Research progress in the generation and applications of high-flux neutron sources driven by high-power laser facilities
-
摘要: 简要回顾了中物院激光聚变研究中心研究团队基于星光-Ⅲ等强激光装置,在激光驱动中子源产生及应用研究方面开展的系列工作。介绍了研究团队通过新型靶设计提升光核中子产生效率、基于靶背鞘场加速机制提高中子产额,以及利用无碰撞静电冲击波加速获得高品质中子源等若干技术途径的探索。在应用方面,研究团队初步开展了该中子源在快中子照相、器件辐照效应与核材料检测等方向的实验研究,展现了其作为短脉冲、高通量中子源的潜在应用价值。随着激光技术的不断进步和产生机制的持续优化,这种新型中子源有望在基础科学研究、核能技术发展以及工业应用等领域发挥更加重要的作用,为相关学科的发展提供新的研究手段和技术支撑。Abstract: This paper briefly reviews the series of work carried out by the research team from the Laser Fusion Research Center, China Academy of Engineering Physics, based on the Xingguang-III and Shenguang-II Upgrade laser facilities, in the field of laser-driven neutron source generation and applications. In terms of generation mechanisms, it highlights explorations of several technical approaches, including enhancing photo-nuclear neutron production efficiency through novel target design, increasing neutron yield based on the target normal sheath acceleration mechanism, and obtaining high-quality neutron sources via collisionless electrostatic shock acceleration. On the application front, preliminary experimental studies have been conducted in areas such as fast neutron radiography, material radiation effects, and nuclear material detection, demonstrating the potential application value of such neutron sources as short-pulse, high-flux sources. With continuous advancements in laser technology and ongoing optimization of generation mechanisms, this new type of neutron source is expected to play an increasingly important role in basic scientific research, nuclear energy technology development, and industrial applications, providing new research tools and technical support for the development of related disciplines.
-
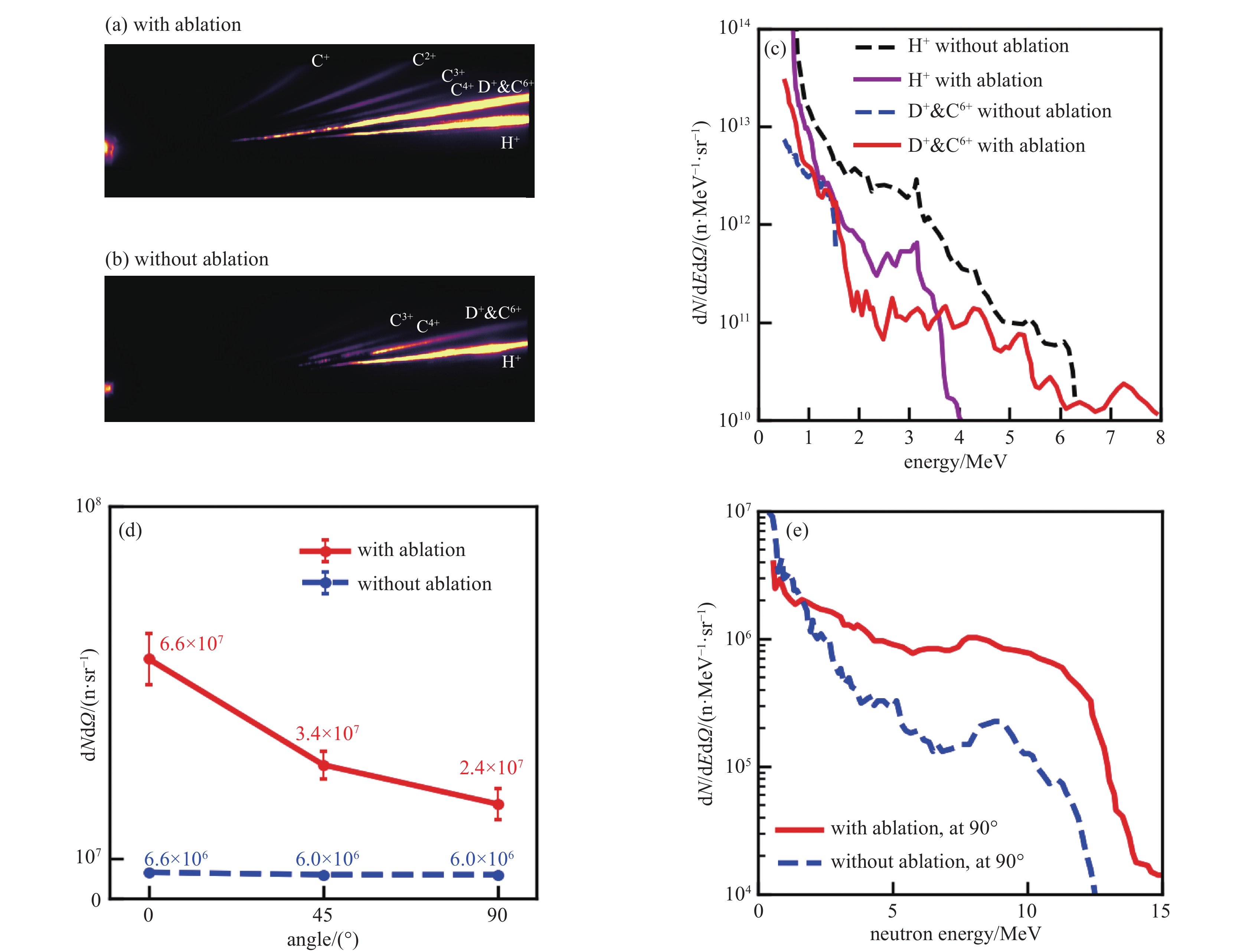
图 7 实验结果(a)和(b)分别为使用和未使用纳秒激光烧蚀时,汤姆逊谱仪的原始数据;(c)通过汤姆逊谱仪获得的离子能谱;(d)使用和未使用烧蚀技术时在0°、45°和90°方向测得的中子产额;(e)相应方向中子能谱。
Figure 7. Experimental results. (a), (b) Raw image plate data of the on-axis Thomson parabola spectrometer for the cases with and without nanosecond laser ablation, respectively. (c) The corresponding ion energy spectra obtained from TP. (d) Neutron yields at 0°, 45°, and 90° for the cases with and without ablation. (e) The corresponding neutron energy spectra
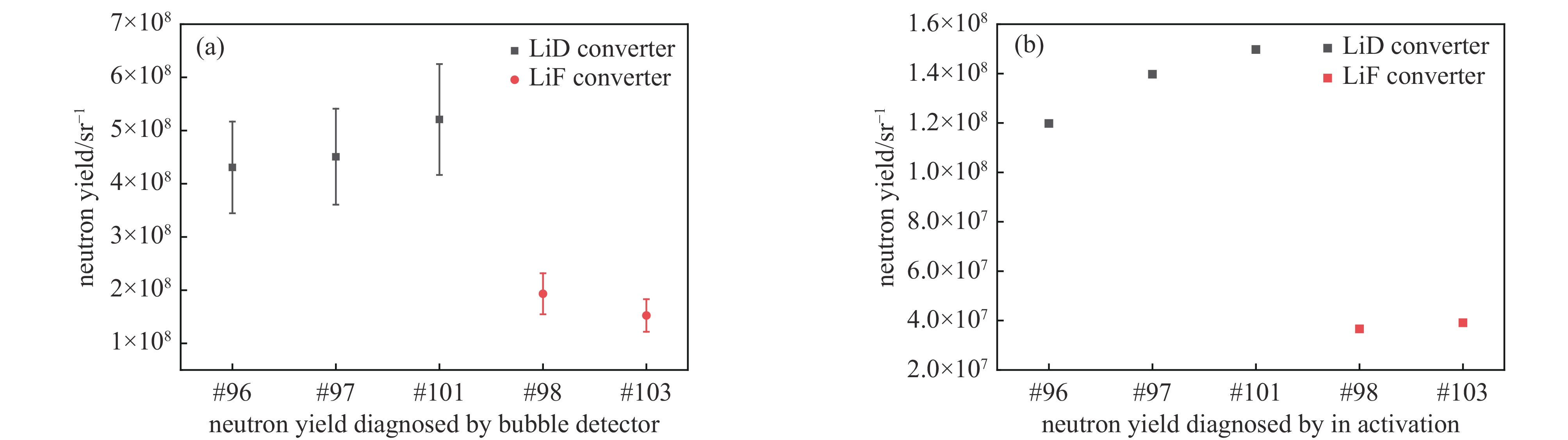
表 1 气泡探测器测量的中子产额
Table 1. Neutron yield diagnosed by bubble detector
shot. target yield/sr #96 Cu-CD+LiD (3.0±0.7)×108 #97 Cu-CD+LiD (4.5±1.1)×108 #98 Cu-CD+LiF (1.9±0.5)×108 #99 Cu+LiD (3.3±0.7)×108 #101 Cu-CD+LiD (5.2±1.1)×108 #103 Cu-CD+LiF (1.5±0.6)×108 -
[1] Dams R, Robbins J A, Rahn K A, et al. Nondestructive neutron activation analysis of air pollution particulates[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1970, 42(8): 861-867. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-239450-8.50101-5 [2] Nishiyama Y, Sugiyama J, Chanzy H, et al. Crystal structure and hydrogen bonding system in cellulose Iα from synchrotron X-ray and neutron fiber diffraction[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(47): 14300-14306. doi: 10.1021/ja037055w [3] Goldhaber M, Teller E. On nuclear dipole vibrations[J]. Physical Review, 1948, 74(9): 1046-1049. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.74.1046 [4] Ageron P. Cold neutron sources at ILL[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 1989, 284(1): 197-199. [5] Wei J, Chen H S, Chen Y W, et al. China Spallation Neutron Source: design, R&D, and outlook[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2009, 600(1): 10-13. [6] Blau B, Clausen K N, Gvasaliya S, et al. The Swiss spallation neutron source SINQ at Paul Scherrer Institut[J]. Neutron News, 2009, 20(3): 5-8. doi: 10.1080/10448630903120387 [7] Yogo A, Mirfayzi S R, Arikawa Y, et al. Single shot radiography by a bright source of laser-driven thermal neutrons and x-rays[J]. Applied Physics Express, 2021, 14: 106001. doi: 10.35848/1882-0786/ac2212 [8] Guler N, Volegov P, Favalli A, et al. Neutron imaging with the short-pulse laser driven neutron source at the Trident laser facility[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2016, 120: 154901. doi: 10.1063/1.4964248 [9] Nelson R O, Vogel S C, Hunter J F, et al. Neutron imaging at LANSCE—from cold to ultrafast[J]. Journal of Imaging, 2018, 4: 45. doi: 10.3390/jimaging4020045 [10] Lee S, Park S, Lee K, et al. A laser-induced repetitive fast neutron source applied for gold activation analysis[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2012, 83: 123504. doi: 10.1063/1.4769055 [11] Abe Y, Nakao A, Arikawa Y, et al. Predictive capability of material screening by fast neutron activation analysis using laser-driven neutron sources[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2022, 93: 093523. doi: 10.1063/5.0099217 [12] Perkins L J, Logan B G, Rosen M D, et al. The investigation of high intensity laser driven micro neutron sources for fusion materials research at high fluence[J]. Nuclear Fusion, 2000, 40(1): 1-19. doi: 10.1088/0029-5515/40/1/301 [13] Hill P, Wu Y B. Exploring laser-driven neutron sources for neutron capture cascades and the production of neutron-rich isotopes[J]. Physical Review C, 2021, 103: 014602. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevC.103.014602 [14] Fultz S C, Bramblett R L, Caldwell J T, et al. Photoneutron cross-section measurements on gold using nearly monochromatic photons[J]. Physical Review, 1962, 127(4): 1273-1279. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.127.1273 [15] Yogo A, Lan Z, Arikawa Y, et al. Laser-driven neutron generation realizing single-shot resonance spectroscopy[J]. Physical Review X, 2023, 13: 011011. [16] Hidding B, Karger O, Königstein T, et al. Laser-plasma-based Space Radiation Reproduction in the Laboratory[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 42354. doi: 10.1038/srep42354 [17] Leemans W P, Rodgers D, Catravas P E, et al. Gamma-neutron activation experiments using laser wakefield accelerators[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2001, 8(5): 2510-2516. doi: 10.1063/1.1352617 [18] Reed S A, Chvykov V, Kalintchenko G, et al. Efficient initiation of photonuclear reactions using quasimonoenergetic electron beams from laser wakefield acceleration[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 102: 073103. doi: 10.1063/1.2787159 [19] Jiao X J, Shaw J M, Wang T, et al. A tabletop, ultrashort pulse photoneutron source driven by electrons from laser wakefield acceleration[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2017, 2(6): 296-302. doi: 10.1016/j.mre.2017.10.003 [20] Galy J, Maučec M, Hamilton D J, et al. Bremsstrahlung production with high-intensity laser matter interactions and applications[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2007, 9: 23. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/9/2/023 [21] Feng J, Fu C B, Li Y F, et al. High-efficiency neutron source generation from photonuclear reactions driven by laser plasma accelerator[J]. High Energy Density Physics, 2020, 36: 100753. doi: 10.1016/j.hedp.2020.100753 [22] 齐伟, 贺书凯, 闫永宏, 等. 超短脉冲激光与固体靶作用产生光核中子的数值模拟研究[J]. 中国激光, 2019, 46: 0901007 doi: 10.3788/CJL201946.0901007Qi Wei, He Shukai, Yan Yonghong, et al. Numerical simulation of photoneutron generation in ultra-intense short laser-solid interactions[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2019, 46: 0901007 doi: 10.3788/CJL201946.0901007 [23] Peralta E A, Soong K, England R J, et al. Demonstration of electron acceleration in a laser-driven dielectric microstructure[J]. Nature, 2013, 503(7474): 91-94. doi: 10.1038/nature12664 [24] Stupakov G V, Zolotorev M S. Ponderomotive laser acceleration and focusing in vacuum for generation of attosecond electron bunches[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2001, 86(23): 5274-5277. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.86.5274 [25] Shkolnikov P L, Kaplan A E, Pukhov A, et al. Positron and gamma-photon production and nuclear reactions in cascade processes initiated by a sub-terawatt femtosecond laser[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1997, 71(24): 3471-3473. doi: 10.1063/1.120362 [26] Pomerantz I, McCary E, Meadows A R, et al. Ultrashort pulsed neutron source[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2014, 113: 184801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.184801 [27] Jiang X R, Zou D B, Zhao Z J, et al. Microstructure-assisted laser-driven photonuclear pulsed neutron source[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2021, 15: 034032. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.15.034032 [28] Günther M M, Rosmej O N, Tavana P, et al. Forward-looking insights in laser-generated ultra-intense γ-ray and neutron sources for nuclear application and science[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 170. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27694-7 [29] Lancaster K L, Karsch S, Habara H, et al. Characterization of 7Li (p, n)7 Be neutron yields from laser produced ion beams for fast neutron radiography[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2004, 11(7): 3404-3408. doi: 10.1063/1.1756911 [30] Higginson D P, McNaney J M, Swift D C, et al. Production of neutrons up to 18 MeV in high-intensity, short-pulse laser matter interactions[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2011, 18: 100703. doi: 10.1063/1.3654040 [31] Roth M, Jung D, Falk K, et al. Bright laser-driven neutron source based on the relativistic transparency of solids[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2013, 110: 044802. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.044802 [32] Kleinschmidt A, Bagnoud V, Deppert O, et al. Intense, directed neutron beams from a laser-driven neutron source at PHELIX[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2018, 25: 053101. doi: 10.1063/1.5006613 [33] Jiao X, Curry C B, Gauthier M, et al. High deuteron and neutron yields from the interaction of a petawatt laser with a cryogenic deuterium jet[J]. Frontiers in Physics, 2023, 10: 964696. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2022.964696 [34] Alejo A, Ahmed H, Krygier A G, et al. Stabilized radiation pressure acceleration and neutron generation in ultrathin deuterated foils[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2022, 129: 114801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.129.114801 [35] Kar S, Green A, Ahmed H, et al. Beamed neutron emission driven by laser accelerated light ions[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2016, 18: 053002. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/18/5/053002 [36] Disdier L, Garçonnet J P, Malka G, et al. Fast neutron emission from a high-energy ion beam produced by a high-intensity subpicosecond laser pulse[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1999, 82(7): 1454-1457. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.82.1454 [37] Zimmer M, Scheuren S, Kleinschmidt A, et al. Demonstration of non-destructive and isotope-sensitive material analysis using a short-pulsed laser-driven epi-thermal neutron source[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 1173. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28756-0 [38] Mirfayzi S R, Ahmed H, Doria D, et al. A miniature thermal neutron source using high power lasers[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2020, 116: 174102. doi: 10.1063/5.0003170 [39] Mirfayzi S R, Yogo A, Lan Z, et al. Proof-of-principle experiment for laser-driven cold neutron source[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 20157. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-77086-y [40] Wu Y C, Zhu B, Dong K G, et al. XingGuang III laser facility and its experimental ability to drive high-energy particle beams[J]. Laser Physics, 2020, 30: 096001. doi: 10.1088/1555-6611/aba3ca [41] Qi W, Zhang X H, Zhang B, et al. Enhanced photoneutron production by intense picoseconds laser interacting with gas-solid hybrid targets[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2019, 26: 043103. doi: 10.1063/1.5079773 [42] 崔波, 张智猛, 戴曾海, 等. 基于多反应通道的高产额激光中子源实验研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33: 094004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210330Cui Bo, Zhang Zhimeng, Dai Zenghai, et al. Experimental study of high yield neutron source based on multi reaction channels[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 094004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210330 [43] Yao Y L, He S K, Lei Z, et al. High-flux neutron generator based on laser-driven collisionless shock acceleration[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2023, 131: 025101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.131.025101 [44] Li J J, Yu B, Xu T, et al. First magnifying neutron/x-ray combined radiography at Shenguang laser facility[J]. AIP Advances, 2022, 12: 115012. doi: 10.1063/5.0121977 [45] 齐伟, 贺书凯, 崔波, 等. 超短脉冲激光驱动束靶中子源产生及应用研究进展(特邀)[J]. 中国激光, 2024, 51: 0101004 doi: 10.3788/CJL231292Qi Wei, He Shukai, Cui Bo, et al. Research progress of beam-target neutron source and applications driven by ultra-short pulse lasers (Invited)[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2024, 51: 0101004 doi: 10.3788/CJL231292 -




 下载:
下载: