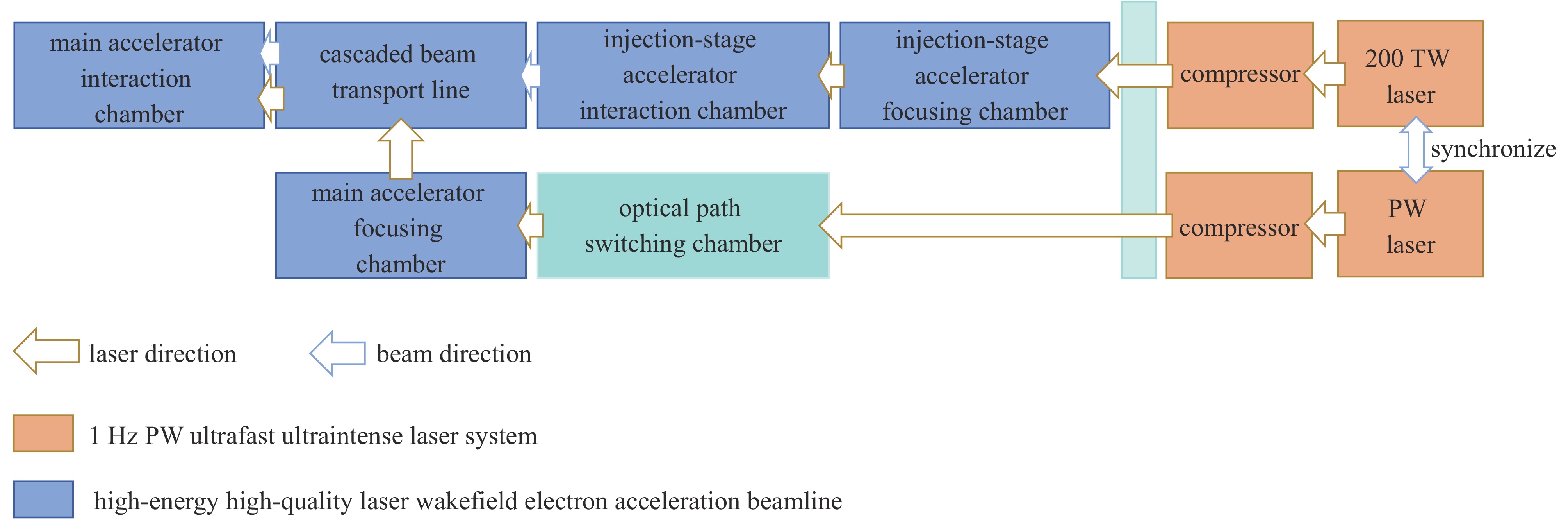
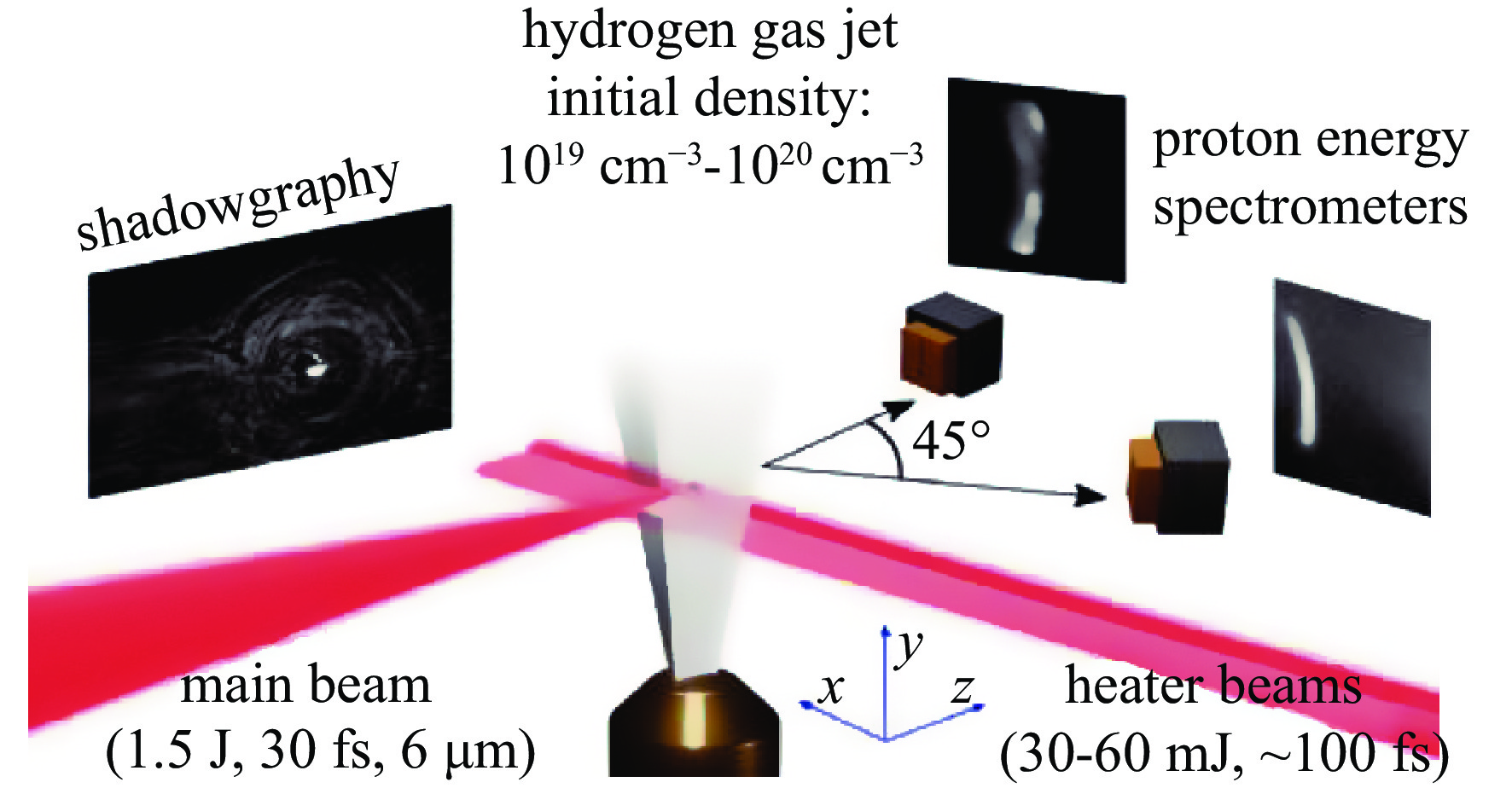
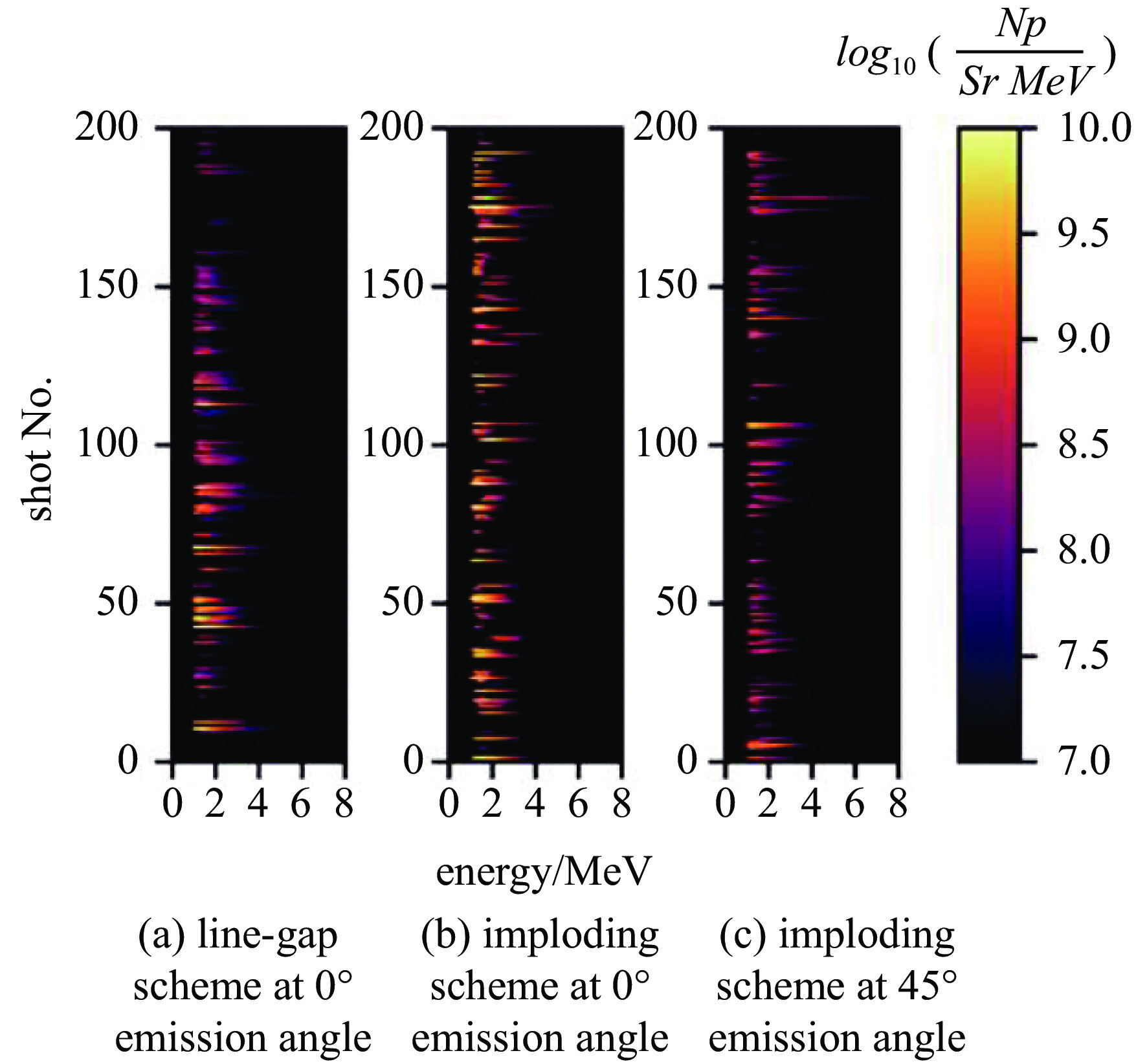
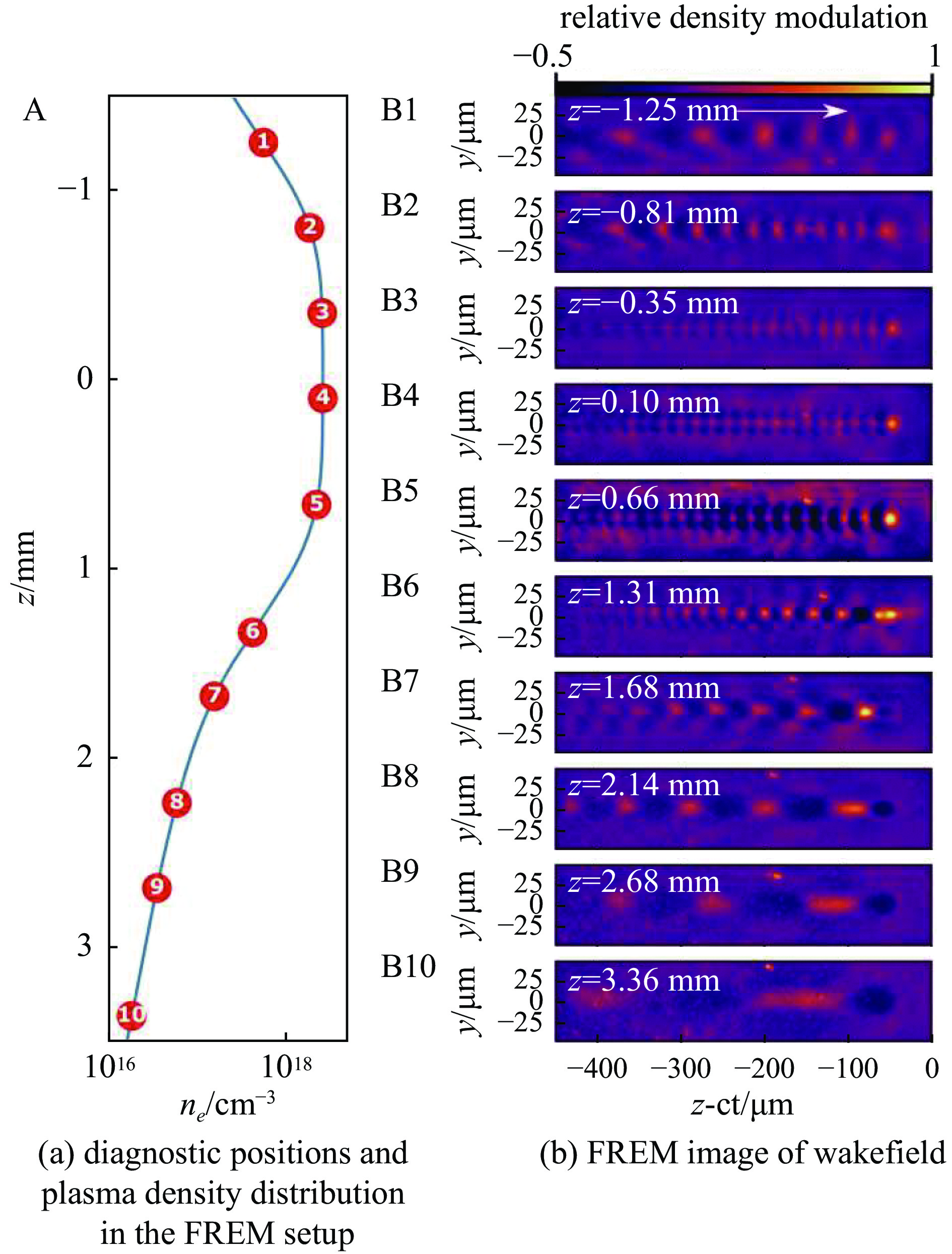
| [1] |
Perry M D, Mourou G. Terawatt to petawatt subpicosecond lasers[J]. Science, 1994, 264(5161): 917-924. doi: 10.1126/science.264.5161.917
|
| [2] |
李儒新, 冷雨欣, 徐至展. 超强超短激光及其应用新进展[J]. 物理, 2015, 44(8): 509-517 doi: 10.7693/wl20150804Li Ruxin, Leng Yuxin, Xu Zhizhan. Progress in superintense ultrafast lasers and their applications[J]. Physics, 2015, 44(8): 509-517 doi: 10.7693/wl20150804
|
| [3] |
Kiriyama H, Mori M, Pirozhkov A S, et al. High-contrast, high-intensity petawatt-class laser and applications[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2015, 21: 1601118.
|
| [4] |
Strickland D, Mourou G. Compression of amplified chirped optical pulses[J]. Optics Communications, 1985, 55(6): 447-449. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(85)90151-8
|
| [5] |
Yoon J W, Kim Y G, Choi I W, et al. Realization of laser intensity over 1023 W/cm2[J]. Optica, 2021, 8(5): 630-635. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.420520
|
| [6] |
Botner O, Ingelman G, Irbäck A, et al. The Nobel committee for physics[Z]. The Nobel Prize in Physics 2018: Popular Science Background, 2018: 1-7.
|
| [7] |
Mourou G A, Korn G, Sandner W, et al. ELI white book: science and technology with ultra-intense lasers[R]. Berlin: THOSS Media GmbH, 2011.
|
| [8] |
Hernandez-Gomez C. Overview of the central laser facility (CLF)[R]. Didcot: CLF, 2016-2017: 6-8.
|
| [9] |
Papadopoulos D N, Zou J P, Le Blanc C, et al. The Apollon 10 PW laser: experimental and theoretical investigation of the temporal characteristics[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2016, 4: e34. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2016.34
|
| [10] |
Khazanov E, Shaykin A, Kostyukov I, et al. eXawatt center for extreme light studies[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2023, 11: e78. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2023.69
|
| [11] |
Bromage J, Bahk S W, Bedzyk M, et al. MTW-OPAL: a technology development platform for ultra-intense optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification systems[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2021, 9: e63. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2021.45
|
| [12] |
. http://sulf.siom.ac.cn/.
|
| [13] |
上海超强超短激光实验装置研制进展——专访中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所李儒新院士[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2020, 32: 011002Development progress of Shanghai superintense ultrafast lasers facility[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2020, 32: 011002
|
| [14] |
Li Hongyang, Liu Keyang, Wang Xinliang, et al. Timing fluctuation correction for the front end of a 100-PW laser[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2023, 11: e52. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2023.41
|
| [15] |
彭宇杰, 许毅, 於亮红, 等. 上海超强超短激光实验装置研制进展[J]. 中国激光, 2024, 51: 1101002Peng Yujie, Xu Yi, Yu Lianghong, et al. Review on development of shanghai super-intense ultra-fast laser facility[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2024, 51: 1101002
|
| [16] |
陈民, 刘峰, 李博原, 等. 激光等离子体尾波加速器的发展和展望[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2020, 32: 092001Chen Min, Liu Feng, Li Boyuan, et al. Development and prospect of laser plasma wakefield accelerator[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2020, 32: 092001
|
| [17] |
Tajima T, Dawson J M. Laser electron accelerator[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1979, 43(4): 267-270. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.43.267
|
| [18] |
Esarey E, Schroeder C B, Leemans W P. Physics of laser-driven plasma-based electron accelerators[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2009, 81(3): 1229-1285. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.81.1229
|
| [19] |
Malka V, Faure J, Gauduel Y, et al. Principles and applications of compact laser–plasma accelerators[J]. Nature Physics, 2008, 4(6): 447-453. doi: 10.1038/nphys966
|
| [20] |
Rousse A, Ta Phuoc K, Shah R, et al. Production of a keV X-ray beam from synchrotron radiation in relativistic laser-plasma interaction[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2004, 93: 135005. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.93.135005
|
| [21] |
Kneip S, McGuey C, Martins J L, et al. Bright spatially coherent synchrotron X-rays from a table-top source[J]. Nature Physics, 2010, 6(12): 980-983. doi: 10.1038/nphys1789
|
| [22] |
Corde S, Ta Phuoc K, Lambert G, et al. Femtosecond x rays from laser-plasma accelerators[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2013, 85(1): 1-48. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.85.1
|
| [23] |
谢波, 张晓辉, 李天月, 等. 拍瓦飞秒激光与近临界密度等离子体相互作用的电子加速及betatron辐射产生数值模拟[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2025, 37: 091002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202537.250033Xie Bo, Zhang Xiaohui, Li Tianyue, et al. Numerical study of electron acceleration and betatron radiation based on interaction of petawatt femtosecond laser with near-critical-density plasma[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2025, 37: 091002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202537.250033
|
| [24] |
Ta Phuoc K, Corde S, Thaury C, et al. All-optical Compton gamma-ray source[J]. Nature Photonics, 2012, 6(5): 308-311. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2012.82
|
| [25] |
Liu Cheng, Golovin G, Chen Shouyuan, et al. Generation of 9 MeV γ-rays by all-laser-driven Compton scattering with second-harmonic laser light[J]. Optics Letters, 2014, 39(14): 4132-4135. doi: 10.1364/OL.39.004132
|
| [26] |
杜应超, 陈寒, 张鸿泽, 等. 紧凑型单能伽马射线源[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2022, 34: 104010 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.220132Du Yingchao, Chen Han, Zhang Hongze, et al. A very compact inverse Compton scattering gamma-ray source[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2022, 34: 104010 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.220132
|
| [27] |
Nakajima K. Towards a table-top free-electron laser[J]. Nature Physics, 2008, 4(2): 92-93. doi: 10.1038/nphys846
|
| [28] |
Wang Wentao, Feng Ke, Ke Lintong, et al. Free-electron lasing at 27 nanometres based on a laser wakefield accelerator[J]. Nature, 2021, 595(7868): 516-520. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03678-x
|
| [29] |
Pompili R, Alesini D, Anania M P, et al. Free-electron lasing with compact beam-driven plasma wakefield accelerator[J]. Nature, 2022, 605(7911): 659-662. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04589-1
|
| [30] |
Labat M, Cabadağ J C, Ghaith A, et al. Seeded free-electron laser driven by a compact laser plasma accelerator[J]. Nature Photonics, 2023, 17(2): 150-156. doi: 10.1038/s41566-022-01104-w
|
| [31] |
Schroeder C B, Esarey E, Geddes C G R, et al. Physics considerations for laser-plasma linear colliders[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2010, 13: 101301. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.13.101301
|
| [32] |
USDOE Office of Science. Advanced accelerator development strategy report: DOE advanced accelerator concepts research roadmap workshop[R]. USDOE Office of Science, 2016.
|
| [33] |
European Strategy Group. 2020 Update of the European strategy for particle physics[R]. Geneva: CERN Council, 2020.
|
| [34] |
Assmann R W, Weikum M K, Akhter T, et al. EuPRAXIA conceptual design report[J]. The European Physical Journal Special Topics, 2020, 229(24): 3675-4284. doi: 10.1140/epjst/e2020-000127-8
|
| [35] |
Seemann O, Wan Yang, Tata S, et al. Laser proton acceleration from a near-critical imploding gas target[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2024, 133: 025001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.133.025001
|
| [36] |
Wan Y, Andriyash I A, Hua J F, et al. Two-stage laser acceleration of high quality protons using a tailored density plasma[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2019, 22: 021301. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.22.021301
|
| [37] |
Wan Yang, Tata S, Seemann O, et al. Real-time visualization of the laser-plasma wakefield dynamics[J]. Science Advances, 2024, 10: eadj3595. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adj3595
|
| [38] |
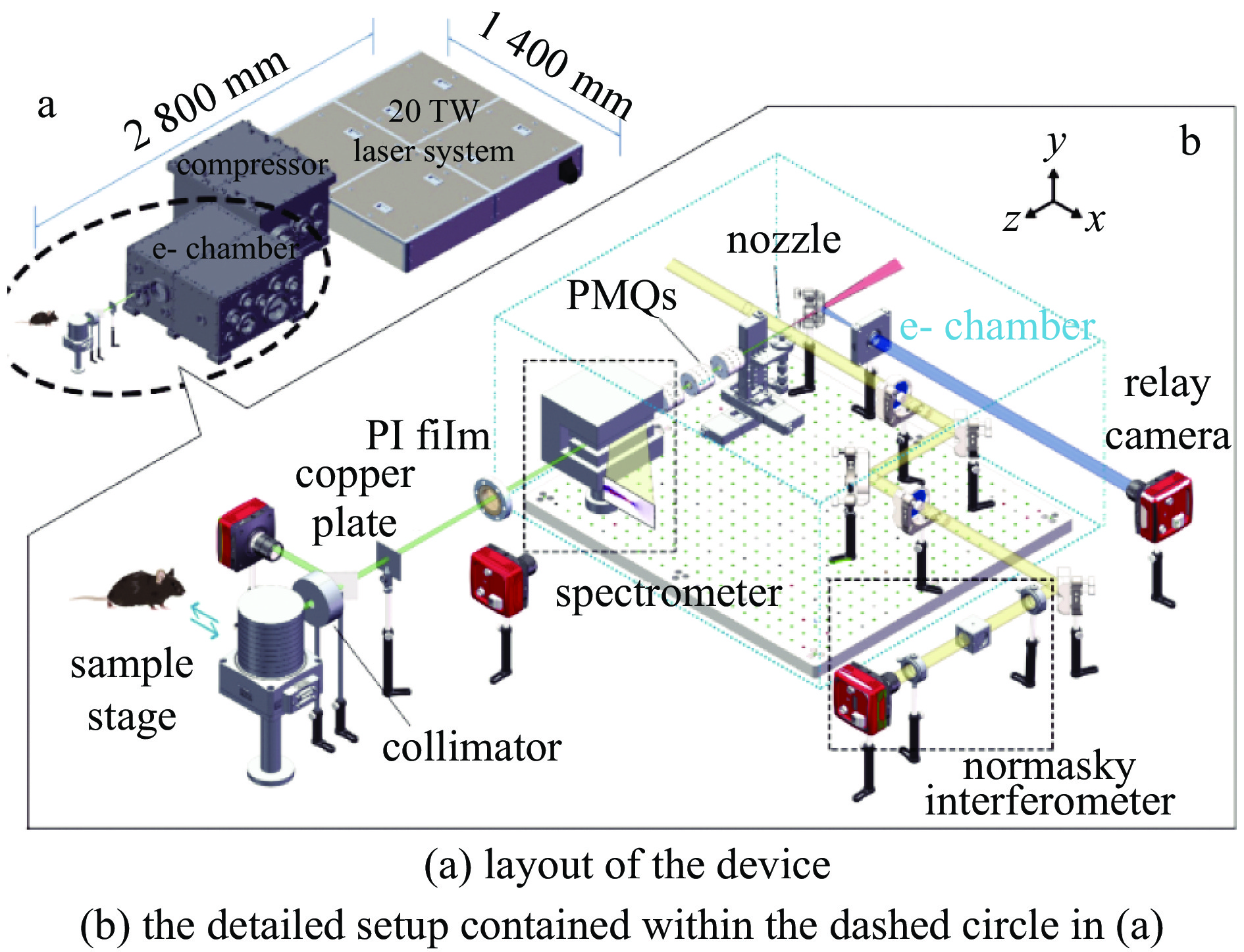
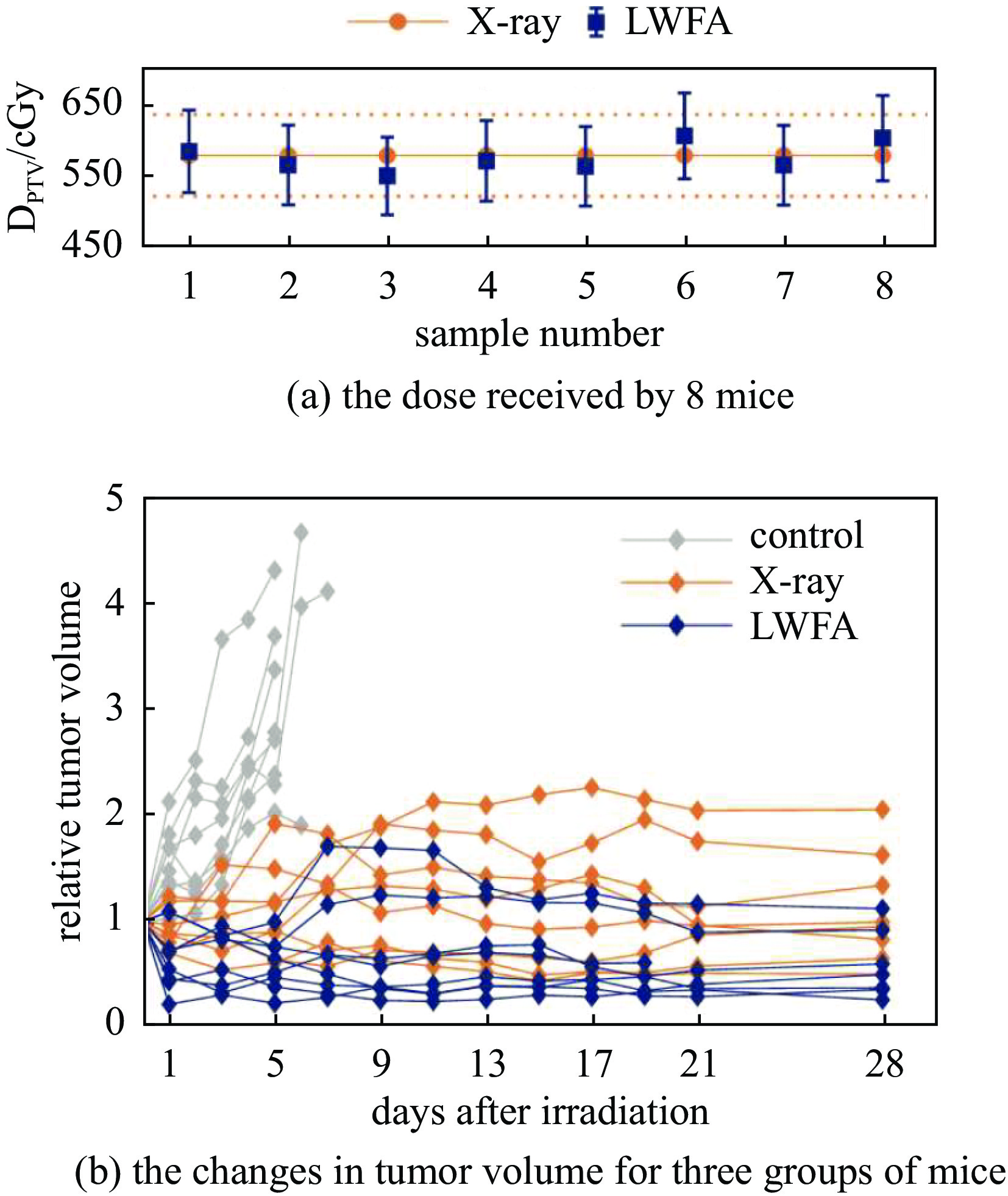
Guo Zhiyuan, Liu Shuang, Zhou Bing, et al. Preclinical tumor control with a laser-accelerated high-energy electron radiotherapy prototype[J]. Nature Communications, 2025, 16: 1895. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57122-z
|
| [39] |
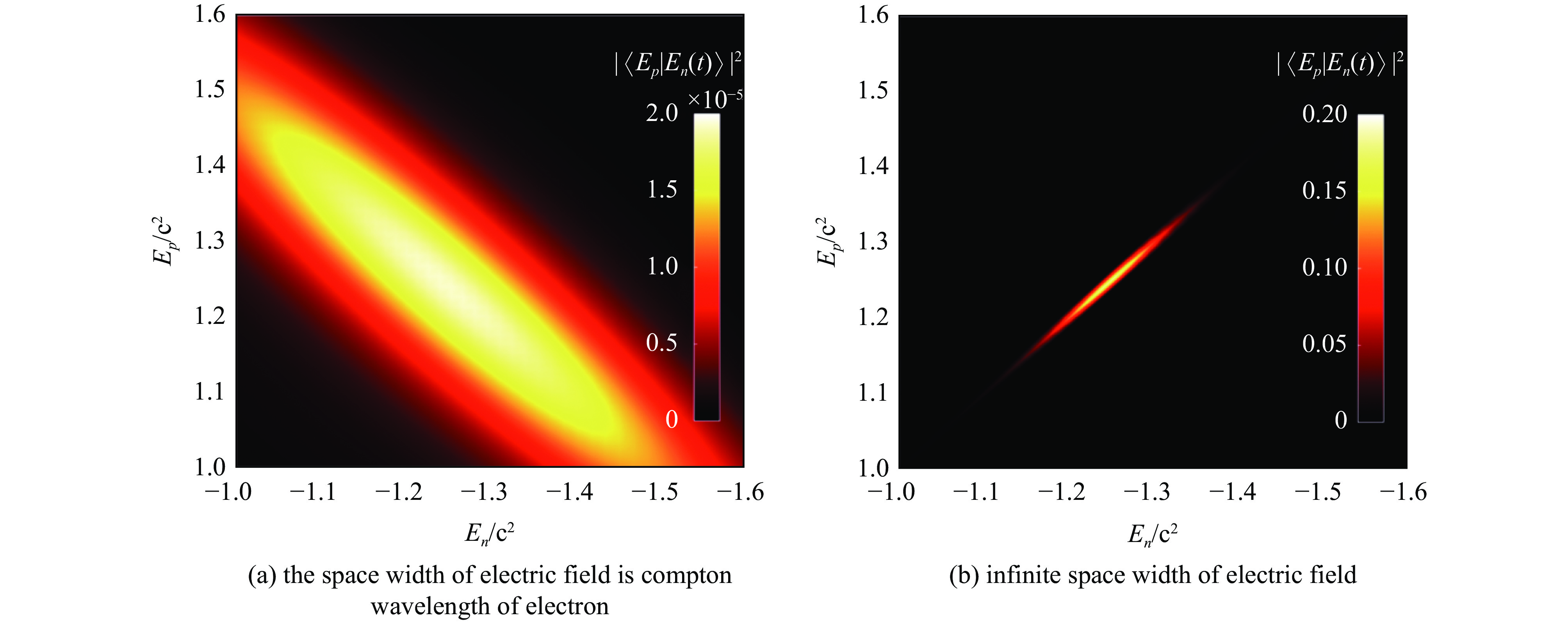
Li C K, Zhou X X, Chen Q, et al. Transition signatures for electron-positron pair creation in space-time inhomogeneous electric field[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:, 2408, 09402: 2024.
|




 下载:
下载: