid advancement of ultra-short and ultra-intense laser technology has established laser-plasma acceleration as a premier approach for generating GeV-level electron beams and high-quality radiation sources. Among these, Betatron radiation—emitted as electrons oscillate transversely in plasma channels—has emerged as a unique source characterized by its femtosecond pulse duration, micron-scale source size, and high peak brightness. It holds significant potential in high-energy-density physics, materials science, and ultrafast imaging. This review systematically outlines the physical principles and reviews the latest research progress of Betatron radiation generated via two core mechanisms: laser wakefield acceleration (LWFA) and direct laser acceleration (DLA). A detailed comparison reveals that while the LWFA scheme excels in producing highly collimated, high-energy photons with superior brilliance, the DLA mechanism within near-critical-density plasmas offers a different trade-off. Although DLA generates a significantly larger number of electrons and a higher photon flux, these are characterized by lower photon energies and a wider angular spread. Consequently, the divergence of the emitted X-rays typically reaches hundreds of milliradians, which limits the overall brilliance. The review concludes that the future of Betatron radiation lies in enhancing repetition rates and achieving active control over radiation parameters. Developing Hybrid schemes and structured targets offer potential to overcome the trade-off between high flux and high brilliance, guiding future experiments at large-scale facilities.-
Key words:
- laser wake field acceleration /
- direct laser acceleration /
- plasma /
- betatron radiation
-
表 1 激光器与等离子体产生Betatron 辐射源的统计结果
Table 1. Summary of Betatron Radiation Sources Generated by Lasers and Plasmas
Schemes Laser Power/
EnergyEc/keV Efficiency/% Photon/sr Divergence
Angle/ (°)Peak Brilliance/
(photons·s−1·mm−2·
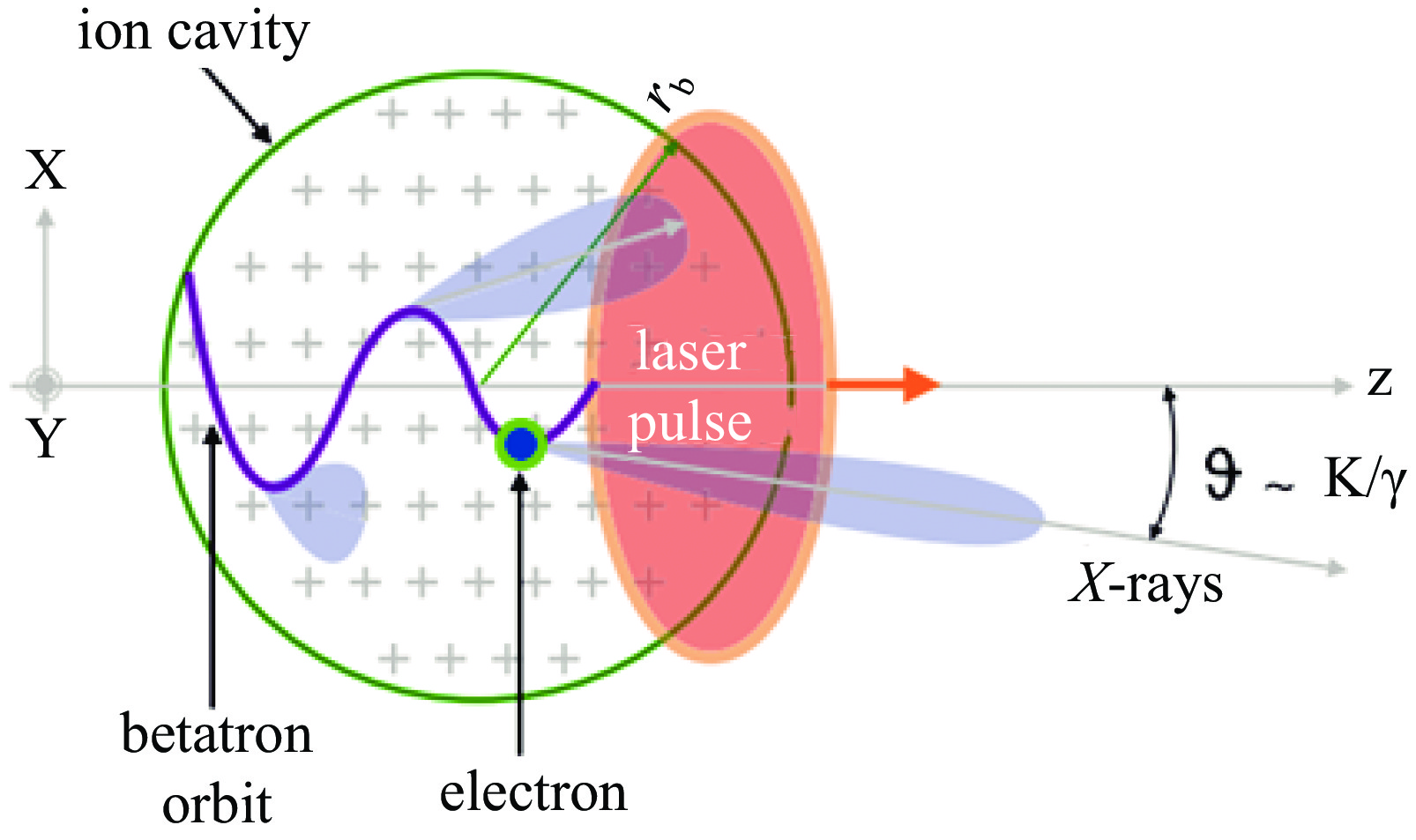
mrad−2· (0.1%bw)−1)Reference LWFA 1 J 2 — $ 1\times {10}^{8} $ (Photon/sr, per shot) 2.9 $ 2.0\times {10}^{22} $ [16] 5.5 J 50 — $ 5\times {10}^{8} \;(\mathrm{Photon}/\mathrm{sr}) $ — $ 1.0\times {10}^{23} $ [21] 2 J 8 10−4 $ 1\times {10}^{8} \;(Photon/sr) $ 0.7 $ 1.0\times {10}^{22} $ [23] 60 TW 5.2 — $ > 5\times {10}^{7} $ (Photon/sr, per shot) — $ 2.0\times {10}^{22} $ [27] 440 TW 36 5×10−3 — >50 $ 1.0\times {10}^{17} $ [33] 100 TW 75 — $ 8\times {10}^{8}\; (\mathrm{Photon}/\mathrm{sr},~\mathrm{per}~\mathrm{shot}) $ — $ 1.0\times {10}^{23} $ [42] 200 TW 5~26 — $ 2.1\times {10}^{8} $ ($ \mathrm{Photon}/\text{sr} $) — $ 1.0\times {10}^{23} $ [43] 7.7 PW — >10 $ 1\times {10}^{9} $ (Photon/0.1%BW) 2 $ 8.0\times {10}^{26} $ [49] 5.9 kJ — ~13 $ 1\times {10}^{14} $ (Photon/sr) 11 $ 1.0\times {10}^{26} $ [50] 1 PW 22 — $ 4\times {10}^{9} $ (Photon/sr, per shot) 0.7 $ 1.0\times {10}^{23} $ [52] 100 TW 13.5 — $ 1\times {10}^{8} $ (Photon/sr, per shot) — — [54] DLA 20 J 10 1.6×10−3 $ 1\times {10}^{13} $ ($ \mathrm{Photon}/\text{sr} $) 14~16 $ 1.0\times {10}^{21} $ [66] 135 TW 150 0.01 $ 3\times {10}^{10} $ ($ \mathrm{Photon}/\text{sr} $) 2.9 $ 1.2\times {10}^{22} $ [68] — — 0.2 $ 2.15\times {10}^{5} $ (Photon/sr+
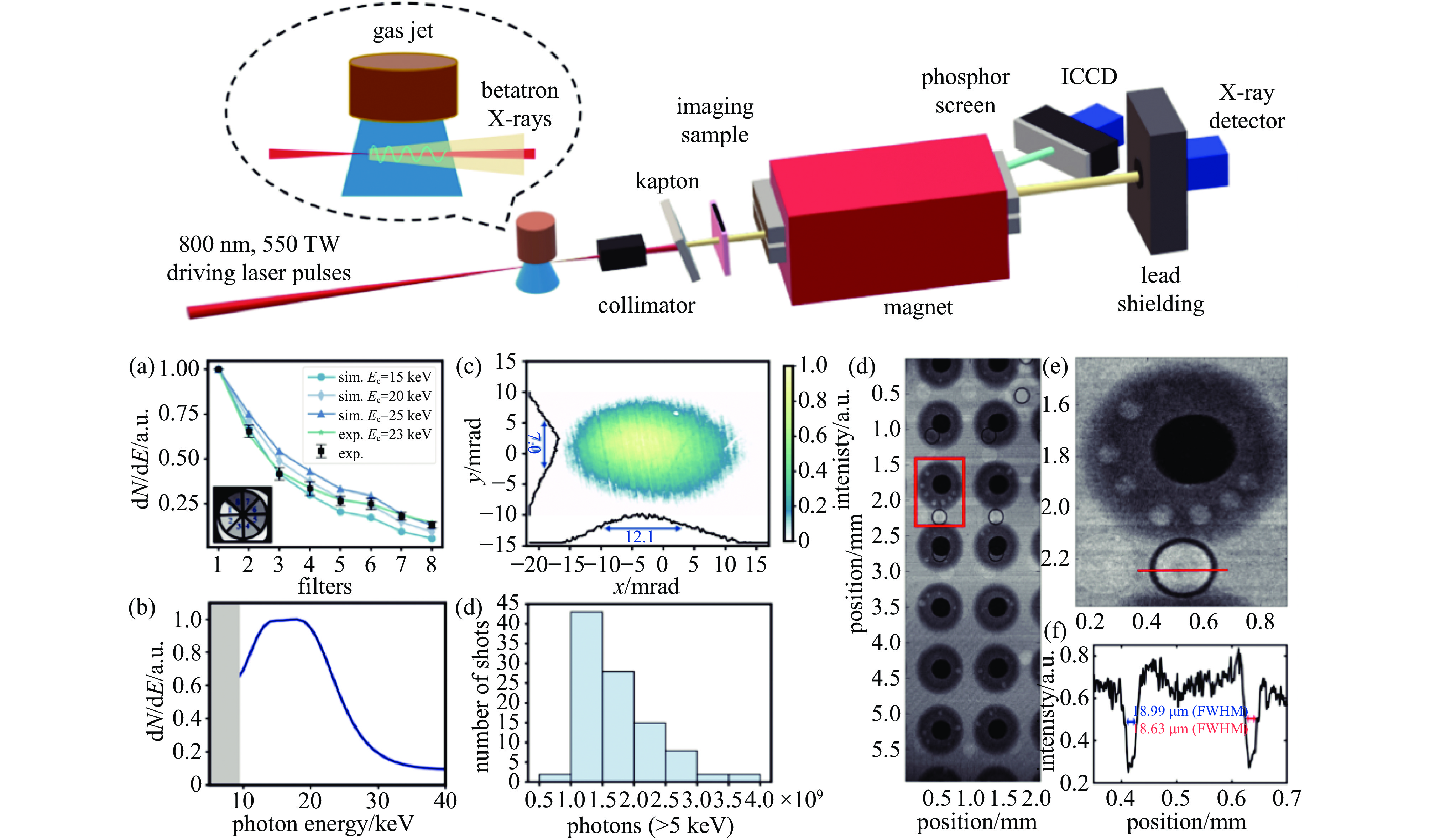
Photon/0.1%BW)10 $ 4.3\times {10}^{22} $ [72] 10 PW — 1.5 $ 1\times {10}^{10} $ (Photon/0.1%BW) — $ 1.0\times {10}^{22} $ [73] 80 J 5 — $ 7\times {10}^{11} $ (Photon/sr) 40 $ 6.0\times {10}^{19} $ [79] 20 J 5 3.4×10−3 $ 2\times {10}^{8} $ (photons/eV) 5~15 $ 3.3\times {10}^{20} $ [81] LWFA+PWFA 500 TW 9 MeV 0.9 $ 3.5\times {10}^{7} $ (Photon/0.1%BW) 0.86 $ 4.4\times {10}^{23} $ [48] -
[1] Aad G, Abajyan T, Abbott B, et al. Observation of a new particle in the search for the Standard Model Higgs boson with the ATLAS detector at the LHC[J]. Physics Letters B, 2012, 716(1): 1-29. doi: 10.1063/1.4826710 [2] Sciaini G, Miller R J D. Femtosecond electron diffraction: heralding the era of atomically resolved dynamics[J]. Reports on Progress in Physics, 2011, 74: 096101. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/74/9/096101 [3] Tajima T, Dawson J M. Laser electron accelerator[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1979, 43(4): 267-270. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.43.267 [4] Strickland D, Mourou G. Compression of amplified chirped optical pulses[J]. Optics Communications, 1985, 55(6): 447-449. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(85)90151-8 [5] Pukhov A, Meyer-ter-Vehn J. Laser wake field acceleration: the highly non-linear broken-wave regime[J]. Applied Physics B, 2002, 74(4/5): 355-361. doi: 10.1007/s003400200795 [6] Mangles S P D, Murphy C D, Najmudin Z, et al. Monoenergetic beams of relativistic electrons from intense laser–plasma interactions[J]. Nature, 2004, 431(7008): 535-538. doi: 10.1038/nature02939 [7] Geddes C G R, Toth C, Van Tilborg J, et al. High-quality electron beams from a laser wakefield accelerator using plasma-channel guiding[J]. Nature, 2004, 431(7008): 538-541. doi: 10.1038/nature02900 [8] Faure J, Glinec Y, Pukhov A, et al. A laser–plasma accelerator producing monoenergetic electron beams[J]. Nature, 2004, 431(7008): 541-544. doi: 10.1038/nature02963 [9] Leemans W P, Nagler B, Gonsalves A J, et al. GeV electron beams from a centimetre-scale accelerator[J]. Nature Physics, 2006, 2(10): 696-699. doi: 10.1038/nphys418 [10] Wang Xiaoming, Zgadzaj R, Fazel N, et al. Quasi-monoenergetic laser-plasma acceleration of electrons to 2 GeV[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 1988. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2988 [11] Leemans W P, Gonsalves A J, Mao H S, et al. Multi-GeV electron beams from capillary-discharge-guided subpetawatt laser pulses in the self-trapping regime[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2014, 113: 245002. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.245002 [12] Mirzaie M, Li S, Zeng M, et al. Demonstration of self-truncated ionization injection for GeV electron beams[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 14659. doi: 10.1038/srep14659 [13] Gonsalves A J, Nakamura K, Daniels J, et al. Petawatt laser guiding and electron beam acceleration to 8 GeV in a laser-heated capillary dischargewaveguide[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2019, 122: 084801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.122.084801 [14] Aniculaesei C, Ha T, Yoffe S, et al. The acceleration of a high-charge electron bunch to 10 GeV in a 10-cm nanoparticle-assisted wakefield accelerator[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2024, 9: 014001. doi: 10.1063/5.0161687 [15] Wang Shuoqin, Clayton C E, Blue B E, et al. X-ray emission from betatron motion in a plasma wiggler[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2002, 88: 135004. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.88.135004 [16] Rousse A, Phuoc K T, Shah R, et al. Production of a keV X-ray beam from synchrotron radiation in relativistic laser-plasma interaction[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2004, 93: 135005. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.93.135005 [17] Shah R C, Albert F, Ta Phuoc K, et al. Coherence-based transverse measurement of synchrotron x-ray radiation from relativistic laser-plasma interaction and laser-accelerated electrons[J]. Physical Review E, 2006, 74: 045401. doi: 10.1109/qels.2007.4431186 [18] Björklund Svensson J, Guénot D, Ferri J, et al. Low-divergence femtosecond X-ray pulses from a passive plasma lens[J]. Nature Physics, 2021, 17(5): 639-645. doi: 10.1038/s41567-020-01158-z [19] Ta Phuoc K, Fitour R, Tafzi A, et al. Demonstration of the ultrafast nature of laser produced betatron radiation[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2007, 14: 080701. doi: 10.1063/1.2754624 [20] Horný V, Nejdl J, Kozlová M, et al. Temporal profile of betatron radiation from laser-driven electron accelerators[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2017, 24: 063107. doi: 10.1063/1.4985687 [21] Cipiccia S, Islam M R, Ersfeld B, et al. Gamma-rays from harmonically resonant betatron oscillations in a plasma wake[J]. Nature Physics, 2011, 7(11): 867-871. doi: 10.1038/nphys2090 [22] Corde S, Ta Phuoc K, Lambert G, et al. Femtosecond X rays from laser-plasma accelerators[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2013, 85(1): 1-48. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.85.1 [23] Kneip S, McGuffey C, Martins J L, et al. Bright spatially coherent synchrotron X-rays from a table-top source[J]. Nature Physics, 2010, 6(12): 980-983. doi: 10.1038/nphys1789 [24] Bilderback D H, Elleaume P, Weckert E. Review of third and next generation synchrotron light sources[J]. Journal of Physics B: Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 2005, 38(9): S773-S797. doi: 10.1088/0953-4075/38/9/022 [25] Mahieu B, Jourdain N, Ta Phuoc K, et al. Probing warm dense matter using femtosecond X-ray absorption spectroscopy with a laser-produced betatron source[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 3276. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05791-4 [26] Wood J C, Chapman D J, Poder K, et al. Ultrafast imaging of laser driven shock waves using betatron X-rays from a laser wakefield accelerator[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 11010. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29347-0 [27] Wenz J, Schleede S, Khrennikov K, et al. Quantitative X-ray phase-contrast microtomography from a compact laser-driven betatron source[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 7568. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8568 [28] Döpp A, Hehn L, Götzfried J, et al. Quick X-ray microtomography using a laser-driven betatron source[J]. Optica, 2018, 5(2): 199-203. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.5.000199 [29] Pukhov A, Sheng Z M, Meyer-ter-Vehn J. Particle acceleration in relativistic laser channels[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 1999, 6(7): 2847-2854. doi: 10.1063/1.873242 [30] Gahn C, Tsakiris G D, Pukhov A, et al. Multi-MeV electron beam generation by direct laser acceleration in high-density plasma channels[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1999, 83(23): 4772-4775. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.83.4772 [31] Meyer-ter-Vehn J, Sheng Z M. On electron acceleration by intense laser pulses in the presence of a stochastic field[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 1999, 6(3): 641-644. doi: 10.1063/1.873347 [32] Kiselev S, Pukhov A, Kostyukov I. X-ray generation in strongly nonlinear plasma waves[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2004, 93: 135004. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.93.135004 [33] Kneip S, Nagel S R, Bellei C, et al. Observation of synchrotron radiation from electrons accelerated in a Petawatt-laser-generated plasma cavity[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2008, 100: 105006. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.105006 [34] Babjak R, Willingale L, Arefiev A, et al. Direct laser acceleration in underdense plasmas with multi-PW lasers: a path to high-charge, GeV-class electron bunches[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2024, 132: 125001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.132.125001 [35] Hussein A E, Arefiev A V, Batson T, et al. Towards the optimisation of direct laser acceleration[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2021, 23: 023031. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/abdf9a [36] Shaw J L, Romo-Gonzalez M A, Lemos N, et al. Microcoulomb (0.7 ± $ \dfrac{0.4}{0.2} $ μC) laser plasma accelerator on OMEGA EP[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11: 7498. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86523-5[37] 黄瑞贤, 奚传易, 韩立琦, 等. 飞秒激光Betatron辐射源的现状与发展趋势分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2023, 35: 012009 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.220229Huang Ruixian, Xi Chuanyi, Han Liqi, et al. Current situation and development trend analysis of femtosecond laser Betatron radiation source[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2023, 35: 012009 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.220229 [38] Lu Wei, Tzoufras M, Joshi C, et al. Generating multi-GeV electron bunches using single stage laser wakefield acceleration in a 3D nonlinear regime[J]. Physical Review Special Topics—Accelerators and Beams, 2007, 10: 061301. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.10.061301 [39] Németh K, Shen Baifei, Li Yuelin, et al. Laser-driven coherent betatron oscillation in a laser-wakefield cavity[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2008, 100: 095002. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.095002 [40] Albert F, Shah R, Phuoc K T, et al. Betatron oscillations of electrons accelerated in laser wakefields characterized by spectral X-ray analysis[J]. Physical Review E, 2008, 77: 056402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.77.056402 [41] Chen L M, Yan W C, Li D Z, et al. Bright betatron X-ray radiation from a laser-driven-clustering gas target[J]. Scientific reports, 2013, 3(1): 1912. doi: 10.1038/srep01912 [42] Huang K, Li Y F, Li D Z, et al. Resonantly enhanced betatron hard x-rays from ionization injected electrons in a laser plasma accelerator[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 27633. doi: 10.1038/srep27633 [43] Yu Changhai, Liu Jiansheng, Wang Wentao, et al. Enhanced betatron radiation by steering a laser-driven plasma wakefield with a tilted shock front[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2018, 112: 133503. doi: 10.1063/1.5019406 [44] Chen Jiyuan, Xu Sa, Tang Ning, et al. Enhanced soft X-ray betatron radiation from a transversely oscillating laser plasma wake[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(9): 13302-13313. doi: 10.1364/OE.420150 [45] Feng Jie, Li Yifei, Wang Jinguang, et al. Gamma-ray emission from wakefield-accelerated electrons wiggling in a laser field[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 2531. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-38777-3 [46] Kozlova M, Andriyash I, Gautier J, et al. Hard X rays from laser-wakefield accelerators in density tailored plasmas[J]. Physical Review X, 2020, 10: 011061. doi: 10.1103/physrevx.10.011061 [47] Lei Bifeng, Wang Jingwei, Kharin V, et al. γ-ray generation from plasma wakefield resonant wiggler[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2018, 120: 134801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.134801 [48] Ferri J, Corde S, Döpp A, et al. High-brilliance betatron γ-ray source powered by laser-accelerated electrons[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2018, 120: 254802. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.254802 [49] Zhu Xinglong, Chen Min, Weng Suming, et al. Extremely brilliant GeV γ-rays from a two-stage laser-plasma accelerator[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6: eaaz7240. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz7240 [50] Lu Yu, Zhang Guobo, Zhao Jie, et al. Ultra-brilliant GeV betatronlike radiation from energetic electrons oscillating in frequency-downshifted laser pulses[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(6): 8926-8940. doi: 10.1364/OE.419761 [51] Cole J M, Symes D R, Lopes N C, et al. High-resolution μCT of a mouse embryo using a compact laser-driven X-ray betatron source[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(25): 6335-6340. [52] Zhang Hong, Deng Zhigang, Jiang Hai, et al. High-brightness betatron X-ray source driven by the SULF-1 PW laser[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2025, 13: e31. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2025.17 [53] Corde S, Phuoc K T, Fitour R, et al. Controlled betatron X-ray radiation from tunable optically injected electrons[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2011, 107: 255003. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.255003 [54] Döpp A, Mahieu B, Lifschitz A, et al. Stable femtosecond X-rays with tunable polarization from a laser-driven accelerator[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2017, 6: e17086. [55] Zhang Guobo, Chen Min, Yang Xaiohu, et al. Betatron radiation polarization control by using an off-axis ionization injection in a laser wakefield acceleration[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(20): 29927-29936. doi: 10.1364/OE.404723 [56] Thaury C, Guillaume E, Corde S, et al. Angular-momentum evolution in laser-plasma accelerators[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2013, 111: 135002. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.135002 [57] Schnell M, Sävert A, Uschmann I, et al. Optical control of hard X-ray polarization by electron injection in a laser wakefield accelerator[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 2421. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3421 [58] Luo J, Chen M, Zeng M, et al. A compact tunable polarized X-ray source based on laser-plasma helical undulators[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 29101. doi: 10.1038/srep29101 [59] Chang H X, Qiao B, Huang T W, et al. Brilliant petawatt gamma-ray pulse generation in quantum electrodynamic laser-plasma interaction[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 45031. doi: 10.1038/srep45031 [60] Luís Martins J, Vieira J, Ferri J, et al. Radiation emission in laser-wakefields driven by structured laser pulses with orbital angular momentum[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 9840. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45474-8 [61] Feng Jie, Li Yifei, Geng Xiaotao, et al. Circularly polarized X-ray generation from an ionization induced laser plasma electron accelerator[J]. Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 2020, 62: 105021. doi: 10.1088/1361-6587/abaf0b [62] Rechatin C, Davoine X, Lifschitz A, et al. Observation of beam loading in a laser-plasma accelerator[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 103: 194804. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.194804 [63] Danson C N, Haefner C, Bromage J, et al. Petawatt and Exawatt class lasers worldwide[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2019, 7: e54. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2019.36 [64] 冷雨欣. 上海超强超短激光实验装置[J]. 中国激光, 2019, 46: 0100001 doi: 10.3788/CJL201946.0100001Leng Yuxin. Shanghai superintense ultrafast laser facility[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2019, 46: 0100001 doi: 10.3788/CJL201946.0100001 [65] Zeng Xiaoming, Zhou Kainan, Zuo Yanlei, et al. Multi-Petawatt laser facility fully based on optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification[J]. Optics Letters, 2017, 42(10): 2014-2017. doi: 10.1364/OL.42.002014 [66] Cikhardt J, Gyrdymov M, Zähter S, et al. Characterization of bright betatron radiation generated by direct laser acceleration of electrons in plasma of near critical density[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2024, 9: 027201. doi: 10.1063/5.0181119 [67] Tan J H, Li Y F, Li D Z, et al. Observation of high efficiency Betatron radiation from femtosecond Petawatt laser irradiated near critical plasmas[DB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2109.12467, 2021. [68] Lobok M G, Andriyash I A, Vais O E, et al. Bright synchrotron radiation from relativistic self-trapping of a short laser pulse in near-critical density plasma[J]. Physical Review E, 2021, 104: L053201. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.104.L053201 [69] Huang Ruixuan, Han Liqi, Shou Yinren, et al. High-flux and bright betatron X-ray source generated from femtosecond laser pulse interaction with sub-critical density plasma[J]. Optics Letters, 2023, 48(3): 819-822. doi: 10.1364/OL.480553 [70] Chu Mengyuan, Luan Shixia, Yang Hetian, et al. Controlled Betatron radiation from high-charge electron beams in multiple plasma channels[J]. Optics Express, 2025, 33(10): 21070-21078. doi: 10.1364/OE.557855 [71] 谢波, 张晓辉, 李天月, 等. 拍瓦飞秒激光与近临界密度等离子体相互作用的电子加速及betatron辐射产生数值模拟D[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2025, 37: 091002Xie Bo, Zhang Xiaohui, Li Tianyue, et al. Numerical study of electron acceleration and betatron radiation based on interaction of petawatt femtosecond laser with near-critical-density plasma[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2025, 37: 091002 [72] Zhao Yan, Lu Haiyang, Zhou Cangtao, et al. Overcritical electron acceleration and betatron radiation in the bubble-like structure formed by re-injected electrons in a tailored transverse plasma[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2023, 8: 014403. doi: 10.1063/5.0121558 [73] Babjak R, Vranić M. Betatron radiation emitted during the direct laser acceleration of electrons in underdense plasmas[J]. Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 2025, 67: 085019. doi: 10.1088/1361-6587/adf50b [74] Ridgers C P, Brady C S, Duclous R, et al. Dense electron-positron plasmas and ultraintense γ rays from laser-irradiated solids[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2012, 108: 165006. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.165006 [75] Capdessus R, d’Humières E, Tikhonchuk V T. Influence of ion mass on laser-energy absorption and synchrotron radiation at ultrahigh laser intensities[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2013, 110: 215003. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.215003 [76] Yu Tongpu, Pukhov A, Sheng Zhengming, et al. Bright Betatronlike X rays from radiation pressure acceleration of a mass-limited foil target[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2013, 110: 045001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.045001 [77] Wang Weimin, Sheng Zhengming, Gibbon P, et al. Collimated ultrabright gamma rays from electron wiggling along a Petawatt laser-irradiated wire in the QED regime[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(40): 9911-9916. [78] Yu J Q, Hu R H, Gong Z, et al. The generation of collimated γ-ray pulse from the interaction between 10 PW laser and a narrow tube target[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2018, 112: 204103. doi: 10.1063/1.5030942 [79] Rosmej O N, Shen Xiaofei, Pukhov A, et al. Bright betatron radiation from direct-laser-accelerated electrons at moderate relativistic laser intensity[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2021, 6: 048401. doi: 10.1063/5.0042315 [80] Shen Xiaofei, Pukhov A, Qiao Bin. High-flux bright x-ray source from femtosecond laser-irradiated microtapes[J]. Communications Physics, 2024, 7: 84. doi: 10.1038/s42005-024-01575-z [81] Shen Xiaofei, Pukhov A, Günther M M, et al. Bright betatron X-rays generation from picosecond laser interactions with long-scale near critical density plasmas[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2021, 118: 134102. doi: 10.1063/5.0042997 [82] Brady C S, Ridgers C P, Arber T D, et al. Gamma-ray emission in near critical density plasmas[J]. Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 2013, 55: 124016. doi: 10.1088/0741-3335/55/12/124016 [83] Brady C S, Ridgers C P, Arber T D, et al. Laser absorption in relativistically underdense plasmas by synchrotron radiation[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2012, 109: 245006. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.109.245006 [84] Rosmej O N, Gyrdymov M, Andreev N E, et al. Advanced plasma target from pre-ionized low-density foam for effective and robust direct laser acceleration of electrons[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2025, 13: e3. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2024.85 [85] Rosmej O N, Gyrdymov M, Günther M M, et al. High-current laser-driven beams of relativistic electrons for high energy density research[J]. Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 2020, 62: 115024. doi: 10.1088/1361-6587/abb24e -




 下载:
下载: